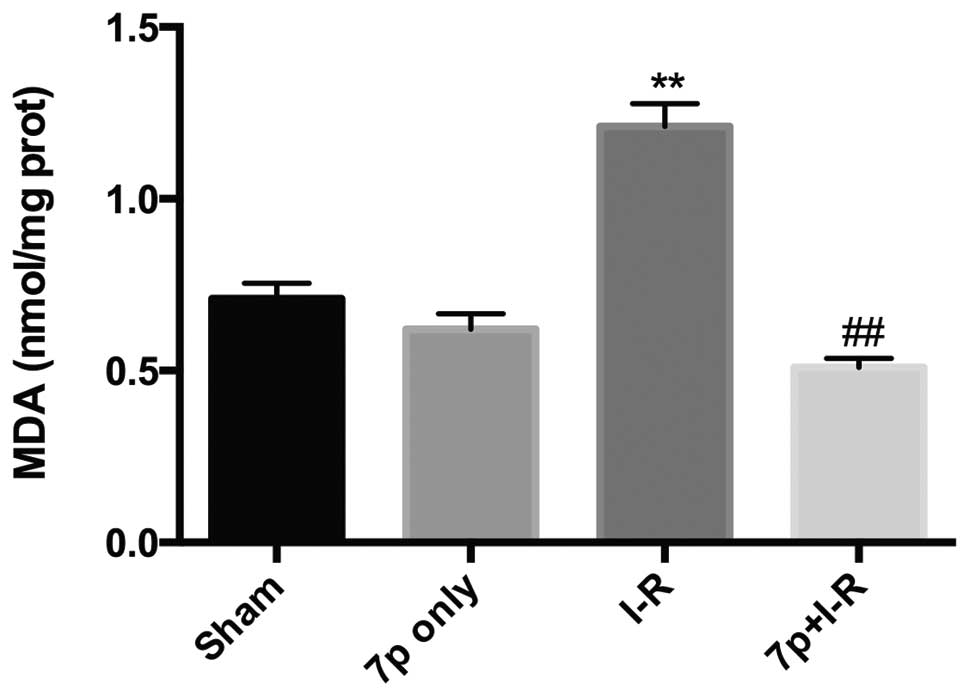
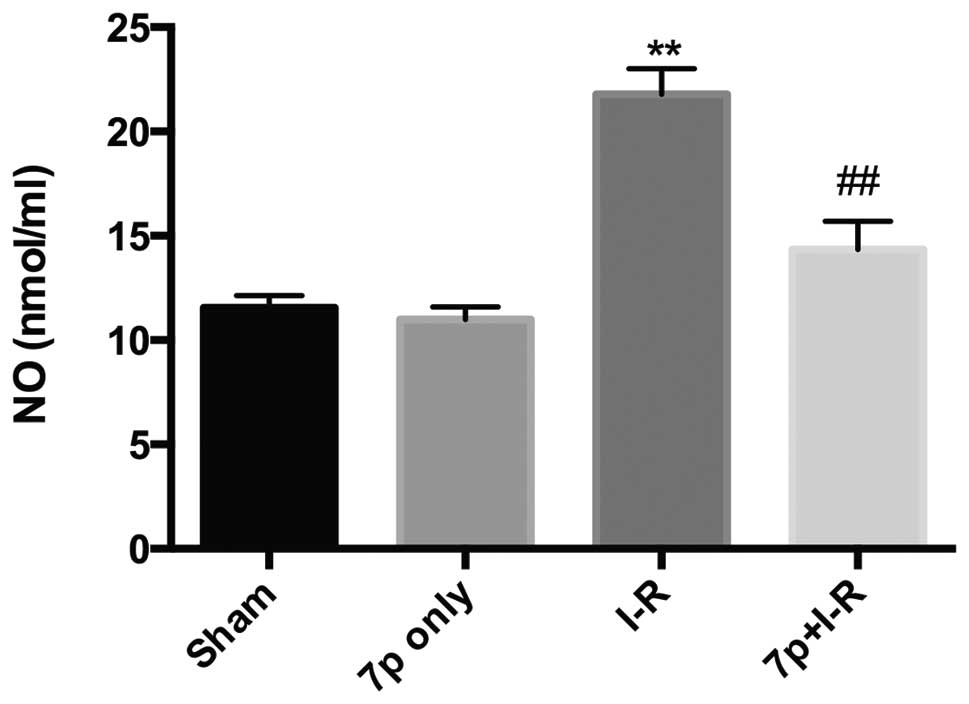
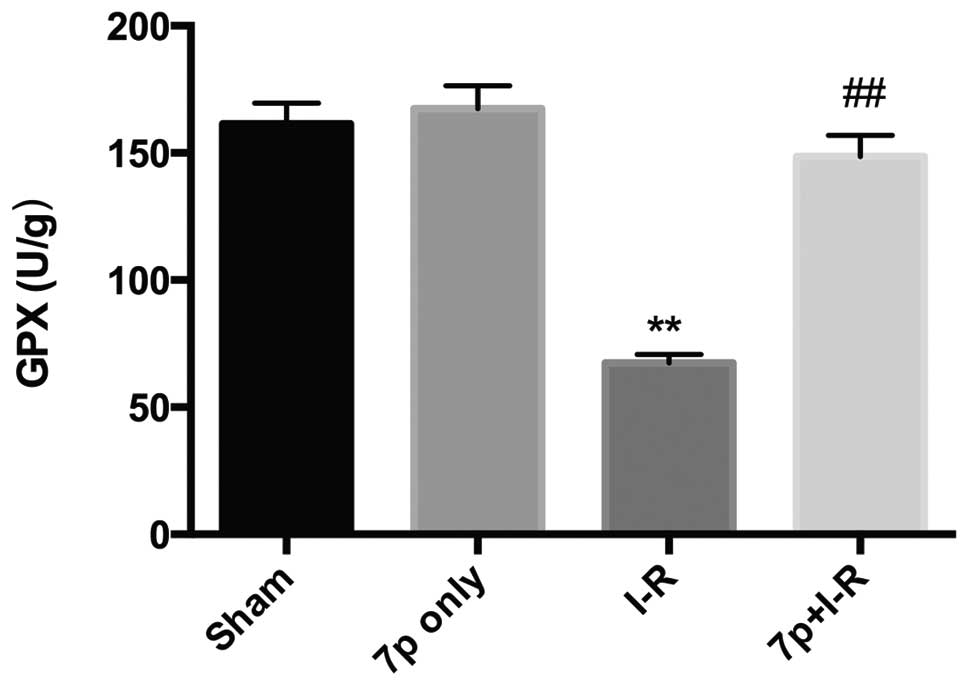
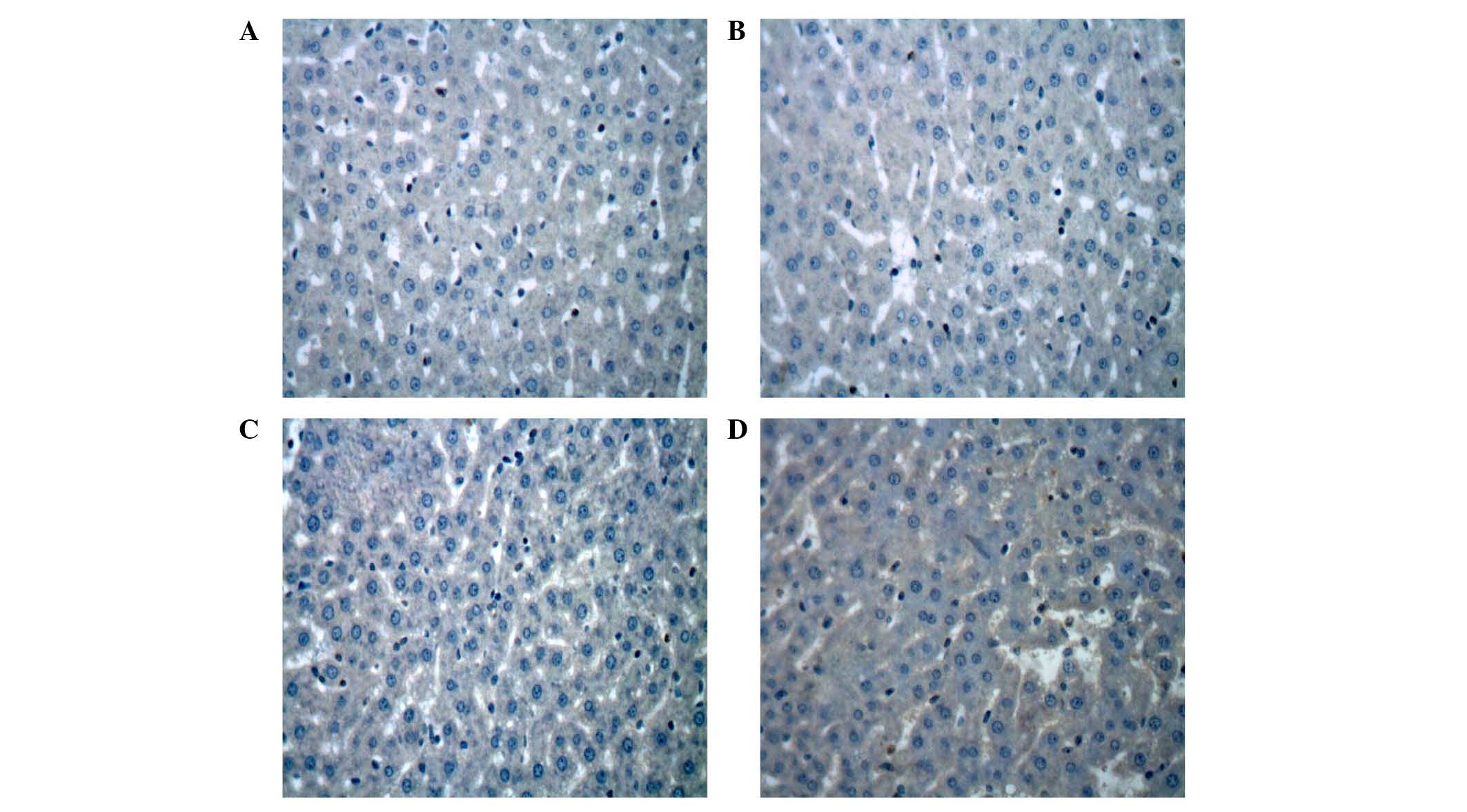
|
1
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Klune JR and Tsung A: Molecular biology of
liver ischemia/reperfusion injury: Established mechanisms and
recent advancements. Surg Clin North Am. 90:665–677. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Taki-Eldin A, Zhou L, Xie HY, Chen KJ, Yu
D, He Y and Zheng SS: Triiodothyronine attenuates hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury in a partial hepatectomy model through
inhibition of proinflammatory cytokines, transcription factors, and
adhesion molecules. J Surg Res. 178:646–656. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Katsumi H, Nishikawa M, Yamashita F and
Hashida M: Prevention of hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by
prolonged delivery of nitric oxide to the circulating blood in
mice. Transplantation. 85:264–269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Katsumi H, Nishikawa M, Yasui H, Yamashita
