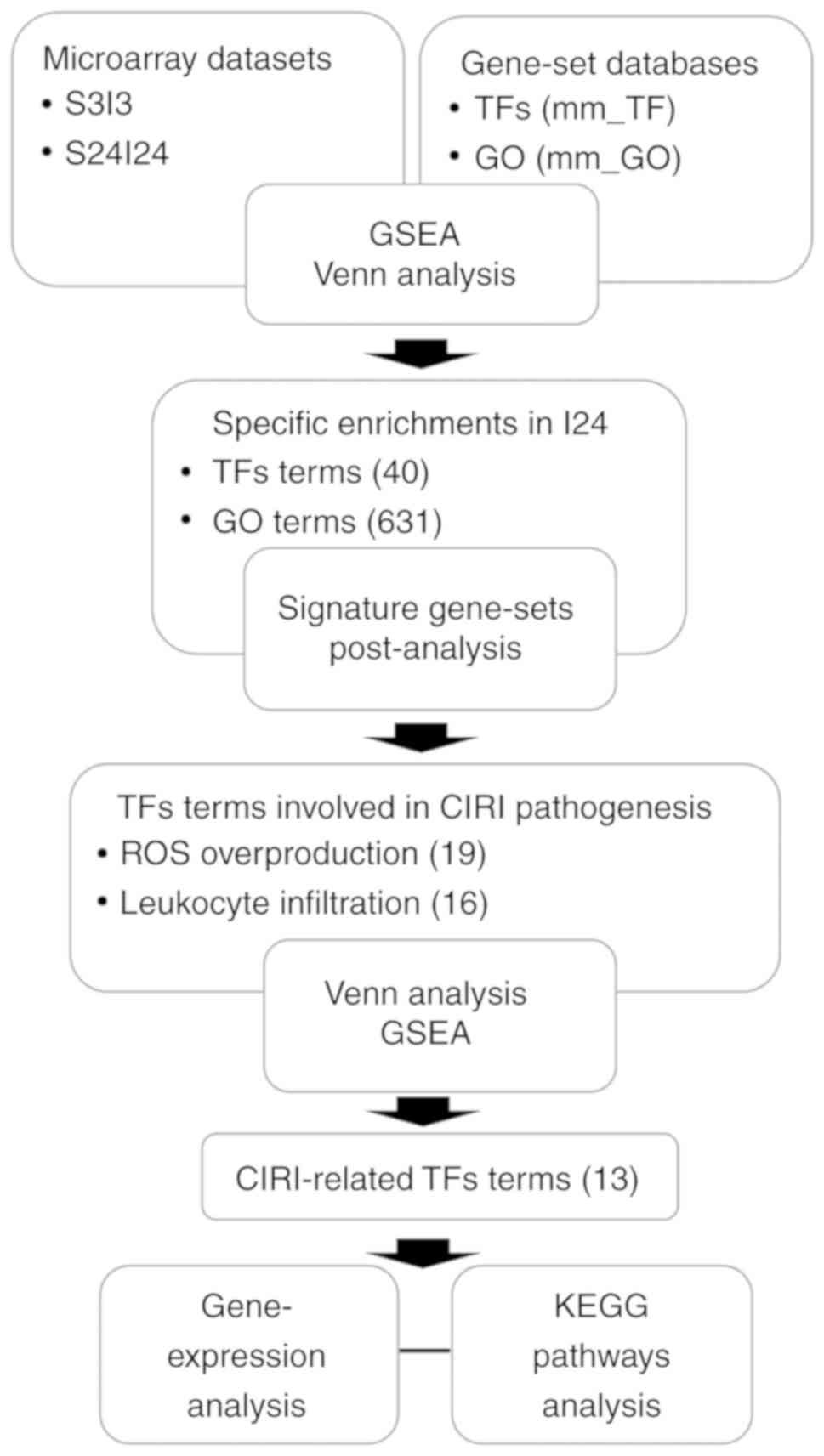
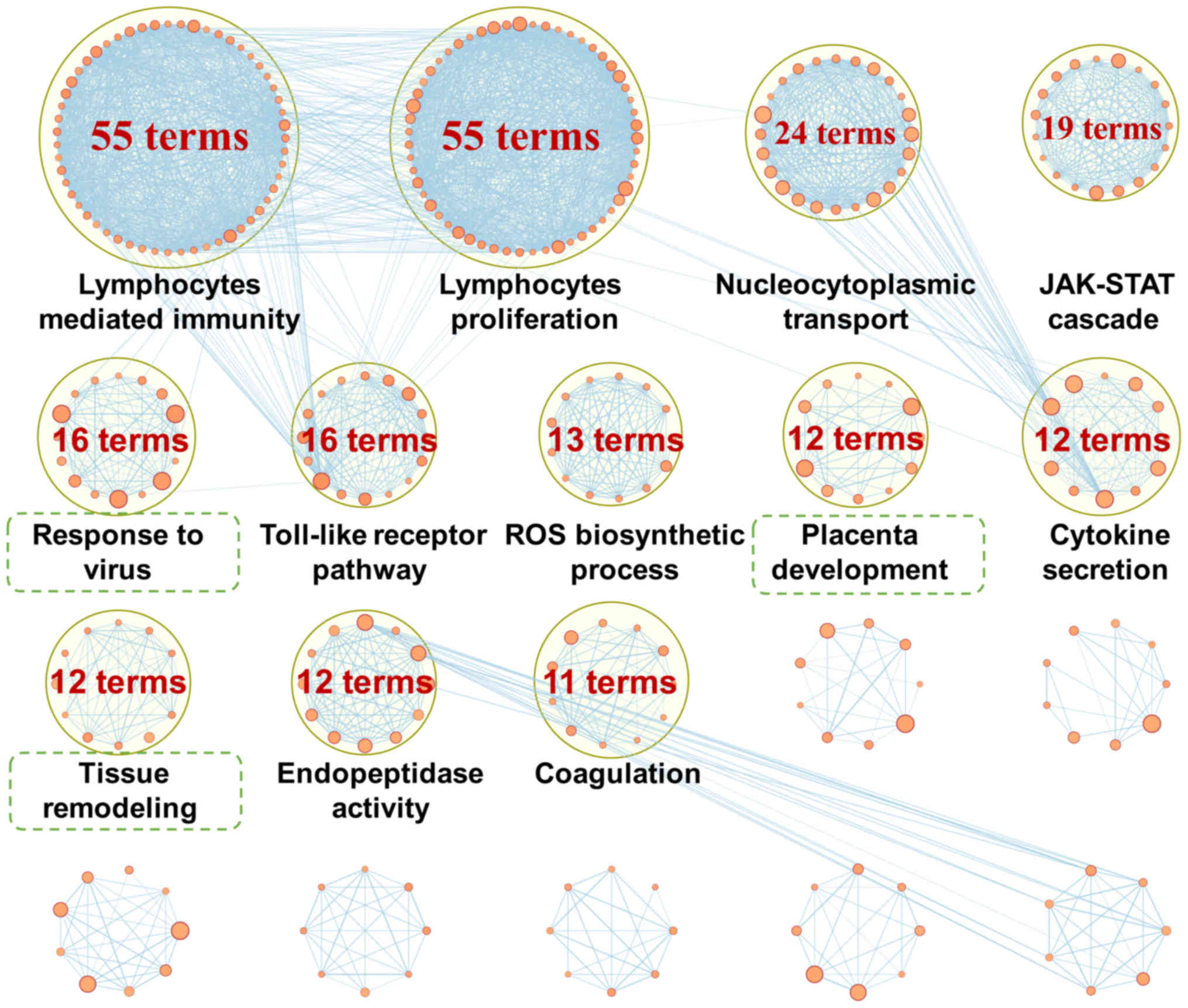
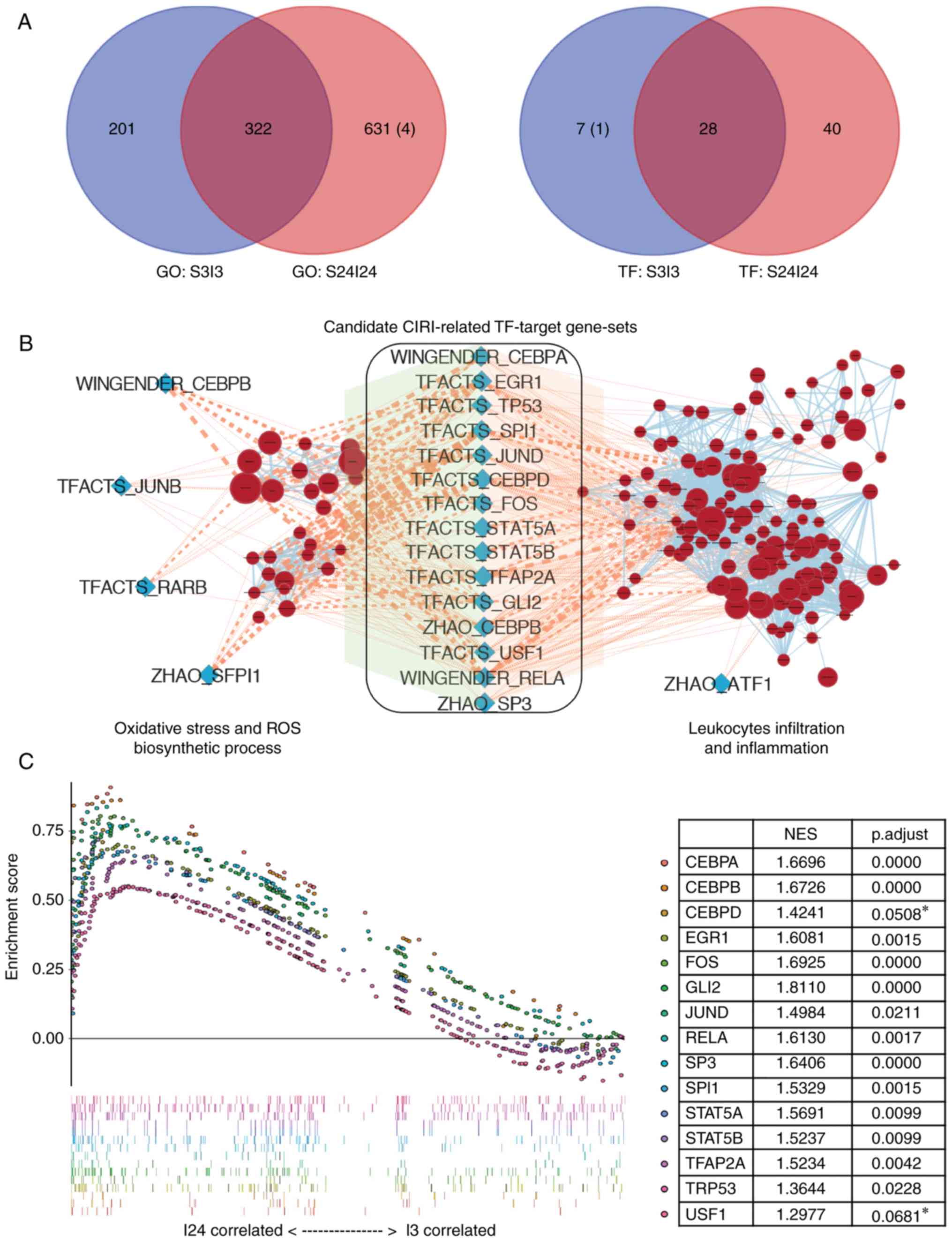
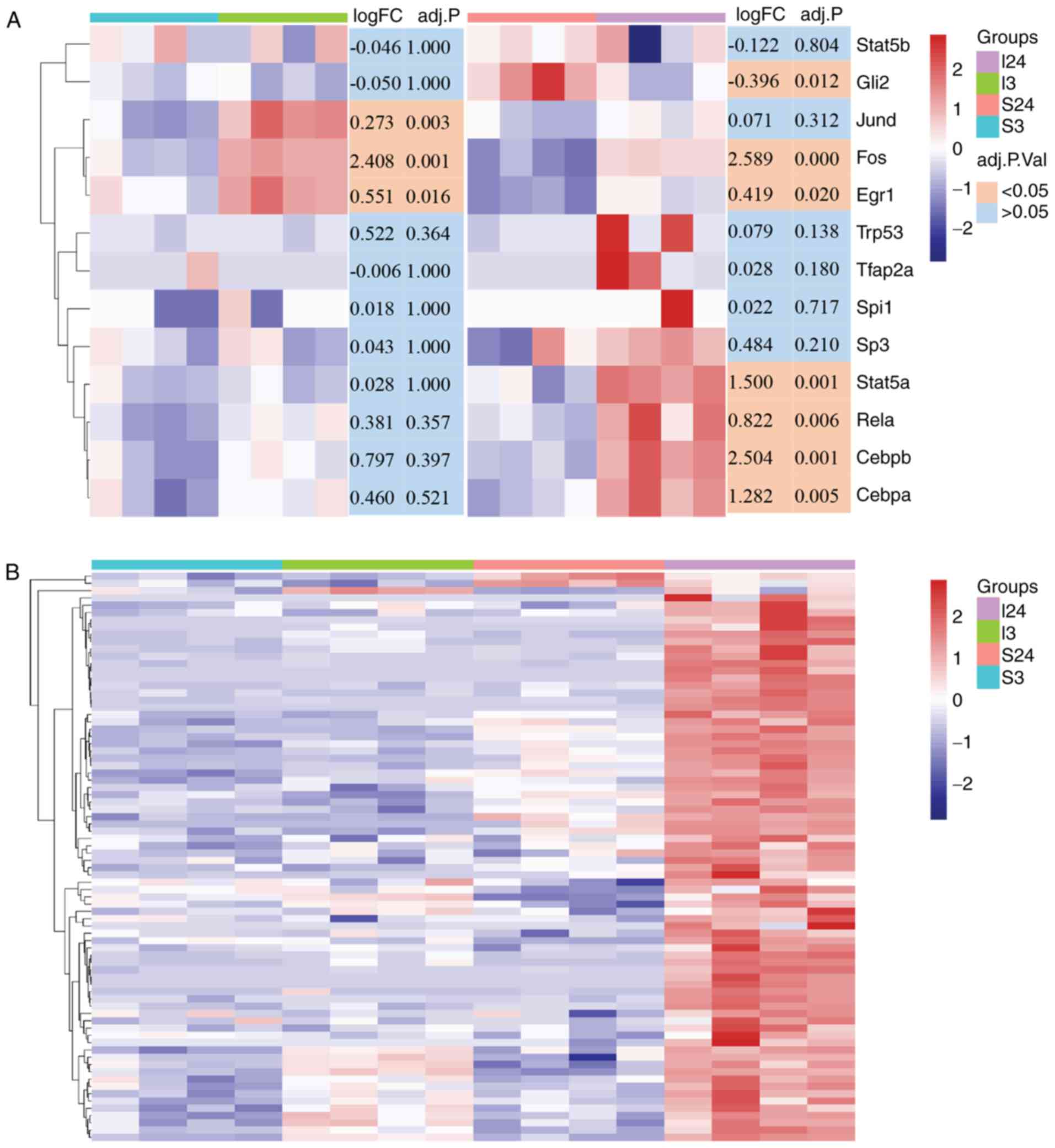
|
1
|
L L, X W and Z Y: Ischemia-reperfusion
injury in the brain: Mechanisms and potential therapeutic
strategies. Biochem Pharmacol (Los Angel). 5:2132016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hossmann KA: The two pathophysiologies of
focal brain ischemia: Implications for translational stroke
research. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 32:1310–1316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
VanGilder RL, Huber JD, Rosen CL and Barr
TL: The transcriptome of cerebral ischemia. Brain Res Bull.
