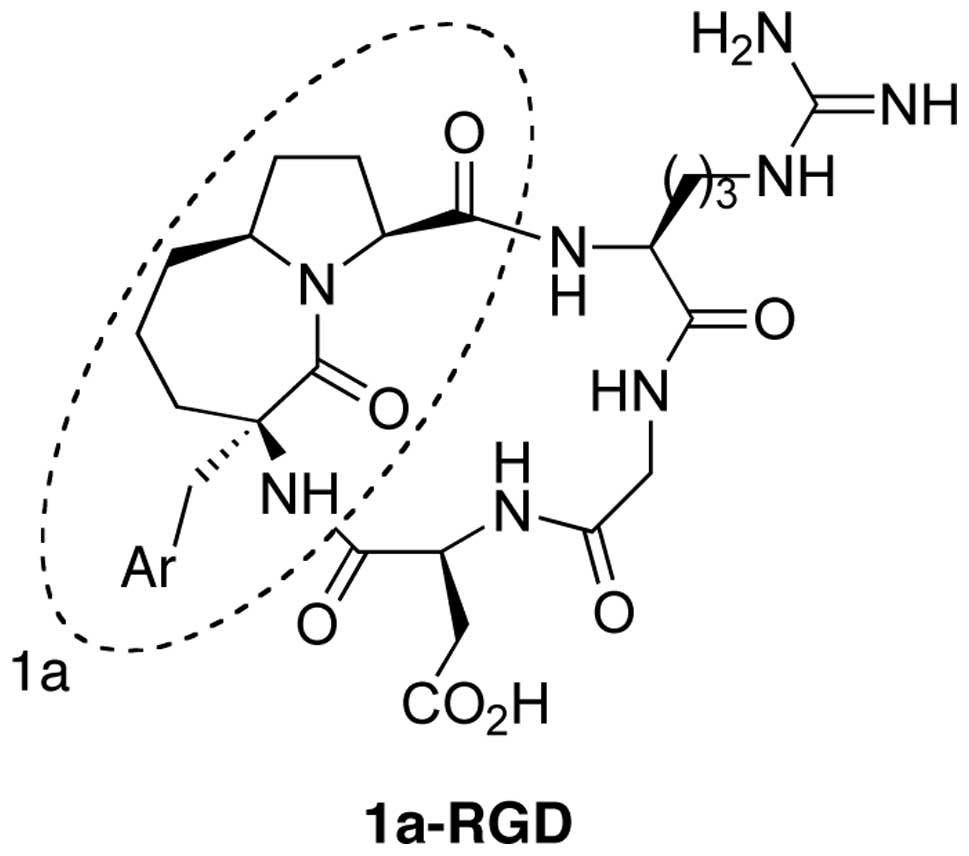
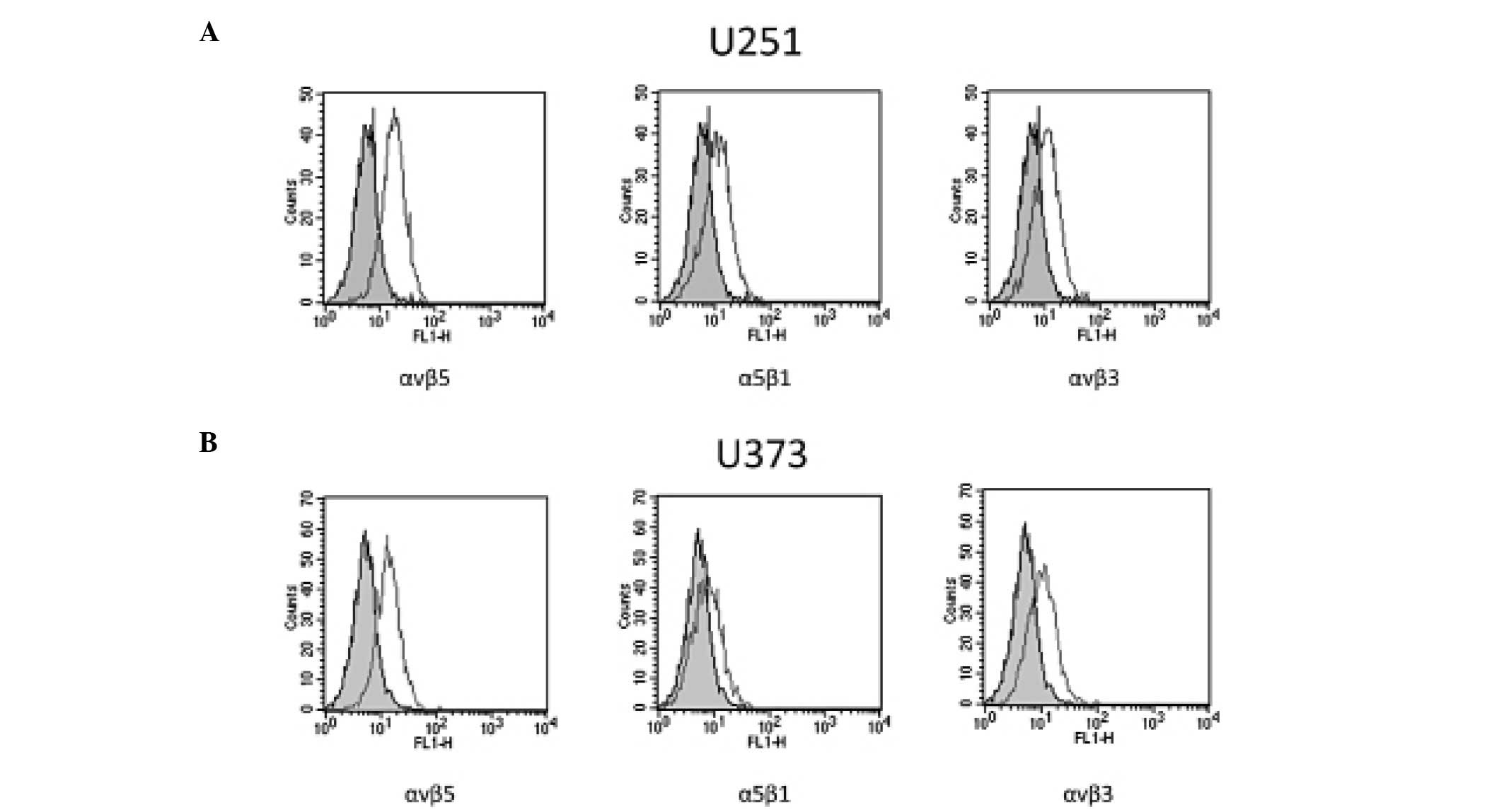
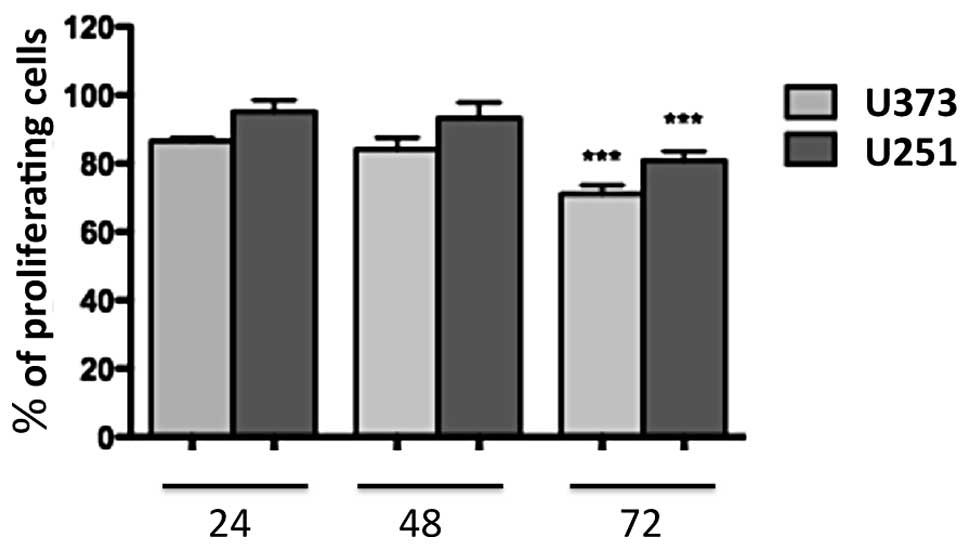
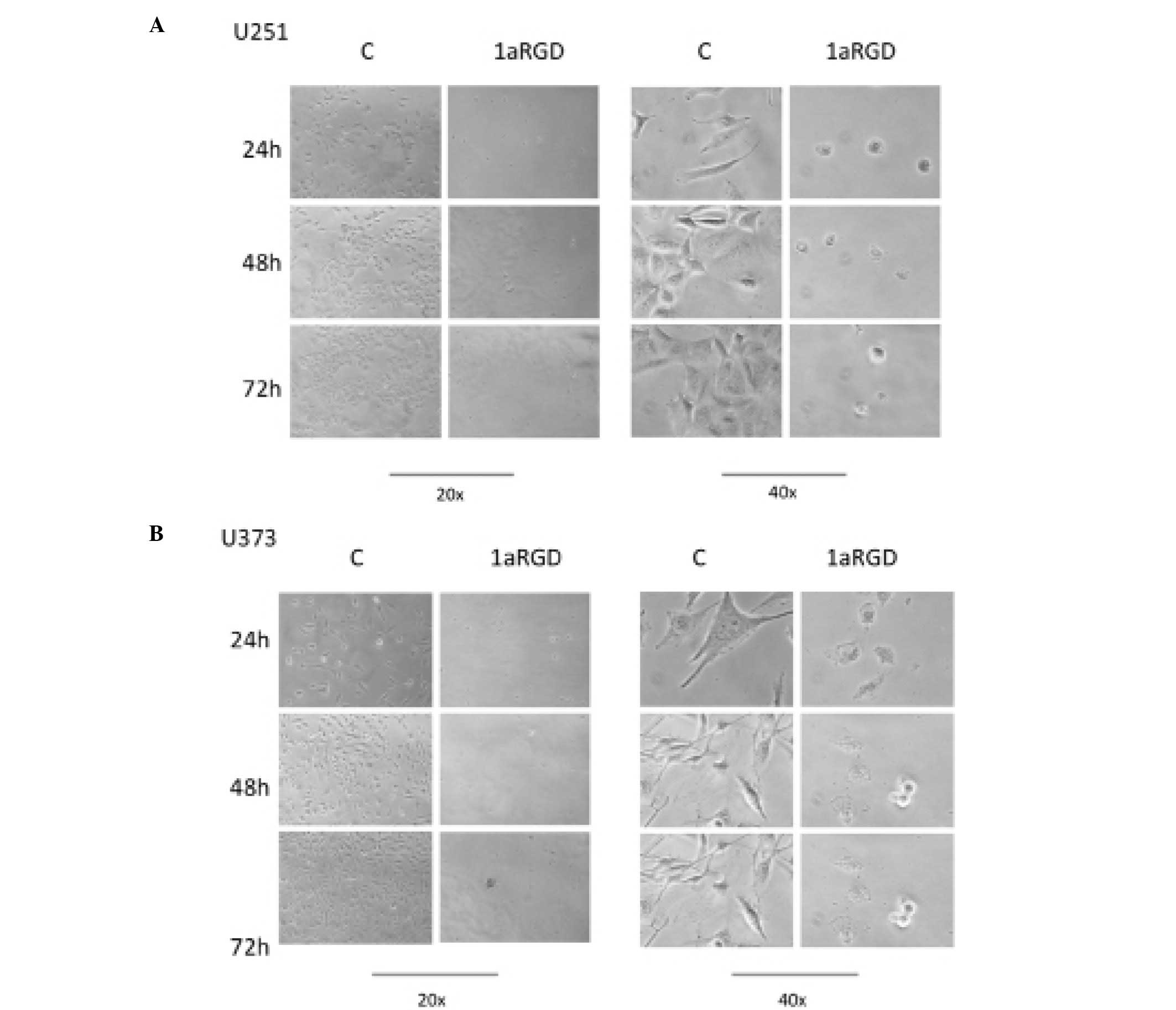
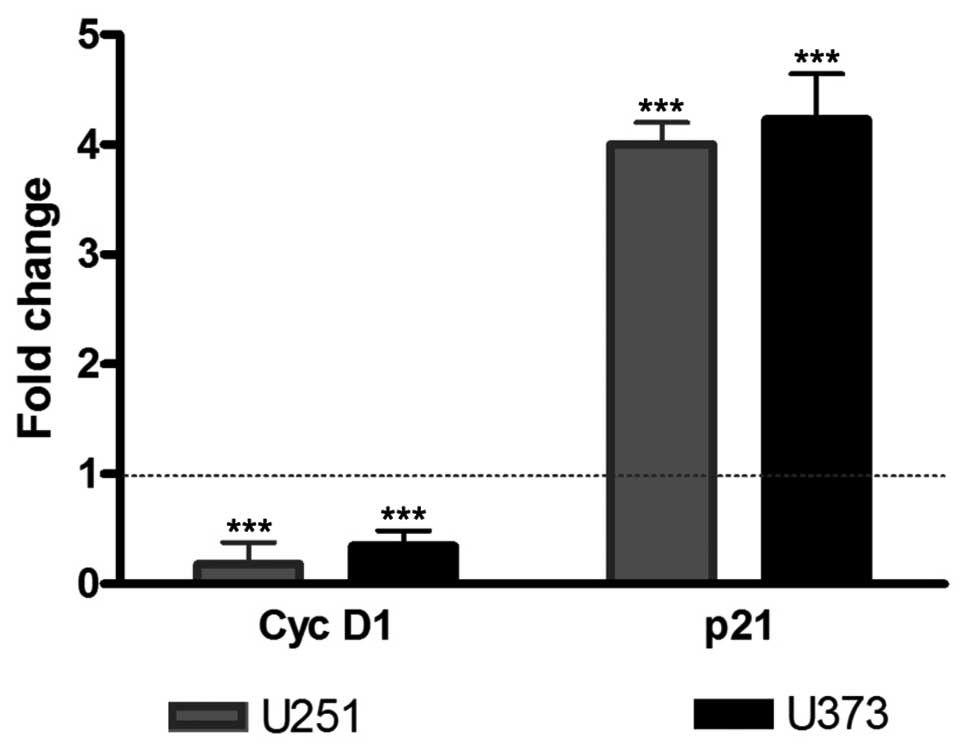
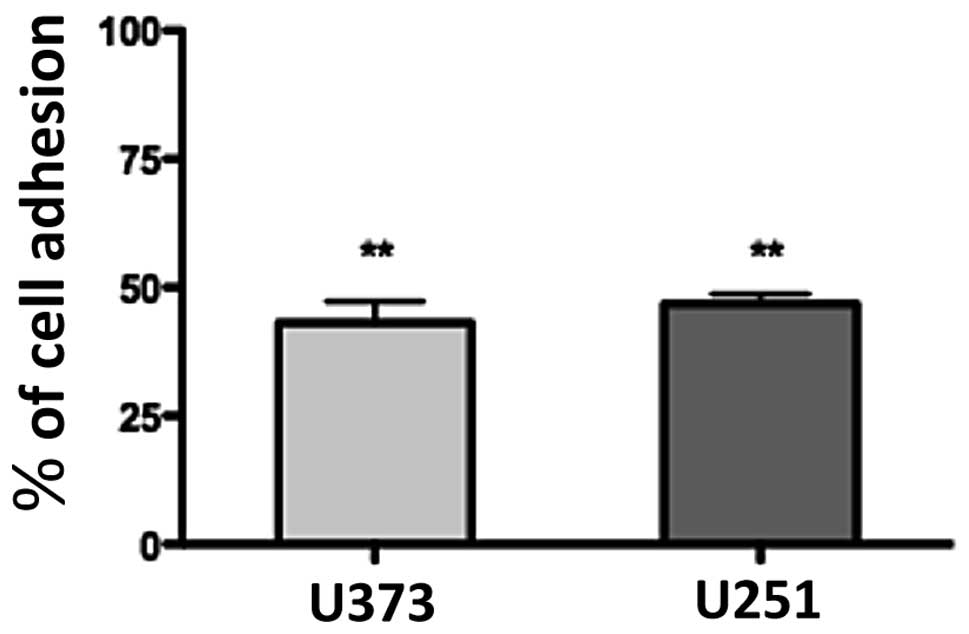
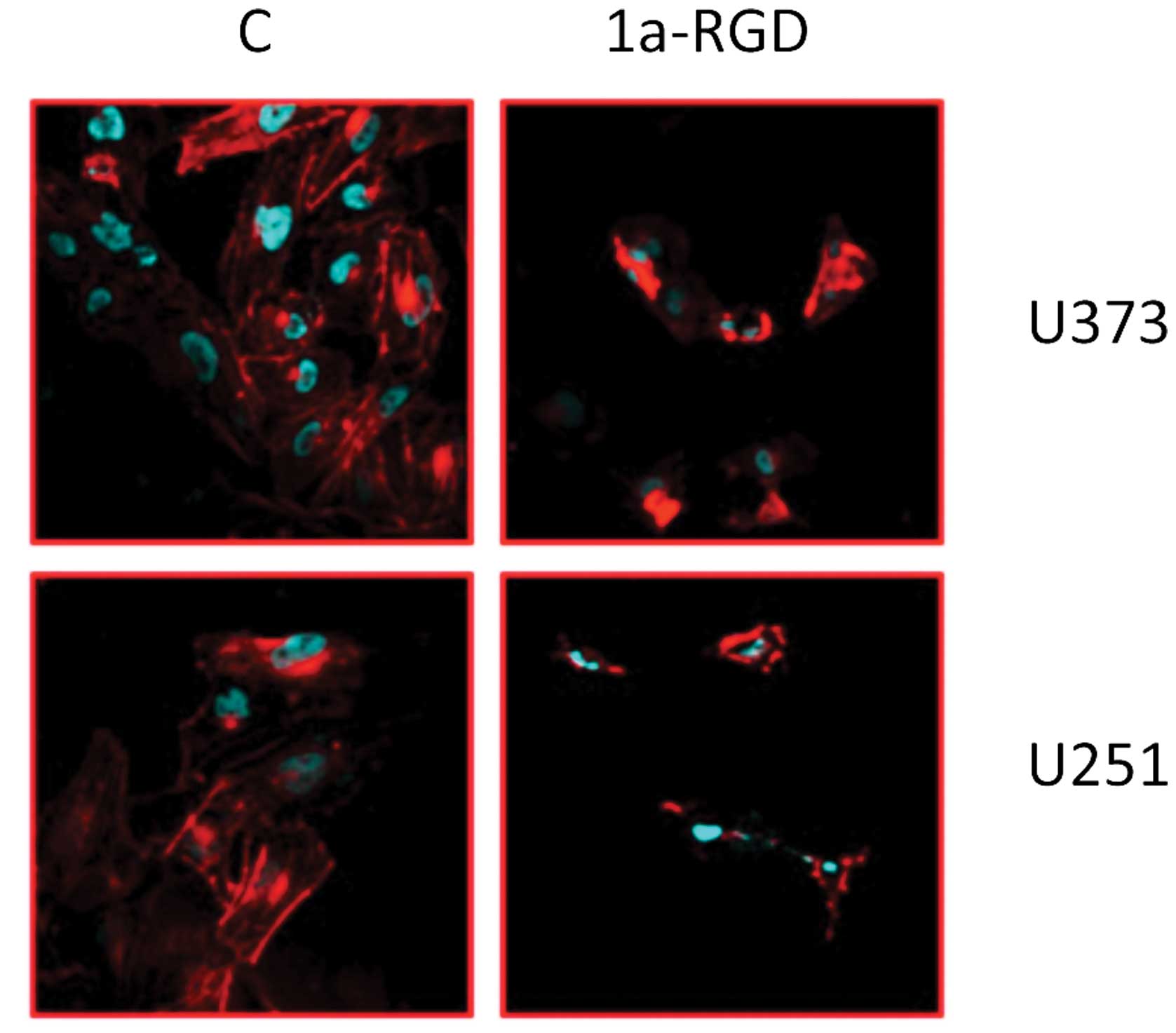
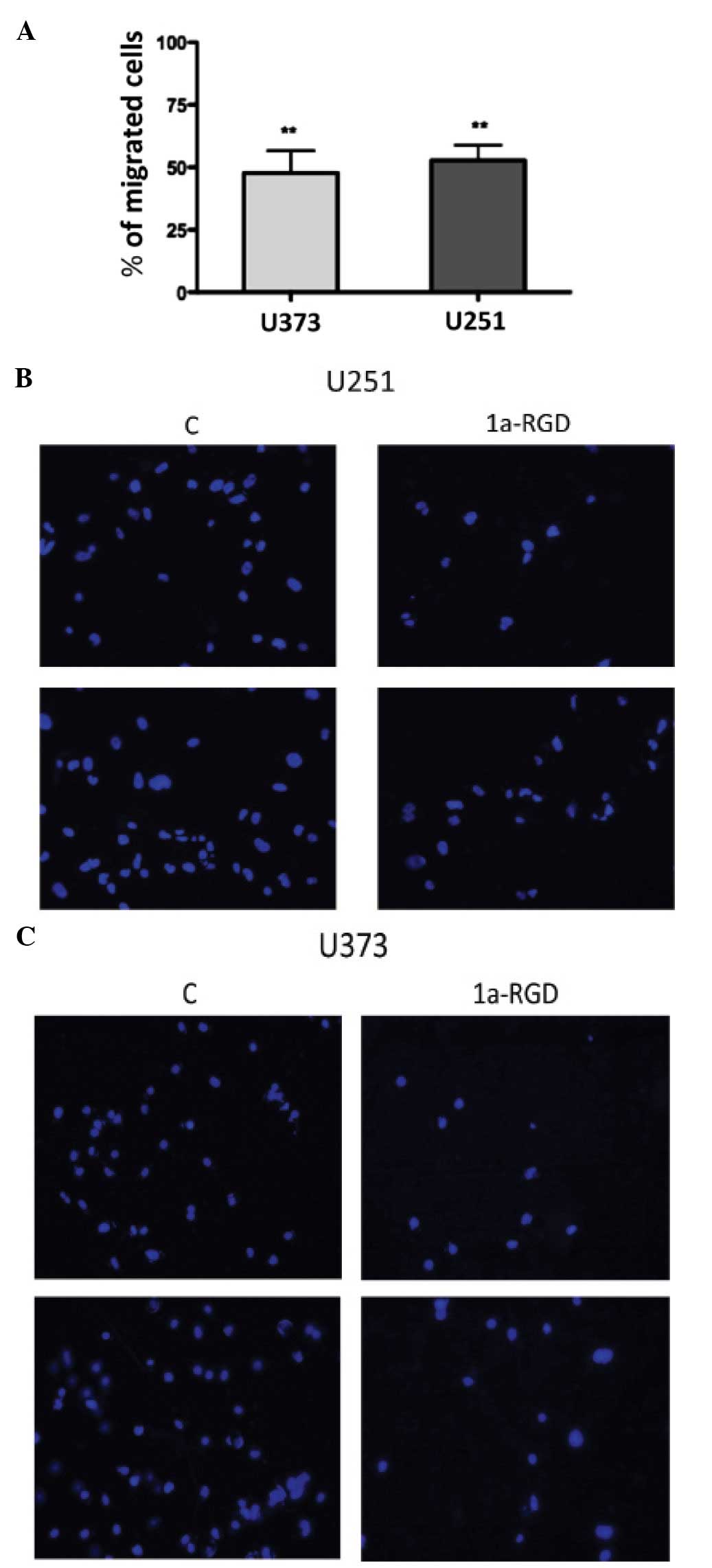
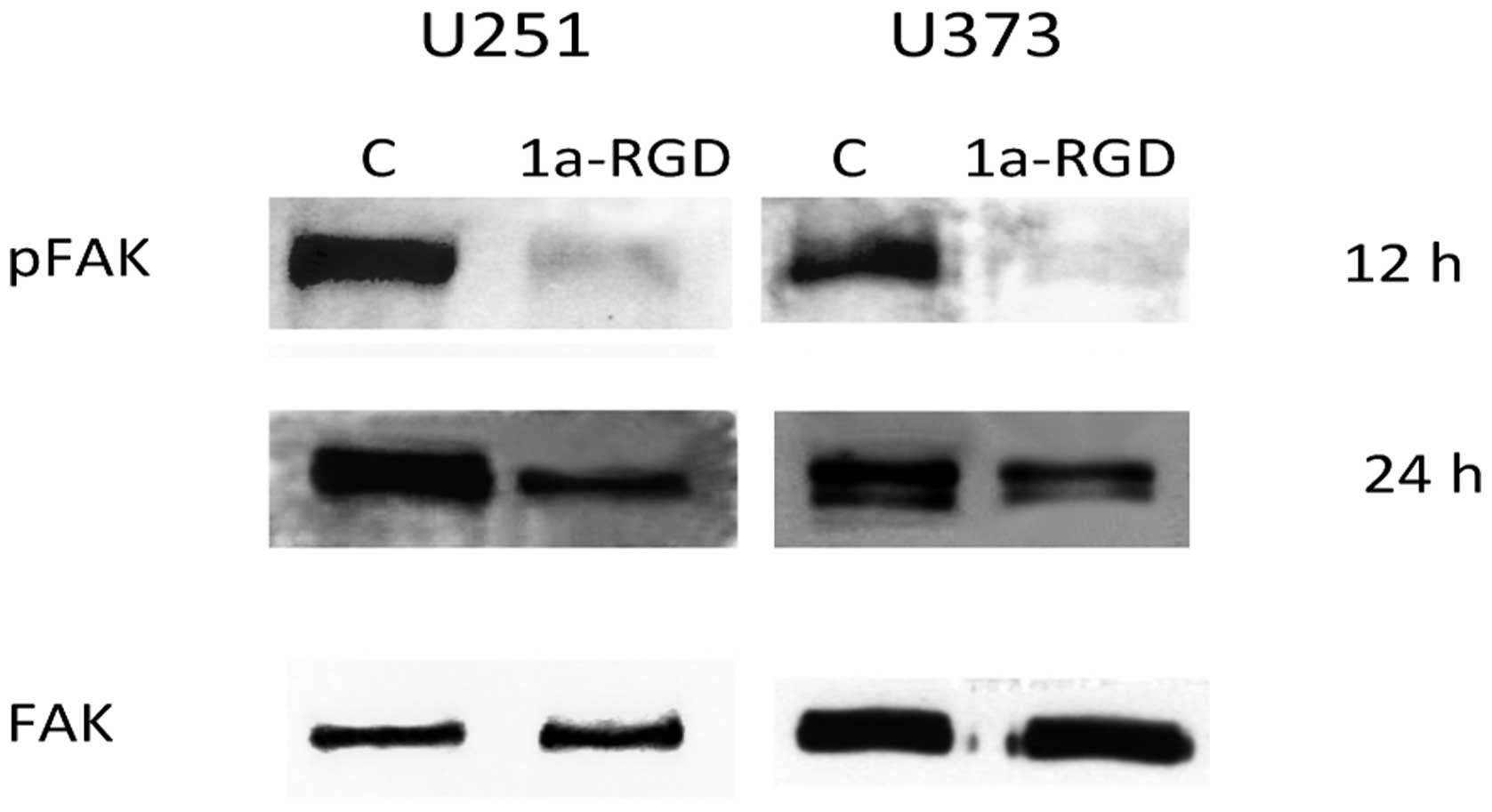
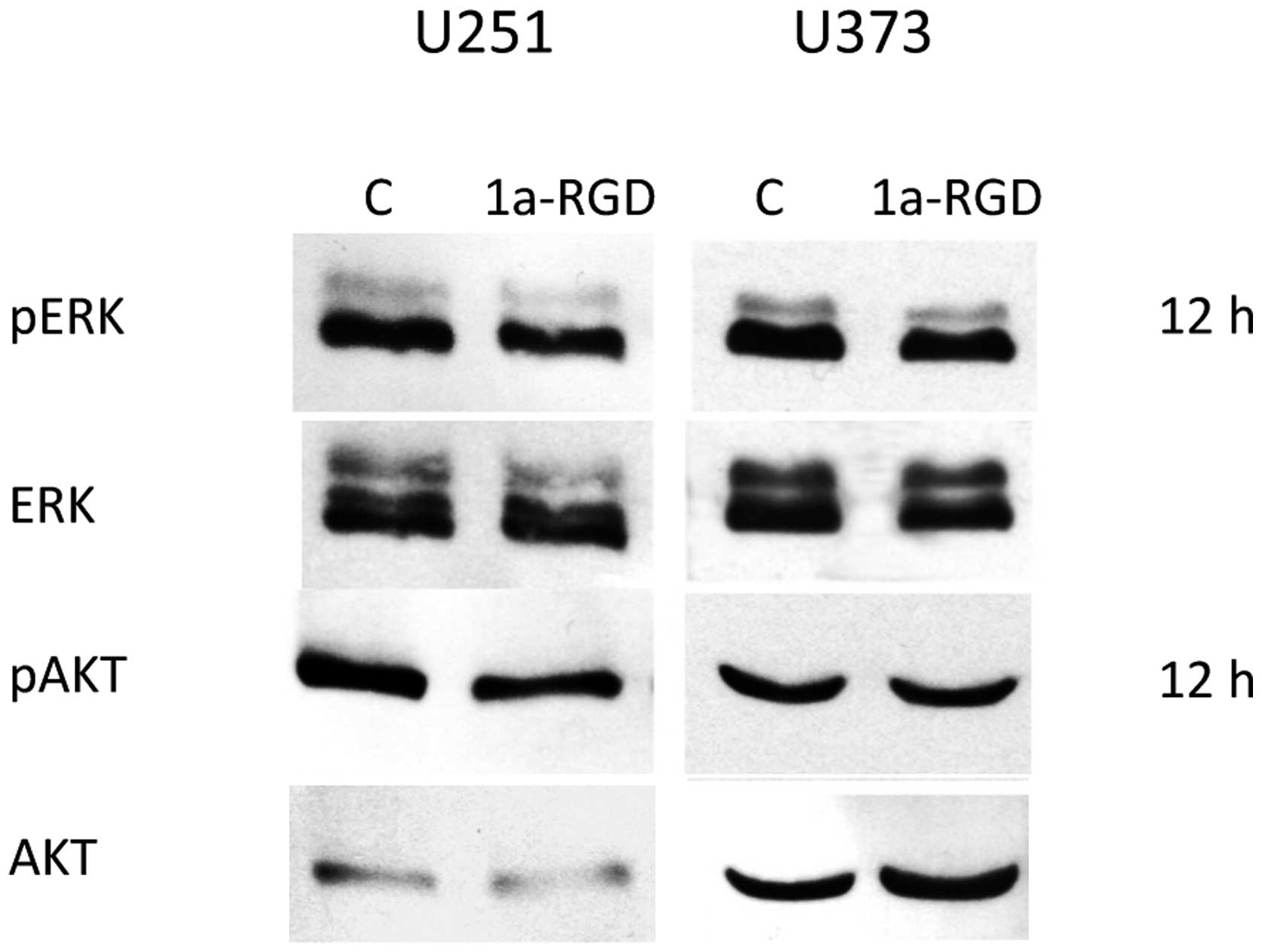
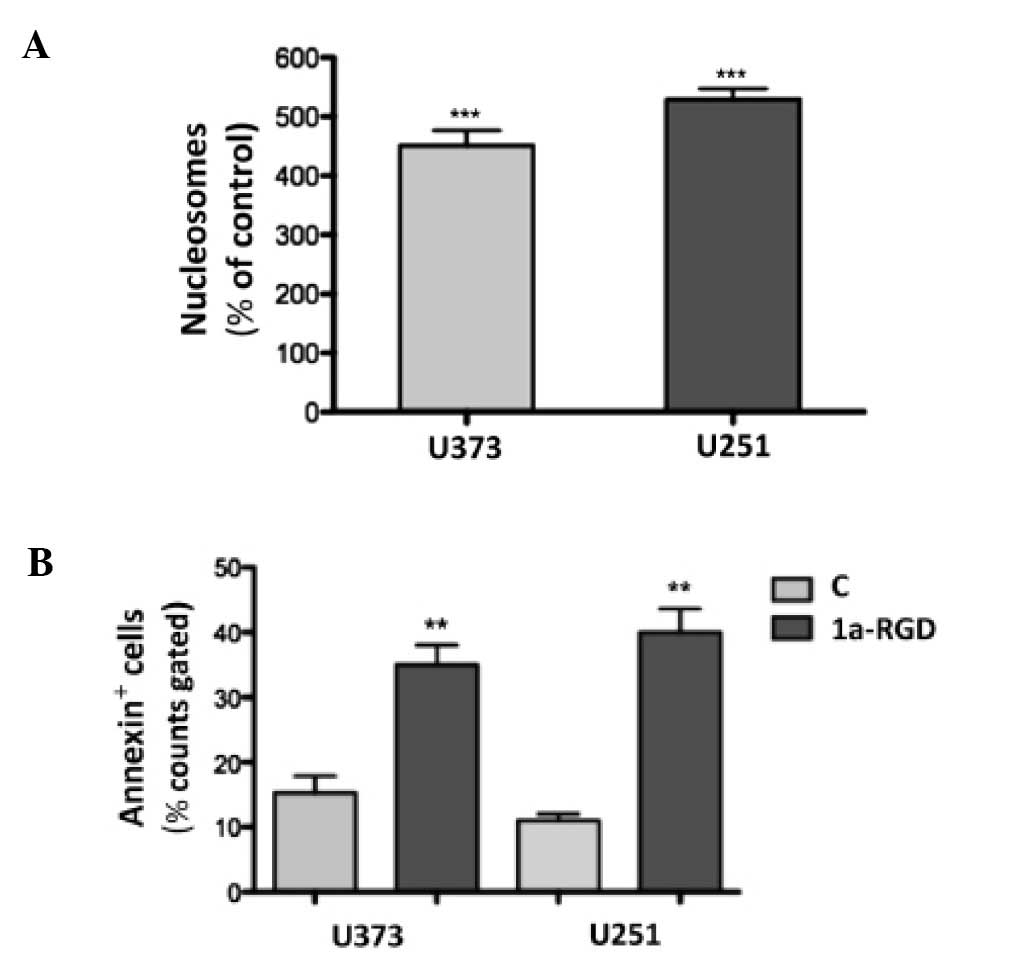
|
1.
|
Paolillo M, Russo MA, Serra M, Colombo L
