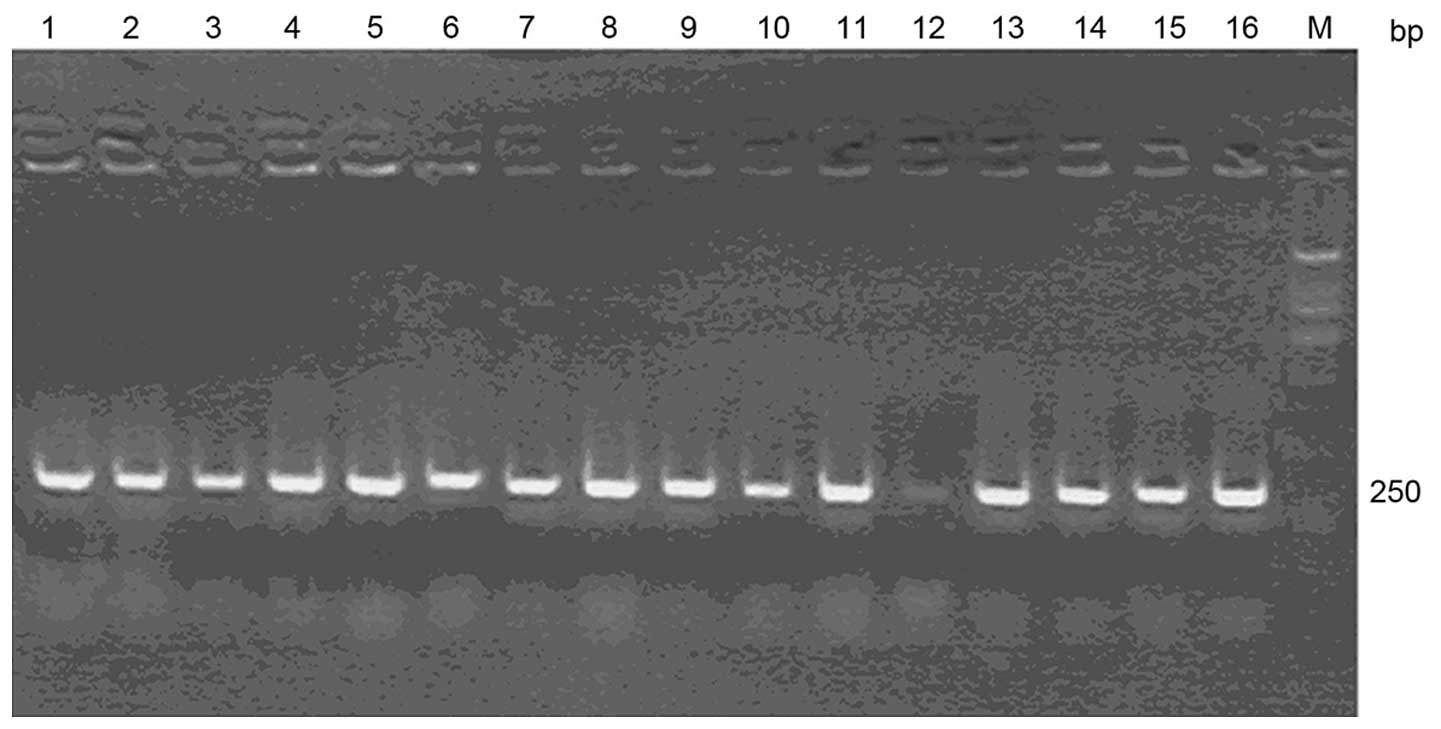
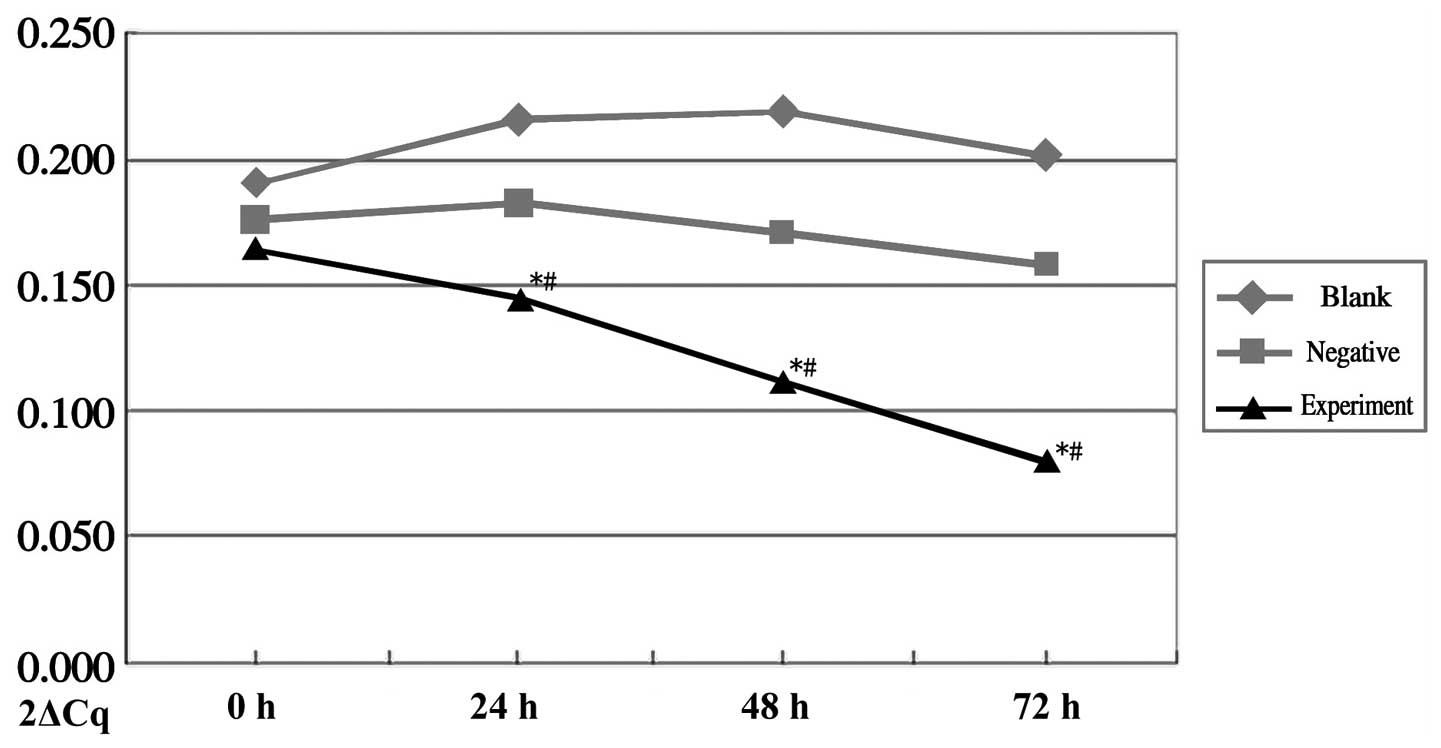
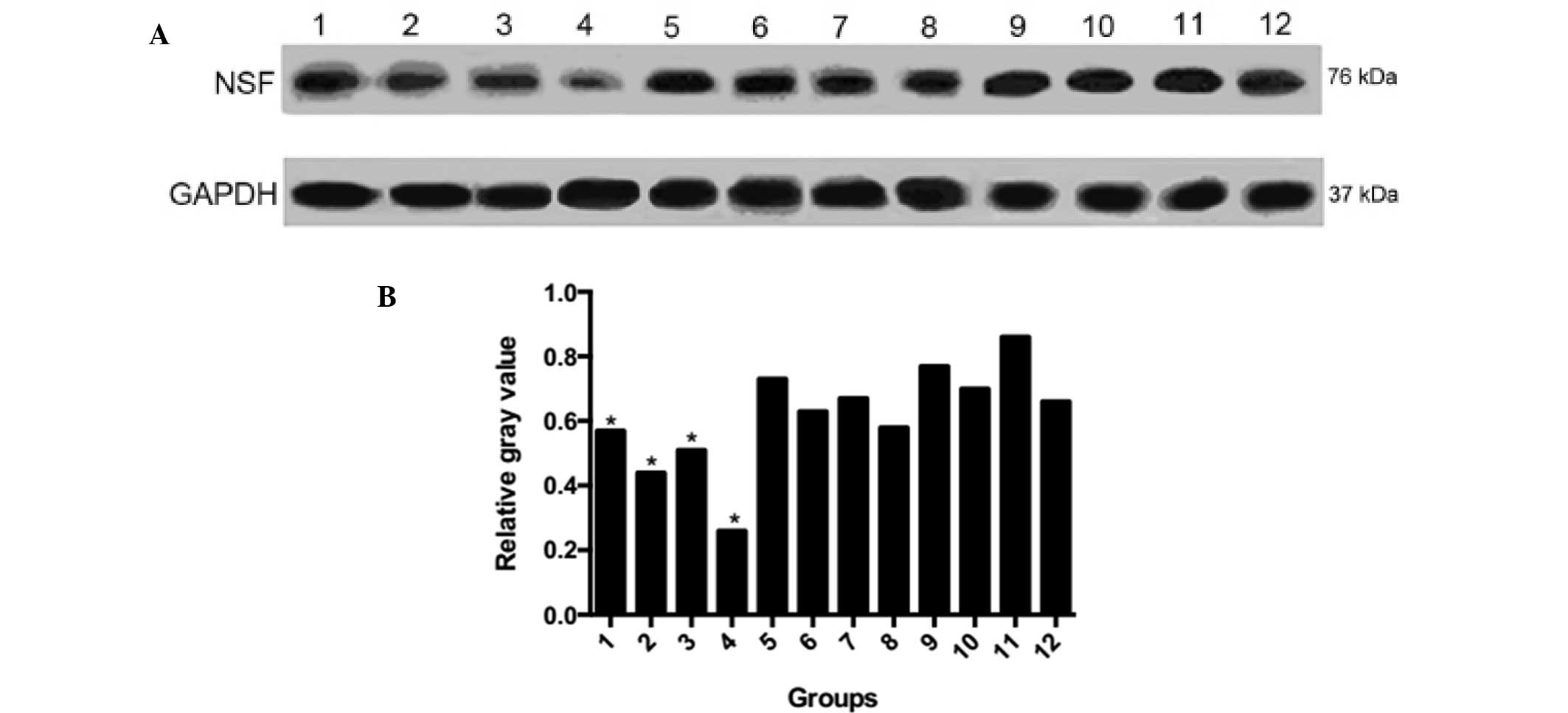
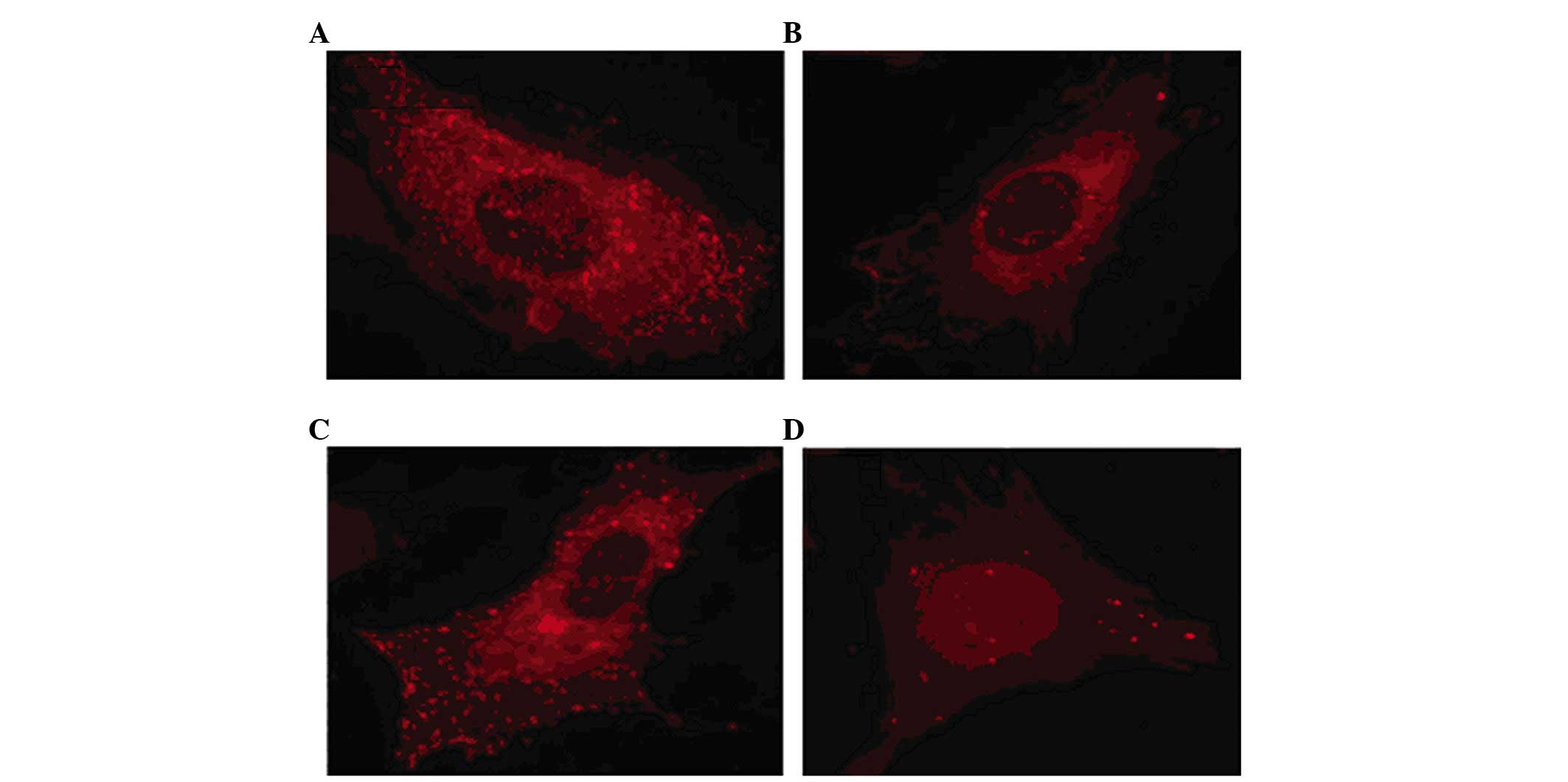
|
1
|
Valentijn KM, van Driel LF, Mourik MJ,
Hendriks GJ, Arends TJ, Koster AJ and Valentijn JA: Multigranular
exocytosis of Weibel-Palade bodies in vascular endothelial cells.
Blood. 116:1807–1816. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kiskin NI, Hellen N, Babich V, Hewlett L,
Knipe L, Hannah MJ and Carter T: Protein mobilities and P-selectin
storage in Weibel-Palade bodies. J Cell Sci. 123:2964–2975. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Berriman JA1, Li S, Hewlett LJ, Wasilewski
S, Kiskin FN, Carter T, Hannah MJ and Rosenthal PB: Structural
organization of Weibel-Palade bodies revealed by cryo-EM of
vitrified endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:17407–17412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lowenstein CJ and Tsuda H:
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor: A redox sensor in exocytosis.
