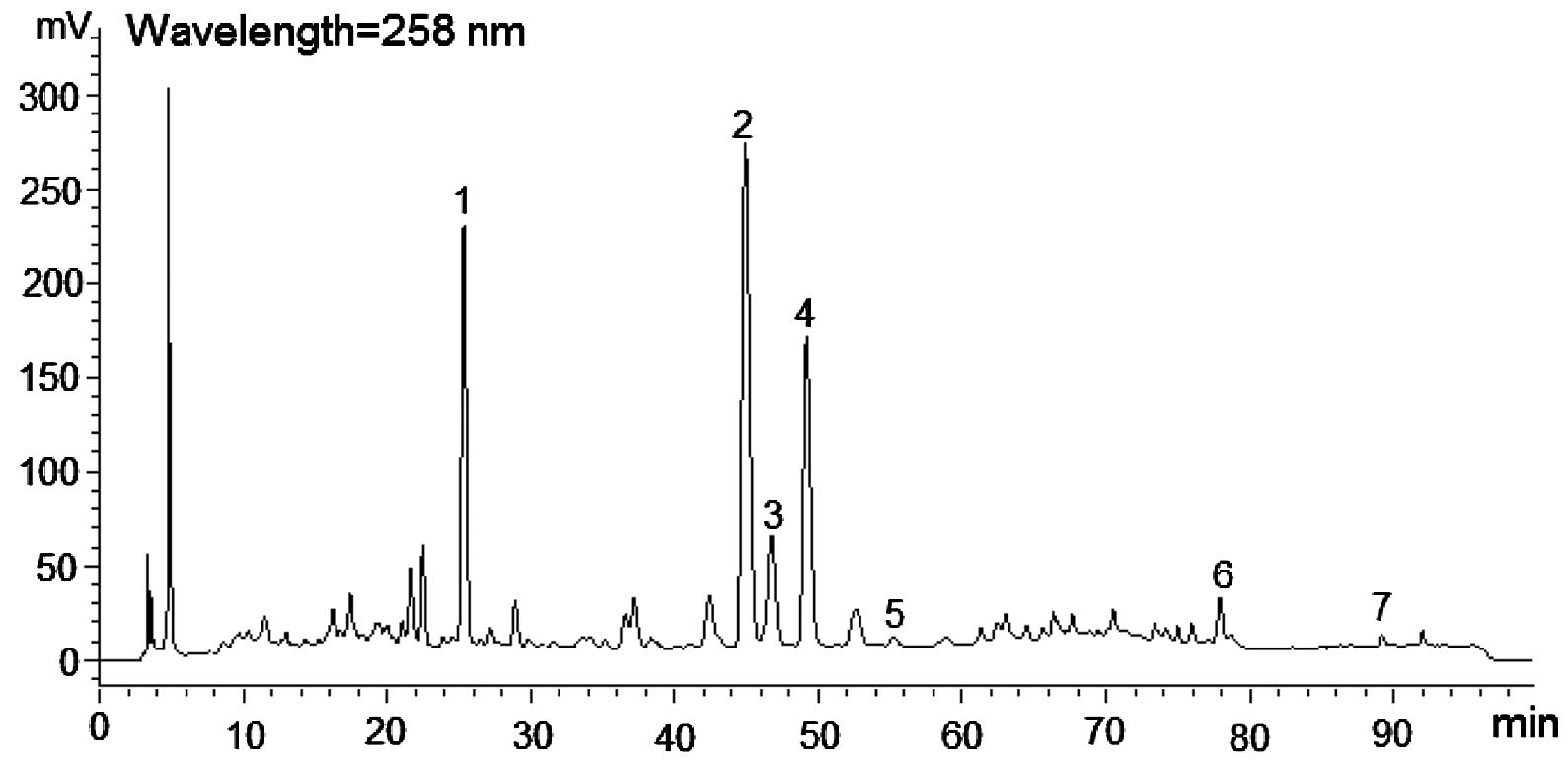
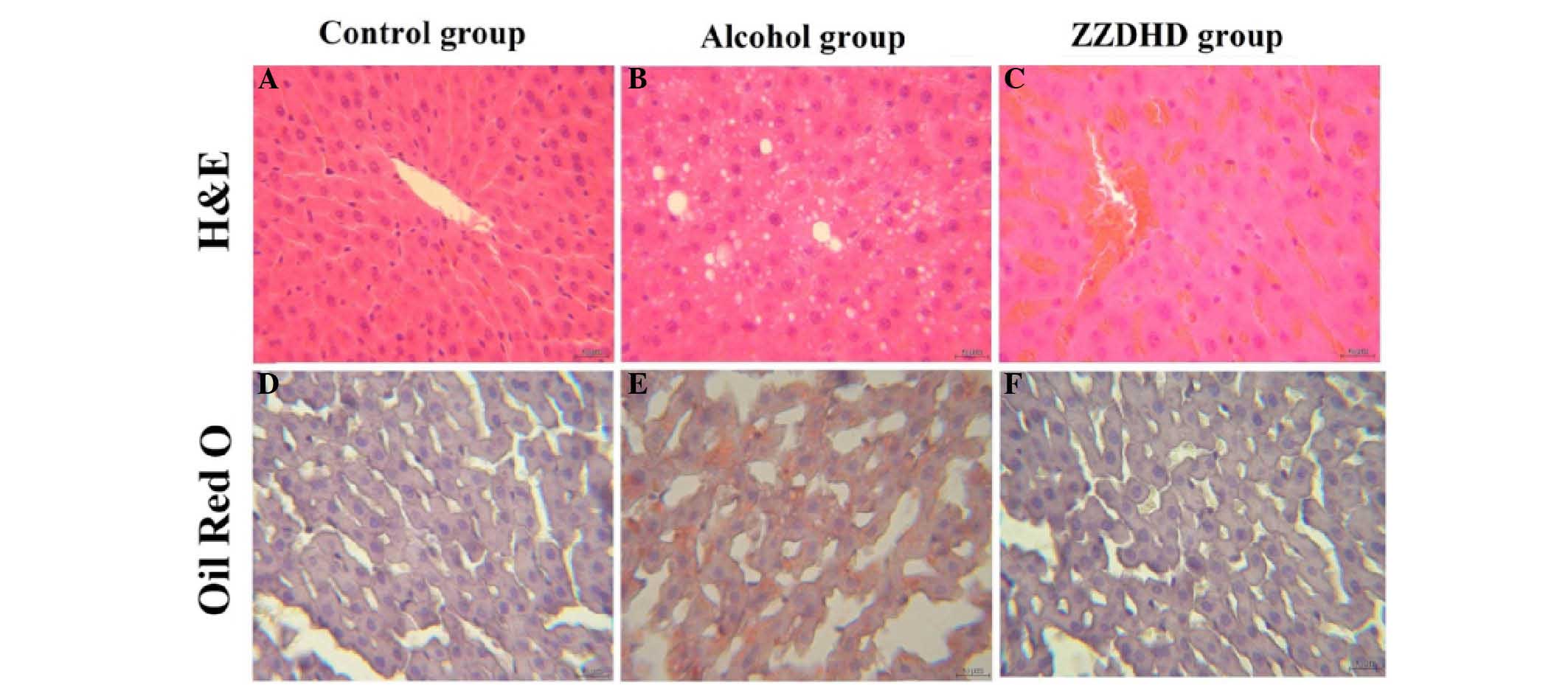
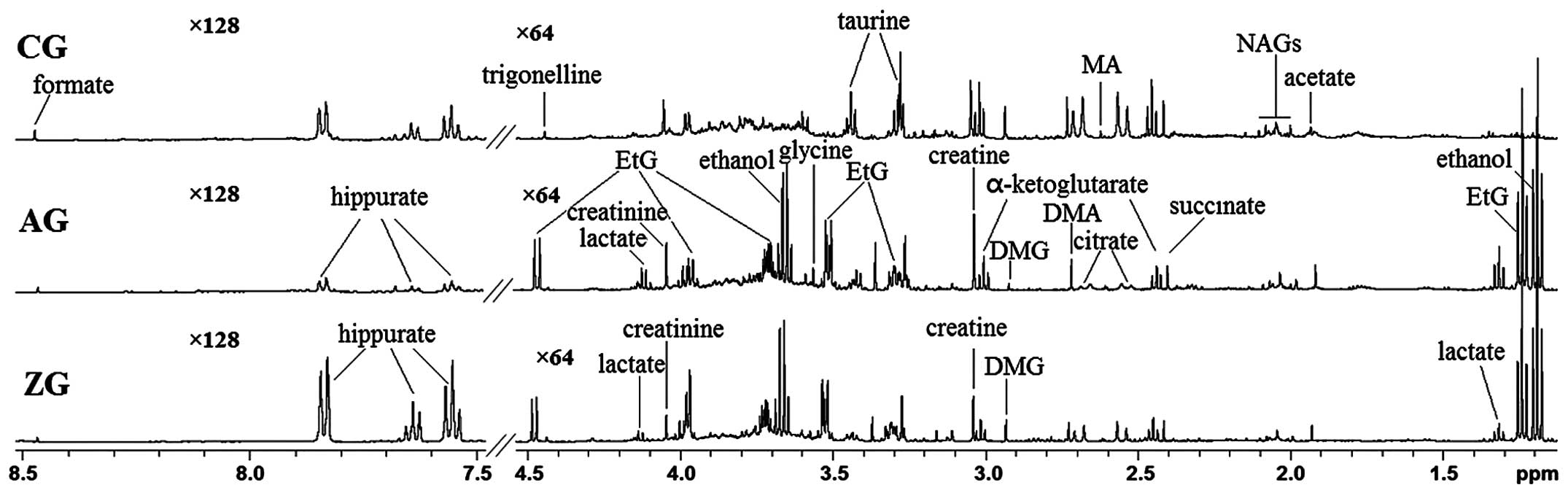
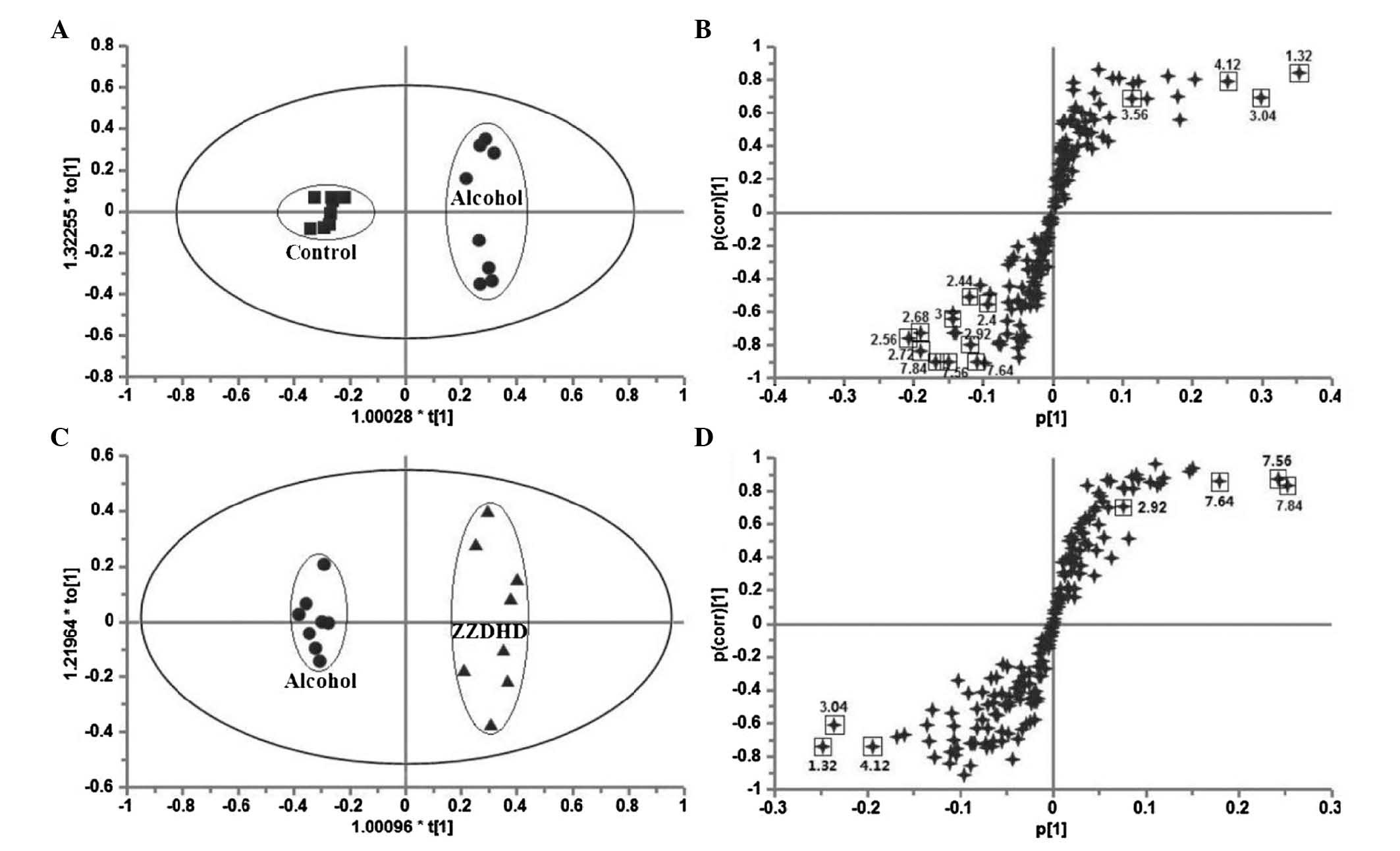
|
1
|
Rehm J, Samokhvalov AV and Shield KD:
Global burden of alcoholic liver diseases. J Hepatol. 59:160–168.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao B and Bataller R: Alcoholic liver
disease: Pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets.
