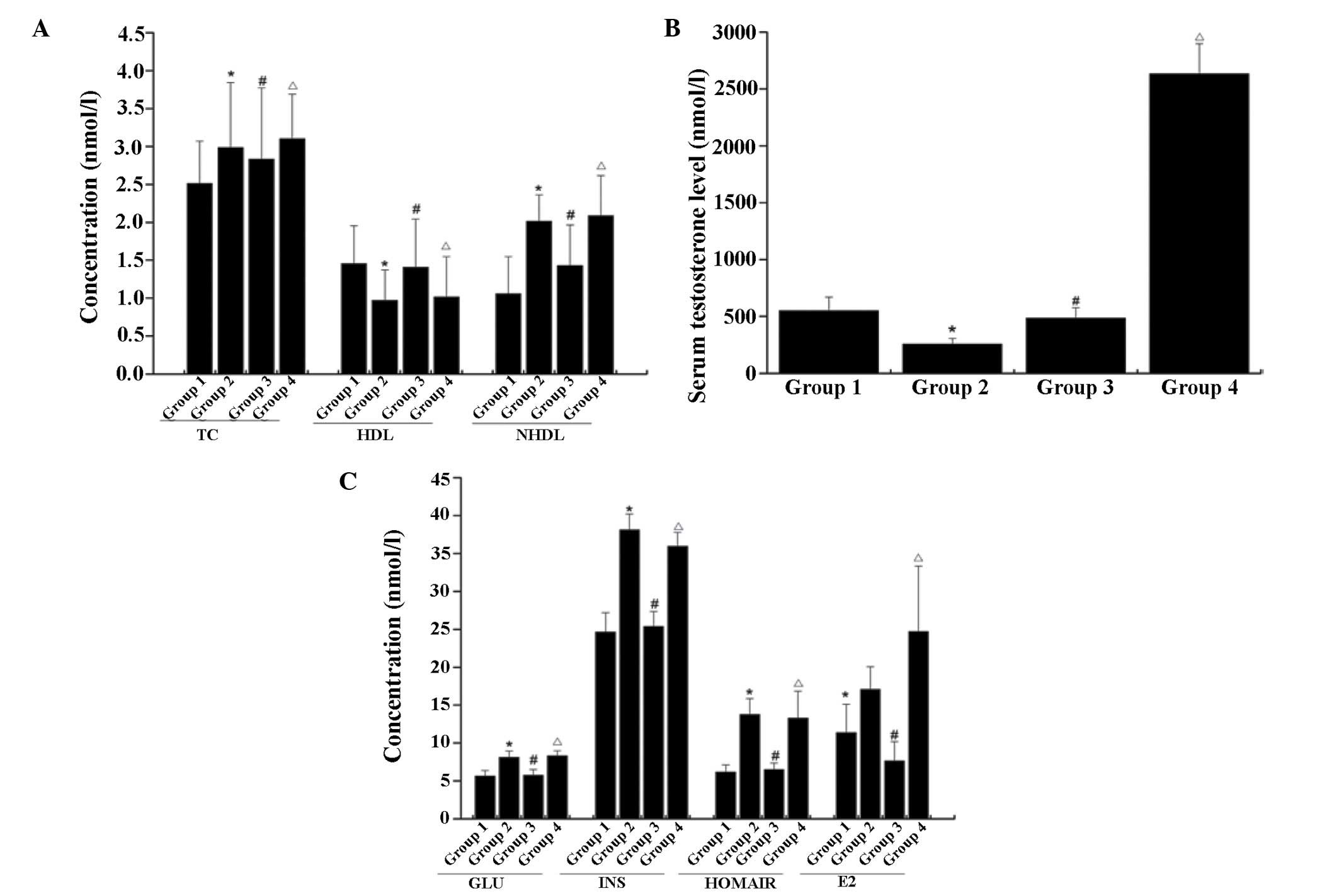
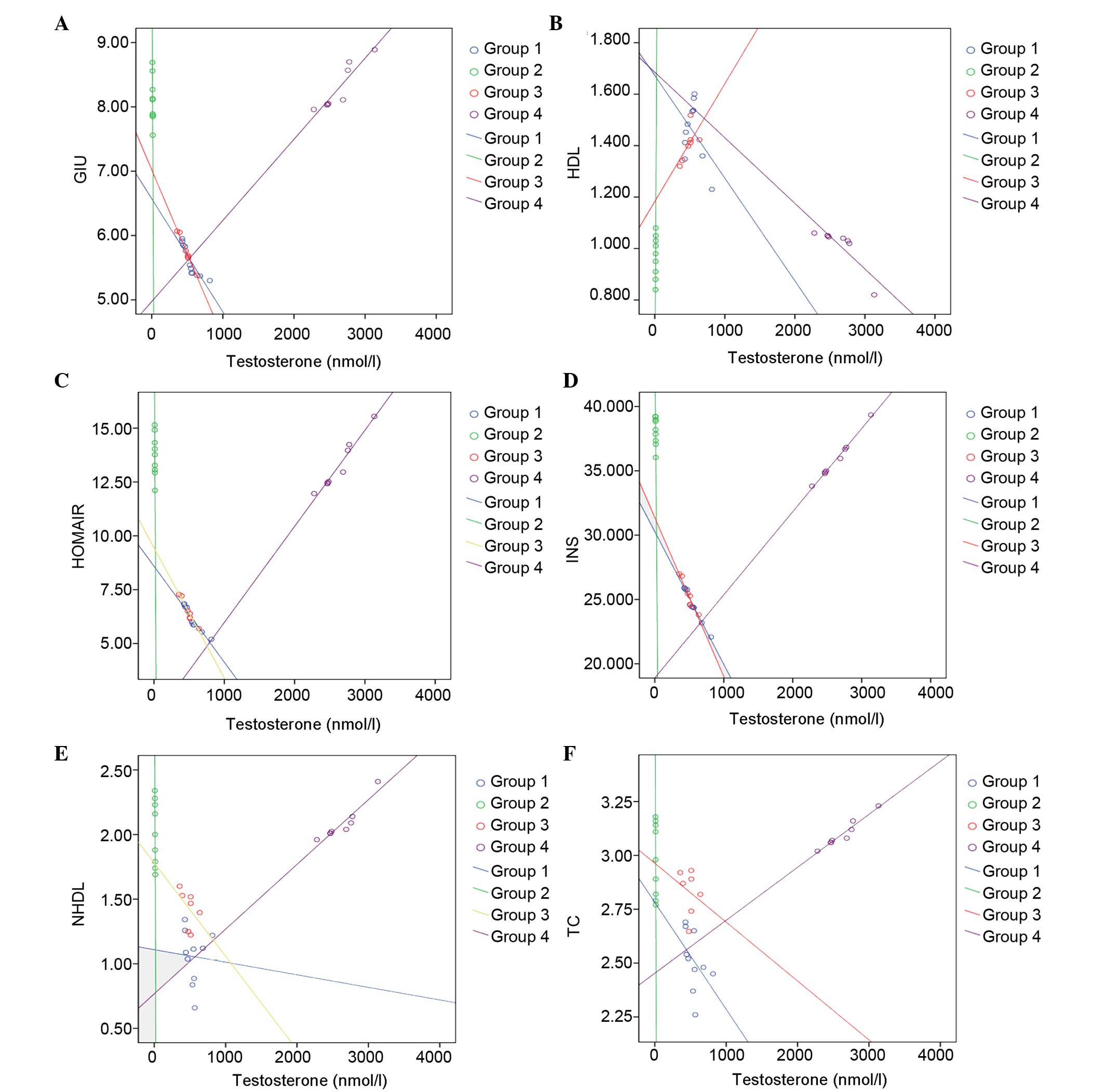
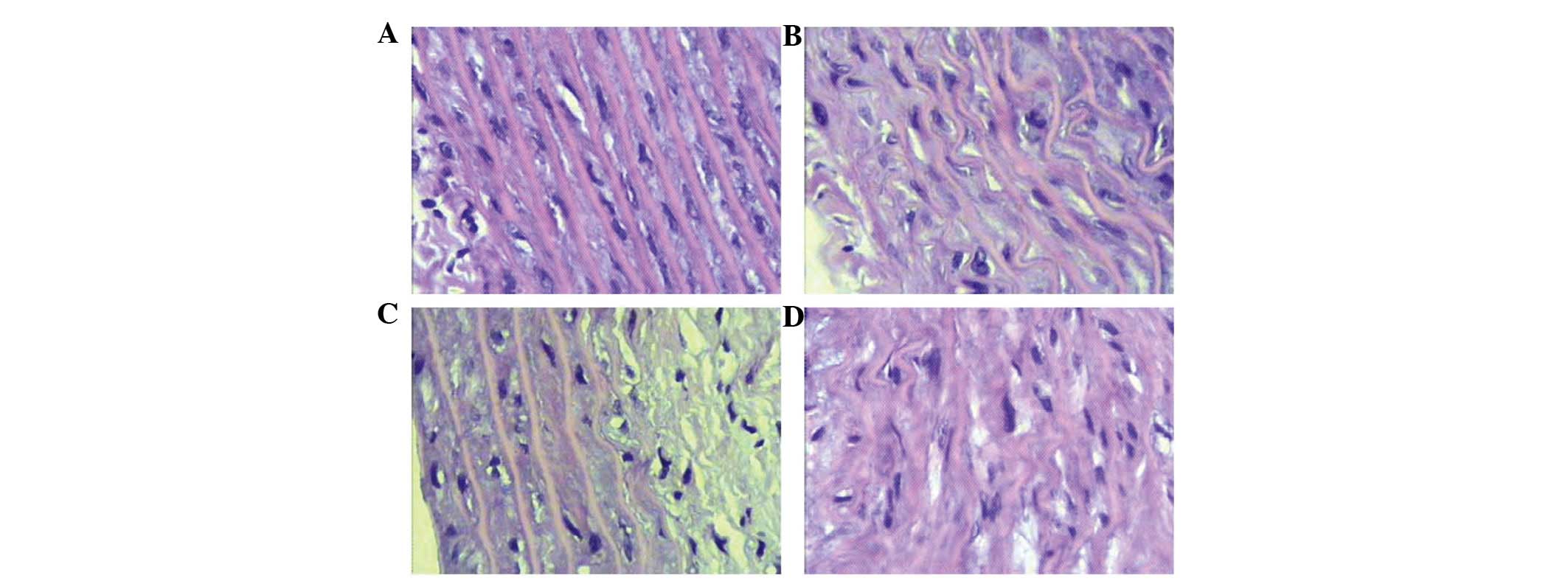
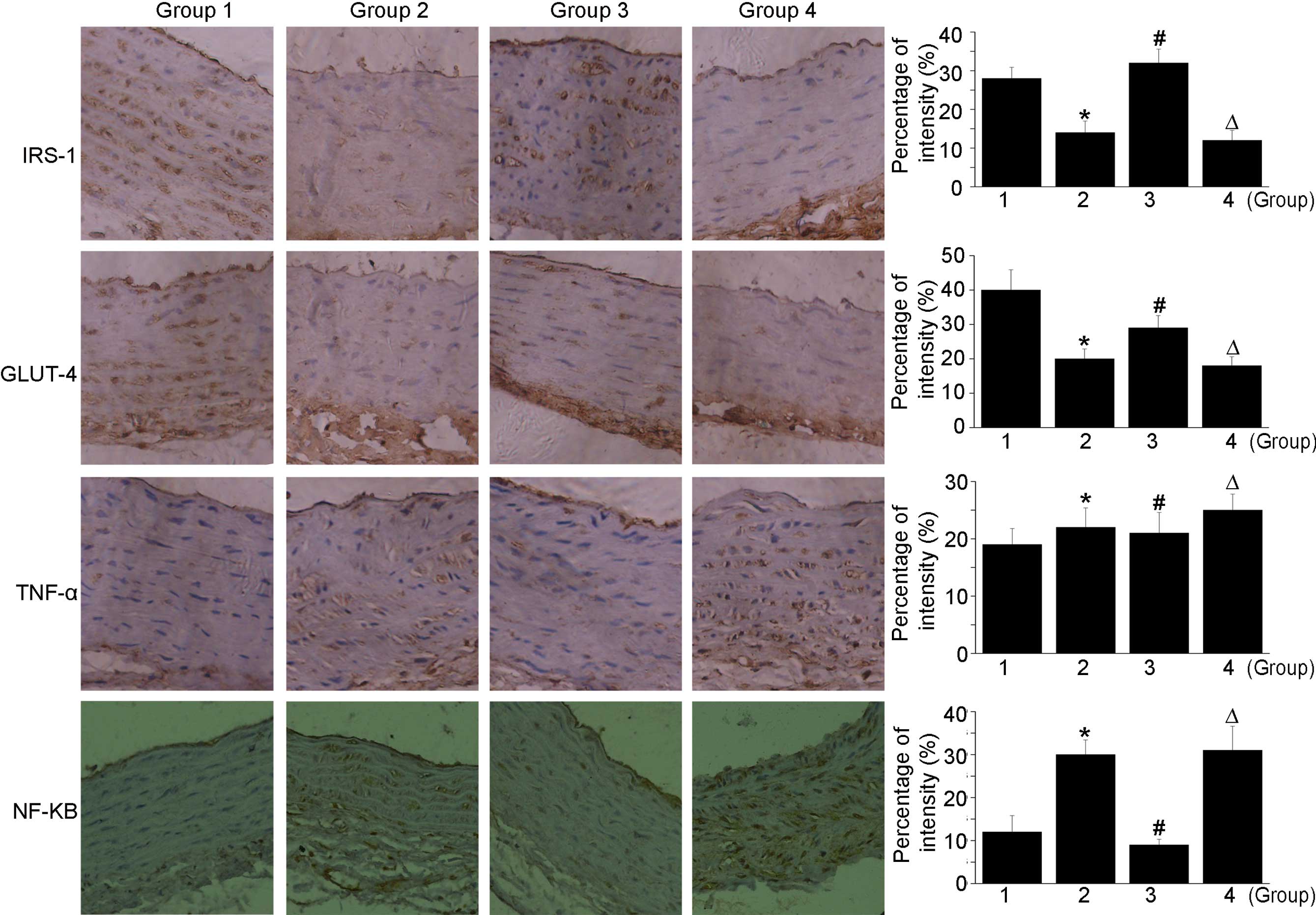
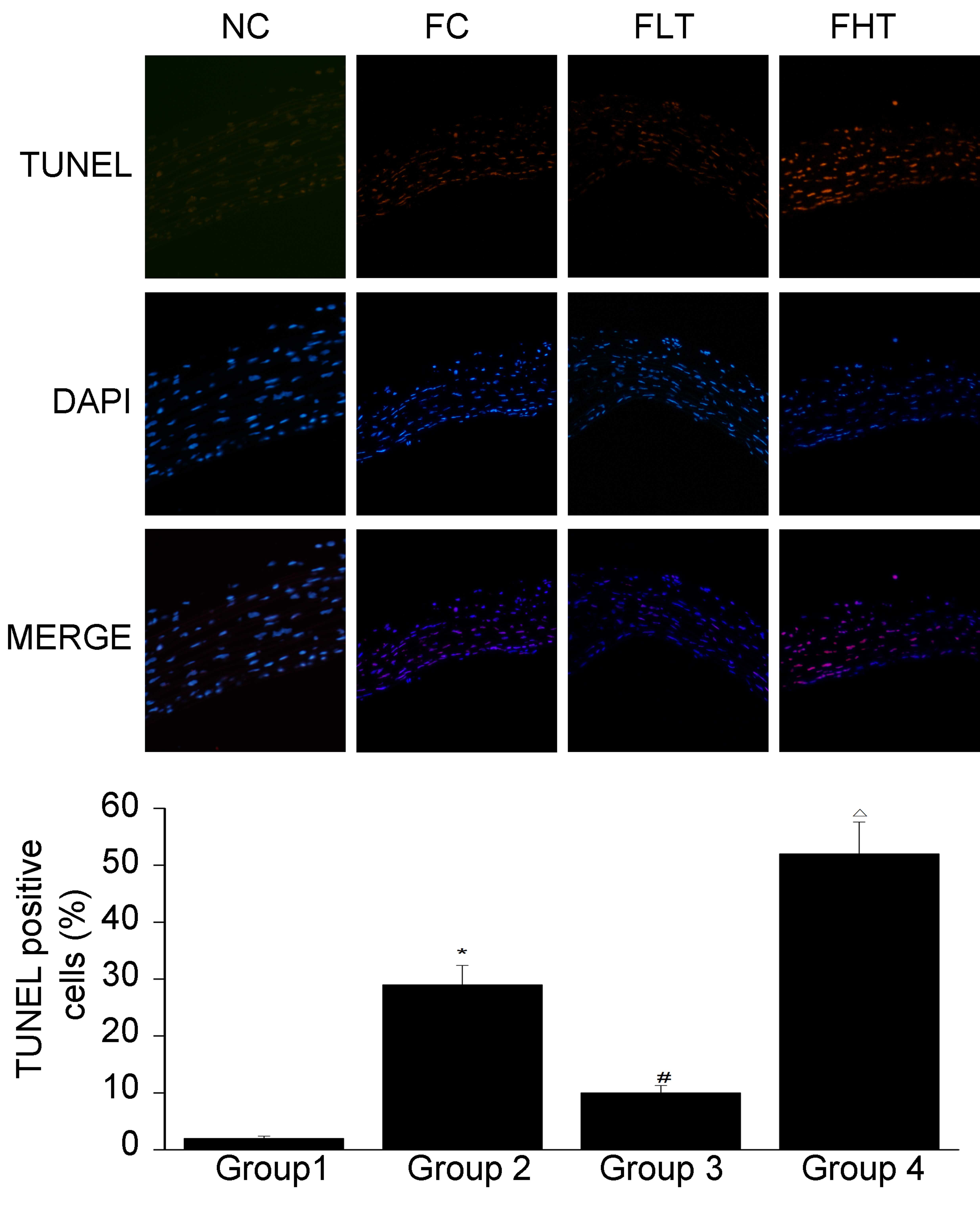
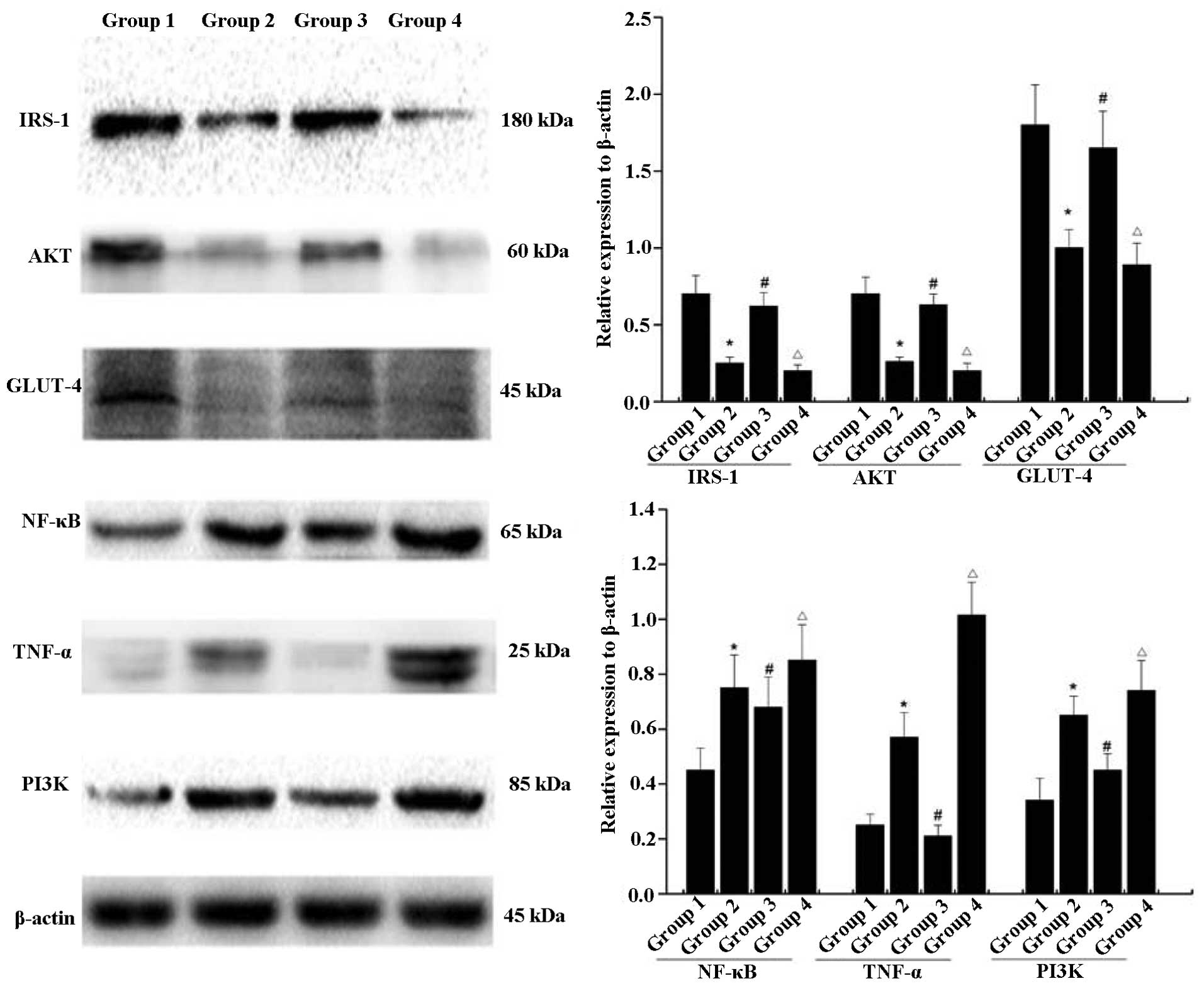
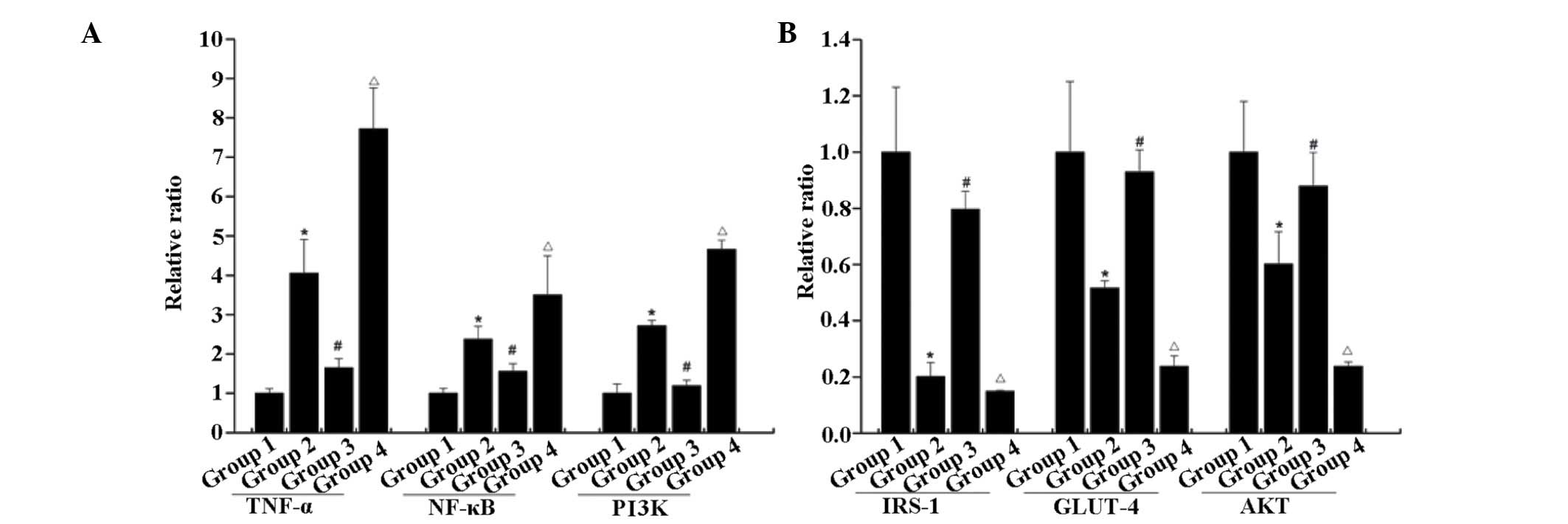
|
1
|
Karoutsou E and Polymeris A: Environmental
