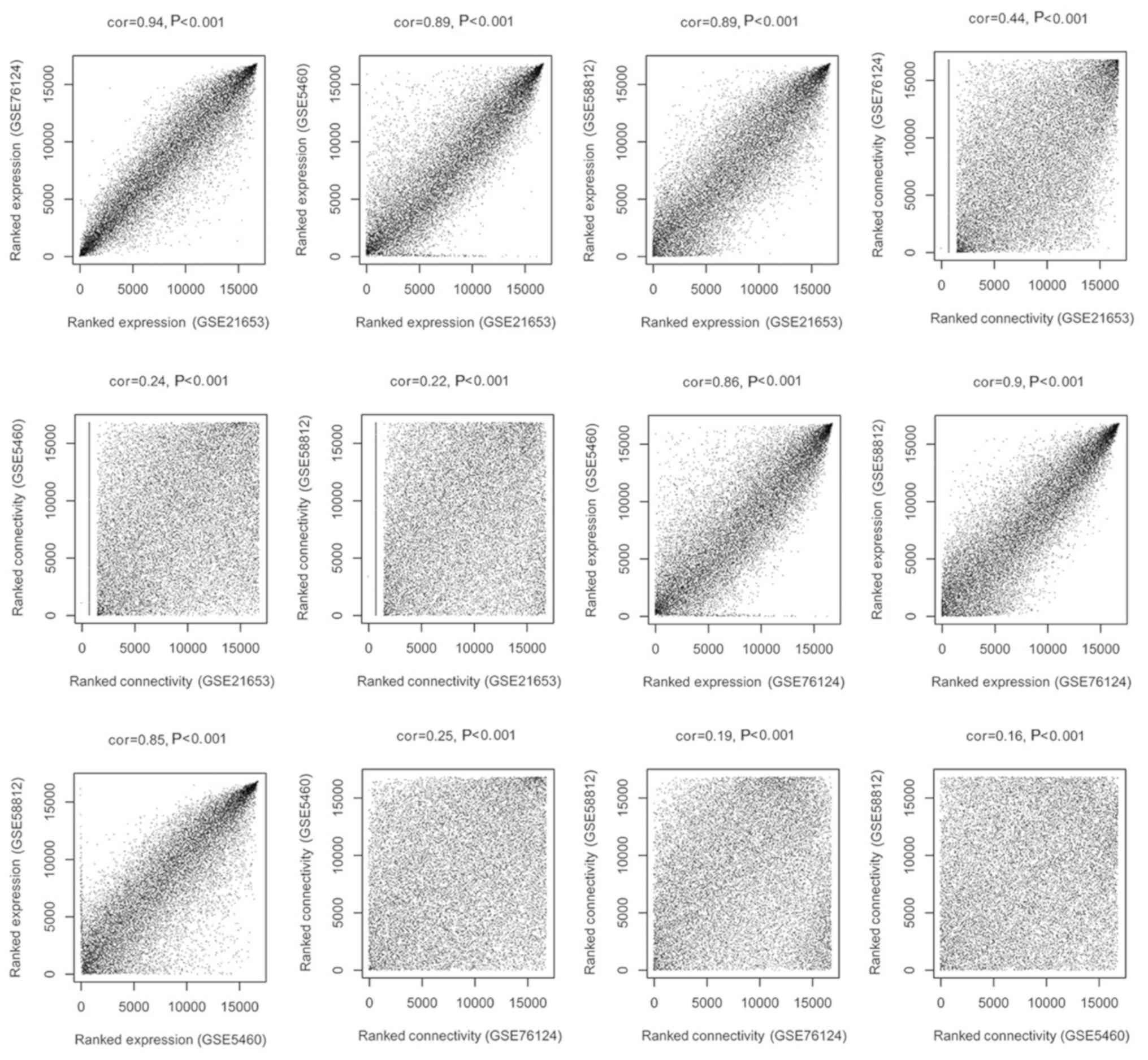
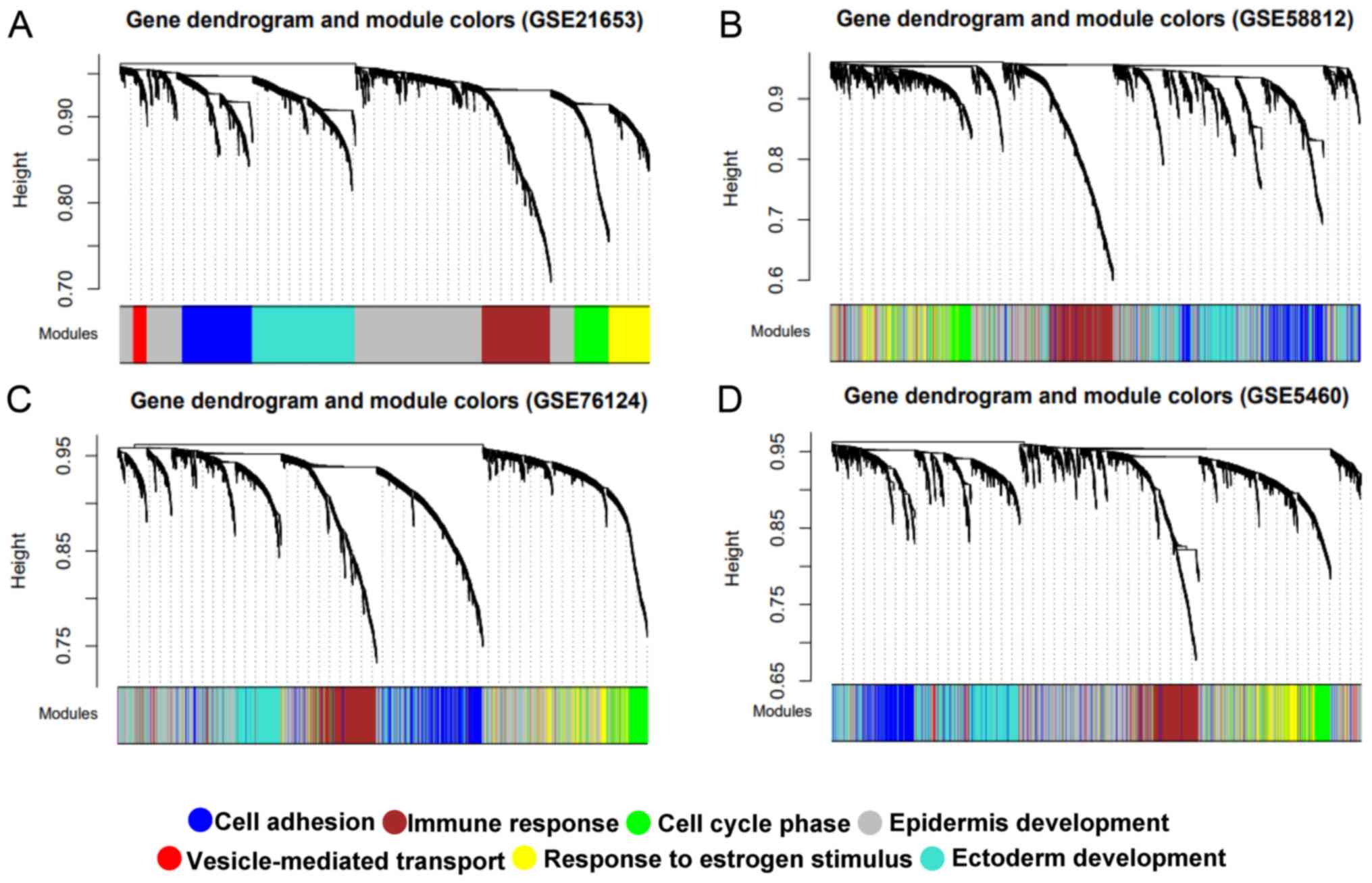
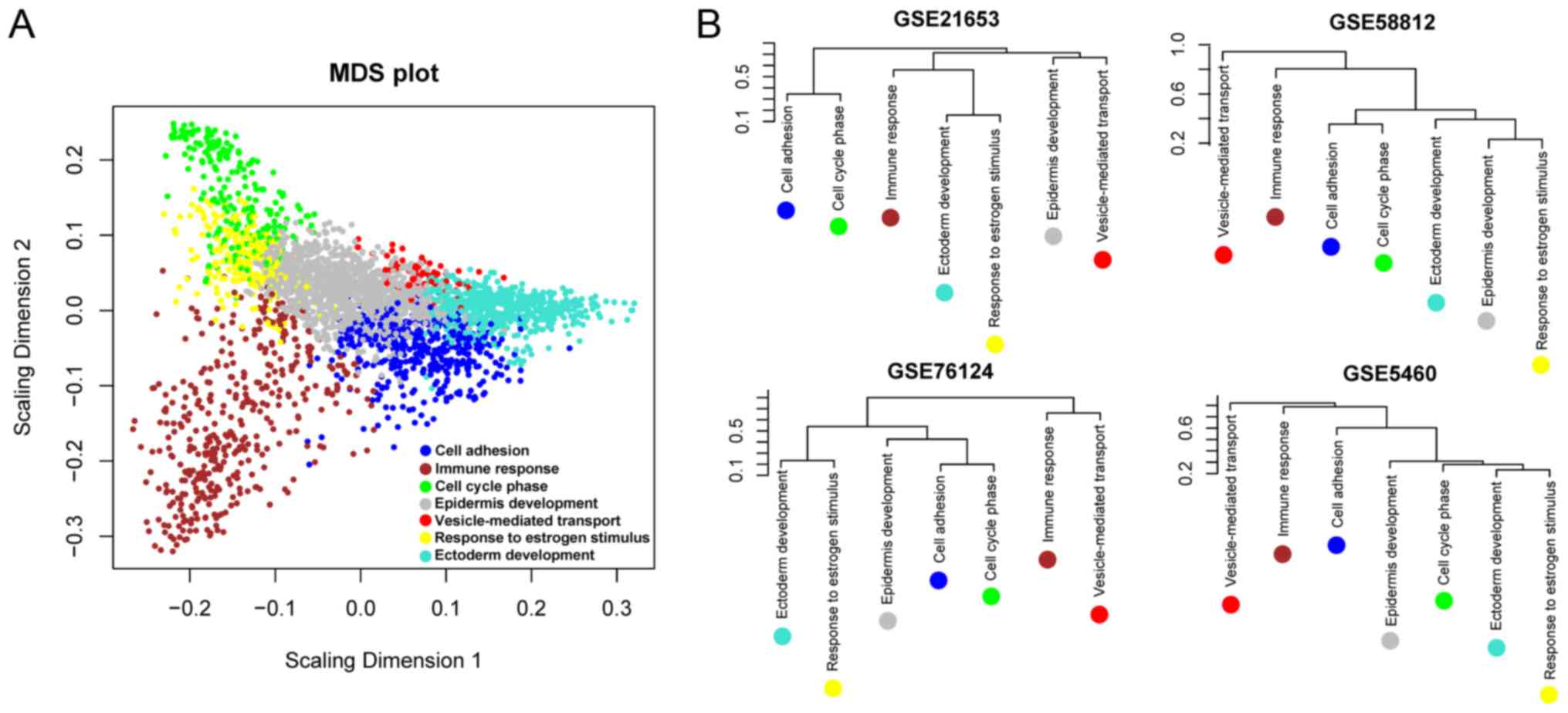
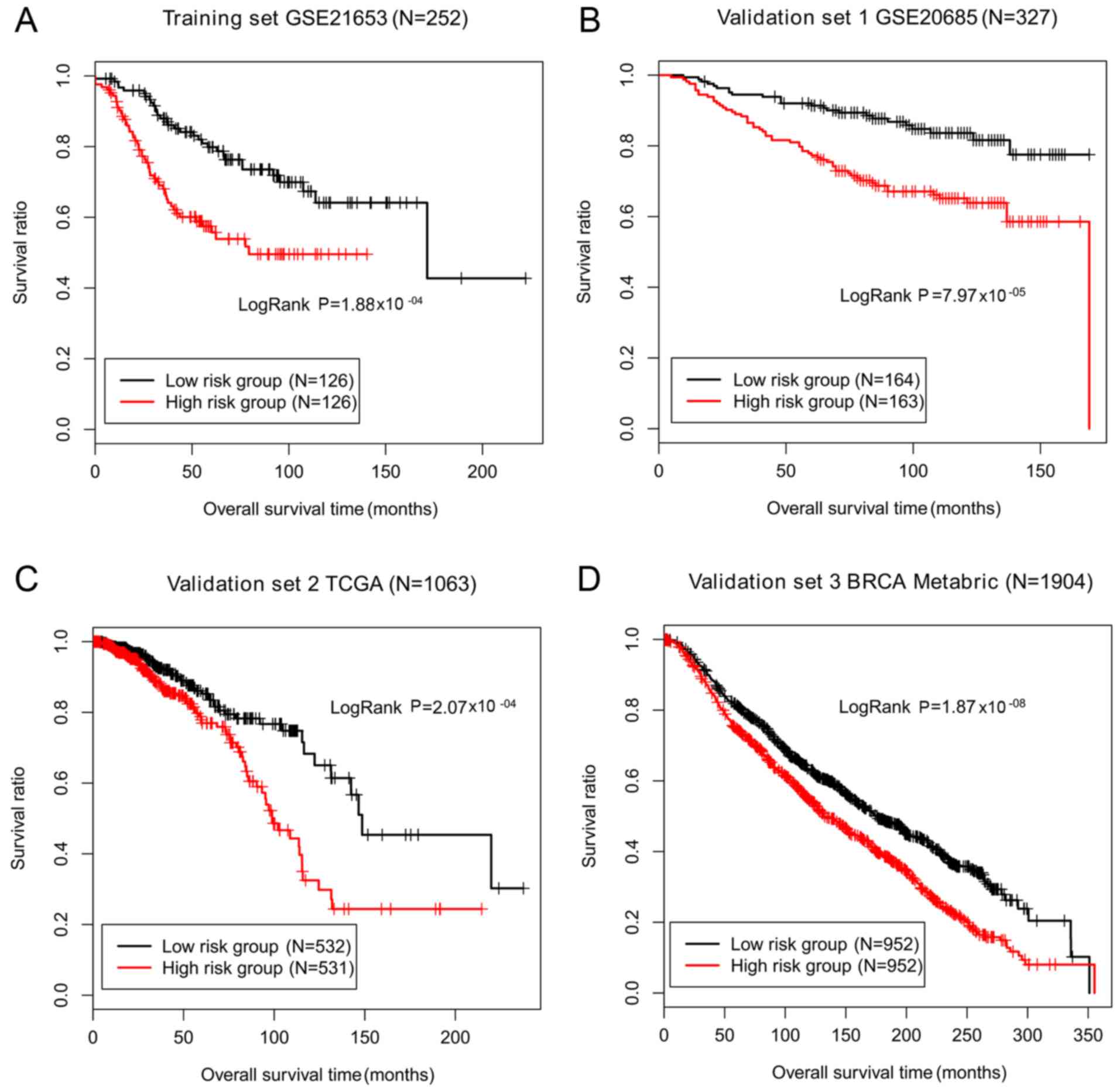
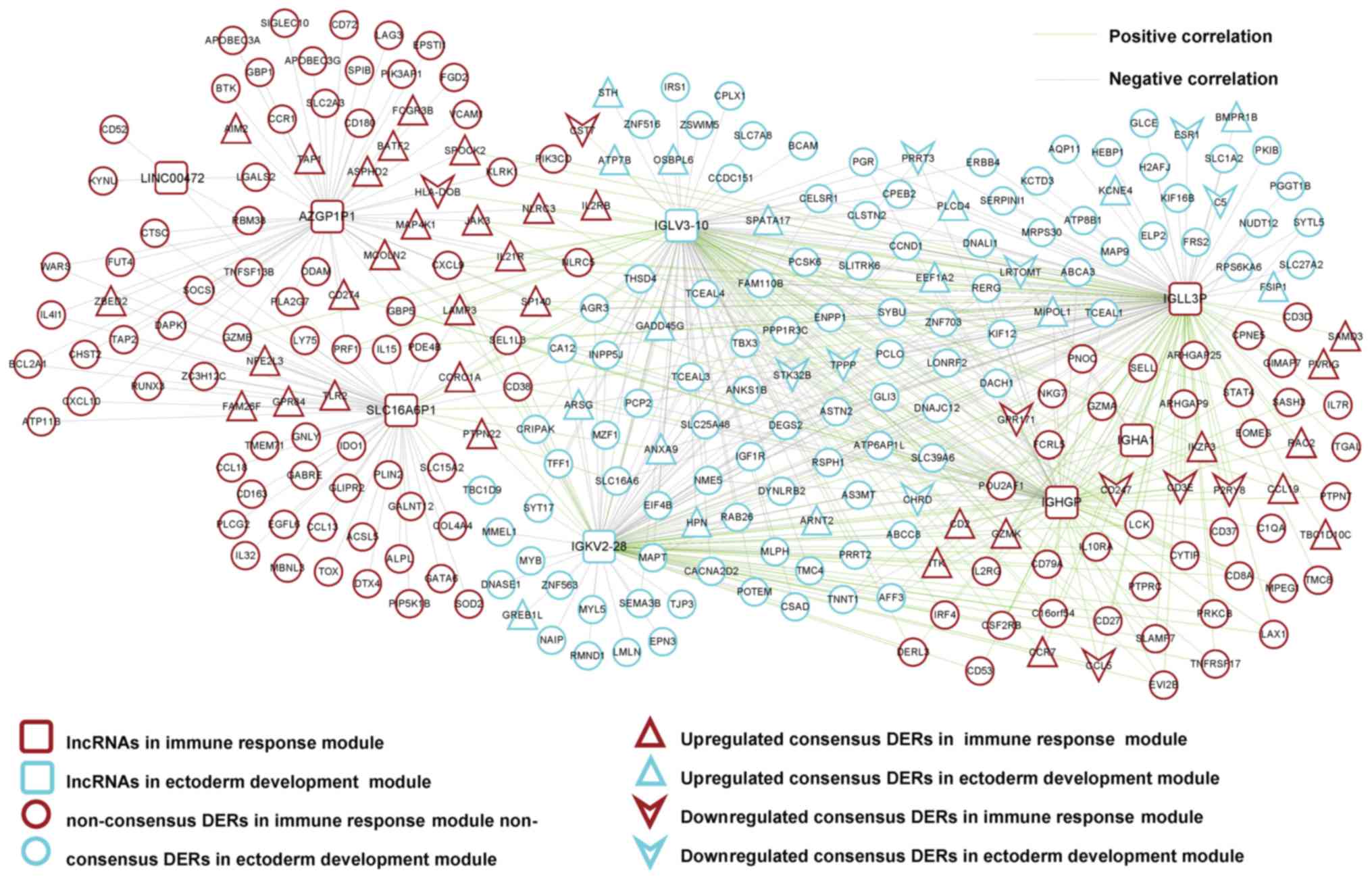
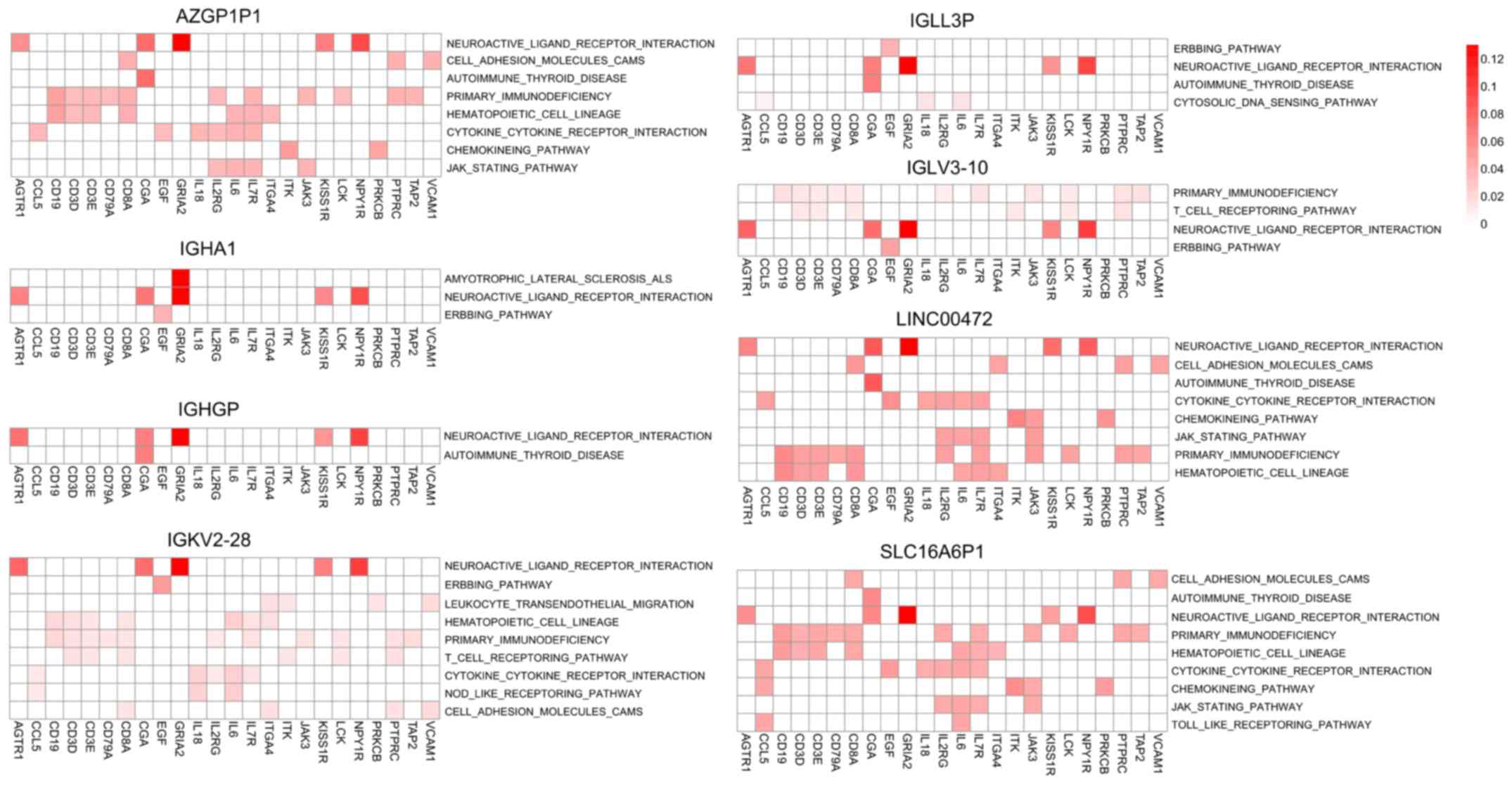
|
1
|
McGuire A, Brown JA, Malone C, Mclaughlin
R and Kerin MJ: Effects of age on the detection and management of
