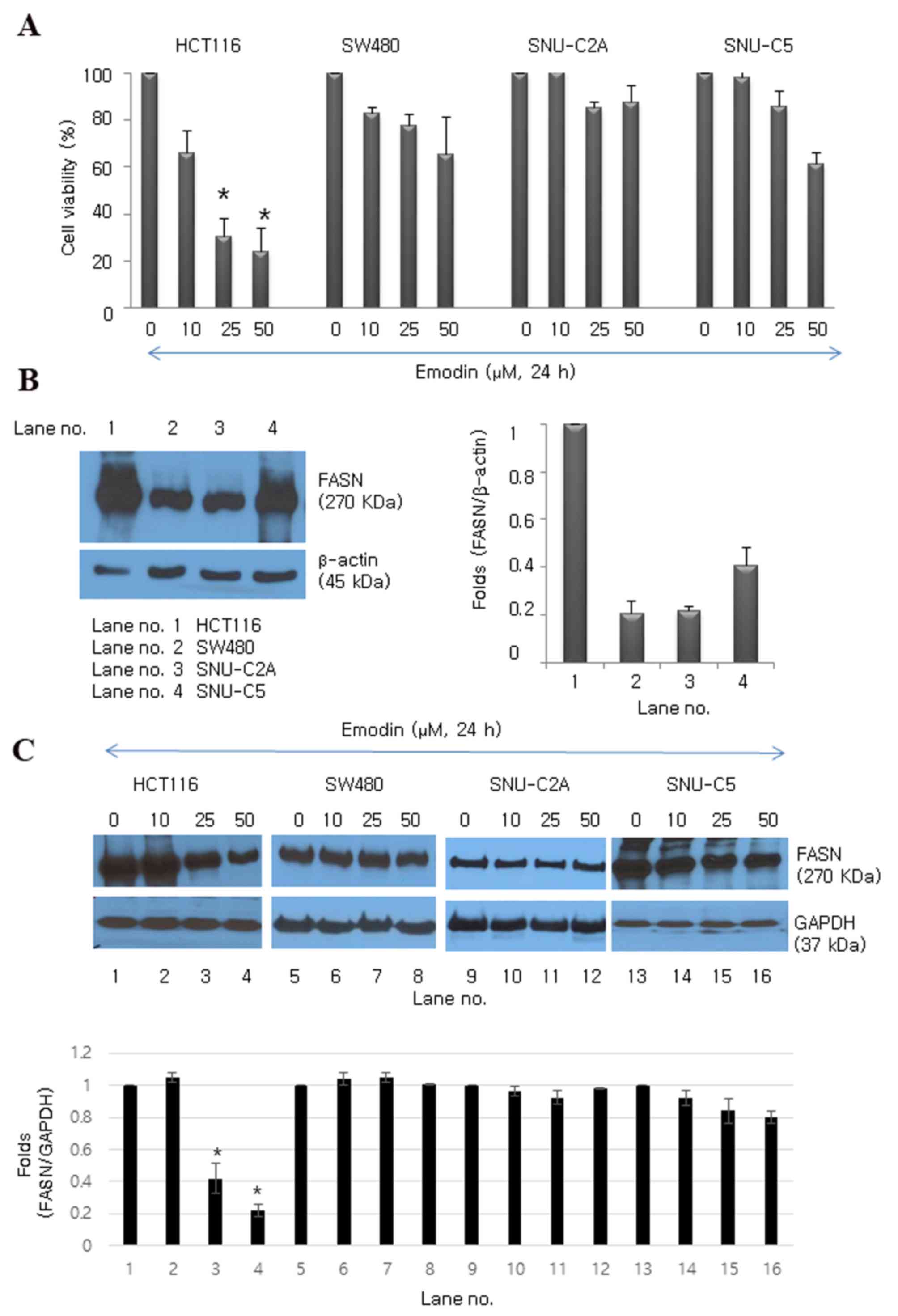
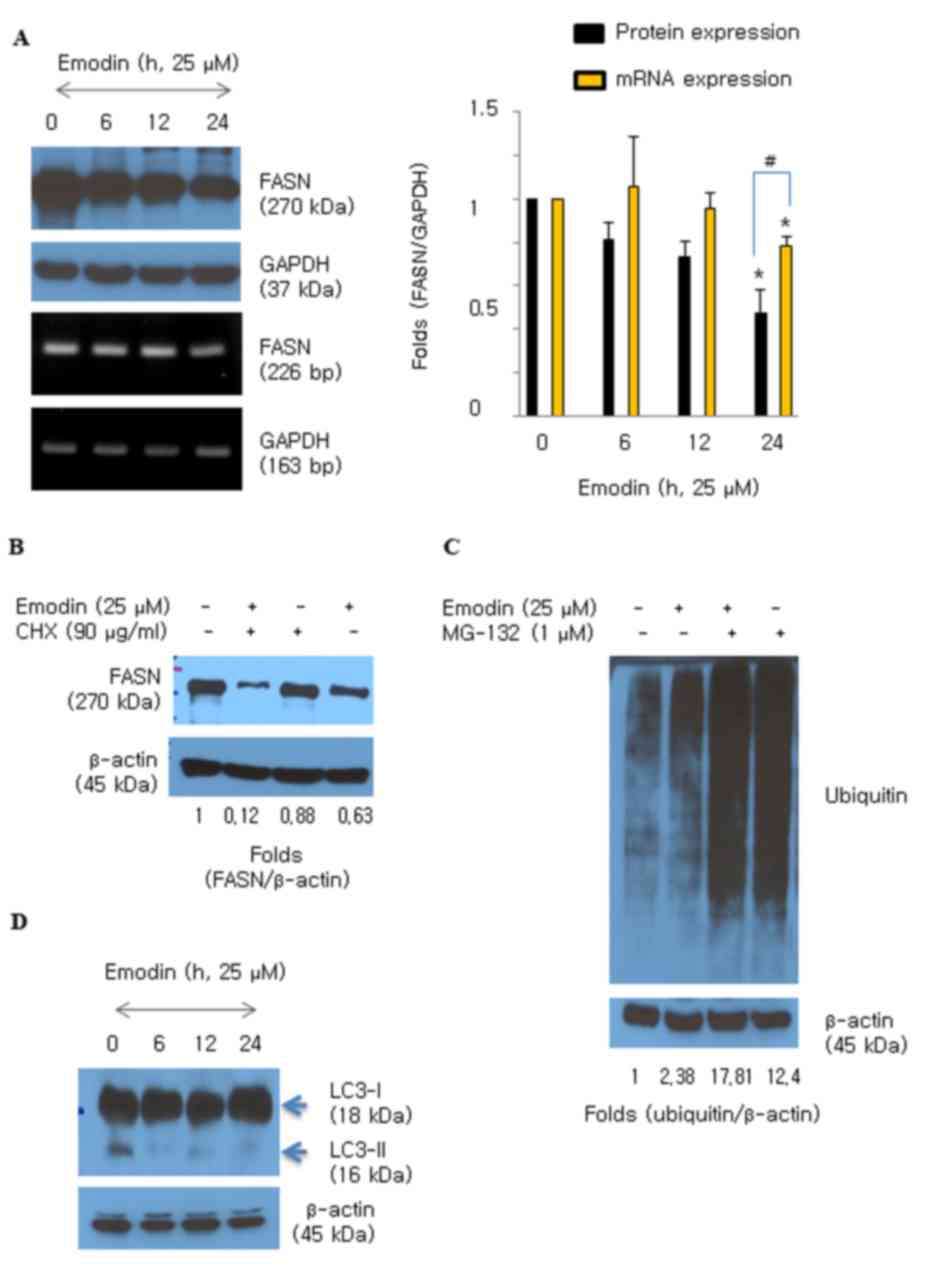
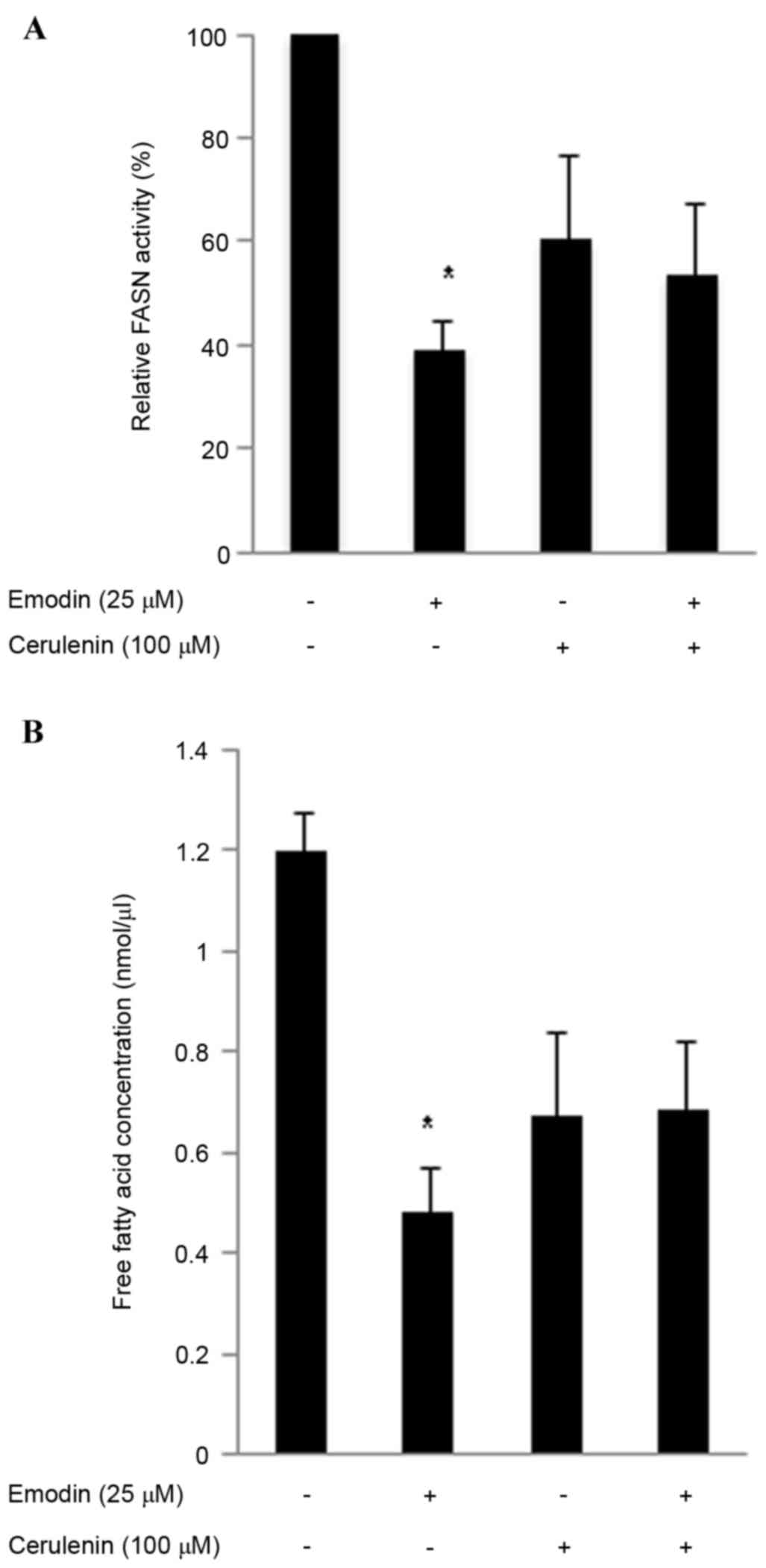
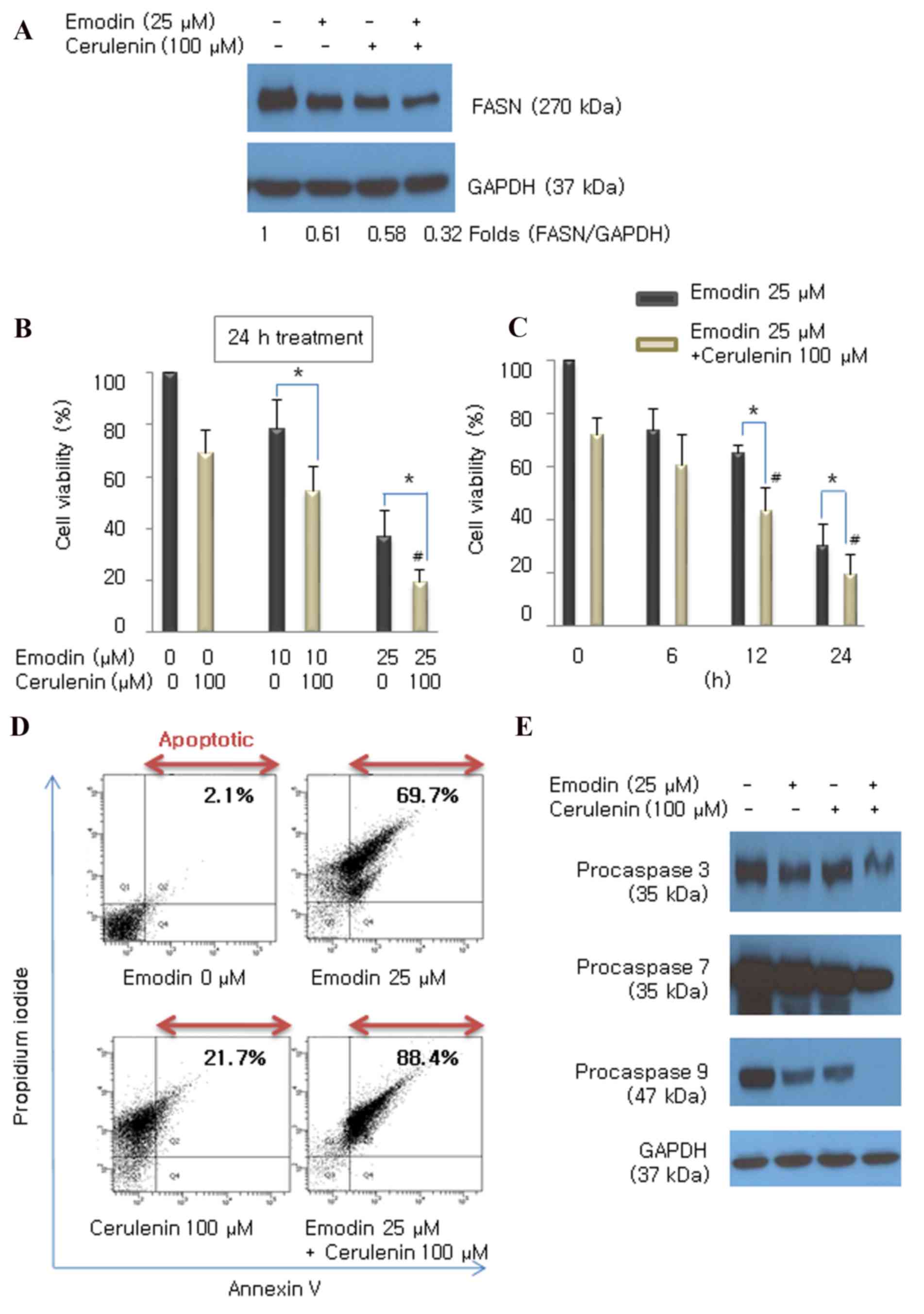
