|
1
|
Drobnis EZ and Johnson M: The question of
sperm DNA fragmentation testing in the male infertility work-up: A
response to Professor Lewis' commentary. Reprod Biomed Online.
31:138–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whitfield M, Pollet-Villard X, Levy R,
Drevet JR and Saez F: Posttesticular sperm maturation, infertility,
and hypercholesterolemia. Asian J Androl. 17:742–748.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hammoud AO, Wilde N, Gibson M, Parks A,
Carell DT and Meikle AW: Male obesity and alteration in sperm
parameters. Fertil Steril. 90:2222–2225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
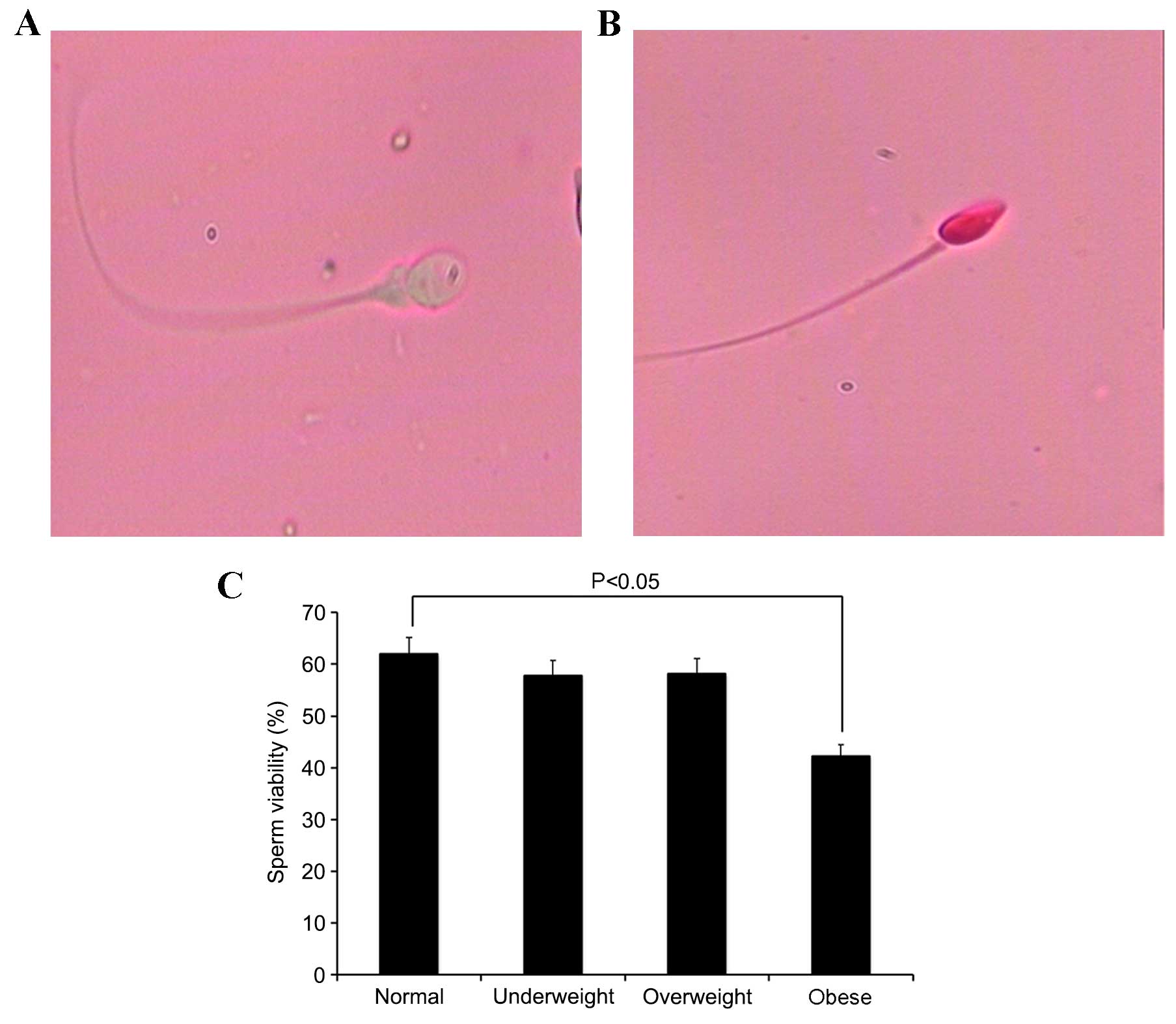
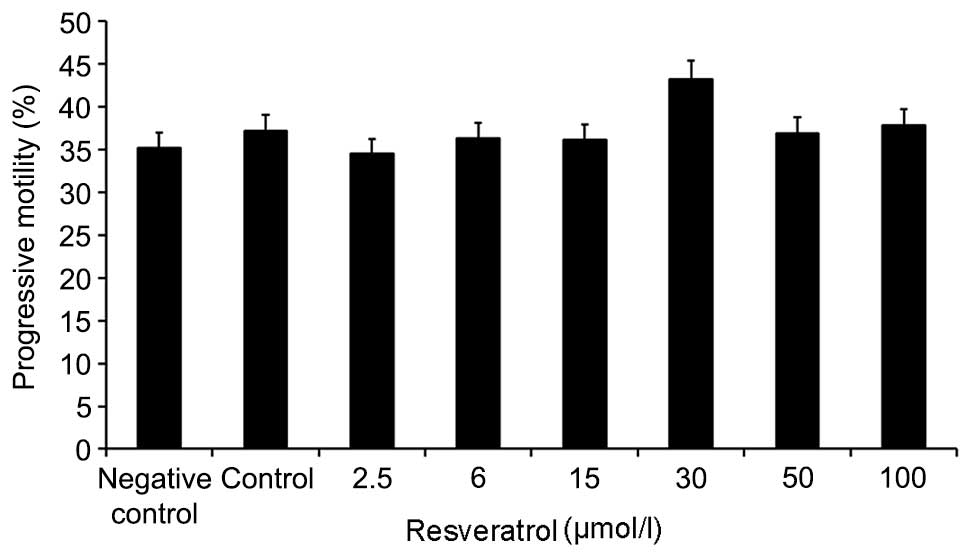
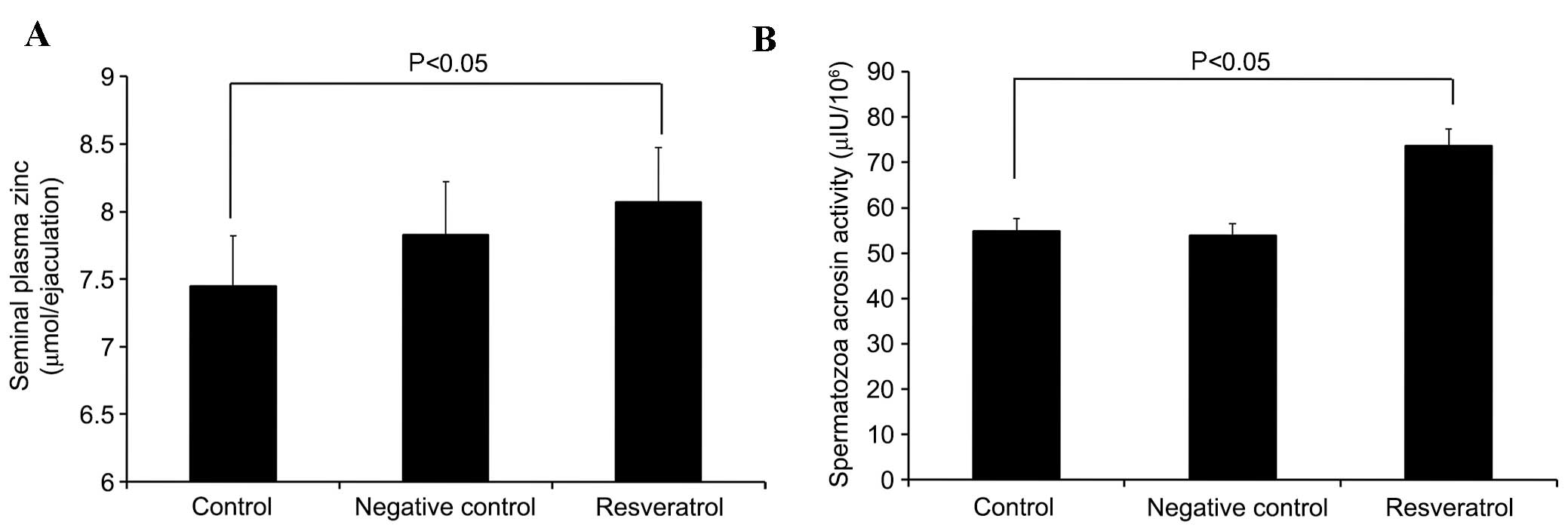
4
|
Ring JD, Lwin AA and Köhler TS: Current
medical management of endocrine-related male infertility. Asian J
Androl. 18:357–363. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cissen M, Bensdorp A, Cohlen BJ, Repping
S, de Bruin JP and van Wely M: Assisted reproductive technologies
for male subfertility. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
2:CD0003602016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dağ ZÖ and Dilbaz B: Impact of obesity on
infertility in women. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc. 16:111–117. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Katib A: Mechanisms linking obesity to
male infertility. Cent European J Urol. 68:79–85. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Esmaeilzadeh S, Andarieh MG, Ghadimi R and
Delavar MA: Body mass index and gonadotropin hormones (LH &
FSH) associate with clinical symptoms among women with polycystic
ovary syndrome. Glob J Health Sci. 7:101–106. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou Y, Chen K, He L, Xia Y, Dai W, Wang
F, Li J, Li S, Liu T, Zheng Y, et al: The protective effect of
resveratrol on concanavalin-A-Induced acute hepatic injury in mice.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2015:5063902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lang F, Qin Z, Li F, Zhang H, Fang Z and
Hao E: Apoptotic cell death induced by resveratrol is partially
mediated by the autophagy pathway in human ovarian cancer cells.