Gastroenterology. 141:1572–1585. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li YM, Fan JG, Wang BY, Lu LG, Shi JP, Niu
JQ and Shen W; Chinese Association for the Study of Liver Disease:
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of alcoholic liver
disease: Update 2010: (Published in Chinese on Chinese Journal of
Hepatology 2010; 18: 167–170). J Dig Dis. 12:45–50. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ramaiah S, Rivera C and Arteel G:
Early-phase alcoholic liver disease: An update on animal models,
pathology, and pathogenesis. Int J Toxicol. 23:217–231. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan HY, Serban SM, Wang N, Hong M, Li S,
Li L, Cheung F, Wen XY and Feng Y B: Preclinical Models for
Investigation of Herbal Medicines in Liver Diseases: Update and
Perspective. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016:47501632016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen JC: Hypothesis and clinical study of
modular formulology. Journal of Chinese Medicine. 12:69–80.
2001.
|
|
7
|
An L and Feng F: Network
pharmacology-based antioxidant effect study of Zhi-Zi-Da-Huang
decoction for alcoholic liver disease. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:4924702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang H, Feng F, Zhuang BY and Sun Y:
Evaluation of hepatoprotective effect of Zhi-Zi-Da-Huang decoction
and its two fractions against acute alcohol-induced liver injury in
rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 126:273–279. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nicholson JK, Lindon JC and Holmes E:
'Metabonomics': Understanding the metabolic responses of living
systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical
analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica.
29:1181–1189. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ghauri FY, Nicholson JK, Sweatman BC, Wood
J, Beddell CR, Lindon JC and Cairns NJ: NMR spectroscopy of human
post mortem cerebrospinal fluid: Distinction of Alzheimer's disease
from control using pattern recognition and statistics. NMR Biomed.
6:163–167. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brindle JT, Antti H, Holmes E, Tranter G,
Nicholson JK, Bethell HW, Clarke S, Schofield PM, McKilligin E,
Mosedale DE and Grainger DJ: Rapid and noninvasive diagnosis of the
presence and severity of coronary heart disease using 1H-NMR based
metabonomics. Nat Med. 8:1439–1444. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang J, Xu G, Kong H, Zheng Y, Pang T and
Yang Q: Artificial neural network classification based on
high-performance liquid chromatography of urinary and serum
nucleosides for the clinical diagnosis of cancer. J Chromatogr B
Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 780:27–33. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Li J, Yang L, Li Y, Tian Y, Li S, Jiang S,
Wang Y and Li X: Metabolomics study on model rats of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease treated with Bu-Fei Jian-Pi. Mol Med
Rep. 11:1324–1333. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Huang M, Liang Q, Li P, Xia J, Wang Y, Hu
P, Jiang Z, He Y, Pang L, Han L, et al: Biomarkers for early
diagnosis of type 2 diabetic nephropathy: A study based on an
integrated biomarker system. Mol Biosyst. 9:2134–2141. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Griffin JL: Metabonomics: NMR spectroscopy
and pattern recognition analysis of body fluids and tissues for
characterisation of xenobiotic toxicity and disease diagnosis. Curr
Opin Chem Biol. 7:648–654. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin WN, Lu HY, Lee MS, Yang SY, Chen HJ,
Chang YS and Chang WT: Evaluation of the cultivation age of dried
ginseng radix and its commercial products by using (1)H-NMR
fingerprint analysis. Am J Chin Med. 38:205–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Saric J, Wang Y, Li J, Coen M, Utzinger J,
Marchesi JR, Keiser J, Veselkov K, Lindon JC, Nicholson JK and
Holmes E: Species variation in the fecal metabolome gives insight
into differential gastrointestinal function. J Proteome Res.
