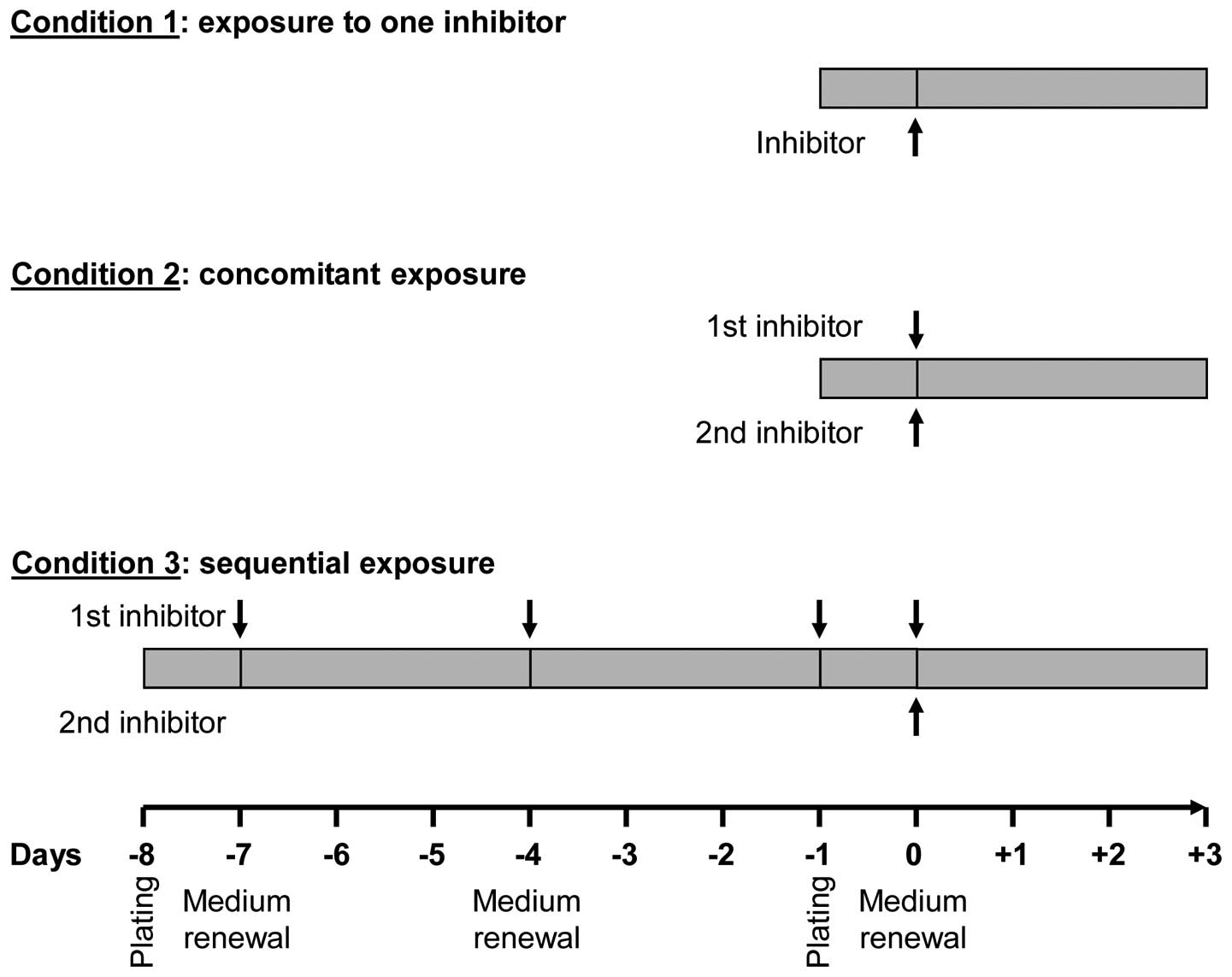
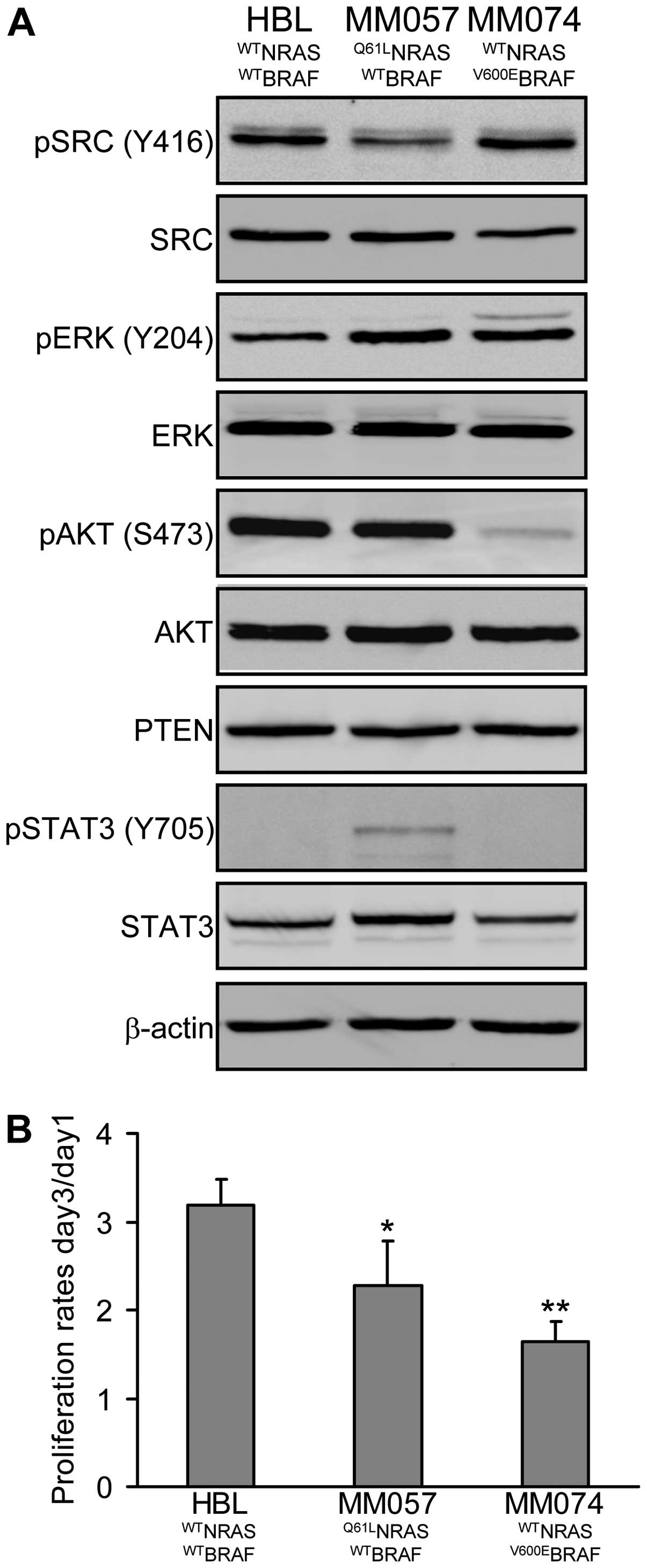
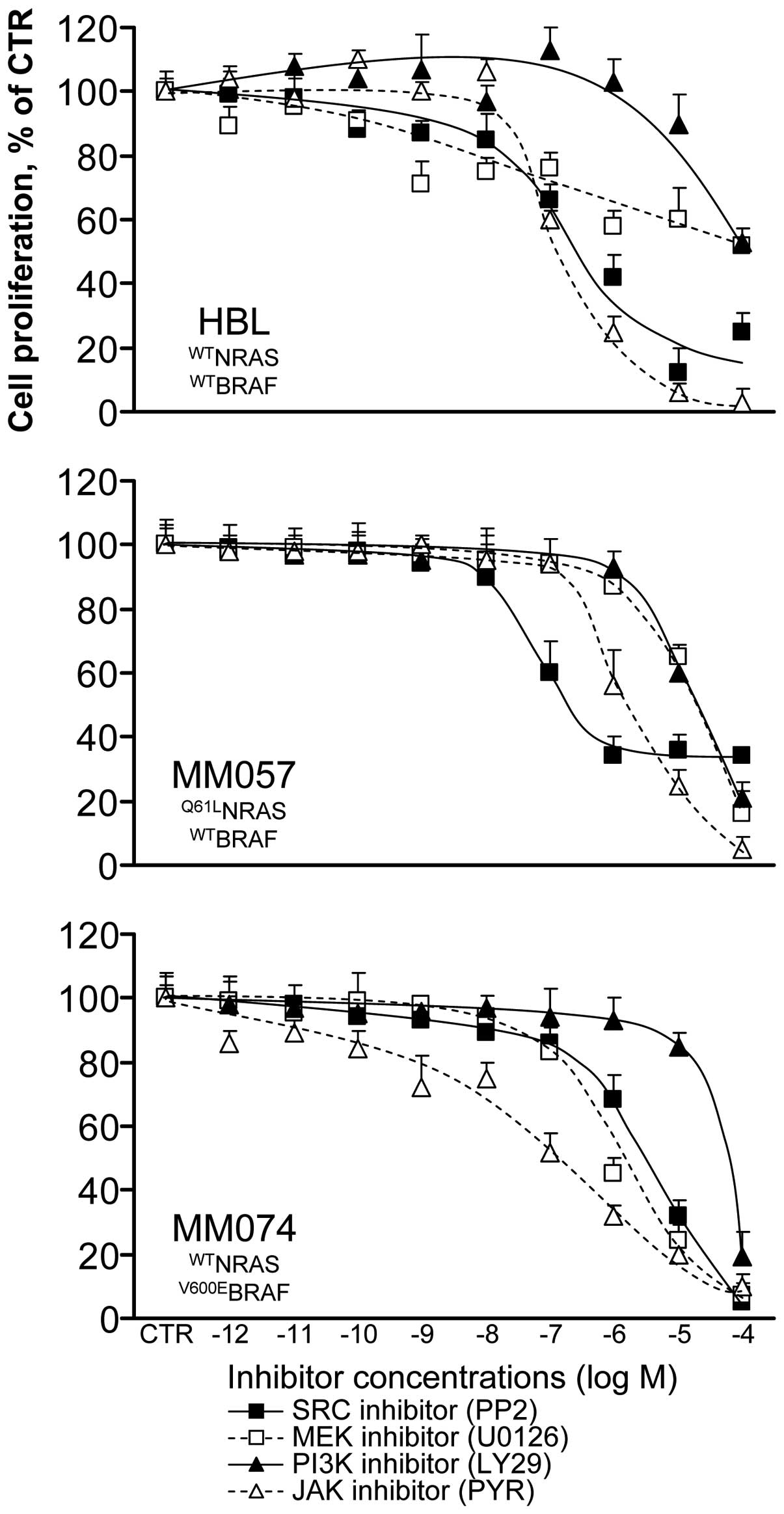
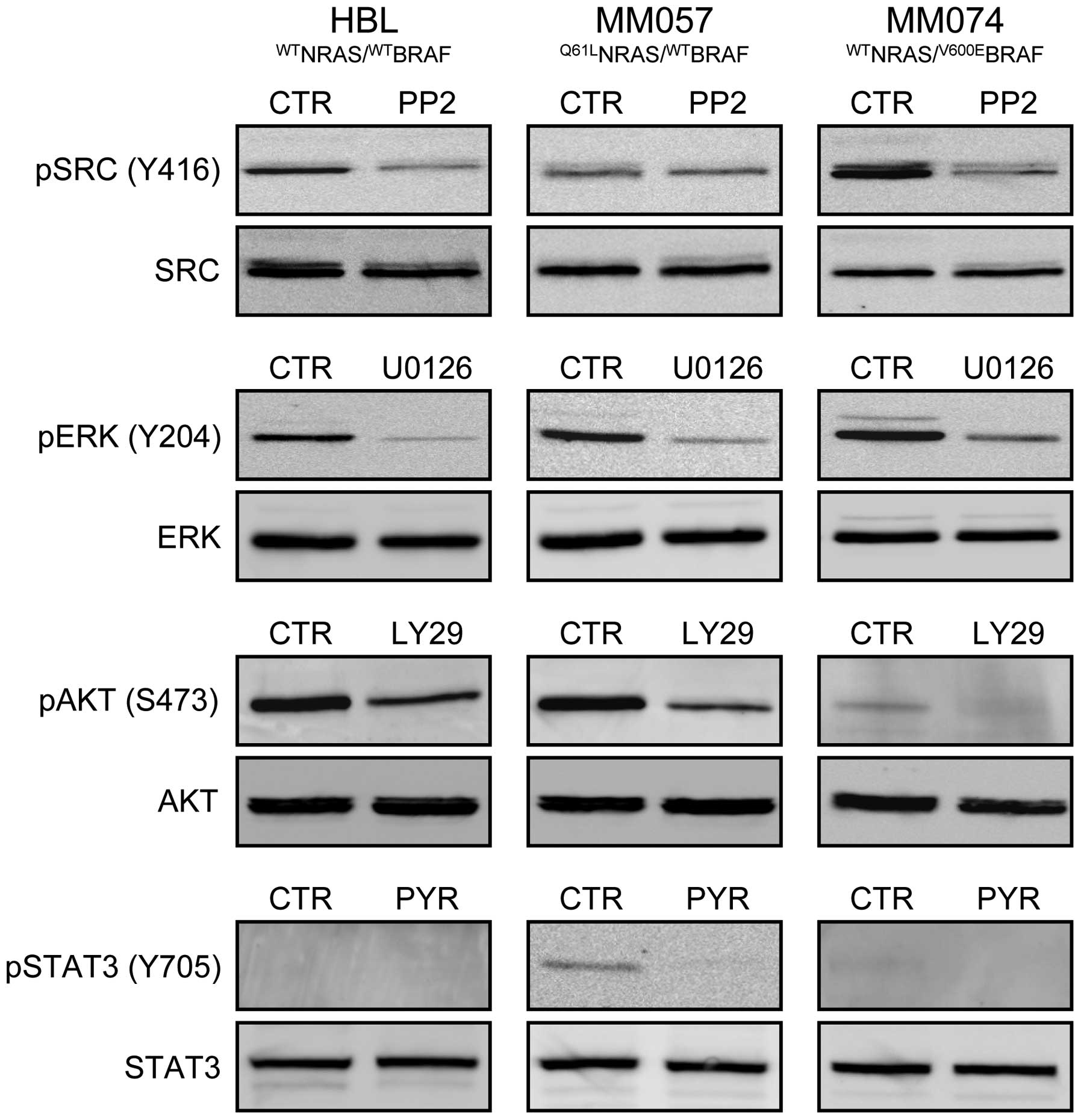
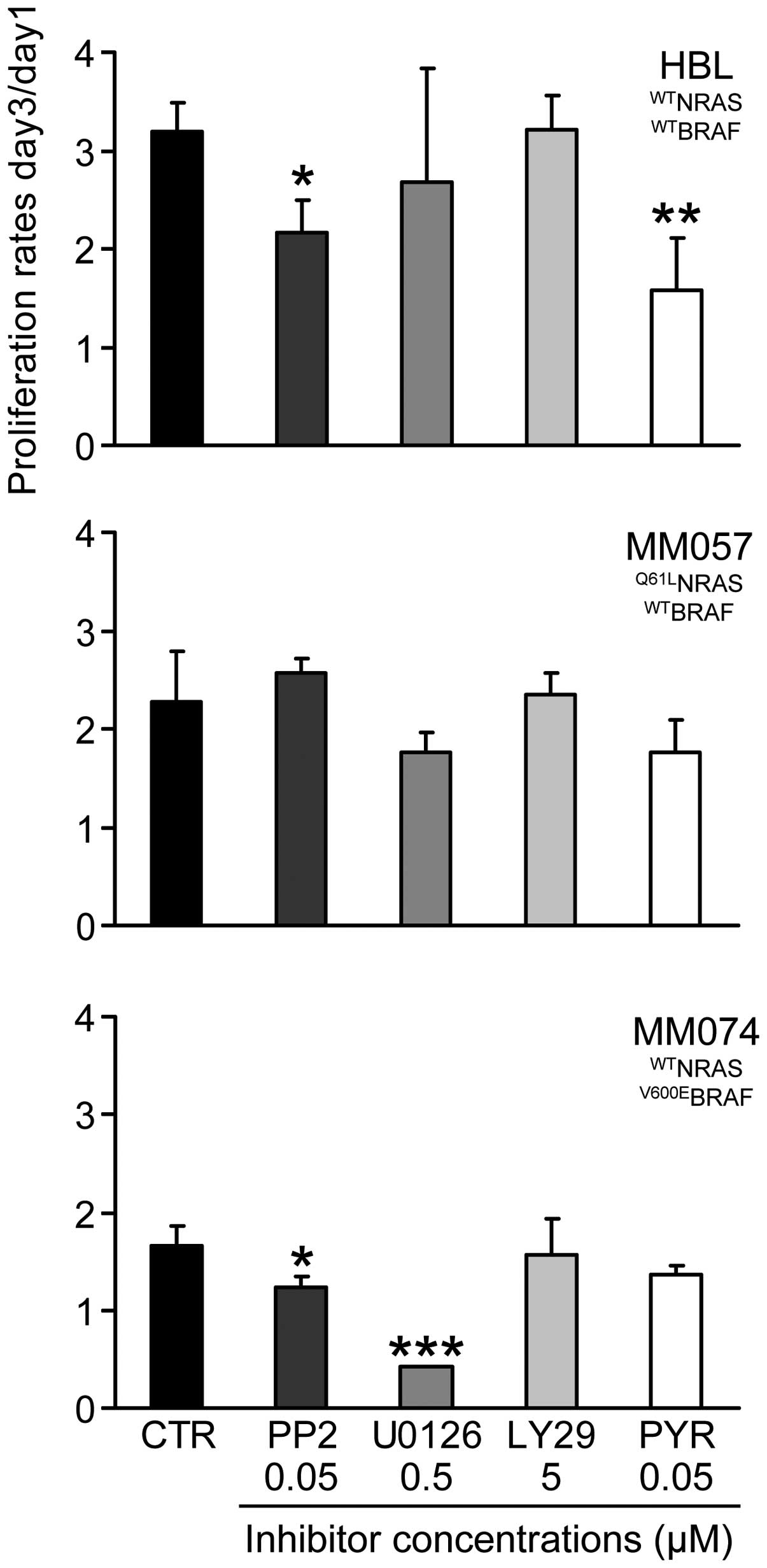
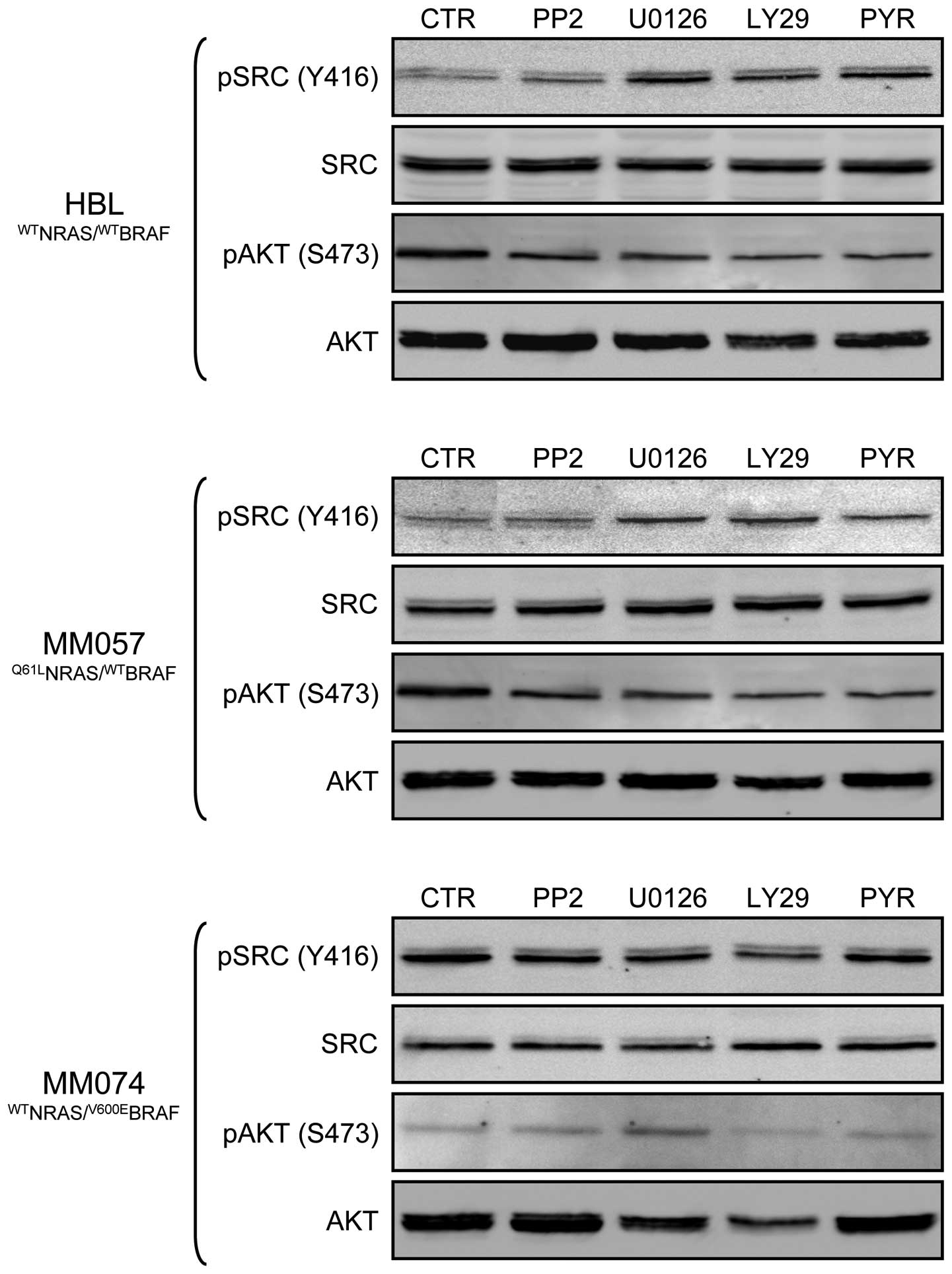
|
1
|
Rokuhara S, Saida T, Oguchi M, Matsumoto
K, Murase S and Oguchi S: Number of acquired melanocytic nevi in
patients with melanoma and control subjects in Japan: Nevus count
is a significant risk factor for nonacral melanoma but not for
acral melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 50:695–700. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller AJ and Mihm MC Jr: Melanoma. N Engl