endocrine disruptors and obesity. Endocr Regul. 46:37–46. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boodai SA, Cherry LM, Sattar NA and Reilly
JJ: Prevalence of cardiometabolic risk factors and metabolic
syndrome in obese Kuwaiti adolescents. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes.
7:505–511. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kursawe R and Santoro N: Metabolic
syndrome in pediatrics. Adv Clin Chem. 65:91–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Özer S, Yılmaz R, Özlem Kazancı N,
Sönmezgöz E, Karaaslan E, Altuntaş B and Emre Kuyucu Y: Higher HDL
levels are a preventive factor for metabolic syndrome in obese
Turkish children. Nutr Hosp. 31:307–312. 2014.
|
|
5
|
Denzer C, Thiere D, Muche R, Koenig W,
Mayer H, Kratzer W and Wabitsch M: Gender-specific prevalences of
fatty liver in obese children and adolescents: Roles of body fat
distribution, sex steroids and insulin resistance. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 94:3872–3881. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shelton JB and Rajfer J: Androgen
deficiency in aging and metabolically challenged men. Urol Clin
North Am. 39:63–75. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Dhindsa S, Prabhakar S, Sethi M,
Bandyopadhyay A, Chaudhuri A and Dandona P: Frequent occurrence of
hypogonadotropic hypogonadism in type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 89:5462–5468. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moriarty-Kelsey M, Harwood JE, Travers SH,
Zeitler PS and Nadeau KJ: Testosterone, obesity and insulin
resistance in young males: Evidence for an association between
gonadal dysfunction and insulin resistance during puberty. J
Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 23:1281–1287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Janjgava S, Zerekidze T, Uchava L,
Giorgadze E and Asatiani K: Influence of testosterone replacement
therapy on metabolic disorders in male patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus and androgen deficiency. Eur J Med Res.
19:562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sattler F, He J, Chukwuneke J, Kim H,
Stewart Y, Colletti P, Yarasheski K and Buchanan T: Testosterone
supplementation improves carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in some
older men with abdominal obesity. J Gerontol Geriatr Res.
