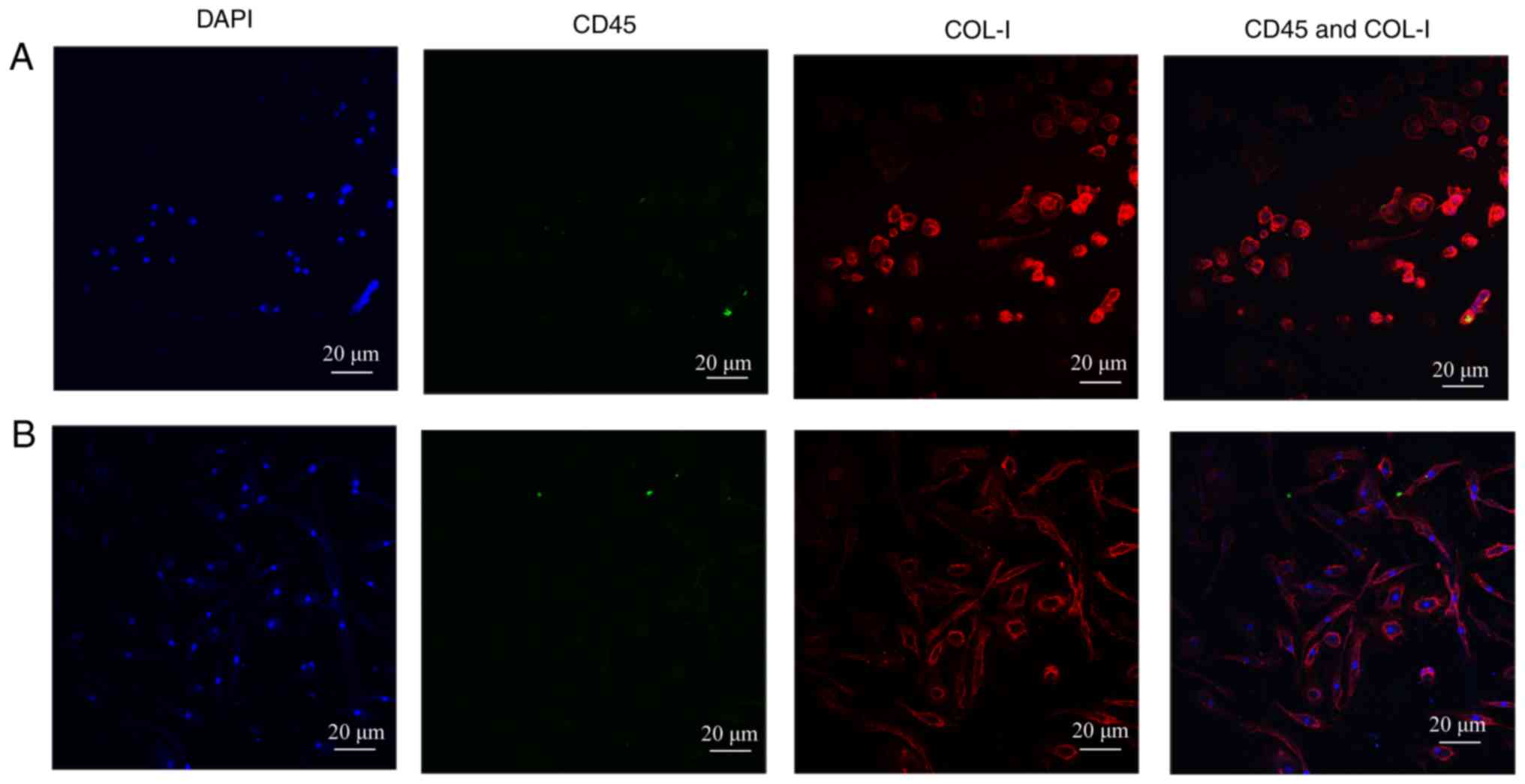
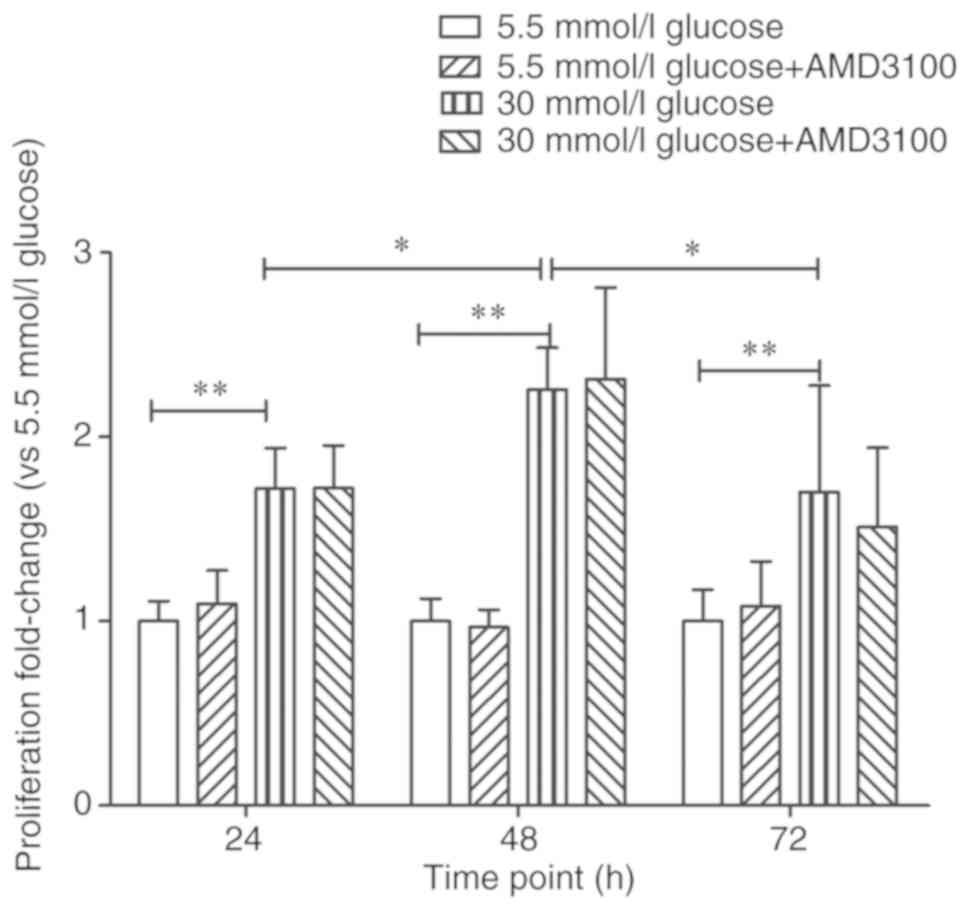
