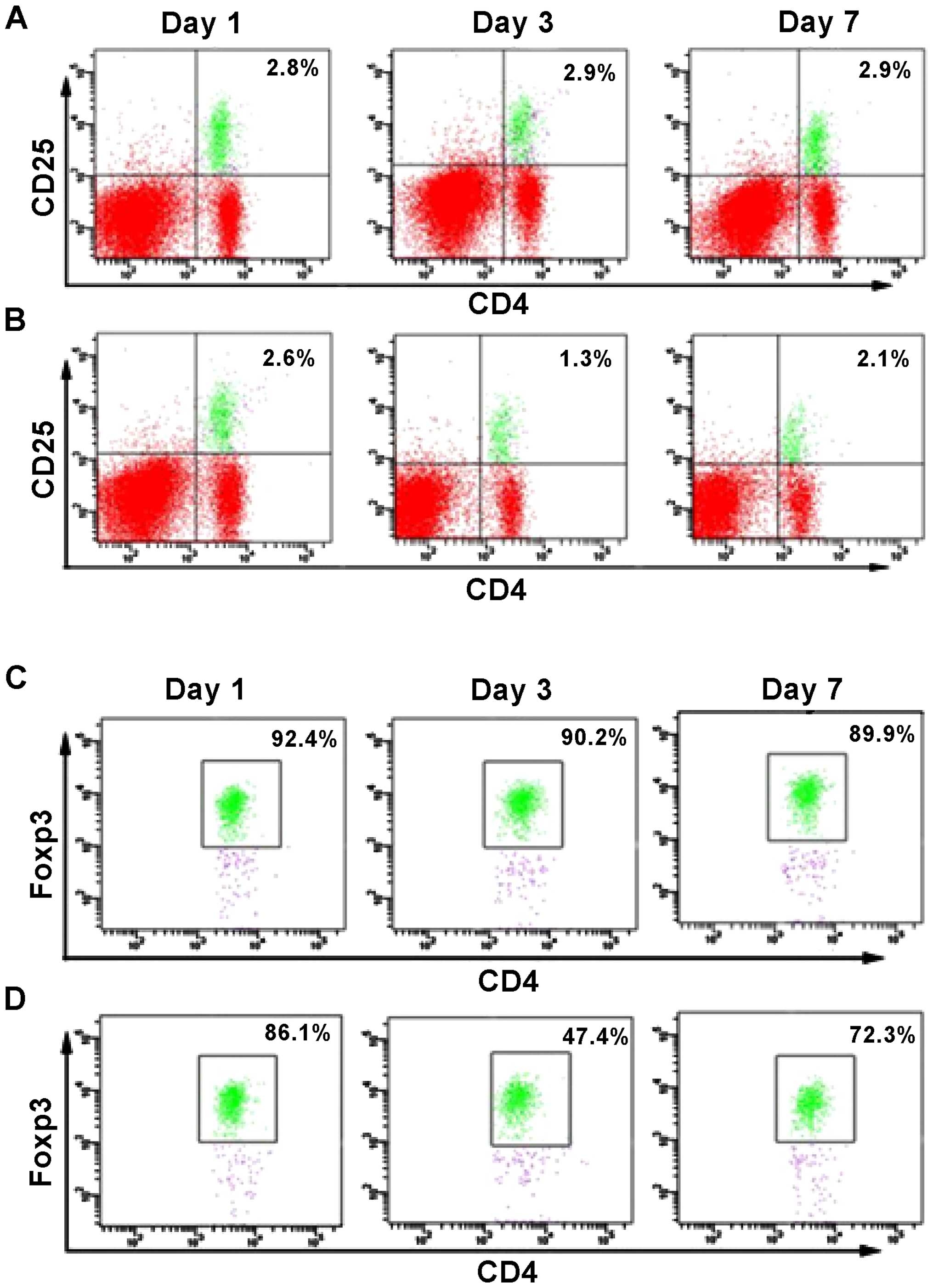
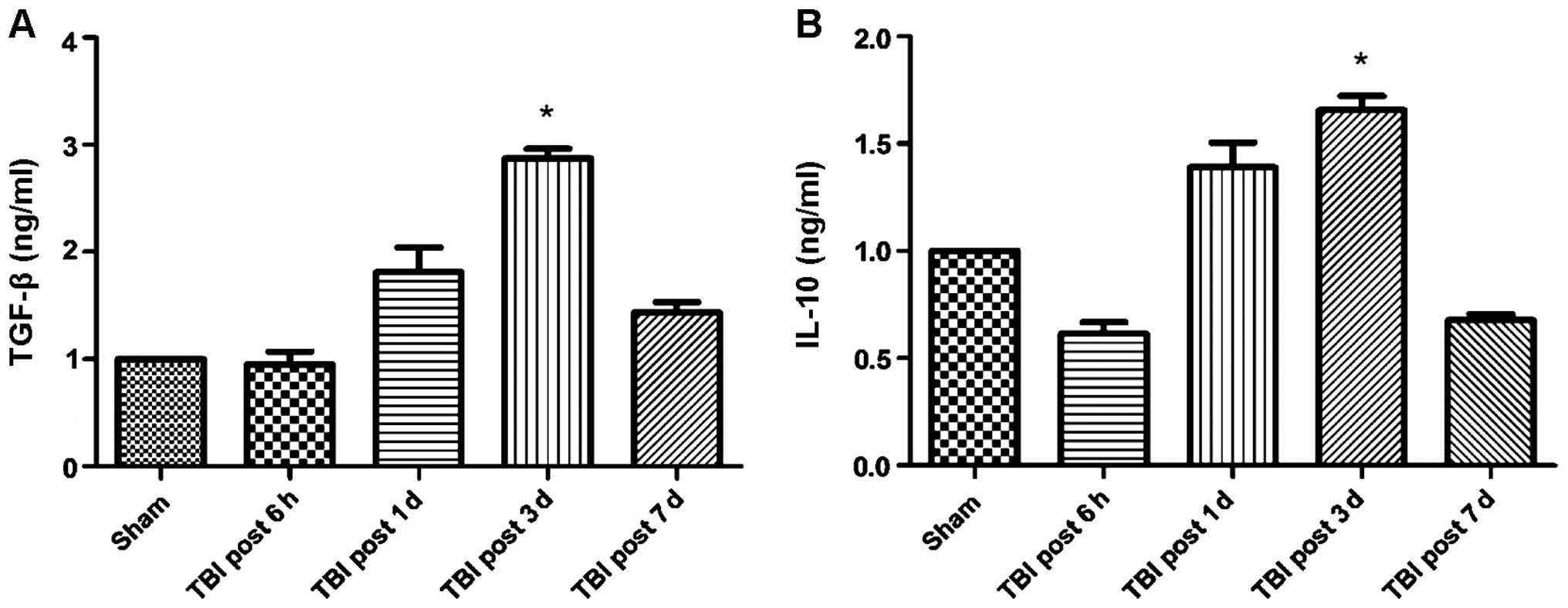
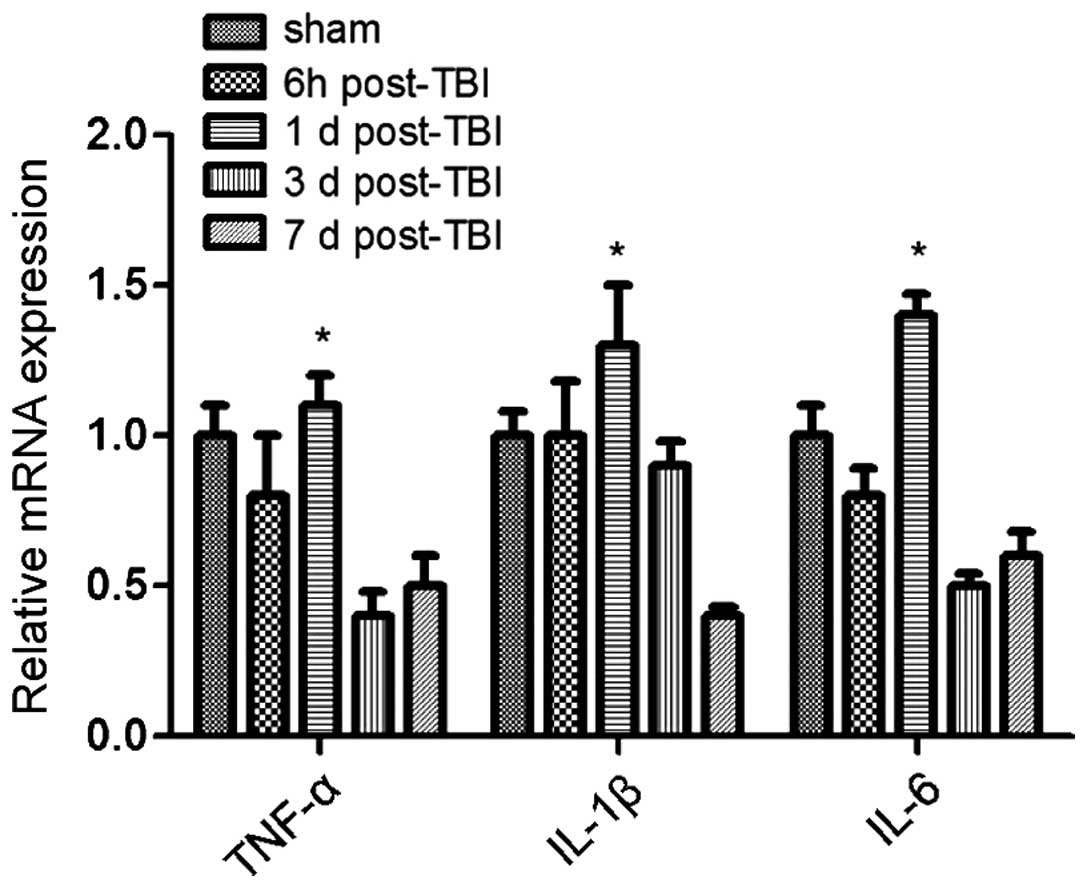
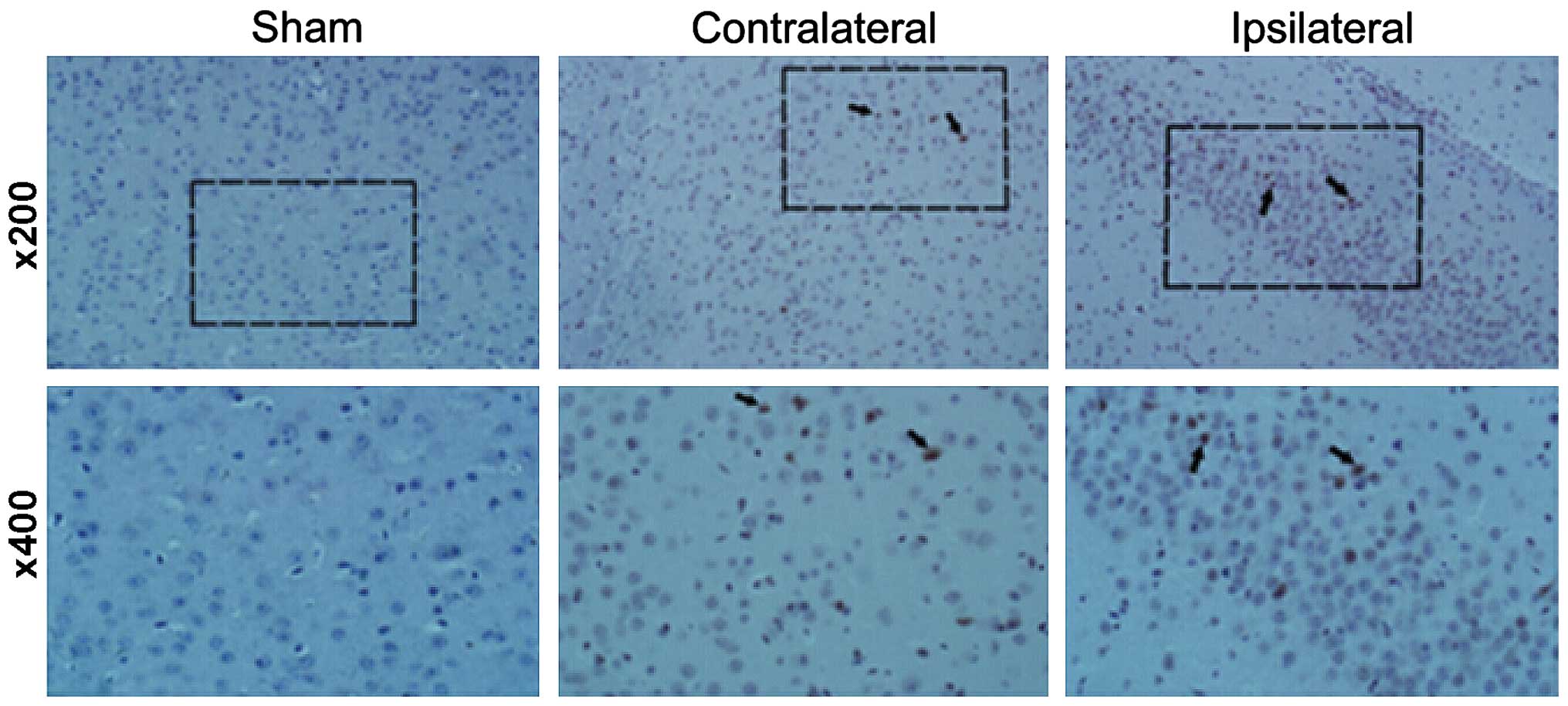
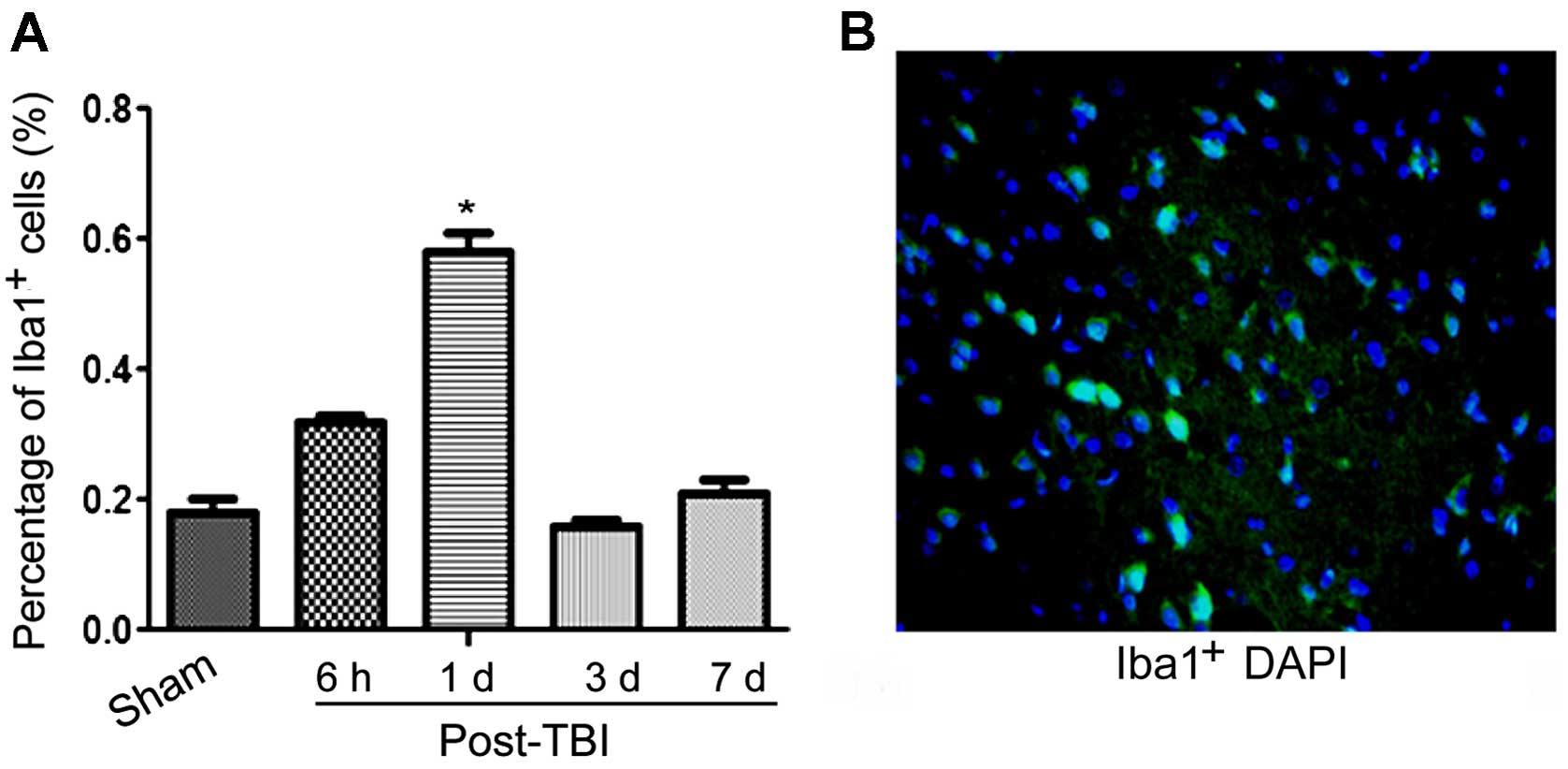
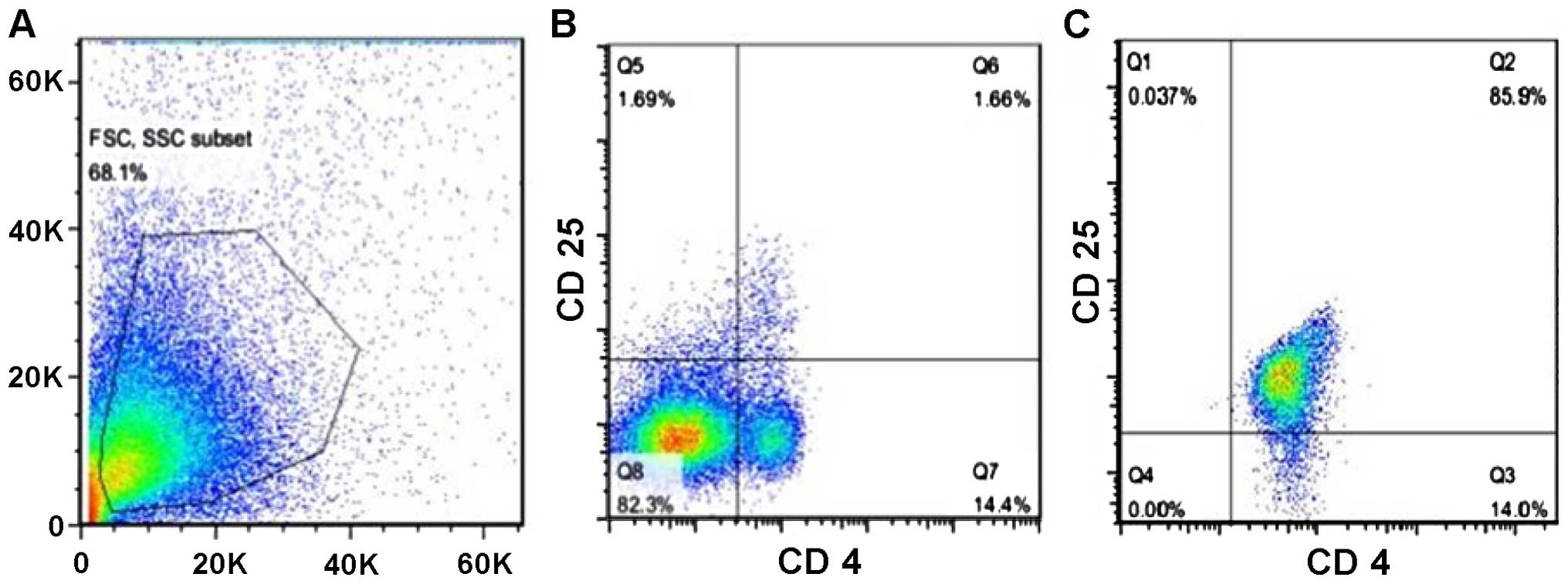
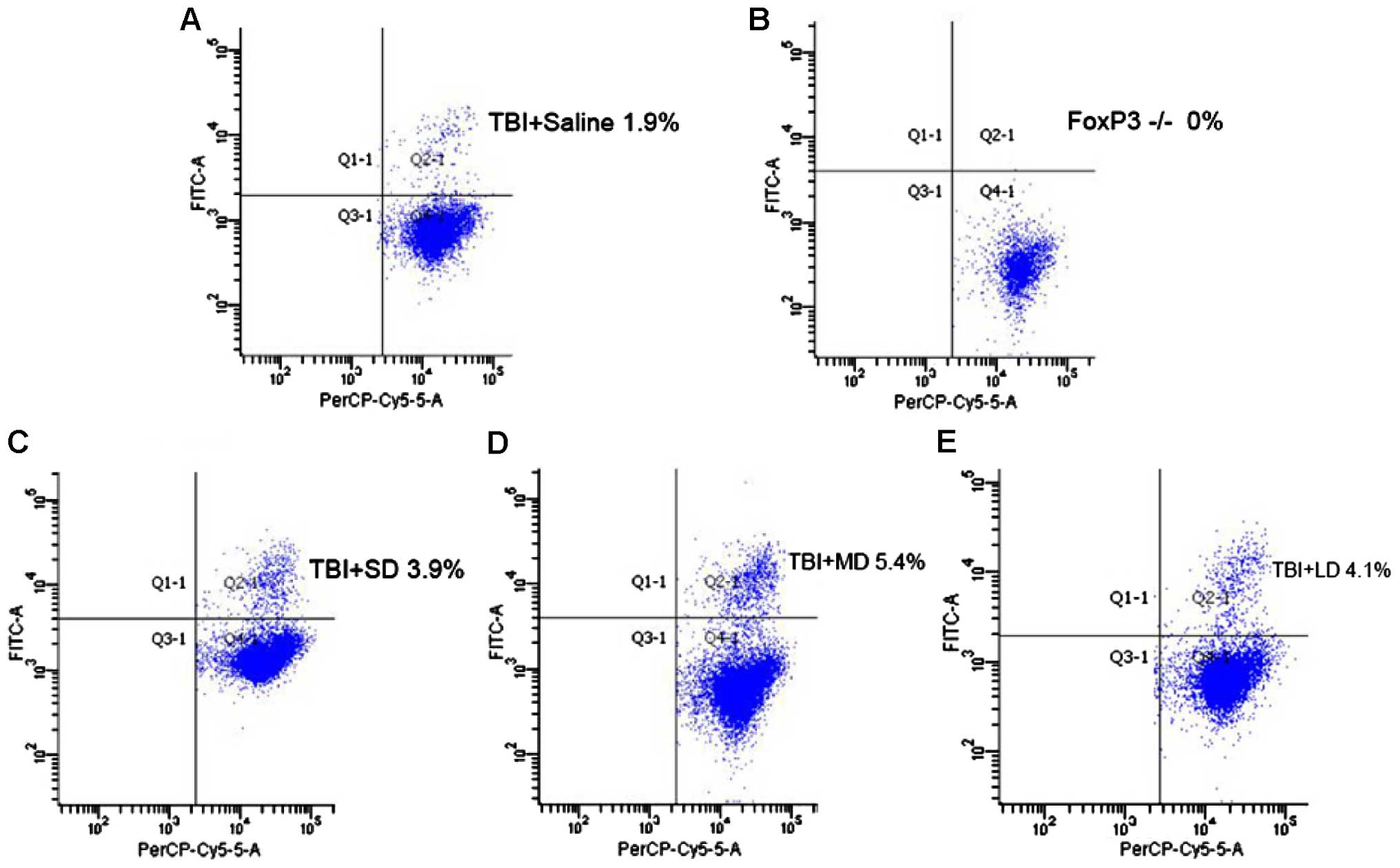
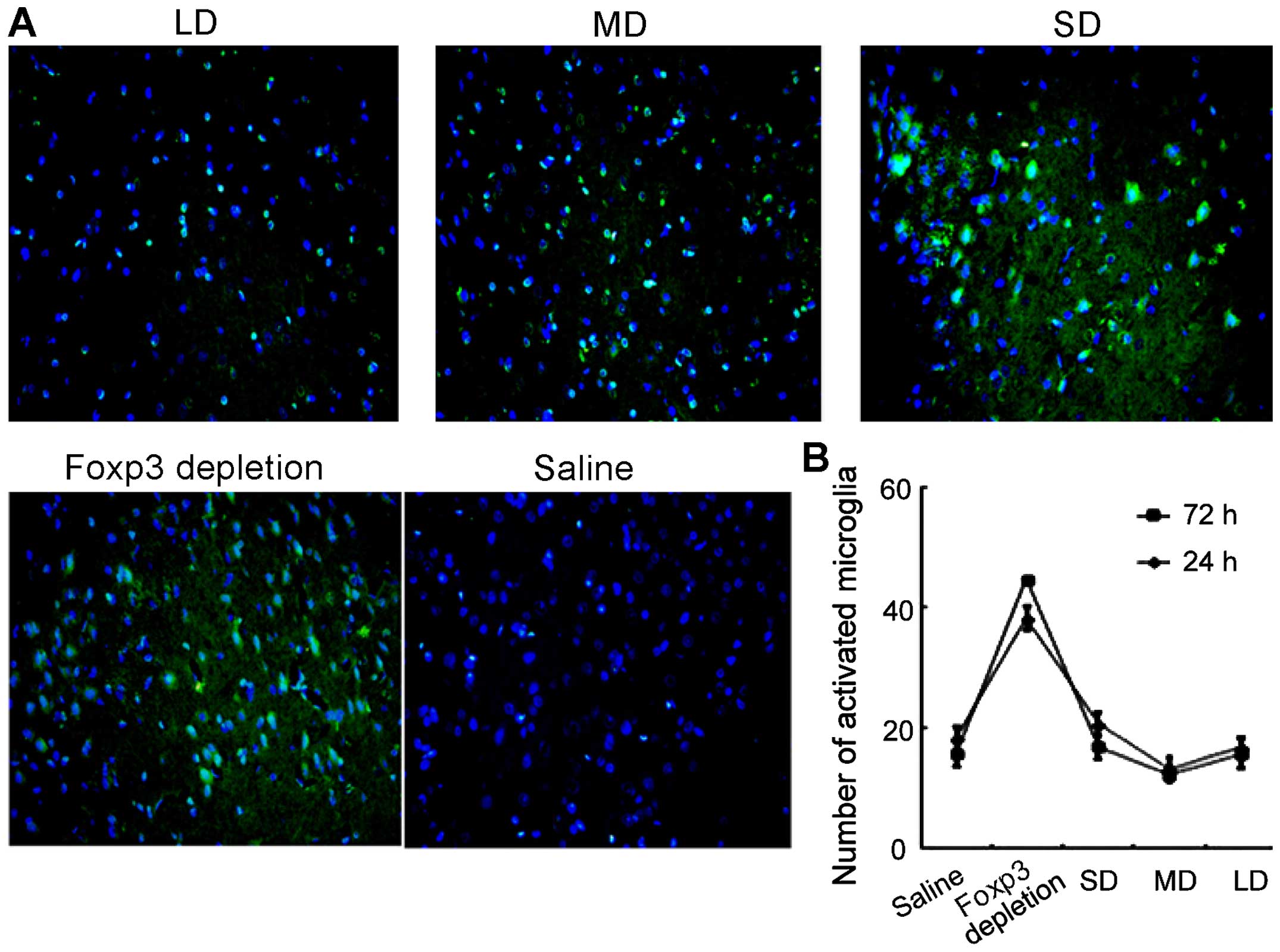
|
1
|
Brasure M, Lamberty GJ, Sayer NA, Nelson
NW, Macdonald R, Ouellette J and Wilt TJ: Participation after
multidisciplinary rehabilitation for moderate to severe traumatic
brain injury in adults: a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.
