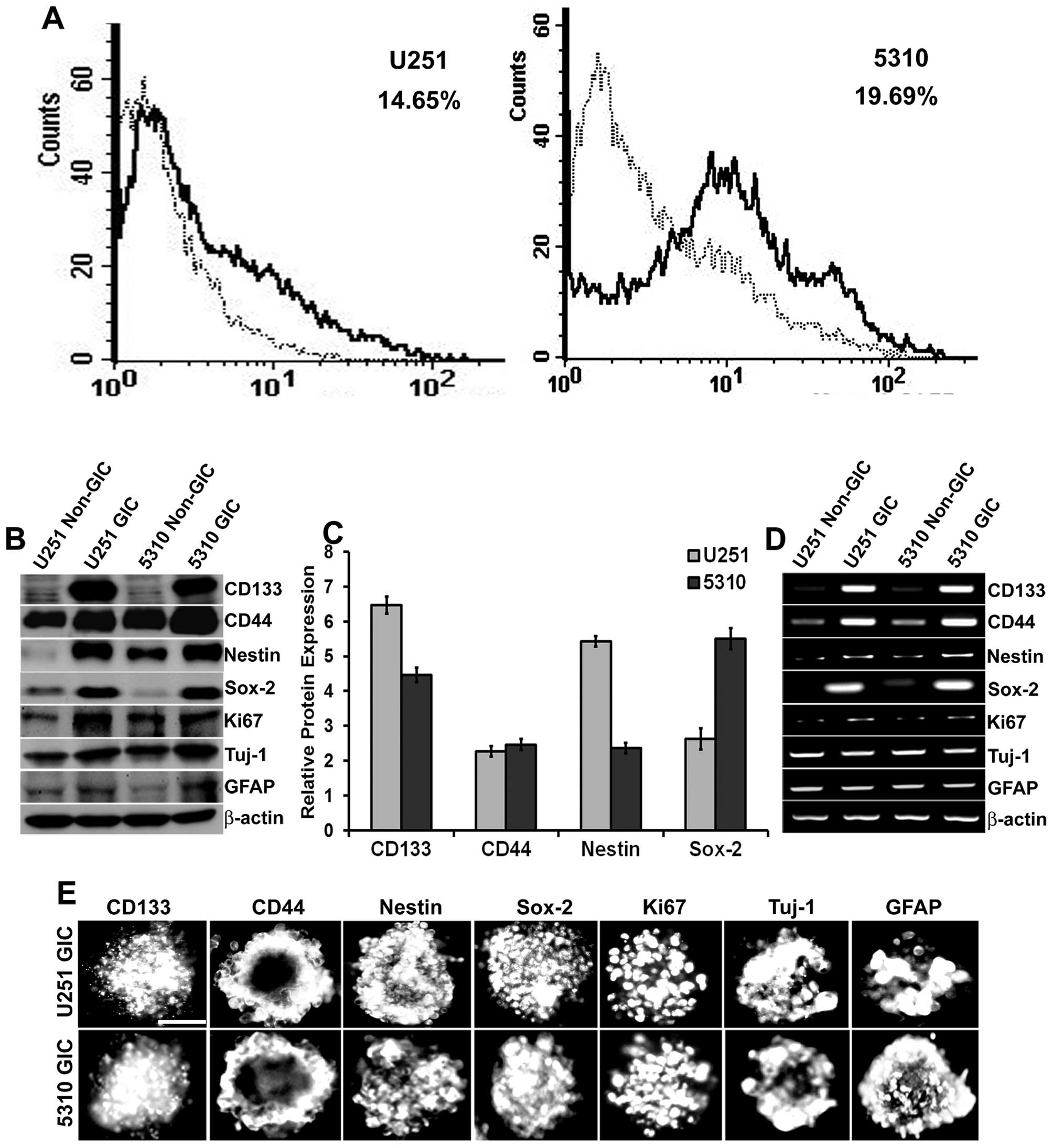
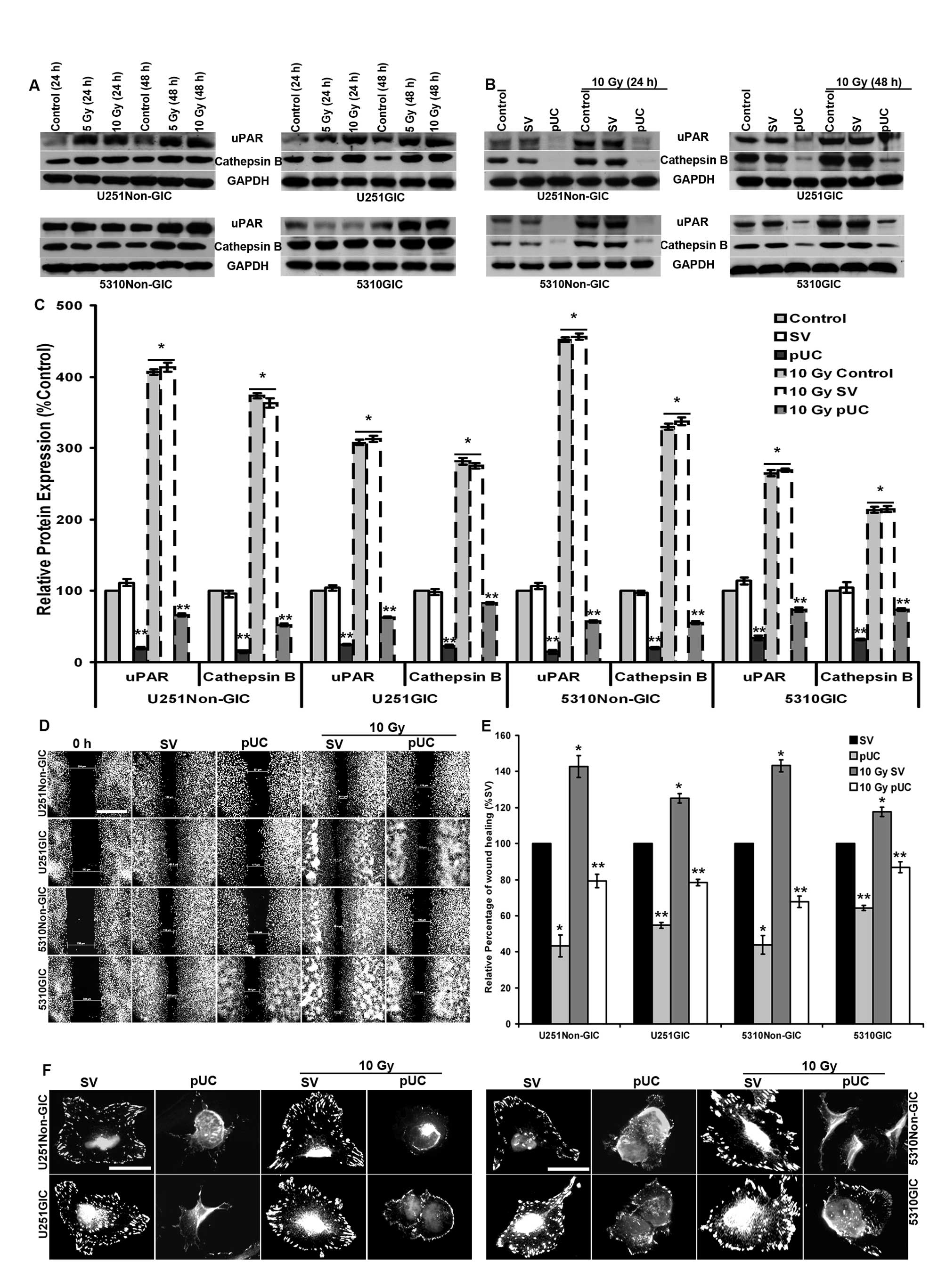
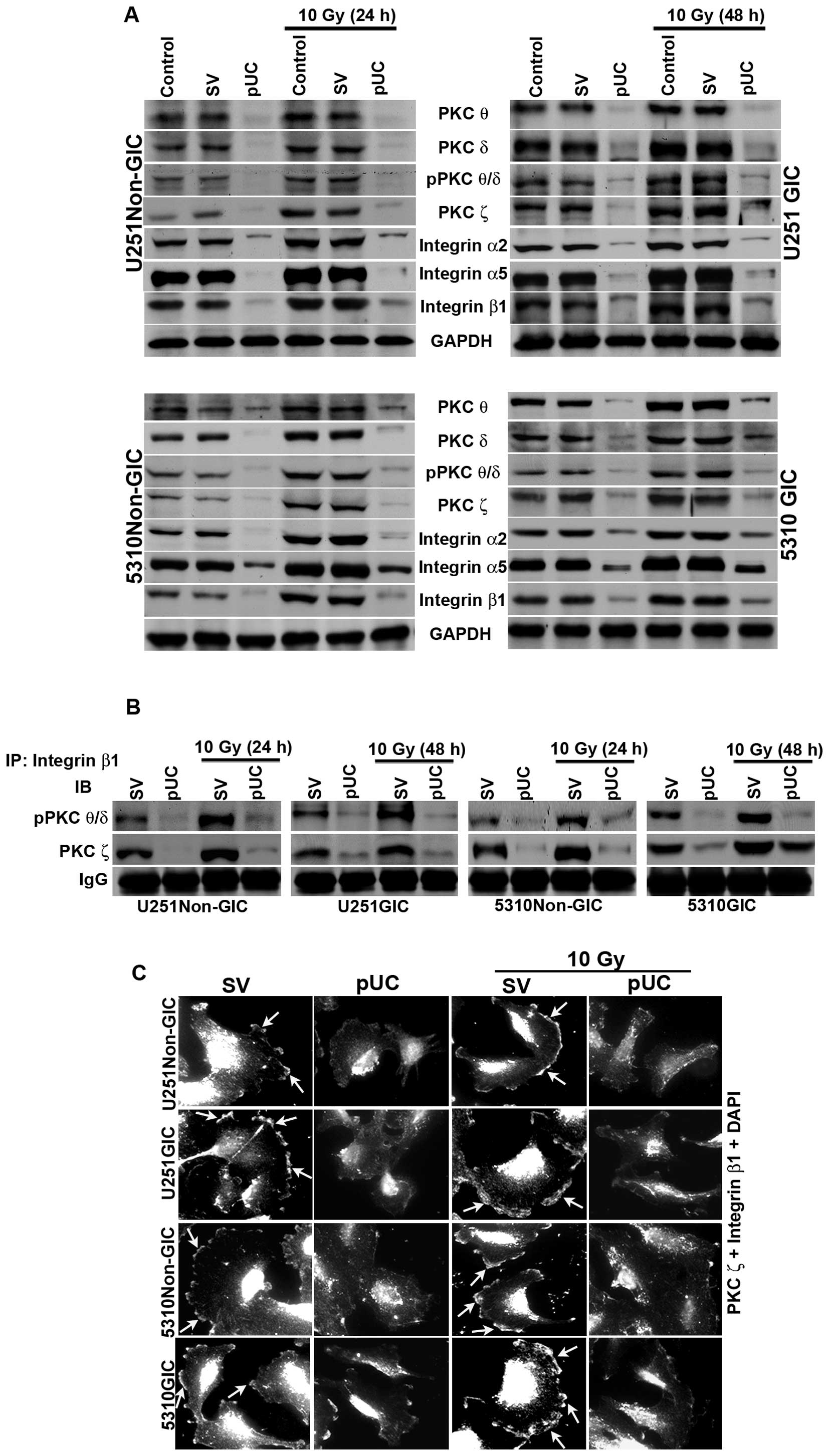
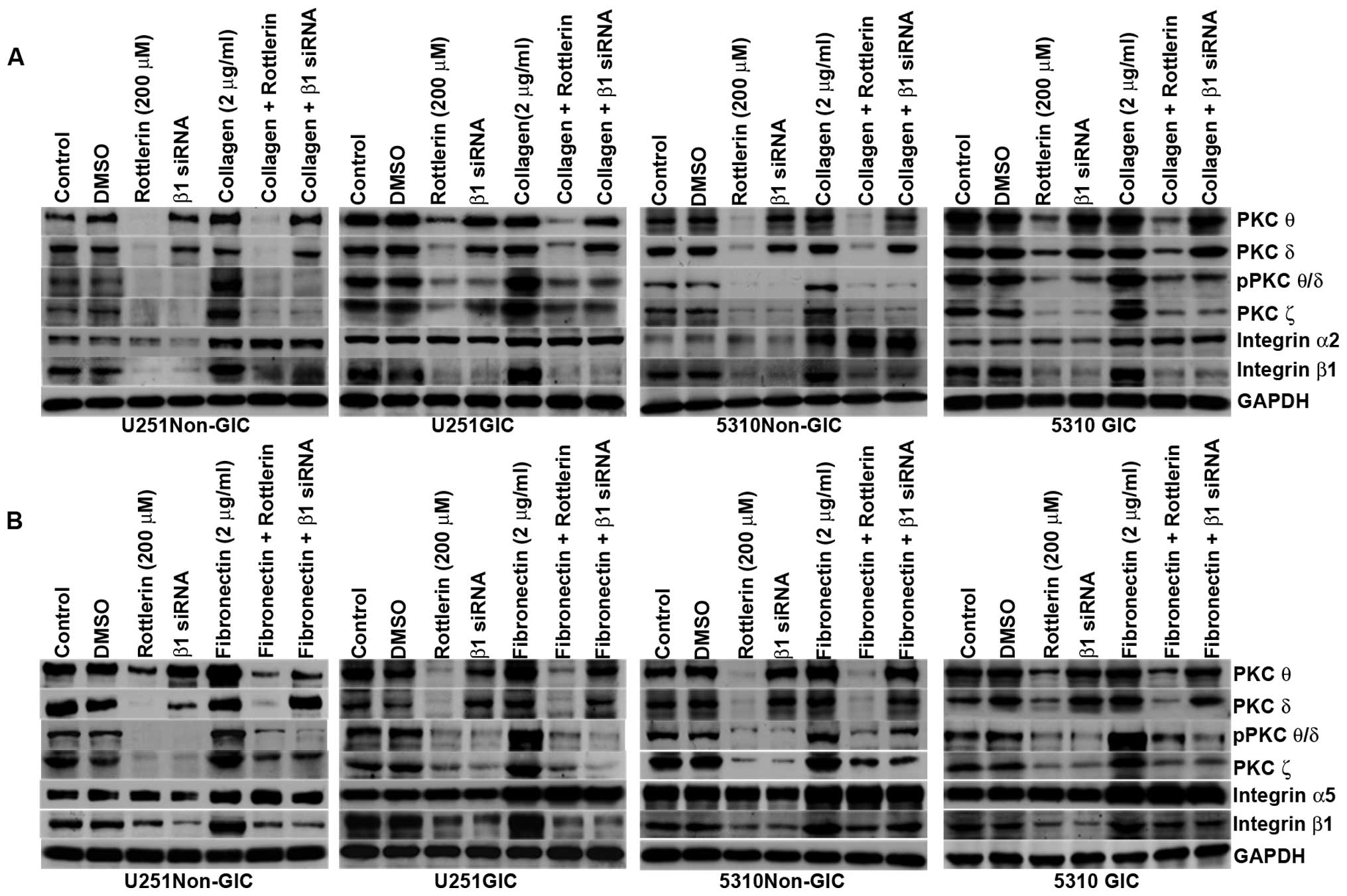