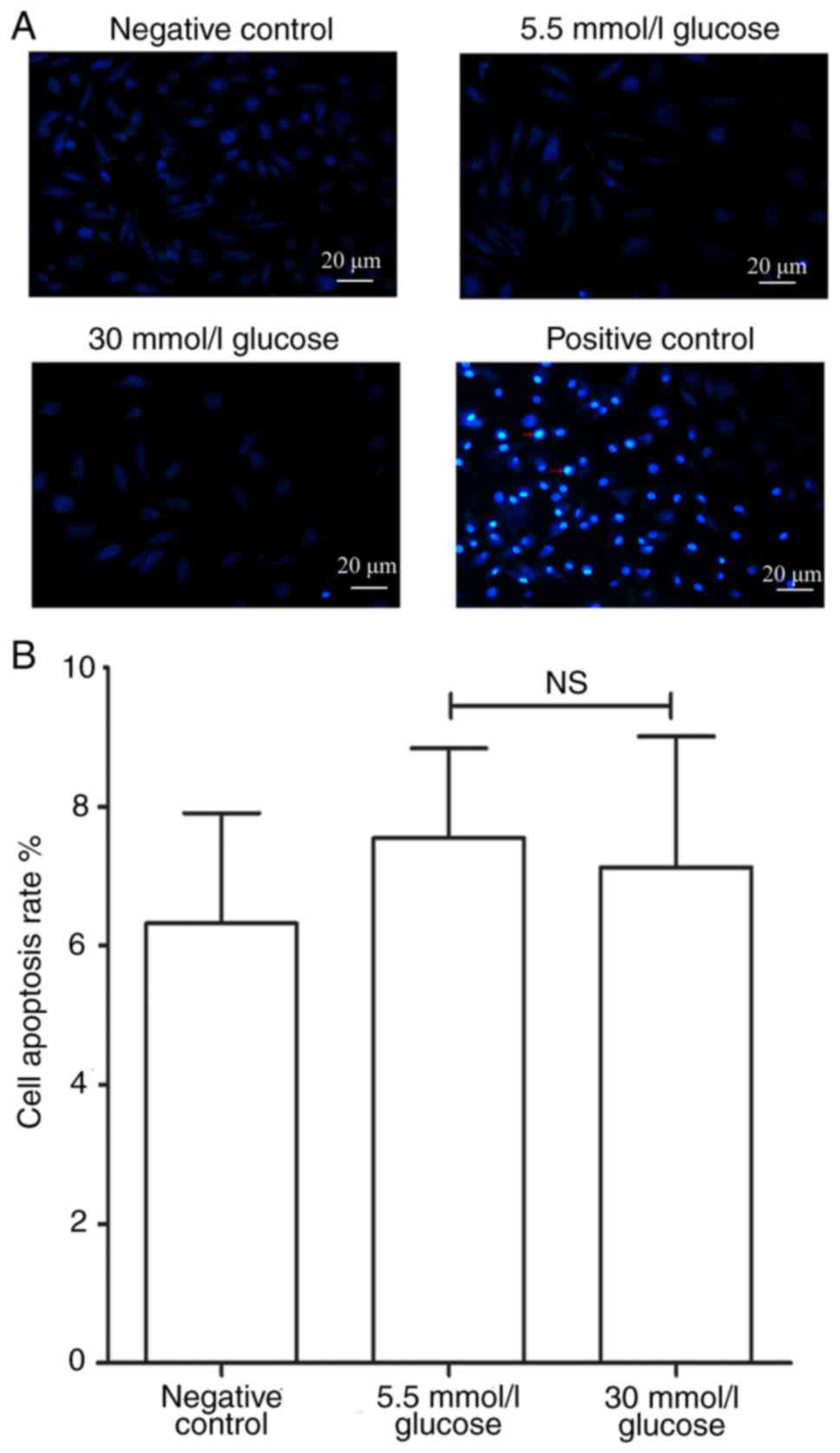
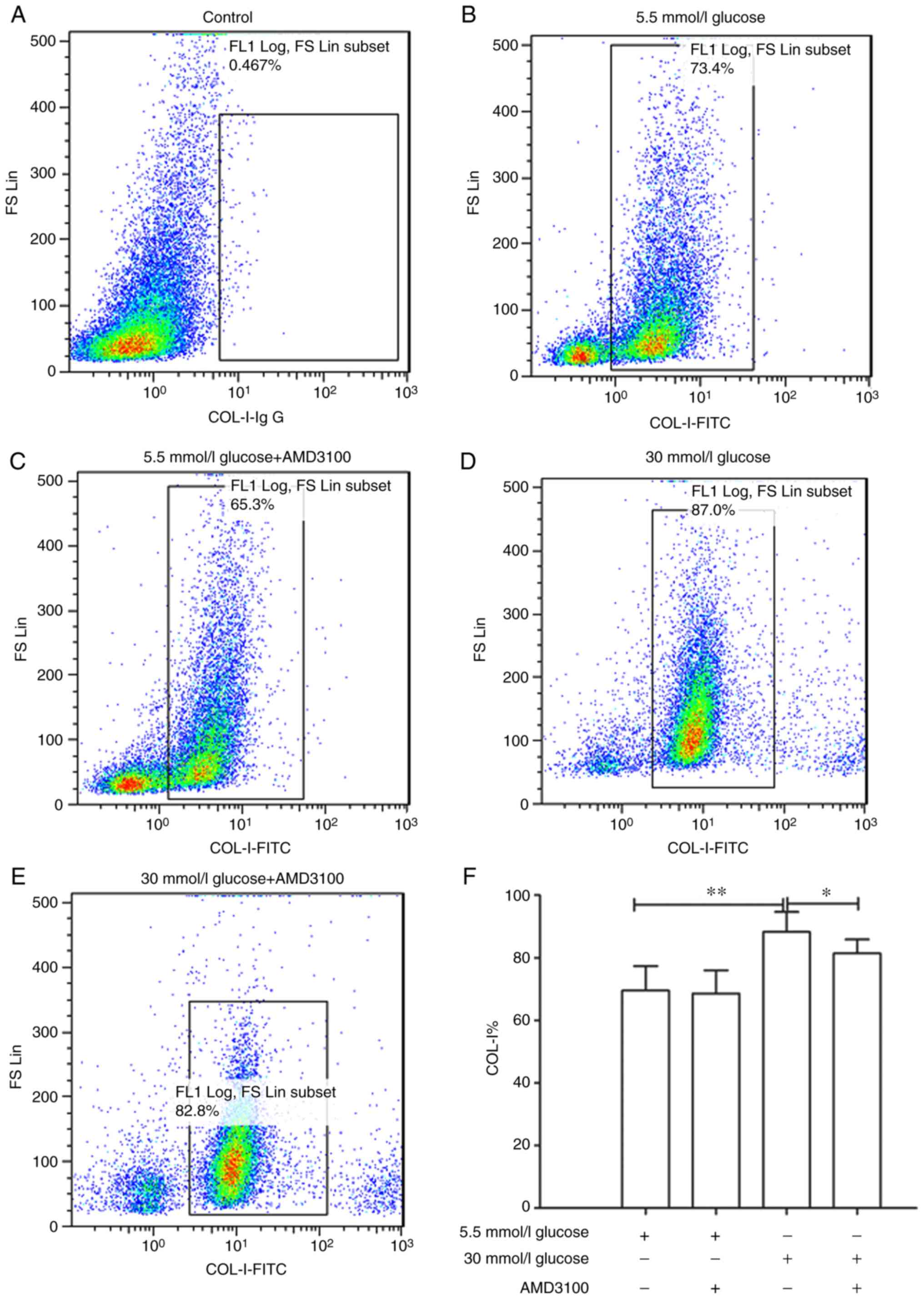