3:10001592014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yeap BB, Alfonso H, Chubb SA, Handelsman
DJ, Hankey GJ, Golledge J, Flicker L and Norman PE: Lower plasma
testosterone or dihydrotestosterone, but not estradiol, is
associated with symptoms of intermittent claudication in older men.
Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 79:725–732. 2013.
|
|
12
|
Srinath R, Hill Golden S, Carson KA and
Dobs A: Endogenous testosterone and its relationship to preclinical
and clinical measures of cardiovascular disease in the
atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 100:1602–1608. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu J, Akishita M, Eto M, Ogawa S, Son BK,
Kato S, Ouchi Y and Okabe T: Androgen receptor-dependent activation
of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells:
Role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/akt pathway. Endocrinology.
151:1822–1828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li F, Li L, Zhong Y, Xie Q, Huang J, Kang
X, Wang D, Xu L and Huang T: Relationship between LTR methylation
and gag expression of HIV-1 in human spermatozoa and sperm-derived
embryos. PLoS One. 8:e548012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Beaudin G: Men and low testosterone.
Diabetes Self Manag. 32:24–27. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jockenhövel F: Testosterone therapy -
what, when and to whom? Aging Male. 7:319–324. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Botella-Carretero JI, Balsa JA,
Gómez-Martin JM, Peromingo R, Huerta L, Carrasco M, Arrieta F,
Zamarron I, Martin-Hidalgo A and Vazquez C: Circulating free
testosterone in obese men after bariatric surgery increases in
parallel with insulin sensitivity. J Endocrinol Invest. 36:227–232.
2013.
|
|
18
|
Zhang N, Zhang H, Zhang X, Zhang B, Wang
F, Wang C, Zhao M, Yu C, Gao L, Zhao J and Guan Q: The relationship
between endogenous testosterone and lipid profile in middle-aged
and elderly Chinese men. Eur J Endocrinol. 170:487–494. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu YQ, Wang XH, Xu D, Peng L, Cheng LF,
Huang MK, Huang ZJ and Zhang Y: A multicenter contraceptive
efficacy study of injectable testosterone undecanoate in healthy
Chinese men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 88:562–568. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gårevik N, Rane A, Björkhem-Bergman L and
Ekström L: Effects of different doses of testosterone on
gonadotropins, 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and blood lipids in healthy
men. Subst Abuse Rehabil. 5:121–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rosano GM, Sheiban I, Massaro R, Pagnotta
P, Marazzi G, Vitale C, Mercuro G, Volterrani M, Aversa A and Fini
M: Low testosterone levels are associated with coronary artery
disease in male patients with angina. Int J Impot Res. 19:176–182.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shores MM, Matsumoto AM, Sloan KL and
Kivlahan DR: Low serum testosterone and mortality in male veterans.
Arch Intern Med. 166:1660–1665. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Duckles SP and Miller VM: Hormonal
modulation of endothelial NO production. Pflugers Arch.
459:841–851. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lapauw B, Ouwens M, 't Hart LM, Wuyts B,
Holst JJ, T'Sjoen G, Kaufman JM and Ruige JB: Sex steroids affect
triglyceride handling, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide
and insulin sensitivity: A 1-week randomized clinical trial in
healthy young men. Diabetes Care. 33:1831–1833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kupelian V, Page ST, Araujo AB, Travison
TG, Bremner WJ and McKinlay JB: Low sex hormone-binding globulin,
total testosterone and symptomatic androgen deficiency are
associated with development of the metabolic syndrome in nonobese
men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 91:843–850. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jones TH, Arver S, Behre HM, Buvat J,
Meuleman E, Moncada I, Morales AM, Volterrani M, Yellowlees A,
Howell JD and Channer KS; TIMES2 Investigators: Testosterone
replacement in hypogonadal men with type 2 diabetes and/or
metabolic syndrome (the TIMES2 study). Diabetes Care. 34:828–837.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guay AT: The emerging link between
hypogonadism and metabolic syndrome. J Androl. 30:370–376. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|