F and Hashida M: Prevention of ischemia/reperfusion injury by
hepatic targeting of nitric oxide in mice. J Control Release.
140:12–17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chan PH: Role of oxidants in ischemic
brain damage. Stroke. 27:1124–1129. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mizoe A, Kondo S, Azuma T, Fujioka H,
Tanaka K, Hashida M and Kanematsu T: Preventive effects of
superoxide dismutase derivatives modified with monosaccharides on
reperfusion injury in rat liver transplantation. J Surg Res.
73:160–165. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kusumoto K, Morimoto T, Minor T, Uchino J
and Isselhard W: Allopurinol effects in rat liver transplantation
on recovery of energy metabolism and free radical-induced damage.
Eur Surg Res. 27:285–291. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koeppel TA, Lehmann TG, Thies JC, Gehrcke
R, Gebhard MM, Herfarth C, Otto G and Post S: Impact of
N-acetylcysteine on the hepatic microcirculation after orthotopic
liver transplantation. Transplantation. 61:1397–1402. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lubos E, Loscalzo J and Handy DE:
Glutathione peroxidase-1 in health and disease: From molecular
mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:1957–1997. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Sies H: Ebselen, a selenoorganic compound
as glutathione peroxidase mimic. Free Radic Bio Med. 14:313–323.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Epp O, Landensteine R and Wendel A: The
refined structure of the selenoenzyme glutathione peroxidase at
0.2-nm resolution. Eur J Biochem. 133:51–69. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kohmoto J, Nakao A, Stolz DB, Kaizu T,
Tsung A, Ikeda A, Shimizu H, Takahashi T, Tomiyama K, Sugimoto R,
et al: Carbon monoxide protects rat lung transplants from
ischemia-reperfusion injury via a mechanism involving p38 MAPK
pathway. Am J Transplant. 7:2279–2290. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gavish M, Zakut R, Wilckek M and Givol D:
Preparation of a semisynthetic antibody. Biochemistry.