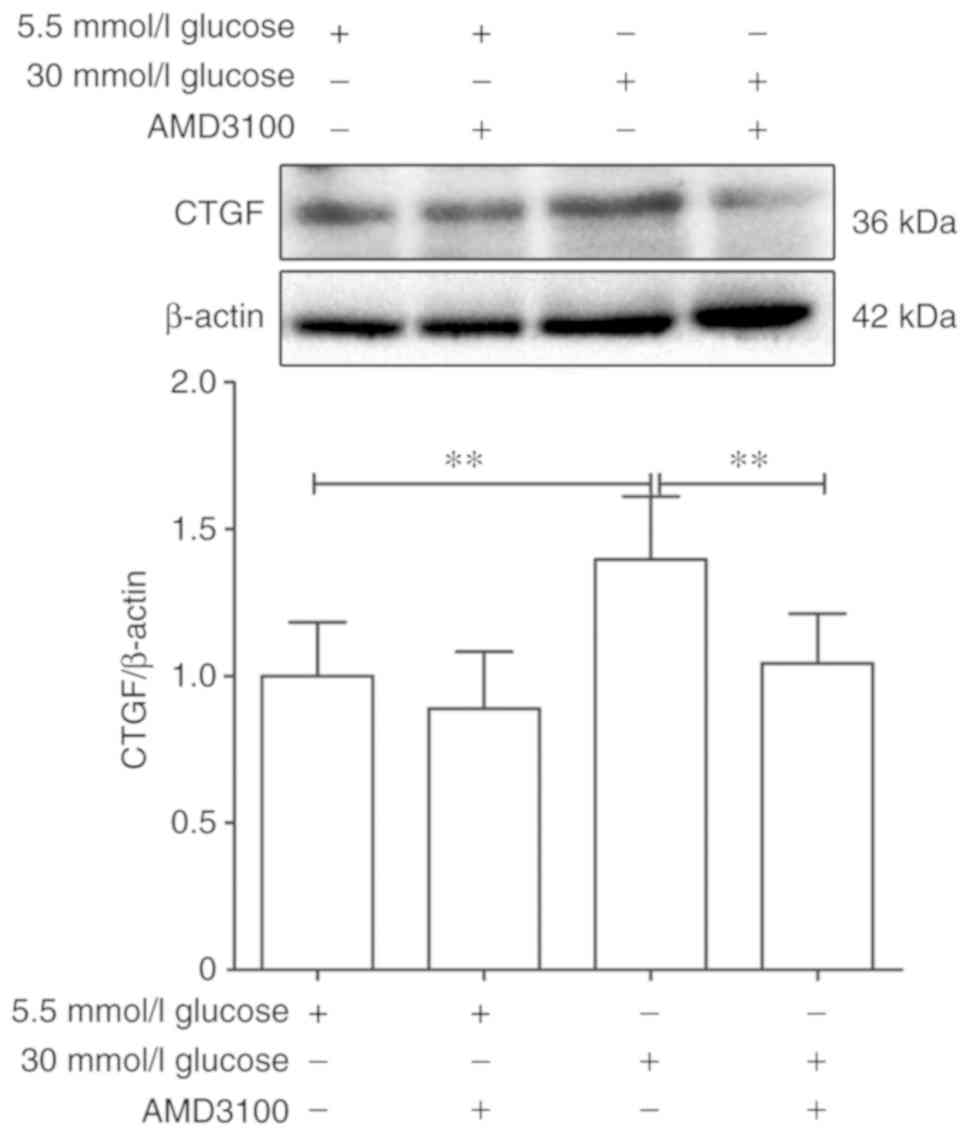
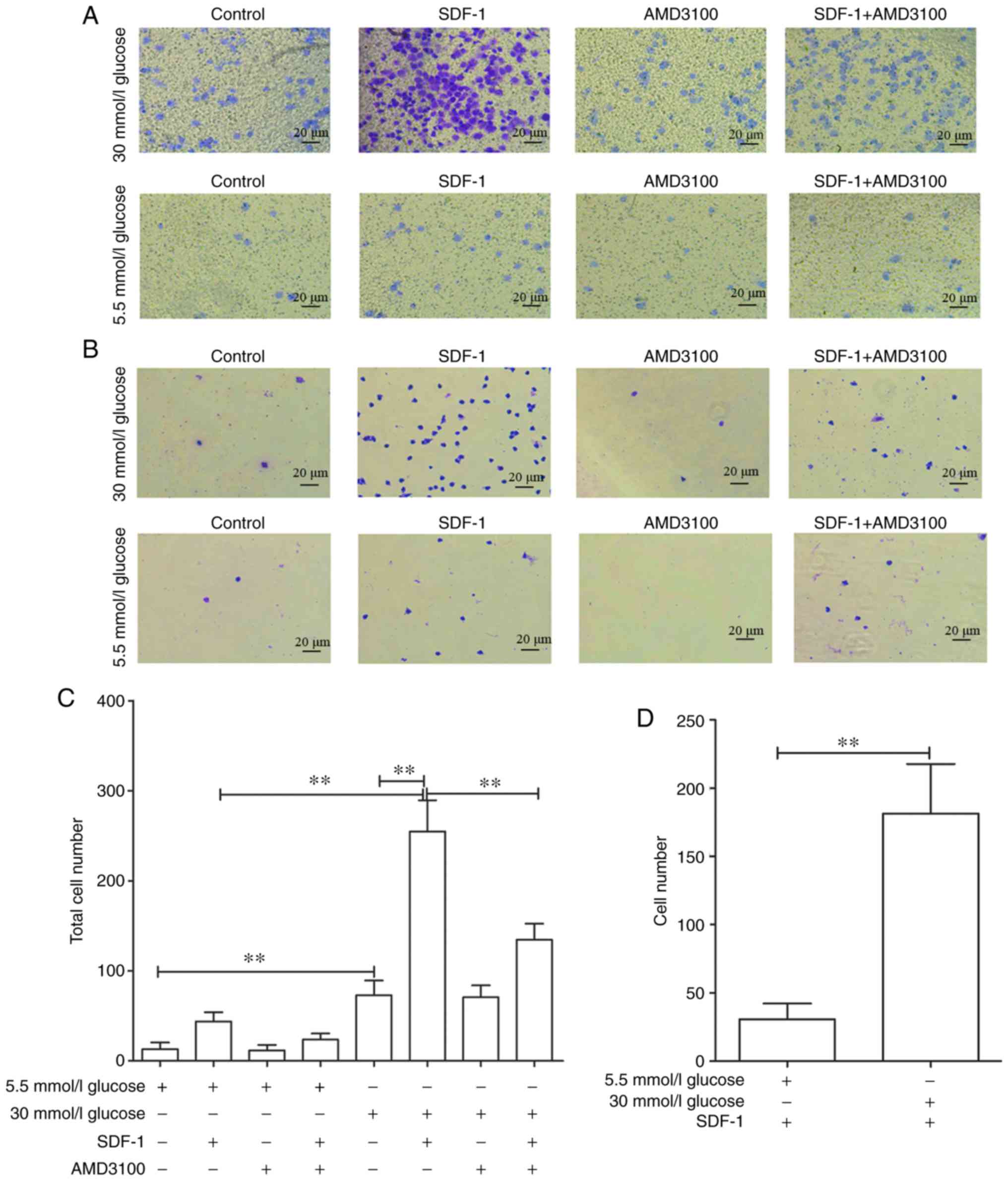
