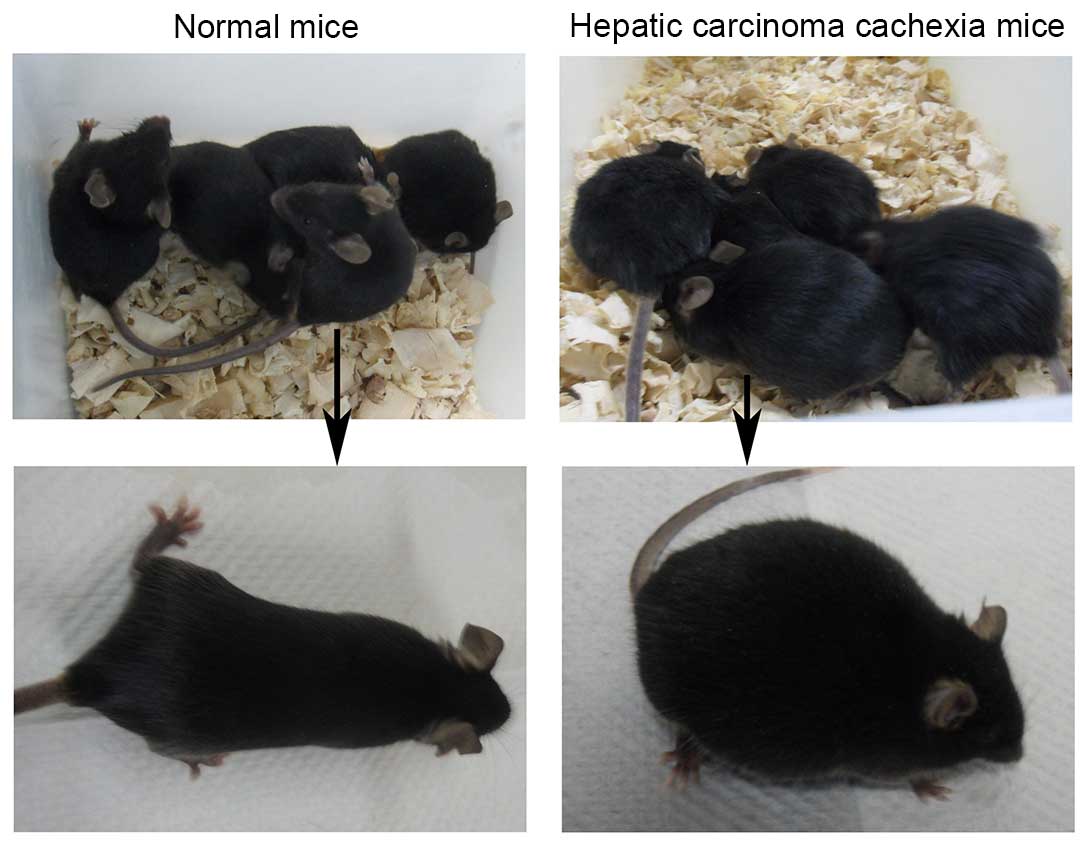
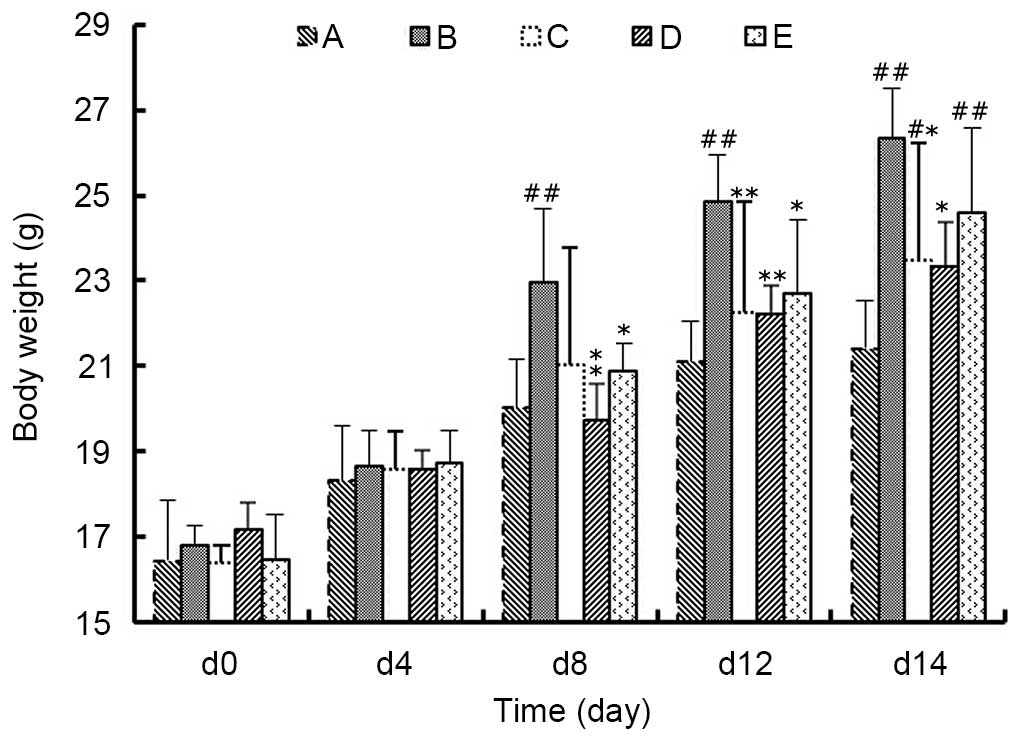
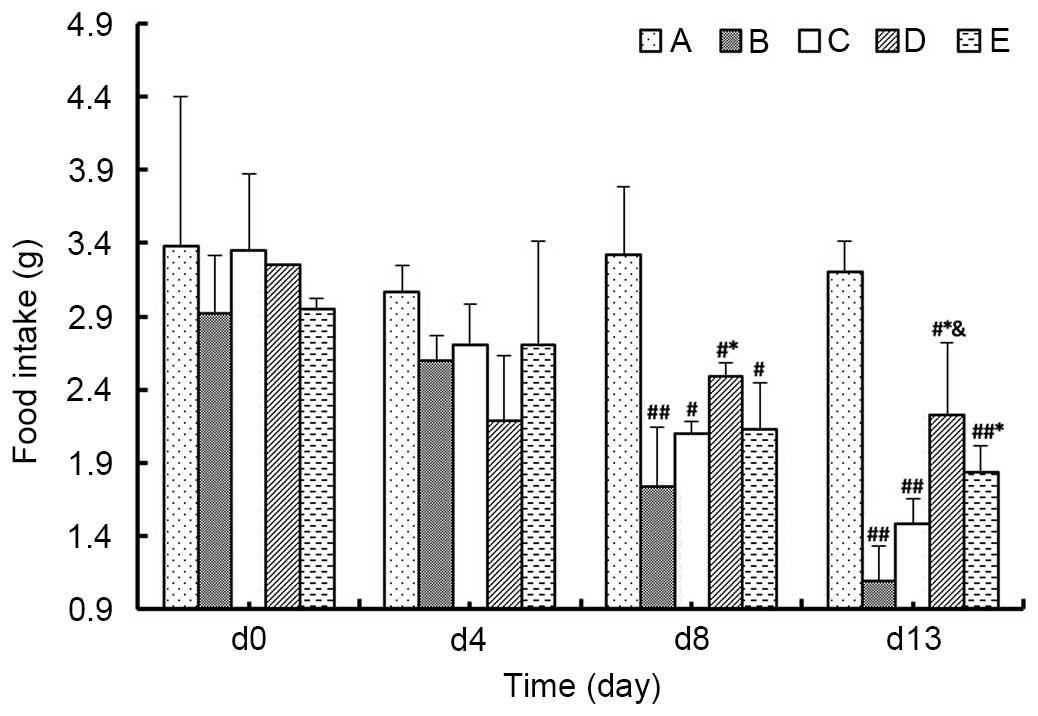
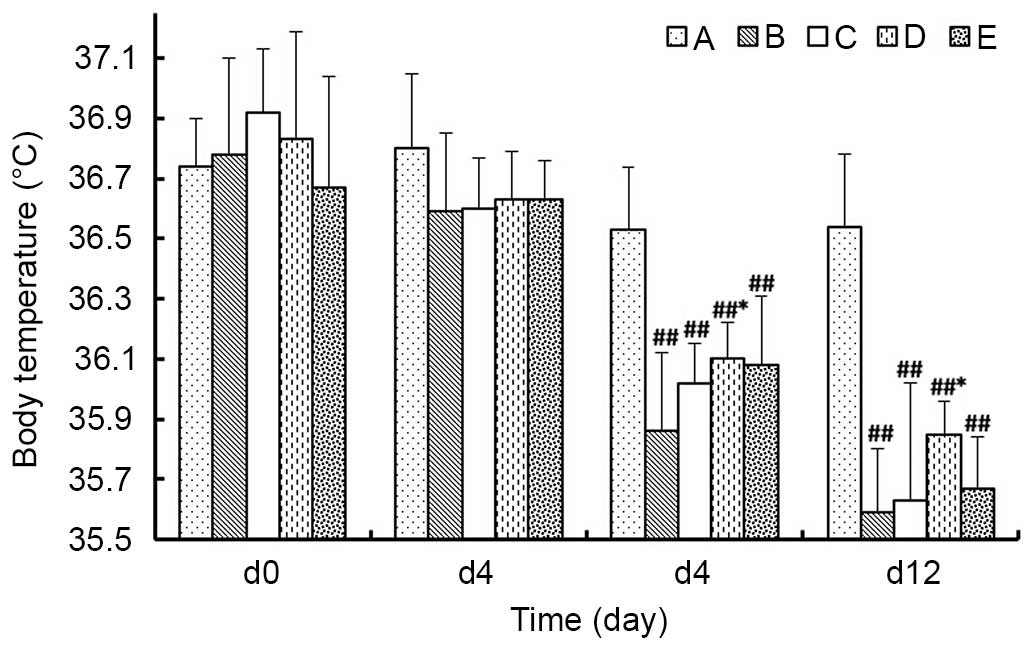