94:1398–1420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Faden AI: Microglial activation and
traumatic brain injury. Ann Neurol. 70:345–346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Whalen MJ, Carlos TM, Wisniewski SR, Clark
RS, Mellick JA, Marion DW and Kochanek PM: Effect of neutropenia
and granulocyte colony stimulating factor-induced neutrophilia on
blood-brain barrier permeability and brain edema after traumatic
brain injury in rats. Crit Care Med. 28:3710–3717. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ahn MJ, Sherwood ER, Prough DS, Lin CY and
DeWitt DS: The effects of traumatic brain injury on cerebral blood
flow and brain tissue nitric oxide levels and cytokine expression.
J Neurotrauma. 21:1431–1442. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Readnower RD, Chavko M, Adeeb S, Conroy
MD, Pauly JR, McCarron RM and Sullivan PG: Increase in blood-brain
barrier permeability, oxidative stress, and activated microglia in
a rat model of blast-induced traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci
Res. 88:3530–3539. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liesz A, Suri-Payer E, Veltkamp C, Doerr
H, Sommer C, Rivest S, Giese T and Veltkamp R: Regulatory T cells
are key cerebroprotective immunomodulators in acute experimental
stroke. Nat Med. 15:192–199. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishibashi S, Maric D, Mou Y, Ohtani R,
Ruetzler C and Hallenbeck JM: Mucosal tolerance to E-selectin
promotes the survival of newly generated neuroblasts via regulatory
T-cell induction after stroke in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:606–620. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shi Y, Fukuoka M, Li G, Liu Y, Chen M,
Konviser M, Chen X, Opavsky MA and Liu PP: Regulatory T cells
protect mice against coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis through the