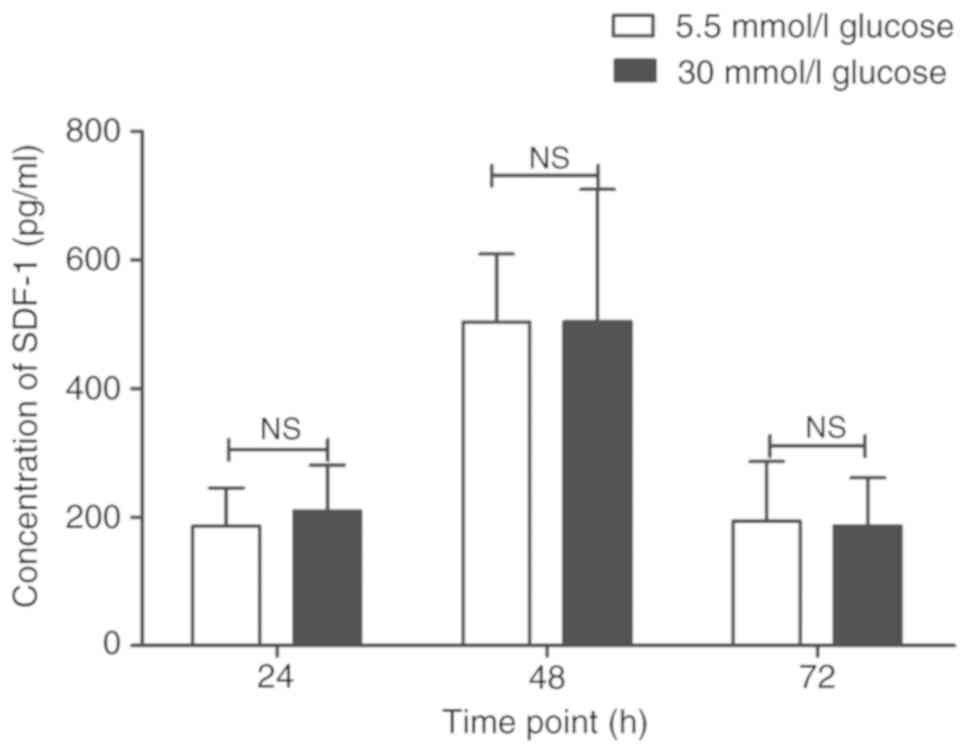
|
1
|
Hayat SA, Patel B, Khattar RS and Malik
RA: Diabetic cardio-myopathy: Mechanisms, diagnosis and treatment.