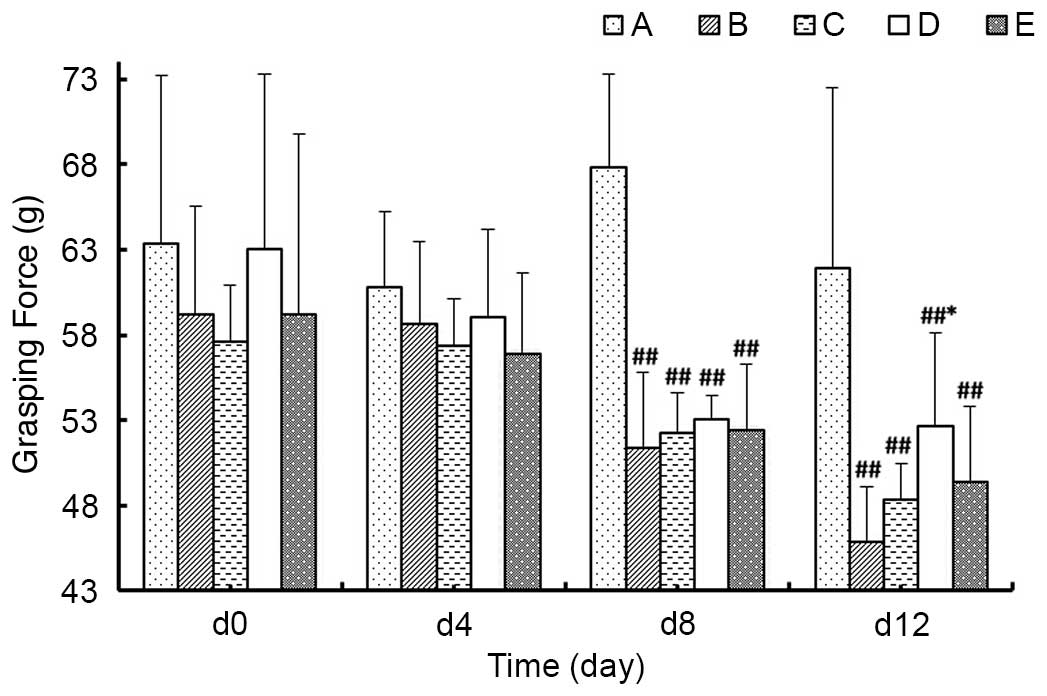
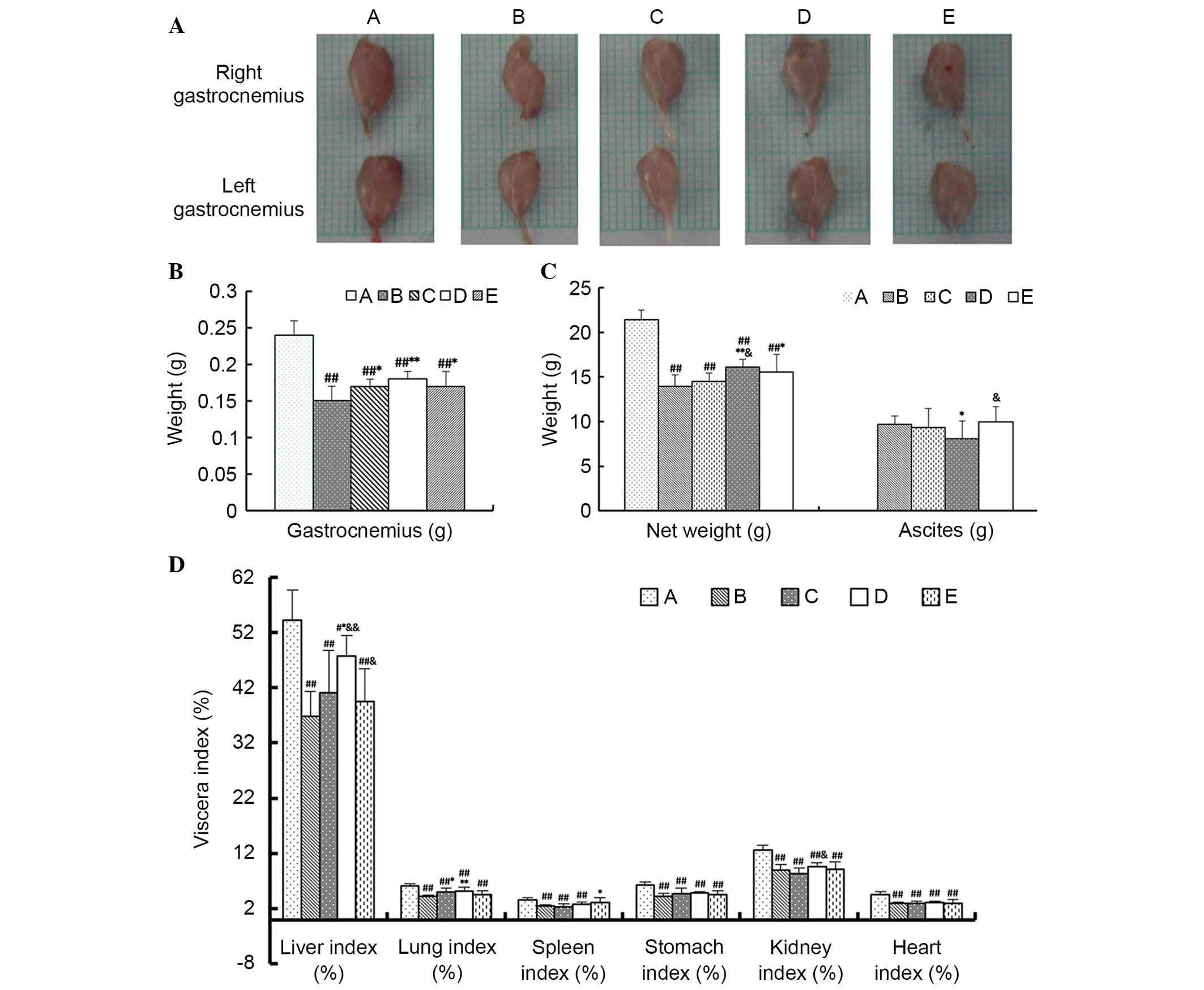
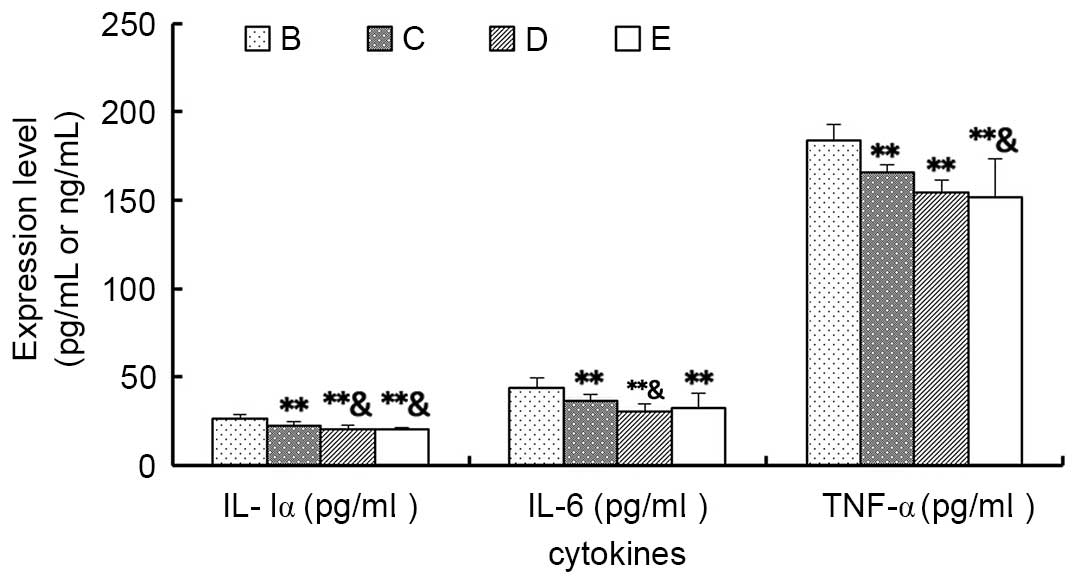
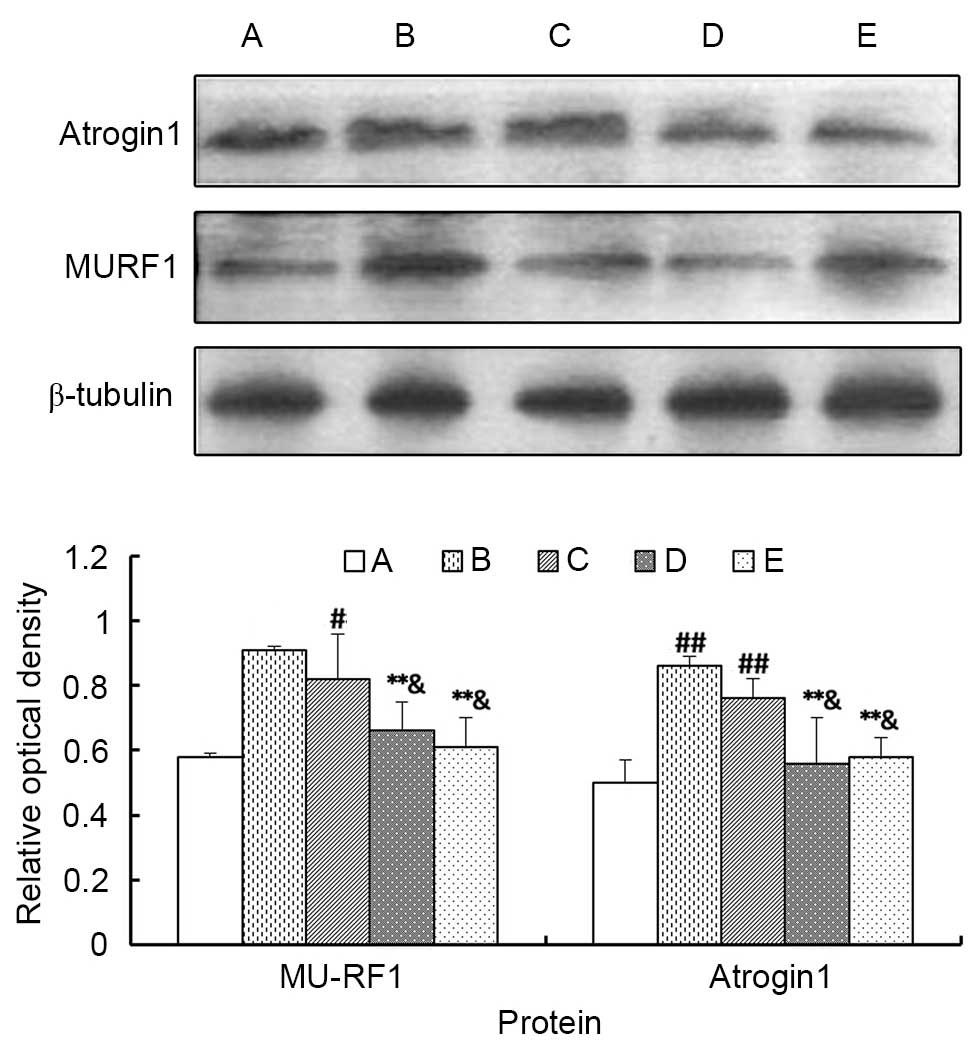
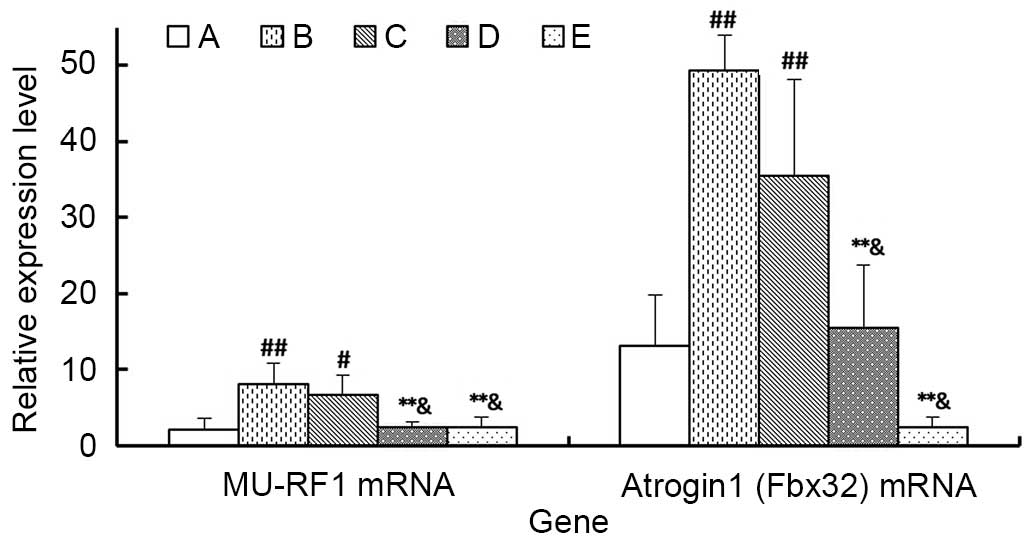