88:313–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu XC, Williams AJ, Yao C, Berti R,
Hartings JA, Whipple R, Vahey MT, Polavarapu RG, Woller KL,
Tortella FC and Dave JR: Microarray analysis of acute and delayed
gene expression profile in rats after focal ischemic brain injury
and reperfusion. J Neurosci Res. 77:843–857. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yi JH, Park SW, Kapadia R and Vemuganti R:
Role of transcription factors in mediating post-ischemic cerebral
inflammation and brain damage. Neurochem Int. 50:1014–1027. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cox-Limpens KE, Gavilanes AW, Zimmermann
LJ and Vles JS: Endogenous brain protection: What the cerebral
transcriptome teaches us. Brain Res. 1564:85–100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun Y, Liu L, Yuan J, Sun Q, Wang N and
Wang Y: RP105 protects PC12 cells from oxygenglucose
deprivation/reoxygenation injury via activation of the PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 41:3081–3089. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iadecola C, Salkowski CA, Zhang F, Aber T,
Nagayama M, Vogel SN and Ross ME: The transcription factor
interferon regulatory factor 1 is expressed after cerebral ischemia
and contributes to ischemic brain injury. J Exp Med. 189:719–727.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nurmi A, Lindsberg PJ, Koistinaho M, Zhang
W, Juettler E, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, Weih F, Frank N,
Schwaninger M and Koistinaho J: Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes
to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke. 35:987–991.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tureyen K, Brooks N, Bowen K, Svaren J and
Vemuganti R: Transcription factor early growth response-1 induction
mediates inflammatory gene expression and brain damage following
transient focal ischemia. J Neurochem. 105:1313–1324. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kapadia R, Tureyen K, Bowen KK, Kalluri H,
Johnson PF and Vemuganti R: Decreased brain damage and curtailed
inflammation in transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer binding protein
beta knockout mice following transient focal cerebral ischemia. J
Neurochem. 98:1718–1731. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Satriotomo I, Bowen KK and Vemuganti R:
JAK2 and STAT3 activation contributes to neuronal damage following
transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 98:1353–1368. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ridder DA, Bulashevska S, Chaitanya GV,
Babu PP, Brors B, Eils R, Schneider A and Schwaninger M: Discovery
of transcriptional programs in cerebral ischemia by in silico
promoter analysis. Brain Res. 1272:3–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pulliam JV, Xu Z, Ford GD, Liu C, Li Y,
Stovall KC, Cannon VS, Tewolde T, Moreno CS and Ford BD:
Computational identification of conserved transcription factor
binding sites upstream of genes induced in rat brain by transient
focal ischemic stroke. Brain Res. 1495:76–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Camos S, Gubern C, Sobrado M, Rodríguez R,
Romera VG, Moro MA, Lizasoain I, Serena J, Mallolas J and
Castellanos M: The high-mobility group I-Y transcription factor is
involved in cerebral ischemia and modulates the expression of
angiogenic proteins. Neuroscience. 269:112–130. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Merico D, Isserlin R, Stueker O, Emili A
and Bader GD: Enrichment map: A network-based method for gene-set
enrichment visualization and interpretation. PLoS One.
5:e139842010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stevens SL, Leung PY, Vartanian KB,
Gopalan B, Yang T, Simon RP and Stenzel-Poore MP: Multiple
preconditioning paradigms converge on interferon regulatory
factor-dependent signaling to promote tolerance to ischemic brain
injury. J Neurosci. 31:8456–8463. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vartanian KB, Stevens SL, Marsh BJ,
Williams-Karnesky R, Lessov NS and Stenzel-Poore MP: LPS
preconditioning redirects TLR signaling following stroke: TRIF-IRF3
plays a seminal role in mediating tolerance to ischemic injury. J
Neuroinflammation. 8:1402011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: Affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kucera M, Isserlin R, Arkhangorodsky A and
Bader GD: AutoAnnotate: A cytoscape app for summarizing networks
with semantic annotations. F1000Res. 5:17172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wickham H: Ggplot2: Elegant graphics for
data analysis. Springer New York, Statistics and
Computing/Statistics Programs VIII; pp. 2132009
|
|
25
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim JB, Piao CS, Lee KW, Han PL, Ahn JI,
Lee YS and Lee JK: Delayed genomic responses to transient middle
cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Neurochem. 89:1271–1282.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang RL, Chopp M, Chen H and Garcia JH:
Temporal profile of ischemic tissue damage, neutrophil response,
and vascular plugging following permanent and transient (2H) middle
cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Neurol Sci. 125:3–10. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oh SH, Kim OJ, Shin DA, Song J, Yoo H, Kim
YK and Kim JK: Alteration of immunologic responses on peripheral
blood in the acute phase of ischemic stroke: Blood genomic
profiling study. J Neuroimmunol. 249:60–65. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shao X, Bao W, Hong X, Jiang H and Yu Z:
Identification and functional analysis of differentially expressed
genes associated with cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through
bioinformatics methods. Mol Med Rep. 18:1513–1523. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang C, Liu M, Pan Y, Bai B and Chen J:
Global gene expression profile of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion
injury in rat MCAO model. Oncotarget. 8:74607–74622. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kamme F and Wieloch T: Induction of junD
mRNA after transient forebrain ischemia in the rat. Effect of
hypothermia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 43:51–56. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sola A, Rogido M, Lee BH, Genetta T and
Wen TC: Erythropoietin after focal cerebral ischemia activates the
Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription
signaling pathway and improves brain injury in postnatal day 7
rats. Pediatr Res. 57:481–487. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marden JJ, Zhang Y, Oakley FD, Zhou W, Luo
M, Jia HP, McCray PB Jr, Yaniv M, Weitzman JB and Engelhardt JF:
JunD protects the liver from ischemia/reperfusion injury by
dampening AP-1 transcriptional activation. J Biol Chem.