breast cancer. Cancers. 7:908–929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Radice D and Redaelli A: Breast cancer
management: Quality-of-life and cost considerations.
Pharmacoeconomics. 21:383–396. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiralerspong S and Goodwin PJ: Obesity and
breast cancer prognosis: Evidence, challenges, and opportunities. J
Clin Oncol. 34:4203–4216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kitagawa M, Kitagawa K, Kotake Y, Niida H
and Ohhata T: Cell cycle regulation by long non-coding RNAs. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 70:4785–4794. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liz J and Esteller M: lncRNAs and
microRNAs with a role in cancer development. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1859:169–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hayes EL and Lewis-Wambi JS: Mechanisms of
endocrine resistance in breast cancer: An overview of the proposed
roles of noncoding RNA. Breast Cancer Res. 17:402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Godinho MF, Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Meijer
D, Foekens JA, Dorssers LC and van Agthoven T: Relevance of BCAR4
in tamoxifen resistance and tumour aggressiveness of human breast
cancer. Br J Cancer. 103:1284–1291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sørensen KP, Thomassen M, Tan Q, Bak M,
Cold S, Burton M, Larsen MJ and Kruse TA: Long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker of metastasis in
estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 142:529–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xue X, Yang YA, Zhang A, Fong KW, Kim J,
Song B, Li S, Zhao JC and Yu J: LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling
and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene.