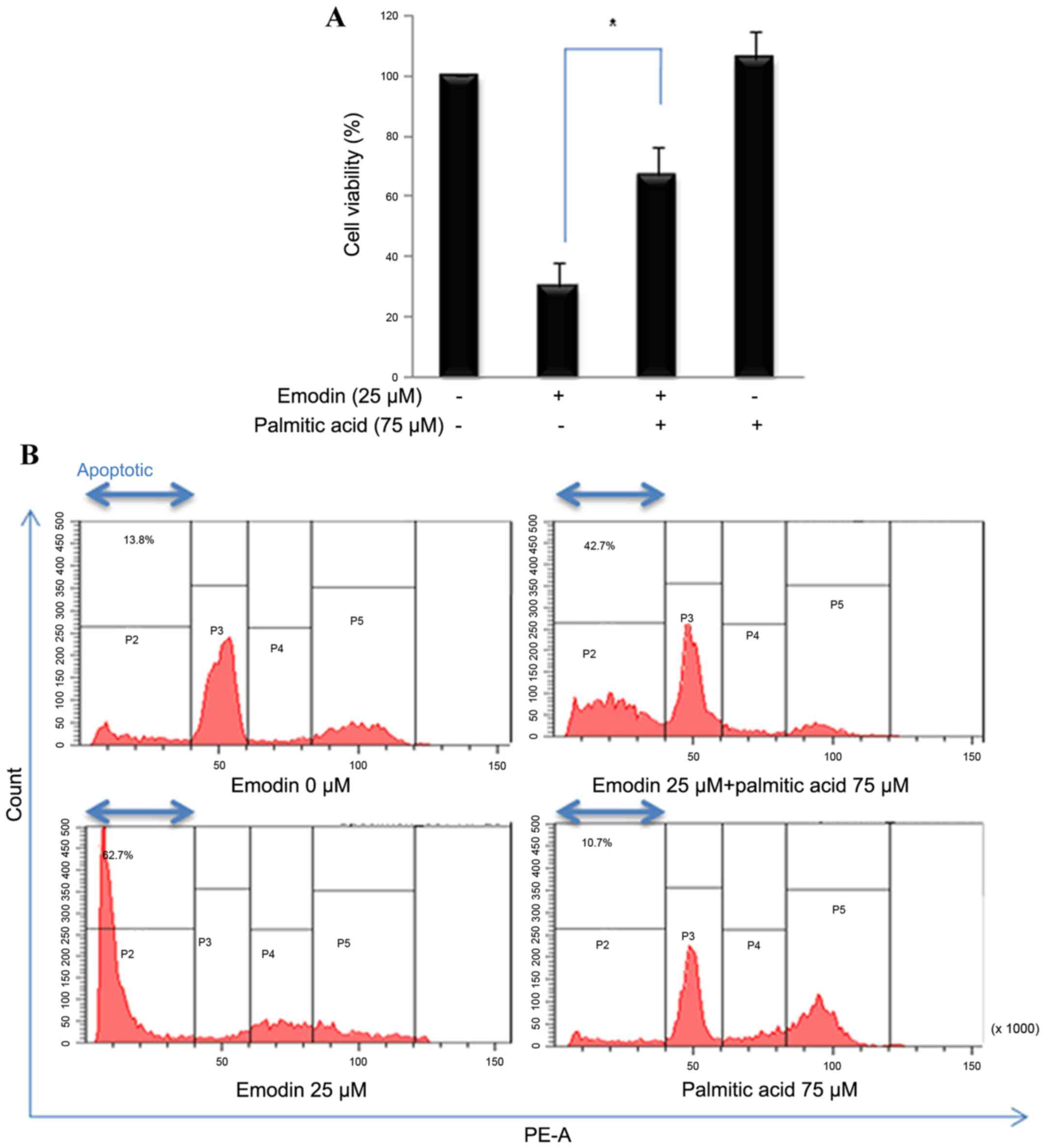
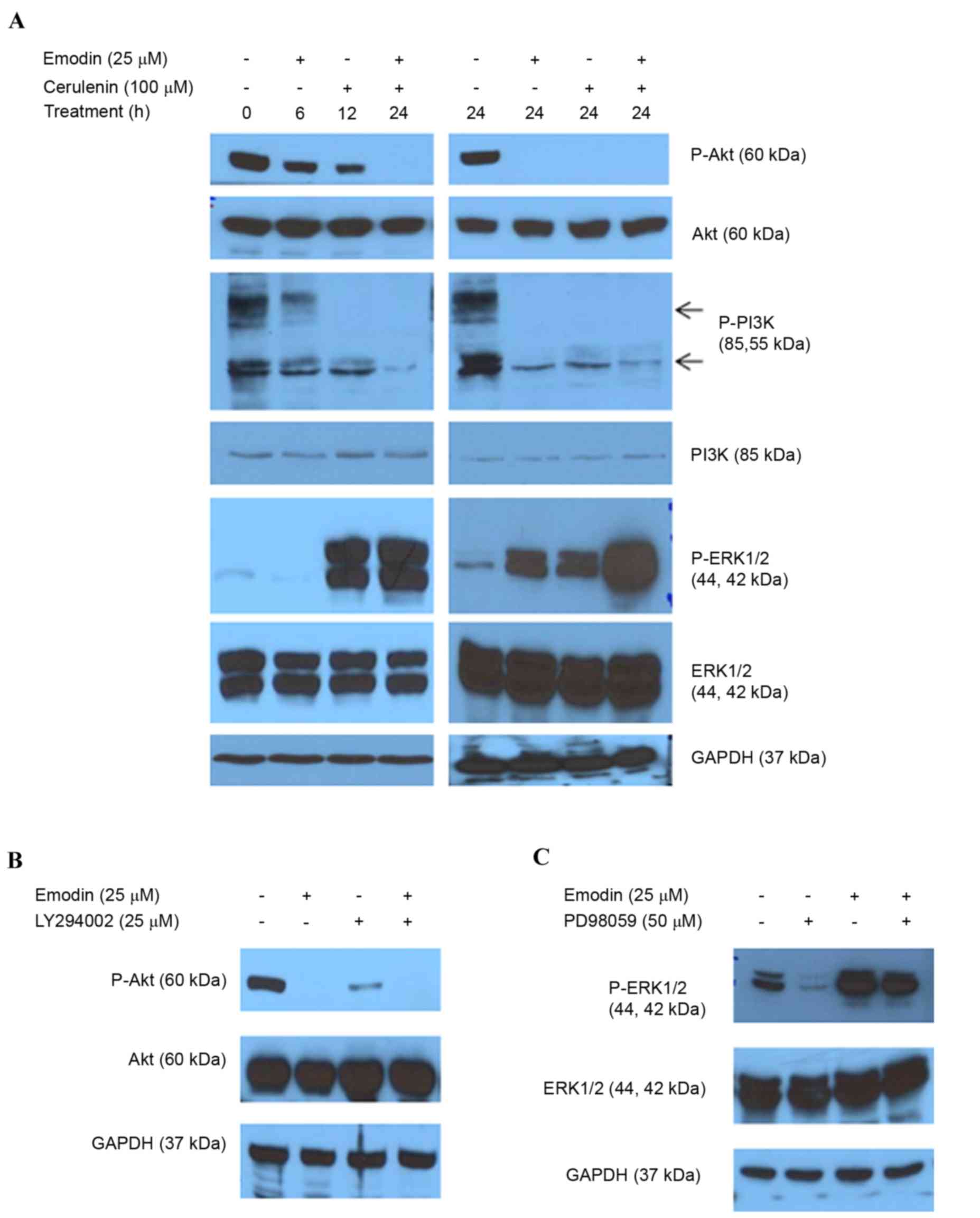
|
1
|
Cunningham D, Atkin W, Lenz HJ, Lynch HT,
Minsky B, Nordlinger B and Starling N: Colorectal cancer. Lancet.
375:1030–1047. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Merika E, Saif MW, Katz A, Syrigos K and
Morse M: Colon cancer vaccines: An update. In vivo. 24:607–628.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuhajda FP: Fatty acid synthase and
cancer: New application of an old pathway. Cancer Res.
66:5977–5980. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Long QQ, Yi YX, Qiu J, Xu CJ and Huang PL:
Fatty acid synthase (FASN) levels in serum of colorectal cancer
patients: Correlation with clinical outcomes. Tumour Biol.
35:3855–3859. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mounier C, Bouraoui L and Rassart E:
Lipogenesis in cancer progression (review). Int J Oncol.
