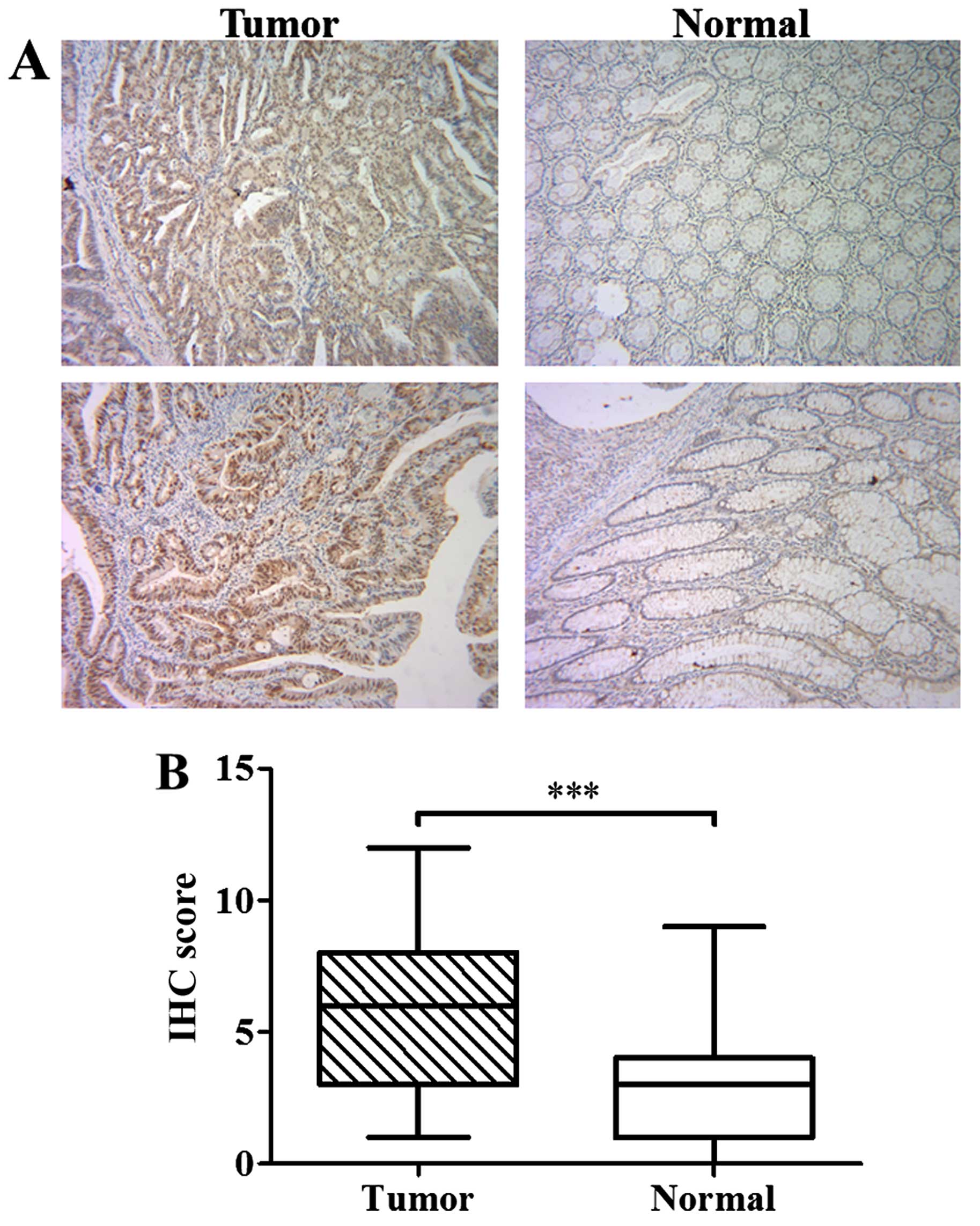
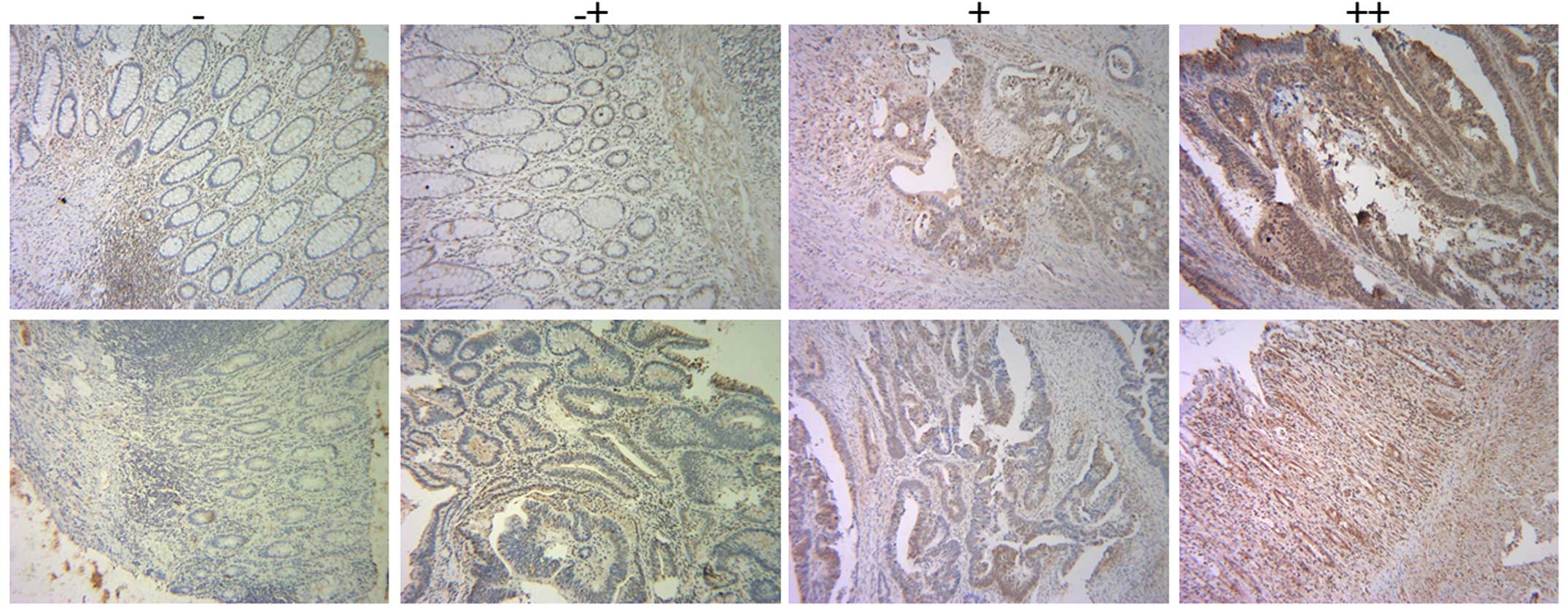
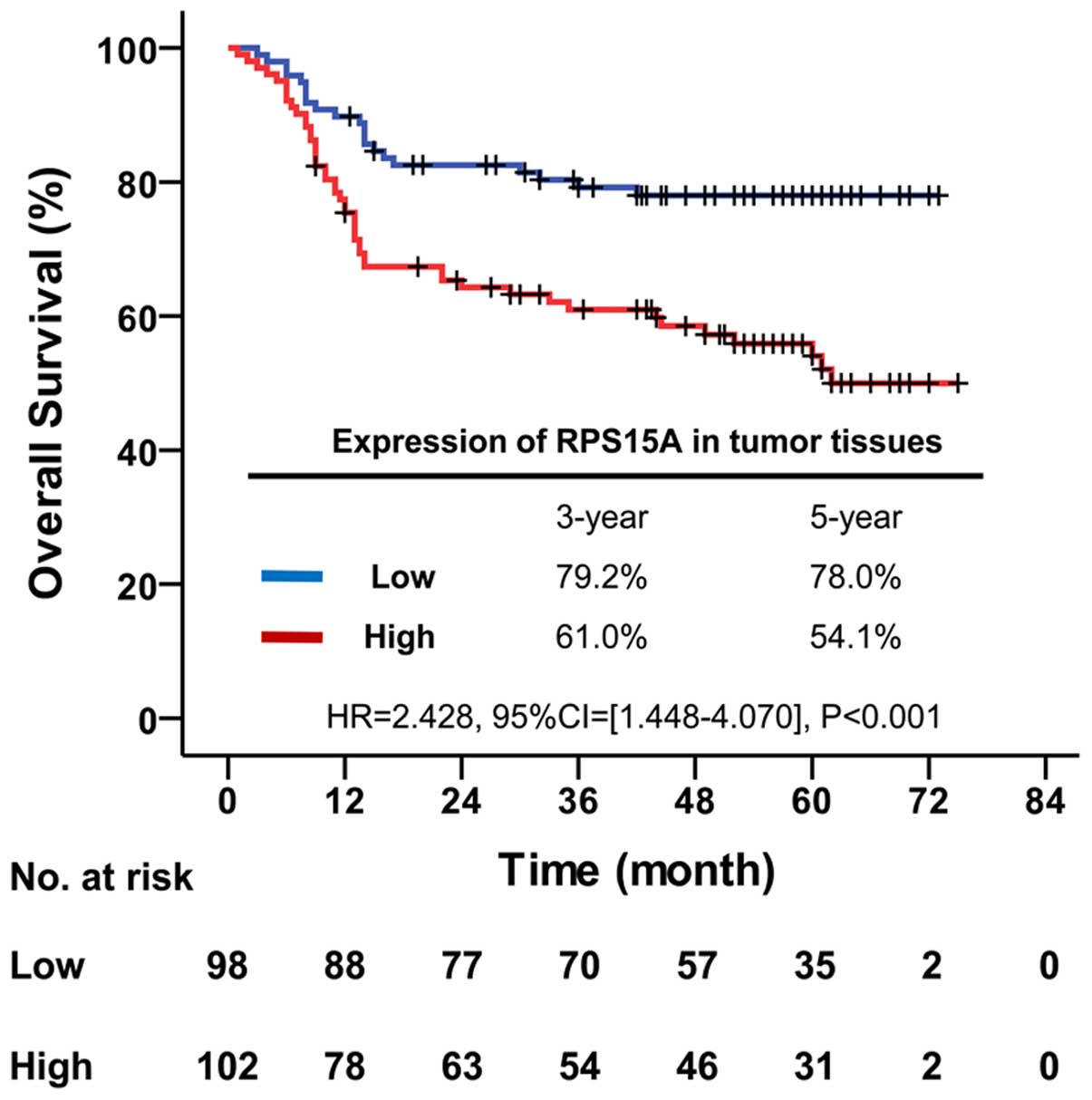
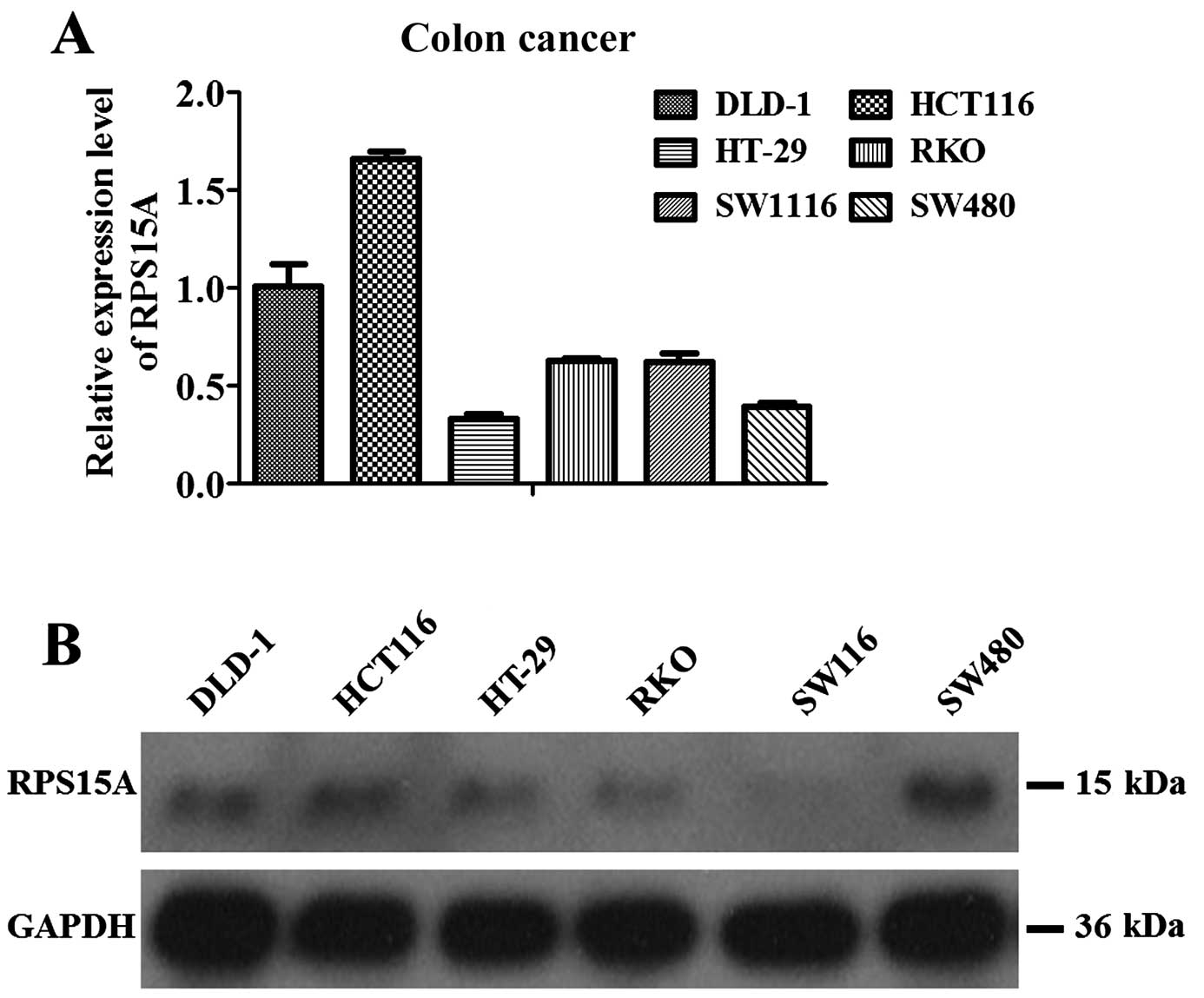
Spandidos Publications style
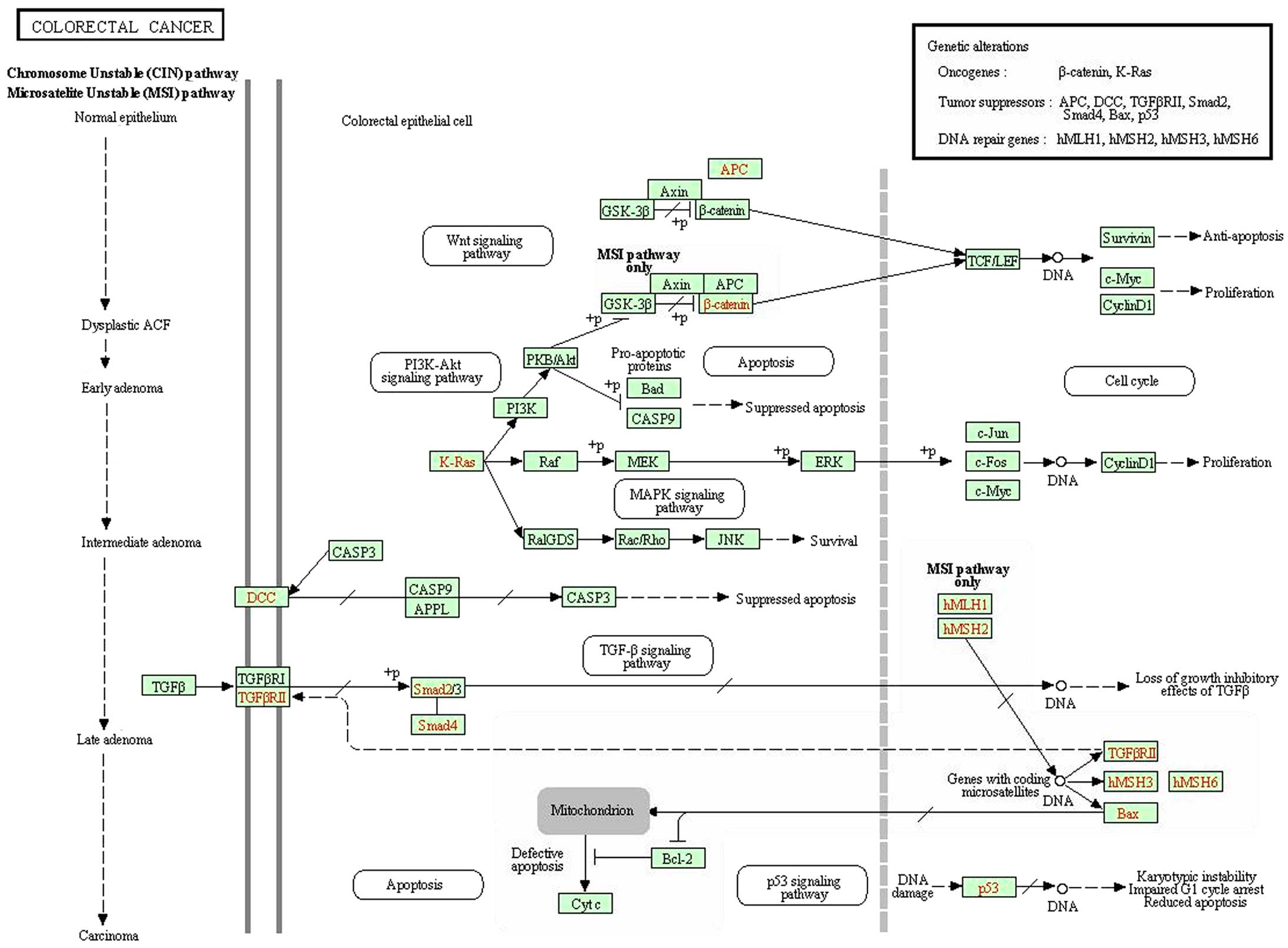
Chen J, Wei Y, Feng Q, Ren L, He G, Chang W, Zhu D, Yi T, Lin Q, Tang W, Tang W, et