35:2746–2755. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Li Z, Hou P, Fan D, Dong M, Ma M, Li H,
Yao R, Li Y, Wang G and Geng P: The degradation of EZH2 mediated by
lncRNA ANCR attenuated the invasion and metastasis of breast
cancer. Cell Death Differ. 24:59–71. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Tracy KM, Tye CE, Page NA, Fritz AJ, Stein
JL, Lian JB and Stein GS: Selective expression of long non-coding
RNAs in a breast cancer cell progression model. J Cell Physiol.
233:1291–1299. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Meng J, Li P, Zhang Q, Yang Z and Fu S: A
four-long non-coding RNA signature in predicting breast cancer
survival. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun M, Wu D, Zhou K, Li H, Gong X, Wei Q,
Du M, Lei P, Zha J and Zhu H: An eight-lncRNA signature predicts
survival of breast cancer patients: A comprehensive study based on
weighted gene co-expression network analysis and competing
endogenous RNA network. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 175:59–75. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Maubant S, Tesson B, Maire V, Ye M,
Rigaill G, Gentien D, Cruzalegui F, Tucker GC, Roman-Roman S and
Dubois T: Transcriptome analysis of Wnt3a-treated triple-negative
breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 10:e01223332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Colak D, Nofal A, Albakheet A, Nirmal M,
Jeprel H, Eldali A, Al-Tweigeri T, Tulbah A, Ajarim D, Malik OA, et
al: Age-specific gene expression signatures for breast tumors and
cross-species conserved potential cancer progression markers in
young women. PLoS One. 8:e632042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clarke C, Madden SF, Doolan P, Aherne ST,
Joyce H, O'Driscoll L, Gallagher WM, Hennessy BT, Moriarty M, Crown
J, et al: Correlating transcriptional networks to breast cancer
survival: A large-scale coexpression analysis. Carcinogenesis.
34:2300–2308. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carvalho B: An Introduction to the Oligo
Package. 2009.
|
|
18
|
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M and
Speed TP: A comparison of normalization methods for high density
oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias.
Bioinformatics. 19:185–193. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
O'Leary NA, Wright MW, Brister JR, Ciufo
S, Haddad D, McVeigh R, Rajput B, Robbertse B, Smith-White B,
Ako-Adjei D, et al: Reference sequence (RefSeq) database at NCBI:
Current status, taxonomic expansion, and functional annotation.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D733–D745. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP,
Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm
A, Lopez R, et al: Clustal W and clustal X version 2.0.
Bioinformatics. 23:2947–2948. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lou Y, Tian GY, Song Y, Liu YL, Chen YD,
Shi JP and Yang J: Characterization of transcriptional modules
related to fibrosing-NAFLD progression. Sci Rep. 7:47482017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perumal D, Leshchenko VV, Kuo PY, Jiang Z,
Readhead B, Eden C, Athaluri Divakar SK, Zhang W, Cho HJ, Chari A,
et al: Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA)
identifies highly proliferative myeloma subgroup responsive to
CDK4/ARK5 inhibition. Blood. 124:34452014.
|
|
23
|
Horvath S and Langfelder P: Tutorials for
the WGCNA package for R: WGCNA Background and glossary. 2011.
|
|
24
|
Tibshirani R: The lasso method for
variable selection in the Cox model. Stat Med. 16:385–395. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang S, Yee C, Ching T, Yu H and Garmire
LX: A novel model to combine clinical and pathway-based
transcriptomic information for the prognosis prediction of breast
cancer. PLoS Comput Biol. 10:e10038512014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chong QI, Hong L, Cheng Z and Yin Q:
Identification of metastasis-associated genes in colorectal cancer
using metaDE and survival analysis. Oncol Lett. 11:568–574. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Walker MG and Shi J: Gene set enrichment
analysis (GSEA) for interpreting gene expression profiles. Current
Bioinformatics. 2:133–137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Evans JR, Feng FY and Chinnaiyan AM: The
bright side of dark matter: lncRNAs in cancer. J Clin Invest.
