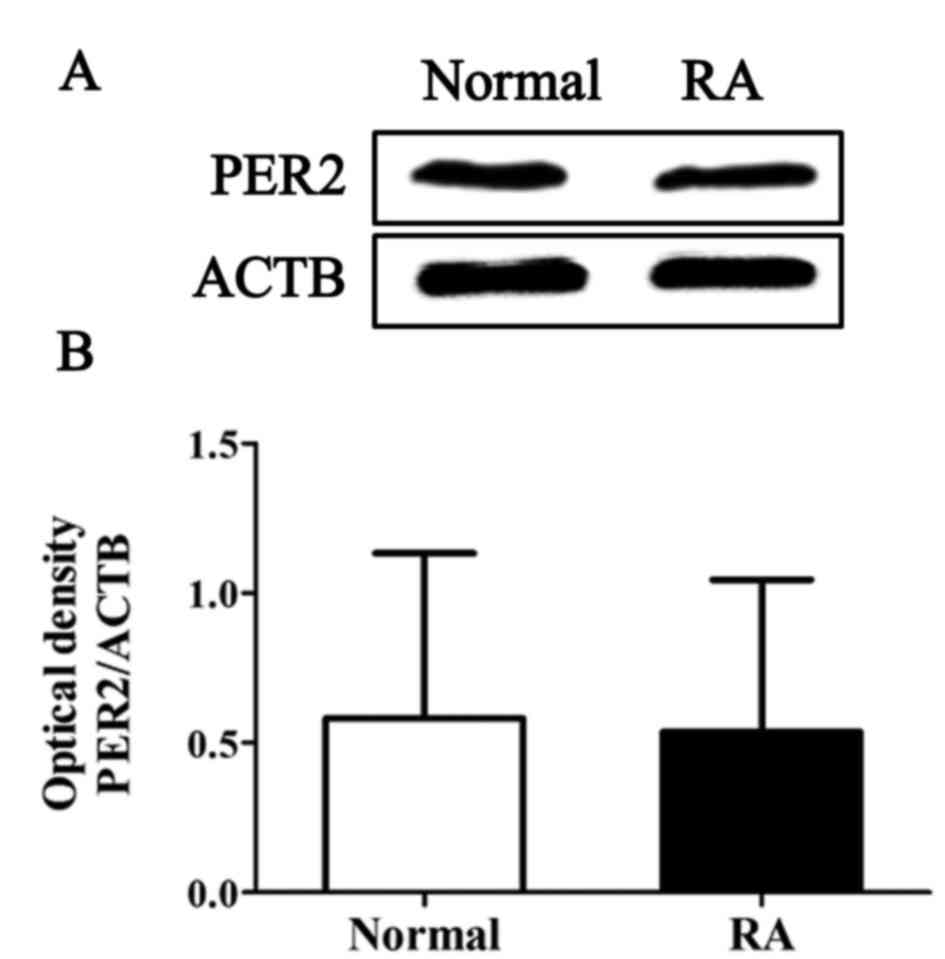
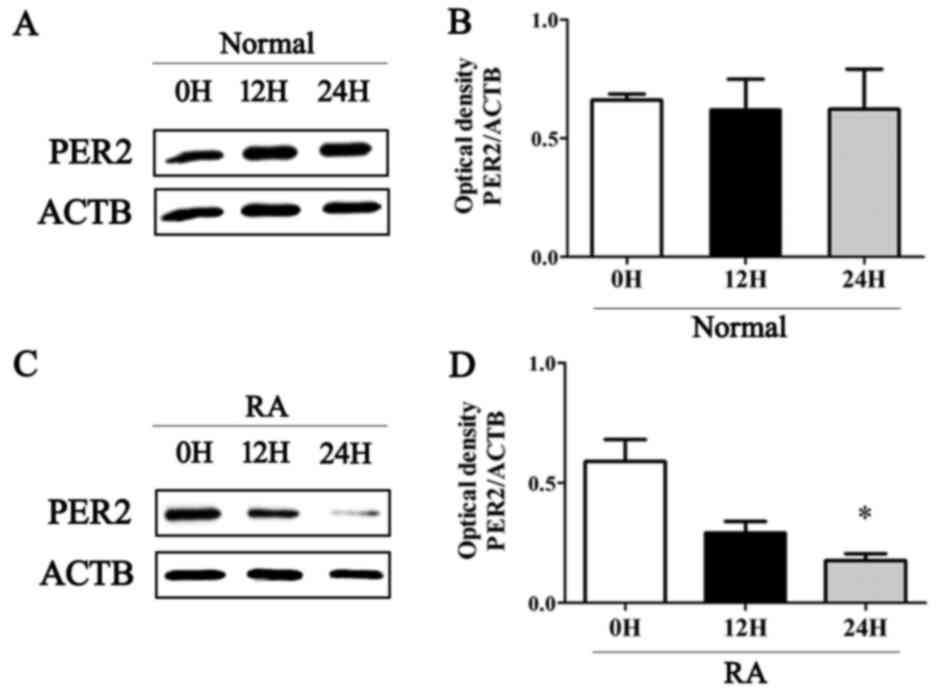
|
1
|
Lee DM and Weinblatt ME: Rheumatoid
arthritis. Lancet. 358:903–911. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Haas S and Straub RH: Disruption of
rhythms of molecular clocks in primary synovial fibroblasts of
patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis, role of
IL-1β/TNF. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:R1222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Straub RH and Cutolo M: Circadian rhythms
in rheumatoid arthritis: Implications for pathophysiology and
therapeutic management. Arthritis Rheum. 56:399–408. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gibbs JE and Ray DW: The role of the
circadian clock in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
15:2052013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Keller M, Mazuch J, Abraham U, Eom GD,
Herzog ED, Volk HD, Kramer A and Maier B: A circadian clock in
macrophages controls inflammatory immune responses. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:21407–21412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Castanon-Cervantes O, Wu M, Ehlen JC, Paul
K, Gamble KL, Johnson RL, Besing RC, Menaker M, Gewirtz AT and
Davidson AJ: Dysregulation of inflammatory responses by chronic
circadian disruption. J Immunol. 185:5796–5805. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coogan AN and Wyse CA: Neuroimmunology of
the circadian clock. Brain Res. 1232:104–112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Segall LA, Perrin JS, Walker CD, Stewart J
and Amir S: Glucocorticoid rhythms control the rhythm of expression
of the clock protein, Period2, in oval nucleus of the bed nucleus
of the stria terminalis and central nucleus of the amygdala in
rats. Neuroscience. 140:753–757. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burioka N, Fukuoka Y, Takata M, Endo M,
Miyata M, Chikumi H, Tomita K, Kodani M, Touge H, Takeda K, et al:
Circadian rhythms in the CNS and peripheral clock disorders:
Function of clock genes: Influence of medication for bronchial
asthma on circadian gene. J Pharmacol Sci. 103:144–149. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Young ME: The circadian clock within the
heart: Potential influence on myocardial gene expression,
metabolism, and function. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
290:H1–H16. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reppert SM and Weaver DR: Coordination of
circadian timing in mammals. Nature. 418:935–941. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roenneberg T and Merrow M: The network of
time: Understanding the molecular circadian system. Curr Biol.
13:R198–R207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dunlap JC: Molecular bases for circadian
clocks. Cell. 96:271–290. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Young MW and Kay SA: Time zones: A
comparative genetics of circadian clocks. Nat Rev Genet. 2:702–715.