al: Ribosomal protein S15A promotes malignant transformation and predicts poor outcome in colorectal cancer through misregulation of p53 signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 48: 1628-1638, 2016.
APA
Chen, J., Wei, Y., Feng, Q., Ren, L., He, G., Chang, W. ... Qin, X. (2016). Ribosomal protein S15A promotes malignant transformation and predicts poor outcome in colorectal cancer through misregulation of p53 signaling pathway. International Journal of Oncology, 48, 1628-1638. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3366
MLA
Chen, J., Wei, Y., Feng, Q., Ren, L., He, G., Chang, W., Zhu, D., Yi, T., Lin, Q., Tang, W., Xu, J., Qin, X."Ribosomal protein S15A promotes malignant transformation and predicts poor outcome in colorectal cancer through misregulation of p53 signaling pathway". International Journal of Oncology 48.4 (2016): 1628-1638.
Chicago
Chen, J., Wei, Y., Feng, Q., Ren, L., He, G., Chang, W., Zhu, D., Yi, T., Lin, Q., Tang, W., Xu, J., Qin, X."Ribosomal protein S15A promotes malignant transformation and predicts poor outcome in colorectal cancer through misregulation of p53 signaling pathway". International Journal of Oncology 48, no. 4 (2016): 1628-1638. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2016.3366