45:485–492. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Grunt TW, Wagner R, Grusch M, Berger W,
Singer CF, Marian B, Zielinski CC and Lupu R: Interaction between
fatty acid synthase- and ErbB-systems in ovarian cancer cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 385:454–459. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JS, Sul JY, Park JB, Lee MS, Cha EY,
Song IS, Kim JR and Chang ES: Fatty acid synthase inhibition by
amentoflavone suppresses HER2/neu (erbB2) oncogene in SKBR3 human
breast cancer cells. Phytother Res. 27:713–720. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tomek K, Wagner R, Varga F, Singer CF,
Karlic H and Grunt TW: Blockade of fatty acid synthase induces
ubiquitination and degradation of phosphoinositide-3-kinase
signaling proteins in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1767–1779.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang Z, Chen G and Shi P: Effects of
emodin on the gene expression profiling of human breast carcinoma
cells. Cancer Detect Prev. 32:286–291. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsu CM, Hsu YA, Tsai Y, Shieh FK, Huang
SH, Wan L and Tsai FJ: Emodin inhibits the growth of hepatoma
cells: Finding the common anti-cancer pathway using Huh7, Hep3B,
and HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 392:473–478. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lai JM, Chang JT, Wen CL and Hsu SL:
Emodin induces a reactive oxygen species-dependent and ATM-p53-Bax
mediated cytotoxicity in lung cancer cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
623:1–9. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cha TL, Qiu L, Chen CT, Wen Y and Hung MC:
Emodin down-regulates androgen receptor and inhibits prostate
cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 65:2287–2295. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Srinivas G, Anto RJ, Srinivas P,
Vidhyalakshmi S, Senan VP and Karunagaran D: Emodin induces
apoptosis of human cervical cancer cells through poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase cleavage and activation of caspase-9. Eur J Pharmacol.
473:117–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chun-Guang W, Jun-Qing Y, Bei-Zhong L,
Dan-Ting J, Chong W, Liang Z, Dan Z and Yan W: Anti-tumor activity
of emodin against human chronic myelocytic leukemia K562 cell lines
in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 627:33–41. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie MJ, Ma YH, Miao L, Wang Y, Wang HZ,
Xing YY, Xi T and Lu YY: Emodin-provoked oxidative stress induces
apoptosis in human colon cancer HCT116 Cells through a
p53-mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:5201–5205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin SZ, Wei WT, Chen H, Chen KJ, Tong HF,
Wang ZH, Ni ZL, Liu HB, Guo HC and Liu DL: Antitumor activity of
emodin against pancreatic cancer depends on its dual role:
Promotion of apoptosis and suppression of angiogenesis. PLoS One.
7:e421462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Manu KA, Shanmugam MK, Ong TH, Subramaniam
A, Siveen KS, Perumal E, Samy RP, Bist P, Lim LH, Kumar AP, et al:
Emodin suppresses migration and invasion through the modulation of
CXCR4 expression in an orthotopic model of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e570152013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yim H, Lee YH, Lee CH and Lee SK: Emodin,
an anthraquinone derivative isolated from the rhizomes of Rheum
palmatum, selectively inhibits the activity of casein kinase II as
a competitive inhibitor. Planta Med. 65:9–13. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee HZ: Protein kinase C involvement in
aloe-emodin- and emodin-induced apoptosis in lung carcinoma cell.
Br J Pharmacol. 134:1093–1103. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Su YJ, Tsai MS, Kuo YH, Chiu YF, Cheng CM,
Lin ST and Lin YW: Role of Rad51 down-regulation and extracellular
signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 inactivation in emodin and
mitomycin C-induced synergistic cytotoxicity in human
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 77:633–643. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu Y, Zhang J and Qian J: The effect of
emodin on VEGF receptors in human colon cancer cells. Cancer
Biother Radiopharm. 23:222–228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang L, Chang CJ, Bacus SS and Hung MC:
Suppressed transformation and induced differentiation of
HER-2/neu-overexpressing breast cancer cells by emodin. Cancer Res.