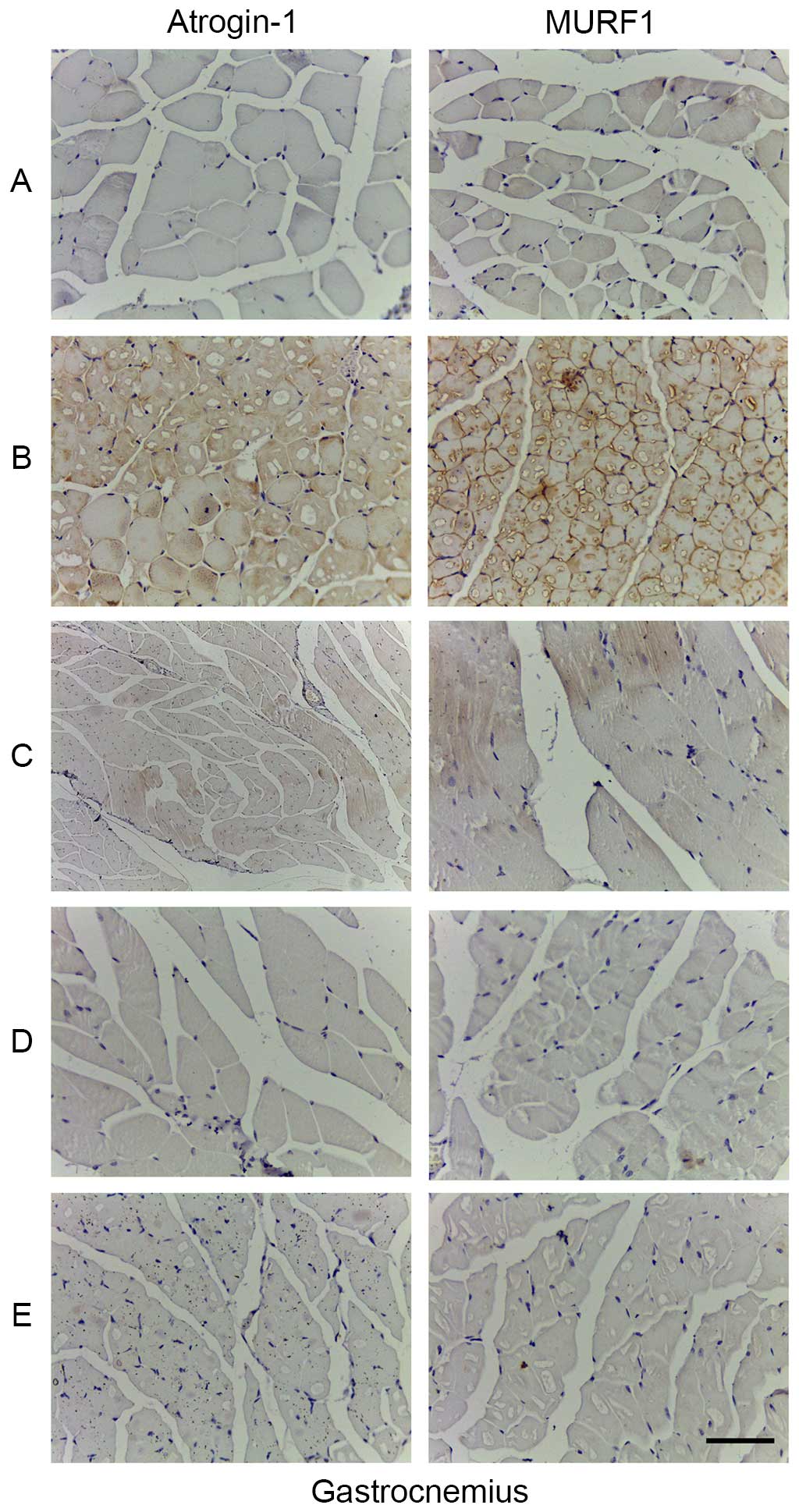
|
1
|
Fearon K, Strasser F, Anker SD, Bosaeus I,
Bruera E, Fainsinger RL, Jatoi A, Loprinzi C, MacDonald N,
Mantovani G, et al: Definition and classification of cancer
cachexia: An international consensus. Lancet Oncol. 12:489–495.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mondello P, Mian M, Aloisi C, Famà F,
Mondello S and Pitini V: Cancer cachexia syndrome: Pathogenesis,
diagnosis, and new therapeutic options. Nutr Cancer. 67:12–26.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wallengren O, Lundholm K and Bosaeus I:
Diagnostic criteria of cancer cachexia: Relation to quality of
life, exercise capacity and survival in unselected palliative care
patients. Support Care Cancer. 21:1569–1577. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
von Haehling S and Anker SD: Treatment of
cachexia: An overview of recent developments. J Am Med Dir Assoc.