Clin Sci (Lond). 107:539–557. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fang ZY, Prins JB and Marwick TH: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy: Evidence, mechanisms, and therapeutic implications.
Endocr Rev. 25:543–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Zhou LN, Shen ZZ, Zhang XY, Yin
M, Liu GZ, Guo P and Zhu XX: Effects of myocardial fibroblasts on
fibrosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Fudan Univ J Med Sci.
29:399–402. 2002.In Chinese.
|
|
4
|
Bucala R, Spiegel LA, Chesney J, Hogan M
and Cerami A: Circulating fibrocytes define a new leukocyte
subpopulation that mediates tissue repair. Mol Med. 1:71–81. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Varcoe RL, Mikhail M, Guiffre AK, Pennings
G, Vicaretti M, Hawthorne WJ, Fletcher JP and Medbury HJ: The role
of the fibrocyte in intimal hyperplasia. J Thromb Haemost.
4:1125–1133. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gomer R and Pilling D: Compositions and
methods for suppressing fibrocytes and for detecting fibrocyte
differentiation. Analyst. 2:217–220. 2010.
|
|
7
|
Laws DA, Kraft AS, Leddy LR and Larue AC:
Abstract A46: The role of circulating fibroblast precursors in
promoting metastatic sarcoma. Cancer Res. 75(Suppl 1): pp.
A462015
|
|
8
|
Li C, Li X, Deng C and Guo C: Circulating
fibrocytes are increased in neonates with bronchopulmonary
dysplasia. PLoS One. 11:pp. e01571812016, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Trimble A, Gochuico BR, Markello TC,
Fischer R, Gahl WA, Lee JK, Kim Y, Burdick MD, Strieter RM and
Mehrad B: Circulating fibrocytes as biomarker of prognosis in
Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
190:1395–1401. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin CH, Shih CH, Tseng CC, Yu CC, Tsai YJ,
Bien MY and Chen BC: CXCL12 induces connective tissue growth factor
expression in human lung fibroblasts through the Rac1/ERK, JNK, and
AP-1 pathways. PLoS One. 9:pp. e1047462014, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Behjati M and Hashemi M: Application of
fibrocytes in the treatment of diabetic foot: As a potential new
therapeutic approach. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 86:152–153. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Weng Y, Qi J, Du C, Liu X, Xu C, Zeng G
and Tang L: Effect of high glucose on circulating fibrocytes
proliferation and the expression of CXCR4 and CTGF. Chin J
Diabetes. 26:227–233. 2018.In Chinese.
|
|
13
|
Murray LA: Commonalities between the
pro-fibrotic mechanisms in COPD and IPF. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
25:276–280. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Janardhanan R,
Salerno M, Hunter JR, Burdick MM, Field JJ, Strieter RM and Kramer
CM: Elevated circulating fibrocyte levels in patients with
hypertensive heart disease. J Hypertens. 30:1856–1861. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
White MJV, Galvis-Carvajal E and Gomer RH:
A brief exposure to tryptase or thrombin potentiates fibrocyte
differentiation in the presence of serum or SAP. J Immunol.
194:142–150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ulmer AJ, Scholz W, Ernst M, Brandt E and
Flad HD: Isolation and subfractionation of human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells (PBMC) by density gradient centrifugation on
percoll. Immunobiology. 166:238–250. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Quan TE, Cowper S, Wu SP, Bockenstedt LK
and Bucala R: Circulating fibrocytes: Collagen-secreting cells of
the peripheral blood. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:598–606. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schmidt M, Sun G, Stacey MA, Mori L and
Mattoli S: Identification of circulating fibrocytes as precursors
of bronchial myofibroblasts in asthma. J Immunol. 171:380–389.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu Y, Zhou J, Wang H, Wu Y, Gao Q, Wang L,
Zhao Q, Liu P, Gao S, Wen W, et al: The activation of p38 MAPK
limits the abnormal proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells
induced by high sodium concentrations. Int J Mol Med. 37:74–82.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Zhou YK and Xue YM: High glucose
inhibiting proliferation of RSC96 schwann cells by high osmotic
pressure. J Kunming Univ Sci Technol. 38:60–64. 2013.In
Chinese.
