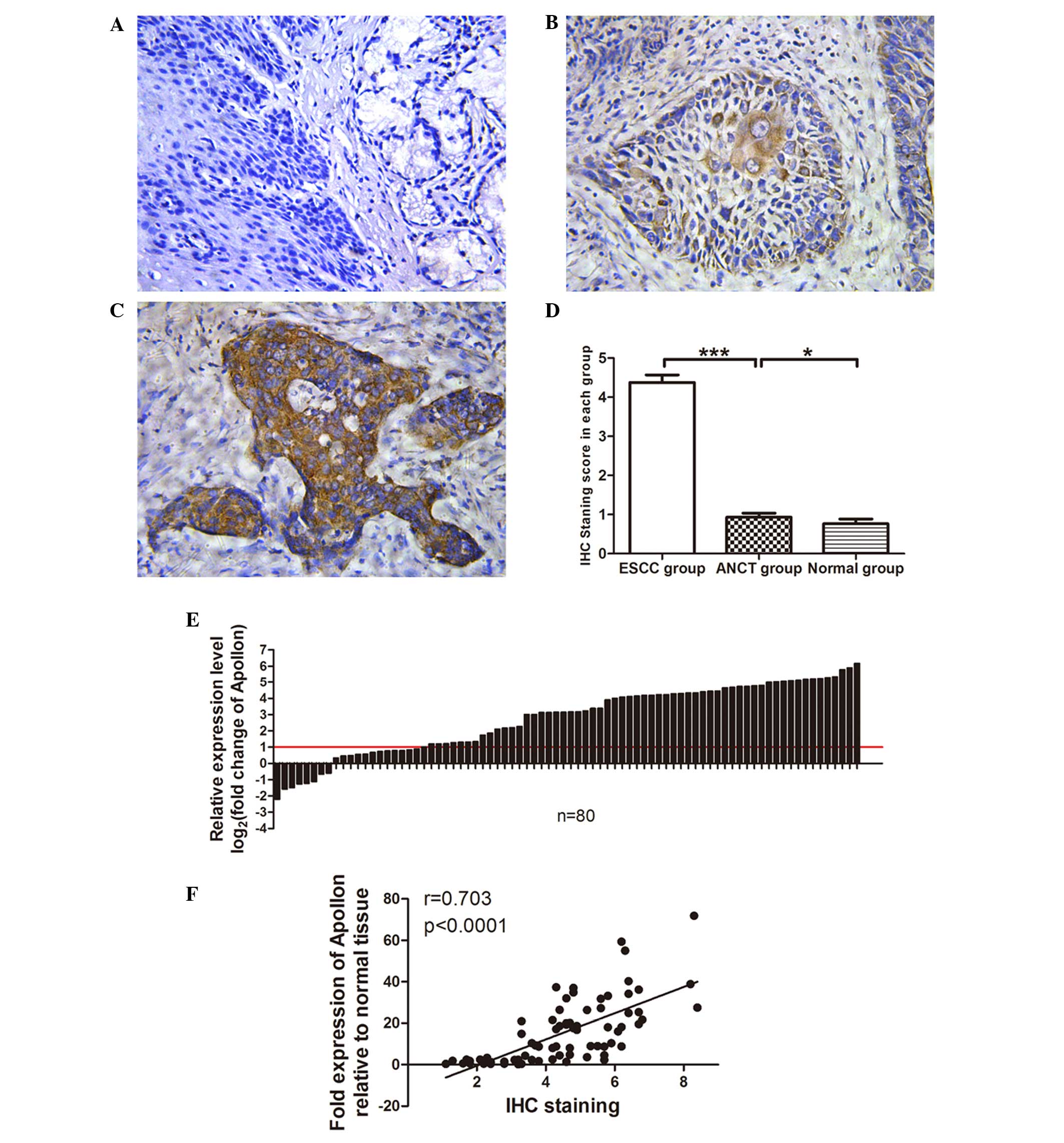
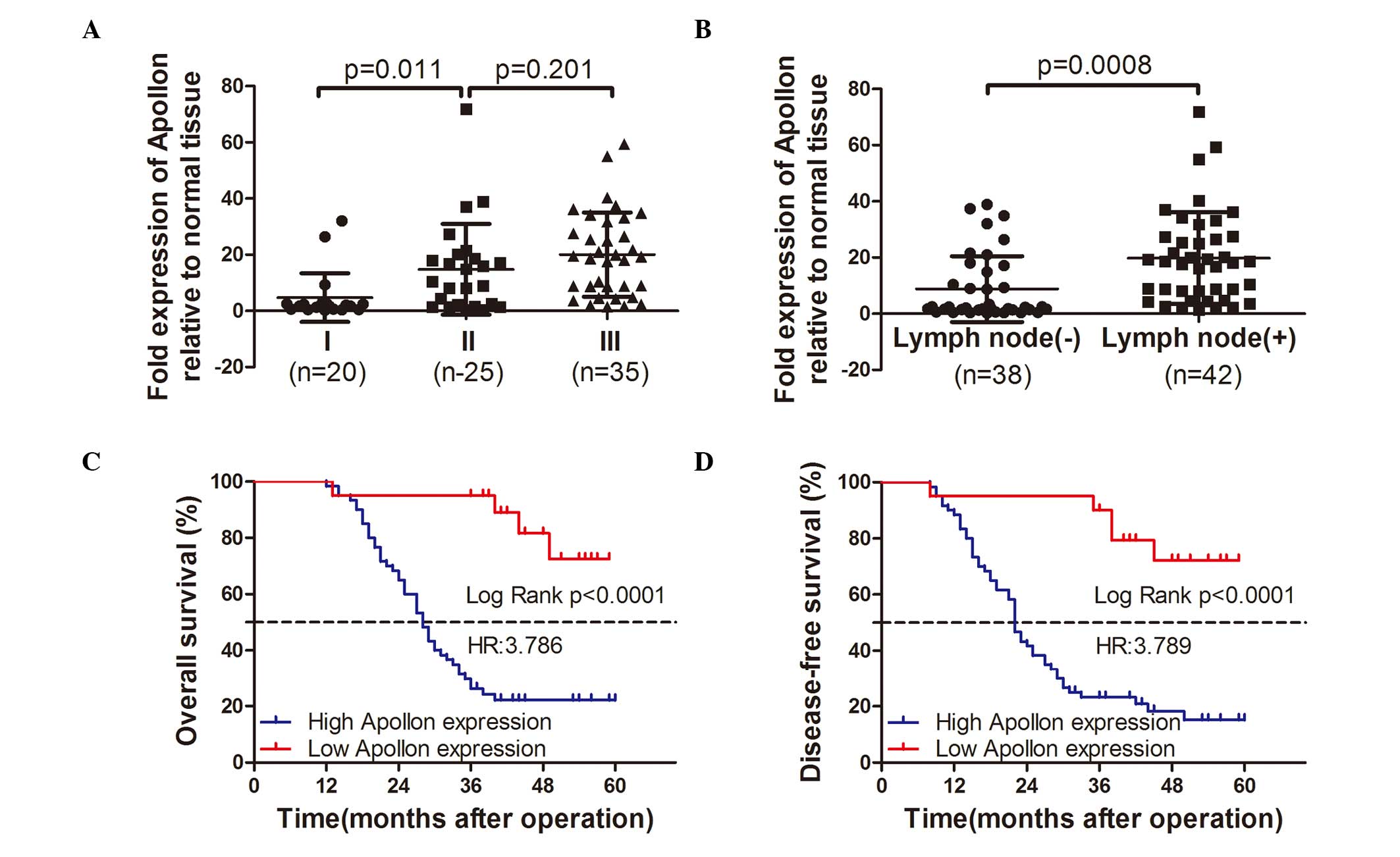
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mariette C, Piessen G and Triboulet JP:
Therapeutic strategies in oesophageal carcinoma: Role of surgery
and other modalities. Lancet Oncol. 8:545–553. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lerut T, Coosemans W, Decker G, De Leyn P,
Nafteux P and Van Raemdonck D: Cancer of the esophagus and
gastroesophageal junction: Potentially curative therapies. Surg
Oncol. 10:113–122. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Giancotti FG and Tarone G: Positional
control of cell fate through joint integrin/receptor protein kinase
signaling. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 19:173–206. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Naito M: Molecular mechanism of apoptosis
inhibition by IAPs and its implication to cancer therapy.
Seikagaku. 78:525–528. 2006.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Evan G: Cancer - a matter of life and cell
death. Int J Cancer. 71:709–711. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Srinivasula SM and Ashwell JD: IAPs:
what's in a name? Mol Cell. 30:123–135. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hauser HP, Bardroff M, Pyrowolakis G and
Jentsch S: A giant ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme related to IAP
apoptosis inhibitors. J Cell Biol. 141:1415–1422. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen Z, Naito M, Hori S, Mashima T, Yamori
T and Tsuruo T: A human IAP-family gene, apollon, expressed in
human brain cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 264:847–854.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qiu XB and Goldberg AL: The