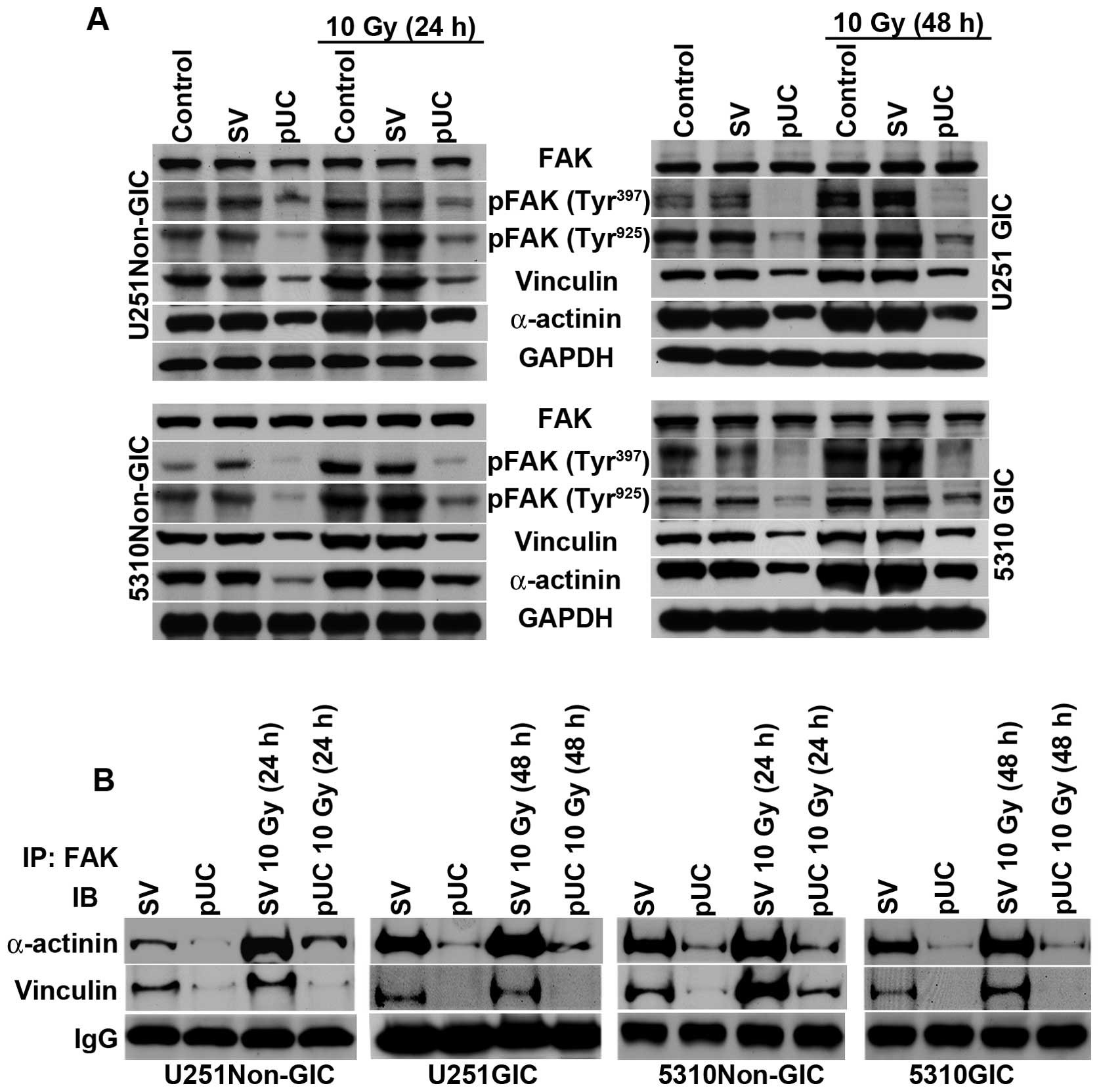
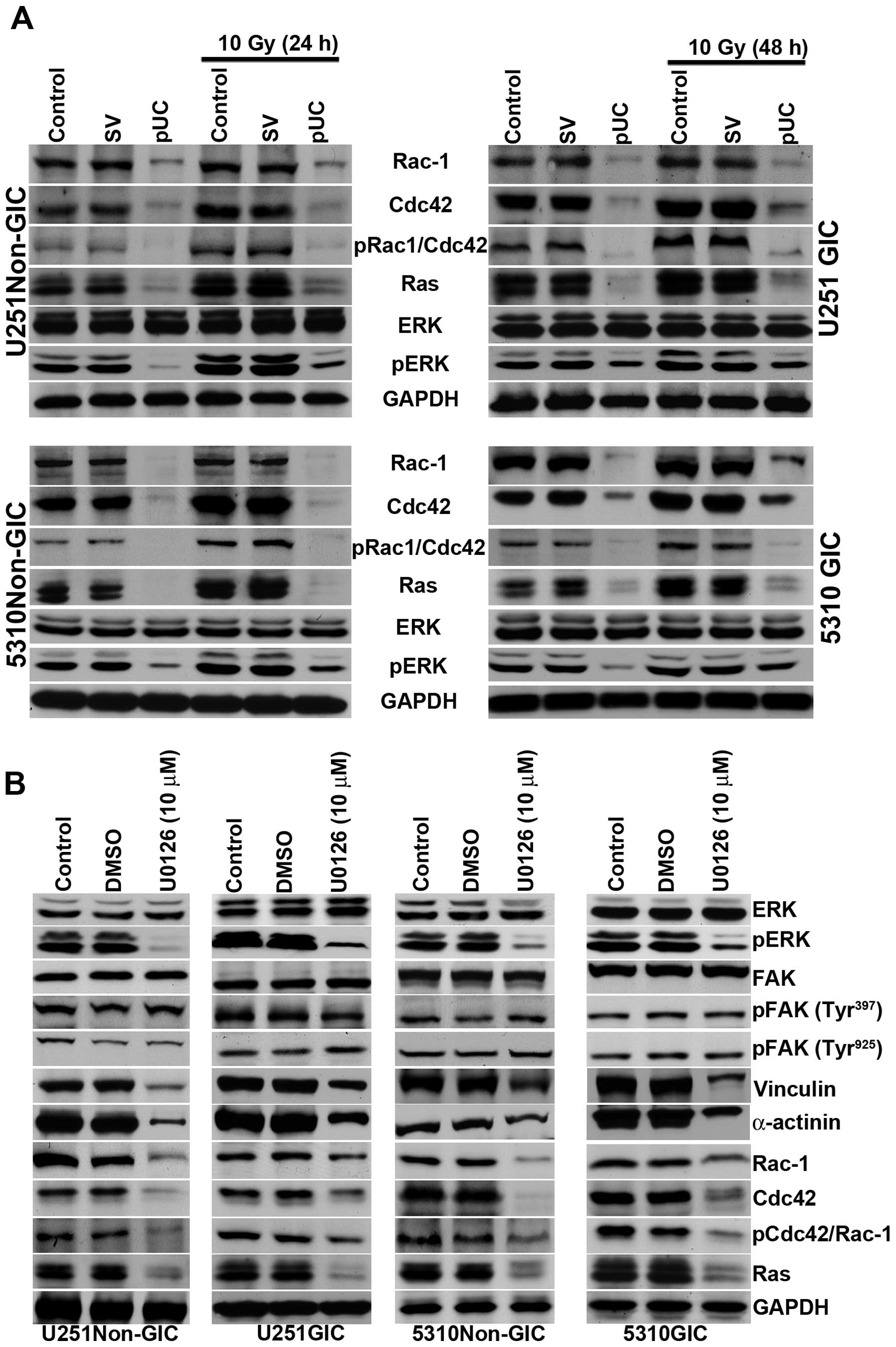
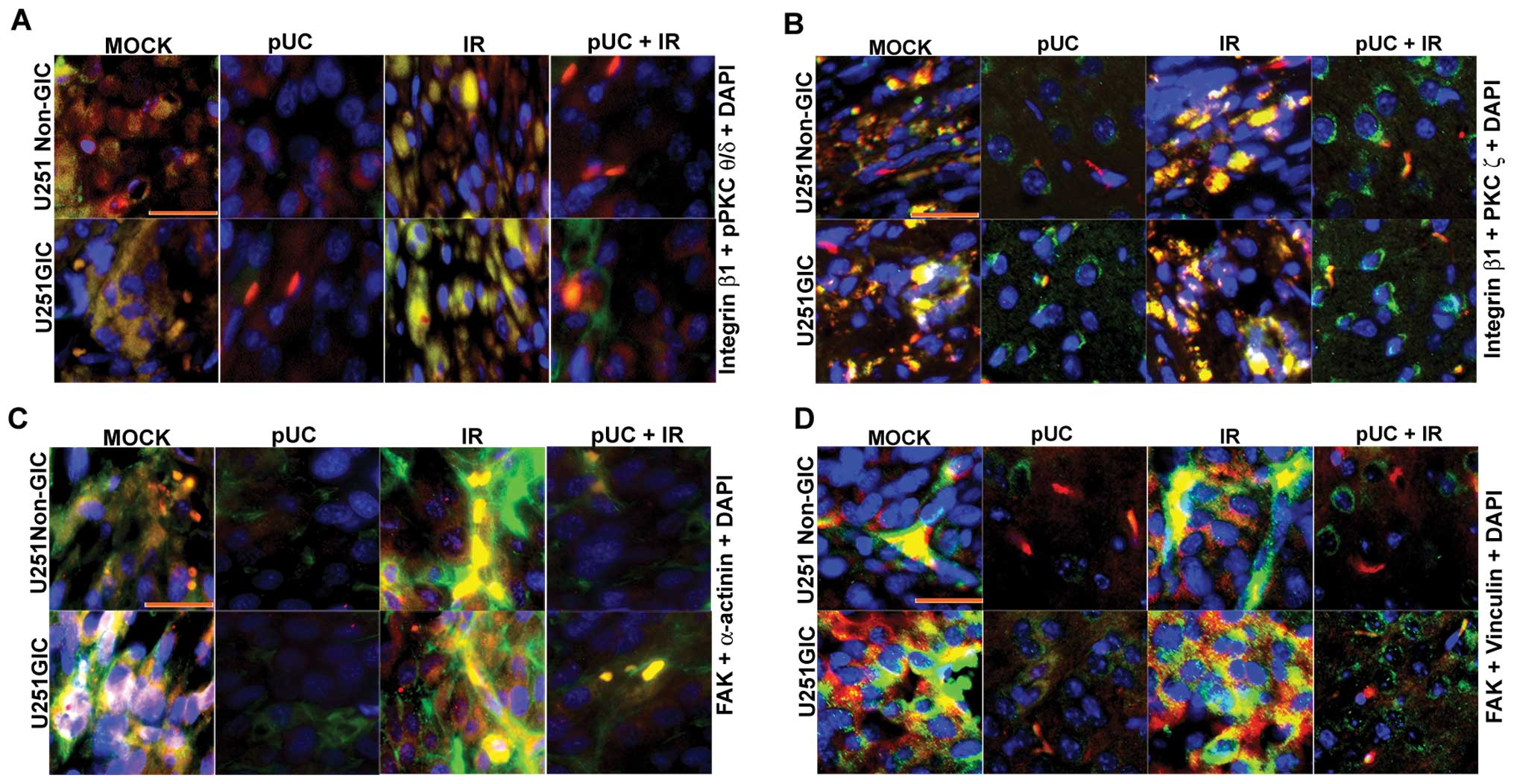
|
1
|
Huang Z, Cheng L, Guryanova OA, Wu Q and
Bao S: Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma - molecular signaling and
therapeutic targeting. Protein Cell. 1:638–655. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang CY, Fong YC, Lee CY, et al: CCL5
increases lung cancer migration via PI3K, Akt and NF-kappaB
pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:794–803. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mitra SK and Schlaepfer DD:
Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 18:516–523. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wolf K and Friedl P: Molecular mechanisms
of cancer cell invasion and plasticity. Br J Dermatol. 154(Suppl
1): 11–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Da Rocha AB, Mans DR, Regner A and
Schwartsmann G: Targeting protein kinase C: new therapeutic
opportunities against high-grade malignant gliomas? Oncologist.