|
|
21
|
Chen HT, Wang DY, Geng HZ, Chen HQ, Wu YX,
Deng SQ and Wang ZL: Adiponectin exerts antiproliferative effect on
high glucose-induced BeWo cell proliferation in vitro. Zhonghua Fu
Chan Ke Za Zhi. 51:204–208. 2016.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ho FM, Liu SH, Lin WW and Liau CS:
Opposite effects of high glucose on MMP-2 and TIMP-2 in human
endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem. 101:442–450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Marchesi F, Monti P, Leone BE, Zerbi A,
Vecchi A, Piemonti L, Mantovani A and Allavena P: Increased
survival, proliferation, and migration in metastatic human
pancreatic tumor cells expressing functional CXCR4. Cancer Res.
64:8420–8427. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rodríguez-Nieves JA, Patalano SC, Almanza
D, Gharaee- Kermani M and Macoska JA: CXCL12/CXCR4 axis activation
mediates prostate myofibroblast phenoconversion through
non-canonical EGFR/MEK/ERK signaling. PLoS One. 11:pp.
e01594902016, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pandey DP, Lappano R, Albanito L, Madeo A,
Maggiolini M and Picard D: Estrogenic GPR30 signalling induces
proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through CTGF.
EMBO J. 28:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li M, Xie Z, Wang P, Li J, Liu W, Tang S,
Liu Z, Wu X, Wu Y and Shen H: The long noncoding RNA GAS5
negatively regulates the adipogenic differentiation of MSCs by
modulating the miR-18a/CTGF axis as a ceRNA. Cell Death Dis.
9:5542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Duan L, Guo T, Gao Y, Tian L, Liu
J, Wang S and Yang J: Downregulation of miR-30c promotes renal
fibrosis by target CTGF in diabetic nephropathy. J Diabetes
Complications. 30:406–414. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu Y, Wang W, Peng XM, He Y, Xiong YX,
Liang HF, Chu L, Zhang BX, Ding ZY and Chen XP: Rapamycin
upregulates connective tissue growth factor expression in hepatic
progenitor cells through TGF-β-Smad2 dependent signaling. Front
Pharmacol. 9:8772018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Guan S and Zhou J: Frizzled-7 mediates
TGF-β-induced pulmonary fibrosis by transmitting non-canonical Wnt
signaling. Exp Cell Res. 359:226–234. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chiang HY, Chu PH and Lee TH: R1R2 peptide
ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in mice through fibrocyte migration
and differentiation. PLoS One. 12:pp. e01858112017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lassance L, Marino GK, Medeiros CS,
Thangavadivel S and Wilson SE: Fibrocyte migration, differentiation
and apoptosis during the corneal wound healing response to injury.
Exp Eye Res. 170:177–187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nakamichi M, Akishimafukasawa Y, Fujisawa
C, Mikami T, Onishi K and Akasaka Y: Basic fibroblast growth factor
induces angiogenic properties of fibrocytes to stimulate vascular
formation during wound healing. Am J Pathol. 186:3203–3216. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Beale A, Fang L, Ellims A, Ling L, Taylor
A, Chin-Dusting J and Dart A: Fibrocytes, a novel fibroblast-like
population, are increased in cardiac fibrosis. Heart Lung Circ.
21(Suppl 1): pp. S59. 2012, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Haudek SB, Cheng J, Du J, Wang Y,
Hermosillo-Rodriguez J, Trial J, Taffet GE and Entman ML: Monocytic
fibroblast precursors mediate fibrosis in angiotensin-II-induced
cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 49:3499–507. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Russo I and Frangogiannis NG:
Diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis: Cellular effectors, molecular
mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
90:84–93. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Feng B, Chen S, Gordon AD and Chakrabarti
S: miR-146a mediates inflammatory changes and fibrosis in the heart
in diabetes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 105:70–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Berning P, Schaefer C, Clemens D,
Korsching E, Dirksen U and Potratz J: The CXCR4 antagonist
plerixafor (AMD3100) promotes proliferation of Ewing sarcoma cell
lines in vitro and activates receptor tyrosine kinase signaling.
Cell Commun Signal. 16:1–13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Reeves PM, Abbaslou MA, Kools FRW and
Poznansky MC: CXCR4 blockade with AMD3100 enhances Taxol
chemotherapy to limit ovarian cancer cell growth. Anticancer Drugs.