transforming growth factor β-coxsackie-adenovirus receptor pathway.
Circulation. 121:2624–2634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Strisciuglio C and van Deventer S:
Regulatory T cells as potential targets for immunotherapy in
inflammatory bowel disease. Immunotherapy. 2:749–752. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu R, Zhou Q, La Cava A, Campagnolo DI,
Van Kaer L and Shi FD: Expansion of regulatory T cells via
IL-2/anti-IL-2 mAb complexes suppresses experimental myasthenia.
Eur J Immunol. 40:1577–1589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meng X, Zhang K, Li J, Dong M, Yang J, An
G, Qin W, Gao F, Zhang C and Zhang Y: Statins induce the
accumulation of regulatory T cells in atherosclerotic plaque. Mol
Med. 18:598–605. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li M, Lin YP, Chen JL, Li H, Jiang RC and
Zhang JN: Role of regulatory T cell in clinical outcome of
traumatic brain injury. Chin Med J (Engl). 128:1072–1078. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M
and Toda M: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T
cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a
single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune
diseases. J Immunol. 155:1151–1164. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sakaguchi S, Miyara M, Costantino CM and
Hafler DA: FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in the human immune
system. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:490–500. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vignali DA, Collison LW and Workman CJ:
How regulatory T cells work. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:523–532. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan R, Maeda Y, Li W, Lu W, Cook S and
Dowling P: Erythropoietin: A potent inducer of peripheral
immuno/inflammatory modulation in autoimmune EAE. PLoS One.