Biol Chem. 387:1377–1383. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lowenstein CJ, Morrell CN and Yamakuchi M:
Regulation of Weibel-Palade body exocytosis. Trends in Cardiovasc
Med. 15:302–308. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sioud M: Promises and challenges in
developing RNAi as a research tool and therapy. Methods in Mol
Biol. 703:173–187. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shimizu H and Fujita T: New short
interfering RNA-based therapies for glomerulonephritis. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 7:407–415. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qian Z, Gelzer-Bell R, Yang SX, Cao W,
Ohnishi T, Wasowska BA, Hruban RH, Rodriguez ER, Baldwin WM III and
Lowenstein CJ: Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition of
weibel-palade body release in cardiac transplant rejection.
Circulation. 104:2369–2375. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang SX, Yan J, Deshpande SS, Irani K and
Lowenstein CJ: Rac1 regulates the release of Weibel-Palade bodies
in human aortic endothelial cells. Chin Med J (Engl).
117:1143–1150. 2004.
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-timequantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ming X: Cellular delivery of siRNA and
antisense oligonucleotides via receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 8:435–449. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Samuel-Abraham S and Leonard JN: Staying
on message: Design principles for controlling nonspecific responses
to siRNA. FEBS J. 277:4828–4836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Amin HM, Ahmad S, Walenga JM, Hoppensteadt
DA, Leitz H and Fareed J: Soluble P-selectin in human plasma:
Effect of anticoagulant matrix and its levels in patients with
cardiovascular disorders. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 6:71–76. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Russell FD, Skepper JN and Davenport AP:
Evidence using immunoelectron microscopy for regulated and
constitutive pathways in the transport and release of endothelin. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 31:424–430. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wolff B, Burns AR, Middleton J and Rot A:
Endothelial cell 'memory' of inflammatory stimulation: Human
venular endothelial cells store interleukin 8 in Weibel-Palade
bodies. J Exp Med. 188:1757–1762. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Alberto P1, Francesca I, Chiara S and
Ranuccio N: Acute coronary syndromes: from the laboratory markers
to the coronary vessels. Biomark Insights. 1:123–130.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ito T, Yamakuchi M and Lowenstein CJ:
Thioredoxin increases exocytosis by denitrosylating
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor. J Biol Chem. 1:11179–11184.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lowenstein CJ: Nitric oxide regulation of
protein trafficking in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc Res.
75:240–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ferlito M, Fulton WB, Zauher MA, Marbán E,
Steenbergen C and Lowenstein CJ: VAMP-1, VAMP-2 and syntaxin-4
regulate ANP release from cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
49:791–800. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Matsushita K, Morrell CN, Cambien B, Yang
SX, Yamakuchi M, Bao C, Hara MR, Quick RA, Cao W, O'Rourke B, et
al: Nitric oxide regulates exocytosis by S-nitrosylation of
N-ethylmaleimdide-sensitive factor. Cell. 115:139–150. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Morrell CN,
Matsushita K, Fletcher CA, Cao W and Lowenstein CJ: Exocytosis of
endothelial cells is regulated by N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive
factor. Methods Mol Biol. 440:203–215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Calvert JW, Gundewar S, Yamakuchi M, Park
PC, Baldwin WM III, Lefer DJ and Lowenstein CJ: Inhibition of
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor protects against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res. 101:1247–1254. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goel A, Su B, Flavahan S, Lowenstein CJ,
Berkowitz DE and Flavahan NA: Increased endothelial exocytosis and
generation of endothelin-1 contributes to constriction of aged
arteries. Circ Res. 107:242–251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Martinez J, Patkaniowska A, Urlaub H,
Lührmann R and Tuschl T: Single-stranded antisense siRNAs guide
target RNA cleavage in RNAi. Cell. 110:563–574. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deng Y, Wang CC, Choy KW, Du Q, Chen J,
Wang Q, Li L, Chung TK and Tang T: Therapeutic potentials of gene
silencing by RNA interference: Principles, challenges and new
strategies. Gene. 538:217–227. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|