15:866–872. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Radbruch L, Elsner F, Trottenberg P,
Strasser F and Fearon K: Clinical practice guidelines on cancer
cachexia in advanced cancer patients. Aachen: Department of
Palliative Medicinen/European Palliative Care Research
Collaborative; 2010
|
|
6
|
Yin LR, Chen ZX, Zhang SJ, Sun BG, Liu YD
and Huang HZ: Expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted
on chromosome ten in liver of athymic mice with hepatocellular
carcinoma and the effect of Fuzheng Jiedu Decoction. World J
Gastroenterol. 14:108–113. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun BG, Chen ZX, Zhou HM, Zhang SJ and
Huang H: Aftereffect of invigorating spleen and soothing liver and
detoxification and dissipating masses compound recipe of Chinese
crude drug to athymic mice with HCC. Chinese Archives of
Traditional Chinese Medicine. 28:1666–1670. 2010.
|
|
8
|
Esper DH and Harb WA: The cancer cachexia
syndrome: A review of metabolic and clinical manifestations. Nutr
Clin Pract. 20:369–376. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kiefer T, Hirt C, Schüler F, Busemann C,
Wodny M, Jaeger B and Dölken G: Statistical analysis of results
obtained by real-time PCR for improvement of absolute
quantification of target sequences. Clin Lab. 58:465–470.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gullett NP, Hebbar G and Ziegler TR:
Update on clinical trials of growth factors and anabolic steroids
in cachexia and wasting. Am J Clin Nutr. 91(Suppl): 1143S–1147S.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Diament MJ, Peluffo GD, Stillitani I,
Cerchietti LC, Navigante A, Ranuncolo SM and Klein SM: Inhibition
of tumor progression and paraneoplastic syndrome development in a
murine lung adenocarcinoma by medroxyprogesterone acetate and
indomethacin. Cancer Invest. 24:126–131. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yamashita JI and Ogawa M:
Medroxyprogesterone acetate and cancer cachexia: Interleukin-6
involvement. Breast Cancer. 7:130–135. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Smith KL and Tisdale MJ: Mechanism of
muscle protein degradation in cancer cachexia. Br J Cancer.
68:314–318. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lundholm K, Gelin J, Hyhander A, Lönnroth
C, Sandström R, Svaninger G, Körner U, Gülich M, Kärrefors I, Norli
B, et al: Anti-inflammatory treatment may prolong survival in
undernourished patients with metastatic solid tumors. Cancer Res.
54:5602–5606. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ferreri NR, McGiff JC, Carroll MA and
Quilley J: Renal COX-2, cytokines and 20-HETE: Tubular and vascular
mechanisms. Curr Pharm Des. 10:613–626. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Argilés JM, Almendro V, Busquets S and
López-Soriano FJ: The pharmacological treatment of cachexia. Curr
Drug Targets. 5:265–277. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baracos VE, DeVivo C, Hoyle DH and
Goldberg AL: Activation of the ATP-ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in
skeletal muscle of cachectic rats bearing a hepatoma. Am J Physiol.
268:E996–E1006. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Llovera M, Garcia-Martinez C, Agell N,
Lopez-Soriano FJ and Argiles JM: Muscle wasting associated with
cancer cachexia is linked to an important activation of the
ATP-dependent ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. Int J Cancer.
61:138–141. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Costelli P, Muscaritoli M, Bossola M,
Penna F, Reffo P, Bonetto A, Busquets S, Bonelli G, Lopez-Soriano
FJ, Doglietto GB, et al: IGF-1 is downregulated in experimental
cancer cachexia. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
291:R674–R683. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|