PLoS One. 10:e01291962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Orihuela-Campos RC, Tamaki N, Mukai R,
Fukui M, Miki K, Terao J and Ito HO: Biological impacts of
resveratrol, quercetin, and N-acetylcysteine on oxidative stress in
human gingival fibroblasts. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 56:220–227. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiao Y, Li H, Liu Y, Guo A, Xu X, Qu X,
Wang S, Zhao J, Li Y and Cao Y: Resveratrol inhibits the invasion
of Glioblastoma-Initiating cells via Down-Regulation of the
PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Nutrients. 7:4383–4402. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J, Yi L, Xiang Z, Zhong J, Zhang H and
Sun T: Resveratrol attenuates spinal cord injury-induced
inflammatory damage in rat lungs. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:1237–1246. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sharma P, Huq AU and Singh R:
Cypermethrin-induced reproductive toxicity in the rat is prevented
by resveratrol. J Hum Reprod Sci. 7:99–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eleawa SM, Alkhateeb MA, Alhashem FH,
Bin-Jaliah I, Sakr HF, Elrefaey HM, Elkarib AO, Alessa RM, Haidara
MA, Shatoor AS and Khalil MA: Resveratrol reverses cadmium
chloride-induced testicular damage and subfertility by
downregulating p53 and Bax and upregulating gonadotropins and Bcl-2
gene expression. J Reprod Dev. 60:115–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Juan ME, González-Pons E, Munuera T,
Ballester J, Rodríguez-Gil JE and Planas JM: trans-Resveratrol, a
natural antioxidant from grapes, increases sperm output in healthy
rats. J Nutr. 135:757–760. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Asia-Pacific Perspective, . Redefining
obesity and its treatment. Health Communications Australia;
Melbourne: 2000
|
|
18
|
World Health Organization, . WHO
laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human
semen. 5th. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010
|
|
19
|
Auger J, Eustache F, Andersen AG, Irvine
DS, Jørgensen N, Skakkebaek NE, Suominen J, Toppari J, Vierula M
and Jouannet P: Sperm morphological defects related to environment,
lifestyle and medical history of 1001 male partners of pregnant
women from four European cities. Hum Reprod. 16:2710–2717. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McTigue KM, Hess R and Ziouras J:
Diagnosis and treatment of obesity in the elderly. AHRQ Technology
Assessments; Rockville (MD): 2003
|
|
21
|
Goulão B, Santos O and Carmo Id: The
impact of migration on body weight: A review. Cad Saude Publica.
31:229–245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jungheim ES, Schon SB, Schulte MB,
DeUgarte DA, Fowler SA and Tuuli MG: IVF outcomes in obese donor
oocyte recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum
Reprod. 28:2720–2727. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sermondade N, Faure C, Fezeu L, Shayeb AG,
Bonde JP, Jensen TK, Van Wely M, Cao J, Martini AC, Eskandar M, et
al: BMI in relation to sperm count: An updated systematic review
and collaborative meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 19:221–231.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Samavat J, Natali I, Degl'Innocenti S,
Filimberti E, Cantini G, Di Franco A, Danza G, Seghieri G, Lucchese
M, Baldi E, et al: Acrosome reaction is impaired in spermatozoa of
obese men: A preliminary study. Fertil Steril. 102:1274–1281.e2.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Macdonald AA, Stewart AW and Farquhar CM:
Body mass index in relation to semen quality and reproductive
hormones in New Zealand men: A cross-sectional study in fertility
clinics. Hum Reprod. 28:3178–3187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hammoud AO, Meikle AW, Peterson CM,
Stanford J, Gibson M and Carrell DT: Association of
25-hydroxy-vitamin D levels with semen and hormonal parameters.
Asian J Androl. 14:855–859. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Eskandar M, Al-Asmari M, Chaduvula S Babu,
Al-Shahrani M, Al-Sunaidi M, Almushait M, Donia O and Al-Fifi S:
Impact of male obesity on semen quality and serum sex hormones. Adv
Urol. 2012:4076012012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan WJ, Mu Y, Yu N, Yi TL, Zhang Y, Pang
XL, Cheng D and Yang J: Protective effects of metformin on
reproductive function in obese male rats induced by high-fat diet.
J Assist Reprod Genet. 32:1097–1104. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hofny ER, Ali ME, Abdel-Hafez HZ, Kamal
Eel-D, Mohamed EE, Abd El-Azeem HG and Mostafa T: Semen parameters
and hormonal profile in obese fertile and infertile males. Fertil
Steril. 94:581–584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Trotta V, Lee WH, Loo CY, Haghi M, Young
PM, Scalia S and Traini D: In vitro biological activity of
resveratrol using a novel inhalable resveratrol spray-dried
formulation. Int J Pharm. 491:190–197. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|