126:27752016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shen Y, Katsaros D, Loo LW, Hernandez BY,
Chong C, Canuto EM, Biglia N, Lu L, Risch H, Chu WM and Yu H:
Prognostic and predictive values of long non-coding RNA LINC00472
in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 6:8579–8592. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shen Y, Wang Z, Loo LW, Ni Y, Jia W, Fei
P, Risch HA, Katsaros D and Yu H: LINC00472 expression is regulated
by promoter methylation and associated with disease-free survival
in patients with grade 2 breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
154:473–482. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu P, Yang X, Yang Y, Wang F, Li L and Gu
Y: Linc00472 suppresses breast cancer progression and enhances
doxorubicin sensitivity through regulation of miR-141 and
programmed cell death 4. Rsc Advances. 8:8455–8468. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mcsherry EA, Brennan K, Hudson L, Hill AD
and Hopkins AM: Breast cancer cell migration is regulated through
junctional adhesion molecule-A-mediated activation of rap1 GTPase.
Breast Cancer Res. 13:R312011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li DM and Feng YM: Signaling mechanism of
cell adhesion molecules in breast cancer metastasis: Potential
therapeutic targets. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:7–21. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Christy J and Priyadharshini L:
Differential expression analysis of JAK/STAT pathway related genes
in breast cancer. Meta Gene. 16:2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hosford SR and Miller TW: Clinical
potential of novel therapeutic targets in breast cancer: CDK4/6,
Src, JAK/STAT, PARP, HDAC, and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways.
Pharmacogenomics Pers Med. 6:203–215. 2014.
|
|
36
|
Ross JS, Fletcher JA, Linette GP, Stec J,
Clark E, Ayers M, Symmans WF, Pusztai L and Bloom KJ: The Her-2/neu
gene and protein in breast cancer 2003: Biomarker and target of
therapy. Oncologist. 8:307–325. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ross JS, Slodkowska EA, Symmans WF,
Pusztai L, Ravdin PM and Hortobagyi GN: The HER-2 receptor and
breast cancer: Ten years of targeted anti-HER-2 therapy and
personalized medicine. Oncologist. 14:320–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boulbes DR, Arold ST, Chauhan GB, Blachno
KV, Deng N, Chang WC, Jin Q, Huang TH, Hsu JM, Brady SW, et al: HER
family kinase domain mutations promote tumor progression and can
predict response to treatment in human breast cancer. Mol Oncol.
9:586–600. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
De Cola A, Volpe S, Budani MC, Ferracin M,
Lattanzio R, Turdo A, D'Agostino D, Capone E, Stassi G, Todaro M,
et al: MiR-205-5p-mediated downregulation of ErbB/HER receptors in
breast cancer stem cells results in targeted therapy resistance.
Cell Death Dis. 6:e18232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Oh E, Kim JY, Cho Y, An H, Lee N, Jo H,
Ban C and Seo JH: Overexpression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor
in breast cancer cells induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:1071–1081. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu L, Xu Q, Cheng L, Ma C, Xiao L, Xu D,
Gao Y, Wang J and Song H: NPY1R is a novel peripheral blood marker
predictive of metastasis and prognosis in breast cancer patients.
Oncol Lett. 9:891–896. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Goertzen CG, Dragan M, Turley E, Babwah AV
and Bhattacharya M: KISS1R signaling promotes invadopodia formation
in human breast cancer cell via β-arrestin2/ERK. Cell Signal.
28:165–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gao D, Rahbar R and Fish EN: CCL5
activation of CCR5 regulates cell metabolism to enhance
proliferation of breast cancer cells. Open Biol. 6:1601222016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|