J Med. 355:51–65. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Berwick M, Erdei E and Hay J: Melanoma
epidemiology and public health. Dermatol Clin. 27:205–214.
viii2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cummins DL, Cummins JM, Pantle H,
Silverman MA, Leonard AL and Chanmugam A: Cutaneous malignant
melanoma. Mayo Clin Proc. 81:500–507. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, et al:
Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 363:711–723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, et al:
Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in
cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sosman JA, Kim KB, Schuchter L, et al:
Survival in BRAF V600-mutant advanced melanoma treated with
vemurafenib. N Engl J Med. 366:707–714. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Falchook GS, Long GV, Kurzrock R, et al:
Dabrafenib in patients with melanoma, untreated brain metastases,
and other solid tumours: a phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet.
379:1893–1901. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Flaherty KT, Robert C, Hersey P, et al:
Improved survival with MEK inhibition in BRAF-mutated melanoma. N
Engl J Med. 367:107–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, et al:
Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature. 417:949–954.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, et al:
Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic melanoma. N
Engl J Med. 363:809–819. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, et al:
Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E
mutation. N Engl J Med. 364:2507–2516. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Christensen C and Guldberg P: Growth
factors rescue cutaneous melanoma cells from apoptosis induced by
knockdown of mutated (V 600 E) B-RAF. Oncogene. 24:6292–6302. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Montagut C, Sharma SV, Shioda T, et al:
Elevated CRAF as a potential mechanism of acquired resistance to
BRAF inhibition in melanoma. Cancer Res. 68:4853–4861. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johannessen CM, Boehm JS, Kim SY, et al:
COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway
reactivation. Nature. 468:968–972. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wagle N, Emery C, Berger MF, et al:
Dissecting therapeutic resistance to RAF inhibition in melanoma by
tumor genomic profiling. J Clin Oncol. 29:3085–3096. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M,
et al: RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of
aberrantly spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature. 480:387–390. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yancovitz M, Litterman A, Yoon J, et al:
Intra- and inter-tumor heterogeneity of BRAF(V600E) mutations in
primary and metastatic melanoma. PLoS One. 7:e293362012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsao H, Zhang X, Benoit E and Haluska FG:
Identification of PTEN/MMAC1 alterations in uncultured melanomas
and melanoma cell lines. Oncogene. 16:3397–3402. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsao H, Goel V, Wu H, Yang G and Haluska
FG: Genetic interaction between NRAS and BRAF mutations and
PTEN/MMAC1 inactivation in melanoma. J Invest Dermatol.