7:352–360. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Diao C, Zhao L, Guan M, Zheng Y, Chen M,
Yang Y, Lin L, Chen W and Gao H: Systemic and characteristic
metabolites in the serum of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats at
different stages as revealed by a (1)H-NMR based metabonomic
approach. Mol Biosyst. 10:686–693. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi X, Wei X, Koo I, Schmidt RH, Yin X,
Kim SH, Vaughn A, McClain CJ, Arteel GE, Zhang X and Watson WH:
Metabolomic analysis of the effects of chronic arsenic exposure in
a mouse model of diet-induced Fatty liver disease. J Proteome Res.
13:547–554. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Liu P, Duan J, Wang P, Qian D, Guo J,
Shang E, Su S, Tang Y and Tang Z: Biomarkers of primary
dysmenorrhea and herbal formula intervention: An exploratory
metabonomics study of blood plasma and urine. Mol Biosyst. 9:77–87.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nicholas PC, Kim D, Crews FT and Macdonald
JM: Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic determination
of ethanol-induced formation of ethyl glucuronide in liver. Anal
Biochem. 358:185–191. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Huang R, Liu L, Peng J, Xiao B,
Yang J, Miao Z and Huang H: Metabonomics study of urine from
Sprague-Dawley rats exposed to Huang-yao-zi using (1)H NMR
spectroscopy. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 52:136–141. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bradford BU, O'Connell TM, Han J, Kosyk O,
Shymonyak S, Ross PK, Winnike J, Kono H and Rusyn I: Metabolomic
profiling of a modified alcohol liquid diet model for liver injury
in the mouse uncovers new markers of disease. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 232:236–243. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sun YJ, Wang HP, Liang YJ, Yang L, Li W
and Wu YJ: An NMR-based metabonomic investigation of the subacute
effects of melamine in rats. J Proteome Res. 11:2544–2550. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu W, Wu J, An Y, Xiao C, Hao F, Liu H,
Wang Y and Tang H: Streptozotocin-induced dynamic metabonomic
Changes in rat biofluids. J Proteome Res. 11:3423–3435. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Riveros-Rosas H, Julian-Sanchez A, Pina E
and Pinã E: Enzymology of ethanol and acetaldehyde metabolism in
mammals. Arch Med Res. 28:453–471. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cederbaum AI: Alcohol metabolism. Clin
Liver Dis. 16:667–685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kennedy NP and Tipton KF: Ethanol
metabolism and alcoholic liver disease. Essays Biochem. 25:137–195.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zakhari S: Overview: How is alcohol
metabolized by the body? Alcohol Res Health. 29:245–254. 2006.
|
|
30
|
Gordon ER: The effect of chronic
consumption of ethanol on the redox state of the rat liver. Can J
Biochem. 50:949–957. 1972. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Veech RL, Guynn R and Veloso D: The
time-course of the effects of ethanol on the redox and
phosphorylation states of rat liverm. Biochem J. 127:387–397. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Arteel GE, Iimuro Y, Yin M, Raleigh JA and
Thurman RG: Chronic enteral ethanol treatment causes hypoxia in rat
liver tissue in vivo. Hepatology. 25:920–926. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ji C: Mechanisms of alcohol-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress and organ injuries. Biochem Res Int.
2012:2164502012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Halsted CH and Medici V: Aberrant hepatic
methionine metabolism and gene methylation in the pathogenesis and
treatment of alcoholic steatohepatitis. Int J Hepatol.
2012:9597462012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kharbanda KK: Alcoholic liver disease and
methionine metabolism. Semin Liver Dis. 29:155–165. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tsukamoto H and Lu SC: Current concepts in
the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver injury. FASEB J. 15:1335–1349.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McGregor DO, Dellow WJ, Lever M, George
PM, Robson RA and Chambers ST: Dimethylglycine accumulates in
uremia and predicts elevated plasma homocysteine concentrations.
Kidney Int. 59:2267–2272. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wei L, Liao P, Wu H, Li X, Pei F, Li W and
Wu Y: Metabolic profiling studies on the toxicological effects of
realgar in rats by (1)H NMR spectroscopy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
234:314–325. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Keller W: Keller on the conversion of
benzoic into hippuric acid. Prov Med J Retrosp Med Sci. 4:256–257.
1842.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Beliveau GP and Brusilow SW: Glycine
availability limits maximum hippurate synthesis in growing rats. J
Nutr. 117:36–41. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|