28:935–942. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li JK, Yu L, Shen Y, Zhou LS, Wang YC and
Zhang JH: Inhibition of CXCR4 activity with AMD3100 decreases
invasion of human colorectal cancer cells in vitro. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:2308–2313. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ishida Y, Kimura A, Nosaka M, Kuninaka Y,
Hemmi H, Sasaki I, Kaisho T, Mukaida N and Kondo T: Essential
involvement of the CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis in bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis via regulation of fibrocyte and M2 macrophage
migration. Sci Rep. 7:168332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Phillips RJ, Burdick MD, Hong K, Lutz MA,
Murray LA, Xue YY, Belperio JA, Keane MP and Strieter RM:
Circulating fibrocytes traffic to the lungs in response to CXCL12
and mediate fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 114:438–446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ishida Y, Kimura A, Kondo T, Hayashi T,
Ueno M, Takakura N, Matsushima K and Mukaida N: Essential roles of
the CC chemokine ligand 3-CC chemokine receptor 5 axis in
bleomycin- induced pulmonary fibrosis through regulation of
macrophage and fibrocyte infiltration. Am J Pathol. 170:843–854.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Luo X, Wang X, Xia Z, Chung SK and Cheung
CW: CXCL12/CXCR4 axis: An emerging neuromodulator in pathological
pain. Rev Neurosci. 27:83–92. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Katsura M, Shoji F, Okamoto T, Shimamatsu
S, Hirai F, Toyokawa G, Morodomi Y, Tagawa T, Oda Y and Maehara Y:
Correlation between CXCR4/CXCR7/CXCL12 chemokine axis expression
and prognosis in lymph-node-positive lung cancer patients. Cancer
Sci. 109:154–165. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ho SY, Ling TY, Lin HY, Liou JT, Liu FC,
Chen IC, Lee SW, Hsu Y, Lai DM and Liou HH: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling
maintains stemness signature in mouse neural stem/progenitor cells.
Stem Cells Int. 2017:24937522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Song JS, Kang CM, Kang HH, Yoon HK, Kim
YK, Kim KH, Moon HS and Park SH: Inhibitory effect of CXC chemokine
receptor 4 antagonist AMD3100 on bleomycin induced murine pulmonary
fibrosis. Exp Mol Med. 42:465–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chun TH: Peri-adipocyte ECM remodeling in
obesity and adipose tissue fibrosis. Adipocyte. 1:89–95. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Friedl P and Gilmour D: Collective cell
migration in morphogenesis, regeneration and cancer. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 10:445–457. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wolf K, Mazo I, Leung H, Engelke K, von
Andrian UH, Deryugina EI, Strongin AY, Bröcker EB and Friedl P:
Compensation mechanism in tumor cell migration: Mesenchymal
amoeboid transition after blocking of pericellular proteolysis. J
Cell Biol. 160:267–277. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sandbothe M, Buurman R, Reich N, Greiwe L,
Vajen B, Gürlevik E, Schäffer V, Eilers M, Kühnel F, Vaquero A, et
al: The microRNA-449 family inhibits TGF-β-mediated liver cancer
cell migration by targeting SOX4. J Hepatol. 66:1012–1021. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Galligan CL and Fish EN: Circulating
fibrocytes contribute to the pathogenesis of collagen
antibody-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 64:3583–3593. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Craig VJ, Zhang L, Hagood JS and Owen CA:
Matrix metal-loproteinases as therapeutic targets for idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 53:585–600. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Singh SR, Sutcliffe A, Kaur D, Gupta S,
Desai D, Saunders R and Brightling CE: CCL2 release by airway
smooth muscle is increased in asthma and promotes fibrocyte
migration. Allergy. 69:1189–1197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Derakhshan R, Arababadi MK, Ahmadi Z,
Karimabad MN, Salehabadi VA, Abedinzadeh M, Khorramdelazad H,
Balaei P, Kennedy D and Hassanshahi G: Increased circulating levels
of SDF-1 (CXCL12) in type 2 diabetic patients are correlated to
disease state but are unrelated to polymorphism of the SDF-1β gene
in the Iranian population. Inflammation. 35:900–904. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lovshin JA, Rajasekeran H, Lytvyn Y,
Lovblom LE, Khan S, Alemu R, Locke A, Lai V, He H, Hittle L, et al:
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition stimulates distal Tubular
natriuresis and increases in circulating SDF-1α (1-67) in patients
with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 40:1073–1081. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kajiyama H, Shibata K, Ino K, Nawa A,
Mizutani S and Kikkawa F: Possible involvement of
SDF-1alpha/CXCR4-DPPIV axis in TGF-beta1-induced enhancement of
migratory potential in human peritoneal mesothelial cells. Cell
Tissue Res. 330:221–229. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|