membrane-associated inhibitor of apoptosis protein, BRUCE/Apollon,
antagonizes both the precursor and mature forms of Smac and
caspase-9. J Biol Chem. 280:174–182. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Qiu XB, Markant SL, Yuan J and Goldberg
AL: Nrdp1-mediated degradation of the gigantic IAP, BRUCE, is a
novel pathway for triggering apoptosis. EMBO J. 23:800–810. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hao Y, Sekine K, Kawabata A, Nakamura H,
Ishioka T, Ohata H, Katayama R, Hashimoto C, Zhang X, Noda T, et
al: Apollon ubiquitinates SMAC and caspase-9, and has an essential
cytoprotection function. Nat Cell Biol. 6:849–860. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lamers F, Schild L, Koster J, Speleman F,
Øra I, Westerhout EM, van Sluis P, Versteeg R, Caron HN and
Molenaar JJ: Identification of BIRC6 as a novel intervention target
for neuroblastoma therapy. BMC Cancer. 12:2852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bianchini M, Levy E, Zucchini C, Pinski V,
Macagno C, De Sanctis P, Valvassori L, Carinci P and Mordoh J:
Comparative study of gene expression by cDNA microarray in human
colorectal cancer tissues and normal mucosa. Int J Oncol. 29:83–94.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Low CG, Luk IS, Lin D, Fazli L, Yang K, Xu
Y, Gleave M, Gout PW and Wang Y: BIRC6 protein, an inhibitor of
apoptosis: Role in survival of human prostate cancer cells. PloS
One. 8:e558372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pohl C and Jentsch S: Final stages of
cytokinesis and midbody ring formation are controlled by BRUCE.