and Schinelli S: Small molecule integrin antagonists in cancer
therapy. Mini Rev Med Chem. 9:1439–1446. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Schnell O, Krebs B, Wagner E, Romagna A,
Beer AJ, Grau SJ, Thon N, Goetz C, Kretzschmar HA, Tonn JC and
Goldbrunner RH: Expression of integrin αvβ3 in gliomas correlates
with tumor grade and is not restricted to tumor vasculature. Brain
Pathol. 18:378–386. 2008.
|
|
3.
|
Zhao J and Guan JL: Signal transduction by
focal adhesion kinase in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 28:35–49.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Assoian RK and Klein EA: Growth control by
intracellular tension and extracellular stiffness. Trends Cell
Biol. 18:347–352. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Yamada S, Bu XY, Khankaldyyan V,
Gonzales-Gomez I, McComb JG and Laug WE: Effect of the angiogenesis
inhibitor cilengitide (EMD 121974) on glioblastoma growth in nude
mice. Neurosurgery. 59:1304–1312. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Reardon DA, Fink KL, Mikkelsen T,
Cloughesy TF, O’Neill A, Plotkin S, Glantz M, Ravin P, Raizer JJ,
Rich KM, Schiff D, Shapiro WR, Burdette-Radoux S, Dropcho EJ,
Wittemer SM, Nippgen J, Picard M and Nabors LB: Randomized phase II
study of cilengitide, an integrin-targeting
arginine-glycine-aspartic acid peptide, in recurrent glioblastoma
multiforme. J Clin Oncol. 26:5610–5617. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Neyns B, Goldbrunner R,
Schlegel U, Clement PM, Grabenbauer GG, Ochsenbein AF, Simon M,
Dietrich PY, Pietsch T, Hicking C, Tonn JC, Diserens AC, Pica A,
Hermisson M, Krueger S, Picard M and Weller M: Phase I/IIa study of
cilengitide and temozolomide with concomitant radiotherapy followed
by cilengitide and temozolomide maintenance therapy in patients
with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 28:2712–2718.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Arosio D, Belvisi L, Colombo L, Colombo M,
Invernizzi D, Manzoni L, Potenza D, Serra M, Castorina M, Pisano C
and Scolastico C: A potent integrin antagonist from a small library
of cyclic RGD pentapeptide mimics including benzyl-substituted
azabicycloalkane amino acids. Chem Med Chem. 3:1589–1603. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Paolillo M, Russo MA, Curti D, Lanni C and
Schinelli S: Endothelin B receptor antagonists block proliferation
and induce apoptosis in glioma cells. Pharmacol Res. 61:306–315.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Dussault AA and Pouliot M: Rapid and
simple comparison of messenger RNA levels using real-time PCR. Biol
Proced Online. 8:1–10. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Wehrle-Haller B: Assembly and disassembly
of cell matrix adhesions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. July 19–2012.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
12.