3:e19242008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dénes A, Humphreys N, Lane TE, Grencis R
and Rothwell N: Chronic systemic infection exacerbates ischemic
brain damage via a CCL5 (regulated on activation, normal T-cell
expressed and secreted)-mediated proinflammatory response in mice.
J Neurosci. 30:10086–10095. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bassil R, Zhu B, Lahoud Y, Riella LV,
Yagita H, Elyaman W and Khoury SJ: Notch ligand delta-like 4
blockade alleviates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by
promoting regulatory T cell development. J Immunol. 187:2322–2328.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Louveau A, Smirnov I, Keyes TJ, Eccles JD,
Rouhani SJ, Peske JD, Derecki NC, Castle D, Mandell JW, Lee KS, et
al: Structural and functional features of central nervous system
lymphatic vessels. Nature. 523:337–341. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H,
Hori S, Fehervari Z, Shimizu J, Takahashi T and Nomura T:
Foxp3+ CD25+ CD4+ natural
regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune
disease. Immunol Rev. 212:8–27. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ghajar J: Traumatic brain injury. Lancet.
356:923–929. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ziebell JM and Morganti-Kossmann MC:
Involvement of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines
in the pathophysiology of traumatic brain injury.
Neurotherapeutics. 7:22–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scheffold A, Murphy KM and Hofer T:
Competition for cytokines: T(reg) cells take all. Nat Immunol.
8:1285–1287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Q, Cui F, Fang L, Hong J, Zheng B
and Zhang JZ: TNF-alpha impairs differentiation and function of
TGF-beta-induced Treg cells in autoimmune diseases through Akt and
Smad3 signaling pathway. J Mol Cell Biol. 5:85–98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nagamoto-Combs K, McNeal DW, Morecraft RJ
and Combs CK: Prolonged microgliosis in the rhesus monkey central
nervous system after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma.
24:1719–1742. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Abbott NJ: Inflammatory mediators and
modulation of blood-brain barrier permeability. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
20:131–147. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amiry-Moghaddam M and Ottersen OP: The
molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci.
4:991–1001. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Balda MS, Whitney JA, Flores C, González
S, Cereijido M and Matter K: Functional dissociation of
paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance
and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion
barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein.
J Cell Biol. 134:1031–1049. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Di Giovanni S, Movsesyan V, Ahmed F,
Cernak I, Schinelli S, Stoica B and Faden AI: Cell cycle inhibition
provides neuroprotection and reduces glial proliferation and scar
formation after traumatic brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:8333–8338. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ramlackhansingh AF, Brooks DJ, Greenwood
RJ, Bose SK, Turkheimer FE, Kinnunen KM, Gentleman S, Heckemann RA,
Gunanayagam K, Gelosa G, et al: Inflammation after trauma:
Microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann Neurol.
70:374–383. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sakaguchi S: Naturally arising
Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells
in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat Immunol.
6:345–352. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schwartz RH: Natural regulatory T cells
and self-tolerance. Nat Immunol. 6:327–330. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
La Cava A, Van Kaer L and Fu-Dong-Shi:
CD4+CD25+ Tregs and NKT cells: Regulators
regulating regulators. Trends Immunol. 27:322–327. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Balandina A, Lécart S, Dartevelle P,
Saoudi A and Berrih-Aknin S: Functional defect of regulatory
CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in the thymus of patients with autoimmune
myasthenia gravis. Blood. 105:735–741. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fattorossi A, Battaglia A, Buzzonetti A,
Ciaraffa F, Scambia G and Evoli A: Circulating and thymic CD4 CD25
T regulatory cells in myasthenia gravis: Effect of
immunosuppressive treatment. Immunology. 116:134–141. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu R, La Cava A, Bai XF, Jee Y, Price M,
Campagnolo DI, Christadoss P, Vollmer TL, Van Kaer L and Shi FD:
Cooperation of invariant NKT cells and
CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells in the
prevention of autoimmune myasthenia. J Immunol. 175:7898–7904.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ji J and Cloyd MW: HIV-1 binding to CD4 on
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells enhances their suppressive function
and induces them to home to, and accumulate in, peripheral and
mucosal lymphoid tissues: An additional mechanism of
immunosuppression. Int Immunol. 21:283–294. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|