Cell. 132:832–845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ren J, Shi M, Liu R, Yang QH, Johnson T,
Skarnes WC and Du C: The Birc6 (Bruce) gene regulates p53 and the
mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis and is essential for mouse
embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:565–570. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chu L, Gu J, Sun L, Qian Q, Qian C and Liu
X: Oncolytic adenovirus-mediated shRNA against Apollon inhibits
tumor cell growth and enhances antitumor effect of 5-fluorouracil.
Gene Ther. 15:484–494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lopergolo A, Pennati M, Gandellini P,
Orlotti NI, Poma P, Daidone MG, Folini M and Zaffaroni N: Apollon
gene silencing induces apoptosis in breast cancer cells through p53
stabilisation and caspase-3 activation. Br J Cancer. 100:739–746.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Van Houdt WJ, Emmink BL, Pham TV, Piersma
SR, Verheem A, Vries RG, Fratantoni SA, Pronk A, Clevers H, Borel
Rinkes IH, et al: Comparative proteomics of colon cancer stem cells
and differentiated tumor cells identifies BIRC6 as a potential
therapeutic target. Mol Cell Proteomics. 10:M111.0113532011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen Y, Fu D, Xi J, Ji Z, Liu T, Ma Y,
Zhao Y, Dong L, Wang Q and Shen X: Expression and clinical
significance of UCH37 in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Dig Dis Sci. 57:2310–2317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 7th ed. Oxford:
Wiley-Blackwell; 2010
|
|
25
|
Zhang S, Tang W, Weng S, Liu X, Rao B, Gu
J, Chen S, Wang Q, Shen X, Xue R and Dong L: Apollon modulates
chemosensitivity in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 5:7183–7197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang L, Chen YJ, Hou J, Wang YY, Tang WQ,
Shen XZ and Tu RQ: Expression and clinical significance of BIRC6 in
human epithelial ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:4891–4896. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sung KW, Choi J, Hwang YK, Lee SJ, Kim HJ,
Lee SH, Yoo KH, Jung HL and Koo HH: Overexpression of Apollon, an
anti-apoptotic protein, is associated with poor prognosis in
childhood de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res.
13:5109–5114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ismail EA, Mahmoud HM, Tawfik LM, Habashy
DM, Adly AA, El-Sherif NH and Abdelwahab MA: BIRC6/Apollon gene
expression in childhood acute leukemia: Impact on therapeutic
response and prognosis. Eur J Haematol. 88:118–127. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tang W, Xue R, Weng S, Wu J, Fang Y, Wang
Y, Ji L, Hu T, Liu T, Huang X, et al: BIRC6 promotes hepatocellular
carcinogenesis: Interaction of BIRC6 with p53 facilitating p53
degradation. Int J Cancer. 136:E475–E487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dong X, Lin D, Low C, Vucic EA, English
JC, Yee J, Murray N, Lam WL, Ling V, Lam S, et al: Elevated
expression of BIRC6 protein in non-small-cell lung cancers is
associated with cancer recurrence and chemoresistance. J Thorac
Oncol. 8:161–170. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abe S, Yamamoto K, Hasegawa M, Inoue M,
Kurata M, Hirokawa K, Kitagawa M, Nakagawa Y and Suzuki K: Bone
marrow cells of myelodysplastic syndromes exhibit significant
expression of apollon, livin and ILP-2 with reduction after
transformation to overt leukemia. Leuk Res. 29:1095–1096. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tassi E, Zanon M, Vegetti C, Molla A,
Bersani I, Perotti V, Pennati M, Zaffaroni N, Milella M, Ferrone S,
et al: Role of Apollon in human melanoma resistance to antitumor
agents that activate the intrinsic or the extrinsic apoptosis
pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 18:3316–3327. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nemoto T, Kitagawa M, Hasegawa M, Ikeda S,
Akashi T, Takizawa T, Hirokawa K and Koike M: Expression of IAP
family proteins in esophageal cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 76:253–259.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou S, Ye W, Shao Q, Qi Y, Zhang M and
Liang J: Prognostic significance of XIAP and NF-κB expression in
esophageal carcinoma with postoperative radiotherapy. World J Surg
Oncol. 11:2882013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Vaĭshlia NA, Zinov'eva MV, Sass AV,
Kopantsev EP, Vinogradova TV and Sverdlov ED: Increase of BIRC5
gene expression in non-small cell lung cancer and esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma does not correlate with expression of genes
SMAC/DIABLO and PML encoding its inhibitors. Mol Biol (Mosk).
42:652–661. 2008.
|