7:17–33. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rigot V, Lehmann M, Andre F, Daemi N,
Marvaldi J and Luis J: Integrin ligation and PKC activation are
required for migration of colon carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci.
111:3119–3127. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Larsson C: Protein kinase C and the
regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Cell Signal. 18:276–284.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chintala SK, Mohanam S, Go Y, et al:
Altered in vitro spreading and cytoskeletal organization in human
glioma cells by down-regulation of urokinase receptor. Mol
Carcinog. 20:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rao JS: Molecular mechanisms of glioma
invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:489–501.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gopinath S, Malla RR, Gondi CS, et al:
Co-depletion of cathepsin B and uPAR induces G0/G1 arrest in glioma
via FOXO3a mediated p27 upregulation. PLoS One. 5:e116682010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malla RR, Gopinath S, Gondi CS, et al:
Cathepsin B and uPAR knockdown inhibits tumor-induced angiogenesis
by modulating VEGF expression in glioma. Cancer Gene Ther.
18:419–434. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kondo T, Setoguchi T and Taga T:
Persistence of a small subpopulation of cancer stem-like cells in
the C6 glioma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:781–786. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gilbert CA and Ross AH: Glioma stem cells:
cell culture, markers and targets for new combination therapies.
Cancer Stem Cells Theories and Practice. Shostak S: InTech; pp.
79–104. 2011
|
|
14
|
Pollard SM, Yoshikawa K, Clarke ID, et al:
Glioma stem cell lines expanded in adherent culture have
tumor-specific phenotypes and are suitable for chemical and genetic
screens. Cell Stem Cell. 4:568–580. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, et al:
Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer
Res. 63:5821–5828. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Singh SK, Hawkins C, Clarke ID, et al:
Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature.
432:396–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gondi CS, Kandhukuri N, Kondraganti S, et
al: RNA interference-mediated simultaneous down-regulation of
urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor and cathepsin B
induces caspase-8-mediated apoptosis in SNB19 human glioma cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 5:3197–3208. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kim MJ, Kim RK, Yoon CH, et al: Importance
of PKCdelta signaling in fractionated-radiation-induced expansion
of glioma-initiating cells and resistance to cancer treatment. J
Cell Sci. 124:3084–3094. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Donald CD, Cooper CR, Harris-Hooker S,
Emmett N, Scanlon M and Cooke DB III: Cytoskeletal organization and
cell motility correlates with metastatic potential and state of
differentiation in prostate cancer. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
47:1033–1038. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Uhm JH, Gladson CL and Rao JS: The role of
integrins in the malignant phenotype of gliomas. Front Biosci.
4:D188–D199. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carriero MV, Del Vecchio S, Capozzoli M,
et al: Urokinase receptor interacts with alpha(v)beta5 vitronectin
receptor, promoting urokinase-dependent cell migration in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 59:5307–5314. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gunther W, Skaftnesmo KO, Arnold H and
Terzis AJ: Molecular approaches to brain tumour invasion. Acta
Neurochir (Wien). 145:1029–1036. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bruce-Staskal PJ and Bouton AH:
PKC-dependent activation of FAK and src induces tyrosine
phosphorylation of Cas and formation of Cas-Crk complexes. Exp Cell
Res. 264:296–306. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen CS, Alonso JL, Ostuni E, Whitesides
GM and Ingber DE: Cell shape provides global control of focal
adhesion assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 307:355–361. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Clark EA, King WG, Brugge JS, Symons M and
Hynes RO: Integrin-mediated signals regulated by members of the rho
family of GTPases. J Cell Biol. 142:573–586. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parsons M, Keppler MD, Kline A, et al:
Site-directed perturbation of protein kinase C-integrin interaction
blocks carcinoma cell chemotaxis. Mol Cell Biol. 22:5897–5911.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin CJ, Lin CY, Chen Y, Huang SH and Wang
SM: Rottlerin inhibits migration of follicular thyroid carcinoma
cells by PKCdelta-independent destabilization of the focal adhesion
complex. J Cell Biochem. 110:428–437. 2010.
|