55:3890–3896. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Menendez JA, Vellon L, Colomer R and Lupu
R: Pharmacological and small interference RNA-mediated inhibition
of breast cancer-associated fatty acid synthase (oncogenic
antigen-519) synergistically enhances Taxol (paclitaxel)-induced
cytotoxicity. Int J Cancer. 115:19–35. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lacroix M and Leclercq G: Relevance of
breast cancer cell lines as models for breast tumours: An update.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 83:249–289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Little JL and Kridel SJ: Fatty acid
synthase activity in tumor cells. Subcell Biochem. 49:169–194.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li P, Tian W and Ma X: Alpha-mangostin
inhibits intracellular fatty acid synthase and induces apoptosis in
breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 13:1382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang YA, Han WF, Morin PJ, Chrest FJ and
Pizer ES: Activation of fatty acid synthesis during neoplastic
transformation: Role of mitogen-activated protein kinase and
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Exp Cell Res. 279:80–90. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yellen P and Foster DA: Inhibition of
fatty acid synthase induces pro-survival Akt and ERK signaling in
K-Ras-driven cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 353:258–263. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Menendez JA and Lupu R: Oncogenic
properties of the endogenous fatty acid metabolism: Molecular
pathology of fatty acid synthase in cancer cells. Curr Opin Clin
Nutr Metab Care. 9:346–357. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Menendez JA, Vazquez-Martin A,
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Garcia-Villalba R, Carrasco-Pancorbo A,
Fernandez-Gutierrez A and Segura-Carretero A: Analyzing effects of
extra-virgin olive oil polyphenols on breast cancer-associated
fatty acid synthase protein expression using reverse-phase protein
microarrays. Int J Mol Med. 22:433–439. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rashid A, Pizer ES, Moga M, Milgraum LZ,
Zahurak M, Pasternack GR, Kuhajda FP and Hamilton SR: Elevated
expression of fatty acid synthase and fatty acid synthetic activity
in colorectal neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 150:201–208. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ogino S, Nosho K, Meyerhardt JA, Kirkner
GJ, Chan AT, Kawasaki T, Giovannucci EL, Loda M and Fuchs CS:
Cohort study of fatty acid synthase expression and patient survival
in colon cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:5713–5720. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhan Y, Ginanni N, Tota MR, Wu M, Bays NW,
Richon VM, Kohl NE, Bachman ES, Strack PR and Krauss S: Control of
cell growth and survival by enzymes of the fatty acid synthesis
pathway in HCT-116 colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
14:5735–5742. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shiragami R, Murata S, Kosugi C, Tezuka T,
Yamazaki M, Hirano A, Yoshimura Y, Suzuki M, Shuto K and Koda K:
Enhanced antitumor activity of cerulenin combined with oxaliplatin
in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 43:431–438.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Murata S, Yanagisawa K, Fukunaga K, Oda T,
Kobayashi A, Sasaki R and Ohkohchi N: Fatty acid synthase inhibitor
cerulenin suppresses liver metastasis of colon cancer in mice.
Cancer Sci. 101:1861–1865. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li JN, Gorospe M, Chrest FJ, Kumaravel TS,
Evans MK, Han WF and Pizer ES: Pharmacological inhibition of fatty
acid synthase activity produces both cytostatic and cytotoxic
effects modulated by p53. Cancer Res. 61:1493–1499. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Notarnicola M, Pisanti S, Tutino V, Bocale
D, Rotelli MT, Gentile A, Memeo V, Bifulco M, Perri E and Caruso
MG: Effects of olive oil polyphenols on fatty acid synthase gene
expression and activity in human colorectal cancer cells. Genes
Nutr. 6:63–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang C, Teng L, Shi Y, Jin J, Xue Y,
Shang K and Gu J: Effect of emodin on proliferation and
differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocyte and FAS activity. Chin Med J
(Engl). 115:1035–1038. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma YS, Weng SW, Lin MW, Lu CC, Chiang JH,
Yang JS, Lai KC, Lin JP, Tang NY, Lin JG and Chung JG: Antitumor
effects of emodin on LS1034 human colon cancer cells in vitro and
in vivo: Roles of apoptotic cell death and LS1034 tumor xenografts
model. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:1271–1278. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim J, Lee JS, Jung J, Lim I, Lee JY and
Park MJ: Emodin suppresses maintenance of stemness by augmenting
proteosomal degradation of epidermal growth factor
receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor variant III in glioma
stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 24:284–295. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chuang HY, Chang YF and Hwang JJ:
Antitumor effect of orlistat, a fatty acid synthase inhibitor, is
via activation of caspase-3 on human colorectal carcinoma-bearing
animal. Biomed Pharmacother. 65:286–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang HQ, Altomare DA, Skele KL, Poulikakos
PI, Kuhajda FP, Di Cristofano A and Testa JR: Positive feedback
regulation between AKT activation and fatty acid synthase
expression in ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 24:3574–3582.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu X, Shi Y, Giranda VL and Luo Y:
Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway
sensitizes MDA-MB468 human breast cancer cells to cerulenin-induced
apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:494–501. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|