122:337–341. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheung M, Sharma A, Madhunapantula SV and
Robertson GP: Akt3 and mutant V600E B-Raf cooperate to promote
early melanoma development. Cancer Res. 68:3429–3439. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Niu G, Bowman T, Huang M, et al: Roles of
activated Src and Stat3 signaling in melanoma tumor cell growth.
Oncogene. 21:7001–7010. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Byers LA, Sen B, Saigal B, et al:
Reciprocal regulation of c-Src and STAT3 in non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6852–6861. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ji Z, Flaherty KT and Tsao H: Molecular
therapeutic approaches to melanoma. Mol Aspects Med. 31:194–204.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yurkovetsky ZR, Kirkwood JM, Edington HD,
et al: Multiplex analysis of serum cytokines in melanoma patients
treated with interferon-alpha2b. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2422–2428.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Robert C, Thomas L, Bondarenko I, et al:
Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 364:2517–2526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Flaherty KT, Infante JR, Daud A, et al:
Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600
mutations. N Engl J Med. 367:1694–1703. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Das Thakur M, Salangsang F, Landman AS, et
al: Modelling vemurafenib resistance in melanoma reveals a strategy
to forestall drug resistance. Nature. 494:251–255. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Held MA, Langdon CG, Platt JT, et al:
Genotype-selective combination therapies for melanoma identified by
high-throughput drug screening. Cancer Discov. 3:52–67. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smalley KS: A pivotal role for ERK in the
oncogenic behaviour of malignant melanoma? Int J Cancer.
104:527–532. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Garnett MJ and Marais R: Guilty as
charged: B-RAF is a human oncogene. Cancer Cell. 6:313–319. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gray-Schopfer VC, Cheong SC, Chong H, et
al: Cellular senescence in naevi and immortalisation in melanoma: a
role for p16? Br J Cancer. 95:496–505. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Michaloglou C, Vredeveld LC, Soengas MS,
et al: BRAFE600-associated senescence-like cell cycle arrest of
human naevi. Nature. 436:720–724. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pollock PM, Harper UL, Hansen KS, et al:
High frequency of BRAF mutations in nevi. Nat Genet. 33:19–20.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dhomen N, Reis-Filho JS, da Rocha Dias S,
et al: Oncogenic Braf induces melanocyte senescence and melanoma in
mice. Cancer Cell. 15:294–303. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wellbrock C, Karasarides M and Marais R:
The RAF proteins take centre stage. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
5:875–885. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gopal YN, Deng W, Woodman SE, et al: Basal
and treatment-induced activation of AKT mediates resistance to cell
death by AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) in Braf-mutant human cutaneous
melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 70:8736–8747. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Solit DB and Rosen N: Resistance to BRAF
inhibition in melanomas. N Engl J Med. 364:772–774. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Villanueva J, Vultur A, Lee JT, et al:
Acquired resistance to BRAF inhibitors mediated by a RAF kinase
switch in melanoma can be overcome by cotargeting MEK and
IGF-1R/PI3K. Cancer Cell. 18:683–695. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Flaherty KT and Smalley KS: Preclinical
and clinical development of targeted therapy in melanoma: attention
to schedule. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 22:529–531. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lui P, Cashin R, Machado M, Hemels M,
Corey-Lisle PK and Einarson TR: Treatments for metastatic melanoma:
synthesis of evidence from randomized trials. Cancer Treat Rev.
33:665–680. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|