283:6687–6695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Harari OA and Liao JK: NF-kappaB and
innate immunity in ischemic stroke. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1207:32–40.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Koschmieder S, Rosenbauer F, Steidl U,
Owens BM and Tenen DG: Role of transcription factors C/EBPalpha and
PU.1 in normal hematopoiesis and leukemia. Int J Hematol.
81:368–377. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang H, Gao W, Qian T, Tang J and Li J:
Transcription factor changes following long term cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 8:916–921.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Walton M, Saura J, Young D, MacGibbon G,
Hansen W, Lawlor P, Sirimanne E, Gluckman P and Dragunow M:
CCAAT-enhancer binding protein alpha is expressed in activated
microglial cells after brain injury. Brain Res Mol Brain Res.
61:11–22. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jin F, Li Y, Ren B and Natarajan R: PU.1
and C/EBP(alpha) synergistically program distinct response to
NF-kappaB activation through establishing monocyte specific
enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5290–5295. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Formisano L, Guida N, Valsecchi V, Cantile
M, Cuomo O, Vinciguerra A, Laudati G, Pignataro G, Sirabella R, Di
Renzo G and Annunziato L: Sp3/REST/HDAC1/HDAC2 Complex represses
and sp1/HIF-1/p300 complex activates ncx1 gene transcription, in
brain ischemia and in ischemic brain preconditioning, by epigenetic
mechanism. J Neurosci. 35:7332–7348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gelderblom M, Weymar A, Bernreuther C,
Velden J, Arunachalam P, Steinbach K, Orthey E, Arumugam TV,
Leypoldt F, Simova O, et al: Neutralization of the IL-17 axis
diminishes neutrophil invasion and protects from ischemic stroke.
Blood. 120:3793–3802. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tanimura A, Dan S and Yoshida M: Cloning
of novel isoforms of the human Gli2 oncogene and their activities
to enhance tax-dependent transcription of the human T-cell leukemia
virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 72:3958–3964. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Regl G, Kasper M, Schnidar H, Eichberger
T, Neill GW, Philpott MP, Esterbauer H, Hauser-Kronberger C,
Frischauf AM and Aberger F: Activation of the BCL2 promoter in
response to Hedgehog/GLI signal transduction is predominantly
mediated by GLI2. Cancer Res. 64:7724–7731. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang L, Chopp M, Meier DH, Winter S, Wang
L, Szalad A, Lu M, Wei M, Cui Y and Zhang ZG: Sonic hedgehog
signaling pathway mediates cerebrolysin-improved neurological
function after stroke. Stroke. 44:1965–1972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi D, Xie F, Zhang Y, Tian Y, Chen W, Fu
L, Wang J, Guo W, Kang T, Huang W and Deng W: TFAP2A regulates
nasopha-ryngeal carcinoma growth and survival by targeting
HIF-1alpha signaling pathway. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 7:266–277.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lin HH, Chen YH, Chiang MT, Huang PL and
Chau LY: Activator protein-2alpha mediates carbon monoxide-induced
stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha expression and vascularization
in ischemic heart. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:785–794. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|