17:1345–1351. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Santos AA, Braga-Neto MB, Oliveira MR,
Freire RS, Barros EB, Santiago TM, Rebelo LM, Mermelstein C, Warren
CA, Guerrant RL and Brito GA: Glutamine and alanyl-glutamine
increase RhoA expression and reduce Clostridium difficile
toxin-a-induced intestinal epithelial cell damage. Biomed Res Int.
2013:1520522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jia CJ, Dai CL, Zhang X, Cui K, Xu F and
Xu YQ: Alanyl-glutamine dipeptide inhibits hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. World J Gastroenterol.
12:1373–1378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Braga-Neto MB, Oliveira BM, Rodrigues RS,
Noronha FJ, Leitao RF, Brito GA, Lima AA, Guerrant RL and Warren
CA: Protective effects of alanyl-glutamine supplementation against
nelfinavir-induced epithelial impairment in IEC-6 cells and in
mouse intestinal mucosa. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1482–1490. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dobashi K, Ghosh B, Orak JK, Singh I and
Singh AK: Kidney ischemia-reperfusion: Modulation of antioxidant
defenses. Mol Cell Biochem. 205:1–11. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim HJ, Joe Y, Kong JS, Jeong SO, Cho GJ,
Ryter SW and Chung HT: Carbon monoxide protects against hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury via ROS-dependent Akt signaling and
inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3ß. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2013:3064212013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pan S, Liu L, Pan H, Ma Y, Wang D, Kang K,
Wang J, Sun B, Sun X and Jiang H: Protective effects of
hydroxytyrosol on liver ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 57:1218–1227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Connor HD, Gao W, Nukina S, Lemasters JJ,
Mason RP and Thurman RG: Evidence that free radicals are involved
in graft failure following orthotopic liver transplantation in the
rat-an electron paramagnetic resonance spin trapping study.
Transplantation. 54:199–204. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Burke A, FitzGerald GA and Lucey MR: A
prospective analysis of oxidative stress and liver transplantation.
Transplantation. 74:217–221. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang XL, Liu HR, Tao L, Liang F, Yan L,
Zhao RR, Lopez BL, Christopher TA and Ma XL: Role of iNOS-derived
reactive nitrogen species and resultant nitrative stress in
leukocytes-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion. Apoptosis. 12:1209–1217. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Vries DK, Kortekaas KA, Tsikas D,
Wijermars LG, van Noorden CJ, Suchy MT, Cobbaert CM, Klautz RJ,
Schaapherder AF and Lindeman JH: Oxidative damage in clinical
ischemia/reperfusion injury: A reappraisal. Antioxid Redox Signal.
19:535–545. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Simonsen U, Rodriguez-Rodriguez R,
Dalsgaard T, Buus NH and Stankevicius E: Novel approaches to
improving endothelium-dependent nitric oxide-mediated
vasodilatation. Pharmacol Rep. 61:105–115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sheng M, Zhou Y, Yu W, Weng Y, Xu R and Du
H: Protective effect of Berberine pretreatment in hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury of rat. Transplant Proc. 47:275–282.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang C, Chen K, Xia Y, Dai W, Wang F, Shen
M, Cheng P, Wang J, Lu J, Zhang Y, et al: N-acetylcysteine
attenuates ischemia-reperfusion-induced apoptosis and autophagy in
mouse liver via regulation of the ROS/JNK/Bcl-2 pathway. PLoS One.
9:e1088552014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhao J, Ming Y, Wan Q, Ye S, Xie S, Zhu Y,
Wang Y, Zhong Z, Li L and Ye Q: Gypenoside attenuates hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via anti-oxidative and
anti-apoptotic bioactivities. Exp Ther Med. 7:1388–1392.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bartling B, Holtz J and Darmer D:
Contribution of myocyte apoptosis to myocardial infarction? Basic
Res Cardiol. 93:71–84. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jin S and Dai CL: Attenuation of
reperfusion-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in associated with
reversed bcl-2/bax ratio in hemi-hepatic artery-preserved portal
occlusion. J Surg Res. 174:298–304. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|