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Desgrosellier JS and Cheresh DA: Integrins
in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:9–22. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Reynolds AR, Hart IR, Watson AR, Welti JC,
Silva RG, Robinson SD, Da Violante G, Gourlaouen M, Salih M, Jones
MC, Jones DT, Saunders G, Kostourou V, Perron-Sierra F, Norman JC,
Tucker GC and Hodivala-Dilke KM: Stimulation of tumor growth and
angiogenesis by low concentrations of RGD-mimetic integrin
inhibitors. Nat Med. 15:392–400. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Belvisi L, Bernardi A, Colombo M, Manzoni
L, Potenza D, Scolastico C, Giannini G, Marcellini M, Riccioni T,
Castorina M, LoGiudice P and Pisano C: Targeting integrins:
insights into structure and activity of cyclic RGD pentapeptide
mimics containing azabicycloalkane amino acids. Bioorg Med Chem.
14:169–180. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Maglott A, Bartik P, Cosgun S, Klotz P,
Ronde P, Fuhrmann G, Takeda K, Martin S and Dontenwill M: The small
alpha5beta1 integrin antagonist, SJ749, reduces proliferation and
clonogenicity of human astrocytoma cells. Cancer Res. 66:6002–6007.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Mattern RH, Read SB, Pierschbacher MD, Sze
CI, Eliceiri BP and Kruse CA: Glioma cell integrin expression and
their interactions with integrin antagonists. Cancer Ther.
3A:325–340. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Maurer GD, Tritschler I, Adams B,
Tabatabai G, Wick W, Stupp R and Weller M: Cilengitide modulates
attachment and viability of human glioma cells, but not sensitivity
to irradiation or temozolomide in vitro. Neurooncology. 11:747–756.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Schaller MD: Cellular functions of FAK
kinases: insight into molecular mechanisms and novel functions. J
Cell Sci. 123:1007–1013. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Oliveira-Ferrer L, Hauschild J, Fiedler W,
Bokemeyer C, Nippgen J, Celik I and Schuch G: Cilengitide induces
cellular detachment and apoptosis in endothelial and glioma cells
mediated by inhibition of FAK/src/AKT pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 27:862008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Kuphal S, Bauer R and Bosserhoff AK:
Integrin signaling in malignant melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
24:195–222. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Puissant A, Dufies M, Fenouille N, Ben
Sahra I, Jacquel A, Robert G, Cluzeau T, Deckert M, Tichet M, Chéli
Y, Cassuto JP, Raynaud S, Legros L, Pasquet JM, Mahon FX, Luciano F
and Auberger P: Imatinib triggers mesenchymal-like conversion of
CML cells associated with increased aggressiveness. J Mol Cell
Biol. 4:207–220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Bianchi-Smiraglia A, Paesante S and Bakin
AV: Integrin β5 contributes to the tumorigenic potential of breast
cancer cells through the Src-FAK and MEK-ERK signaling pathways.
Oncogene. July 23–2012.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24.
|
Muller PA, Caswell PT, Doyle B, Iwanicki
MP, Tan EH, Karim S, Lukashchuk N, Gillespie DA, Ludwig RL,
Gosselin P, Cromer A, Brugge JS, Sansom OJ, Norman JC and Vousden
KH: Mutant p53 drives invasion by promoting integrin recycling.
Cell. 139:1327–1341. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Martinkova E, Maglott A, Leger DY, Bonnet
D, Stiborova M, Takeda K, Martin S and Dontenwill M: alpha5beta1
integrin antagonists reduce chemotherapy-induced premature
senescence and facilitate apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells.
Int J Cancer. 127:1240–1248. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26.
|
Xu J, Millard M, Ren X, Cox OT and
Erdreich-Epstein A: c-Abl mediates endothelial apoptosis induced by
inhibition of integrins alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5 and by
disruption of actin. Blood. 115:2709–2718. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Braun K, Wiessler M, Pipkorn R, Ehemann V,
Bauerle T, Fleischhacker H, Muller G, Lorenz P and Waldeck W: A
cyclic-RGD-BioShuttle functionalized with TMZ by DARinv
‘Click Chemistry’ targeted to αvβ3 integrin for therapy. Int J Med
Sci. 7:326–339. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Pollard SM, Yoshikawa K, Clarke ID, Danovi
D, Stricker S, Russell R, Bayani J, Head R, Lee M, Bernstein M,
Squire JA, Smith A and Dirks P: Glioma stem cell lines expanded in
adherent culture have tumor-specific phenotypes and are suitable
for chemical and genetic screens. Cell Stem Cell. 4:568–580. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|