2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamamoto T, Nakahata Y, Soma H, Akashi M,
Mamine T and Takumi T: Transcriptional oscillation of canonical
clock genes in mouse peripheral tissues. BMC Mol Biol. 5:182004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vukolic A, Antic V, Van Vliet BN, Yang Z,
Albrecht U and Montani JP: Role of mutation of the circadian clock
gene PER2 in cardiovascular circadian rhythms. Am J Physiol Regul
Integr Comp Physiol. 298:R627–R634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Akashi M, Tsuchiya Y, Yoshino T and
Nishida E: Control of intracellular dynamics of mammalian period
proteins by casein kinase I epsilon (CKIepsilon) and CKIdelta in
cultured cells. Mol Cell Biol. 22:1693–1703. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin X, Shearman LP, Weaver DR, Zylka MJ,
de Vries GJ and Reppert SM: A molecular mechanism regulating
rhythmic output from the suprachiasmatic circadian clock. Cell.
96:57–68. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cavadini G, Petrzilka S, Kohler P, Jud C,
Tobler I, Birchler T and Fontana A: TNF-alpha suppresses the
expression of clock genes by interfering with E-box-mediated
transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:12843–12848. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vanselow K, Vanselow JT, Westermark PO,
Reischl S, Maier B, Korte T, Herrmann A, Herzel H, Schlosser A and
Kramer A: Differential effects of PER2 phosphorylation: Molecular
basis for the human familial advanced sleep phase syndrome (FASPS).
Genes. 20:2660–2672. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dunlap JC, Loros JJ and DeCoursey PT:
Biological timekeeping 1st edition. Sunderland (Massachusetts):
Sinauer Associates, Chronobiology; pp. 4062004
|
|
22
|
Lee C, Etchegaray JP, Cagapang FR, Loudon
AS and Reppert SM: Posttranslational mechanisms regulate the
mammalian circadian clock. Cell. 107:855–867. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reppert SM and Weaver DR: Molecular
analysis of mammalian circadian rhythms. Annu Rev Physiol.
63:647–676. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Toh KL, Jones CR, He Y, Eide EJ, Hinz WA,
Virshup DM, Ptácek LJ and Fu YH: An hPer2 phosphorylation site
mutation in familial advanced sleep phase syndrome. Science.
291:1040–1043. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng B, Larkin DW, Albrecht U, Sun ZS,
Sage M, Eichele G, Lee CC and Bradley A: The mPer2 gene encodes a
functional component of the mammalian circadian clock. Nature.
400:169–173. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bae K, Jin X, Maywood ES, Hastings MH,
Reppert SM and Weaver DR: Differential functions of mPer1, mPer2,
and mPer3 in the SCN circadian clock. Neuron. 30:525–536. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mottonen T, Hannonen P, Leirisalo-Repo M,
Nissilä M, Kautiainen H, Korpela M, Laasonen L, Julkunen H,
Luukkainen R, Vuori K, et al: Comparison of combination therapy
with single-drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: A
randomised trial. FIN-RACo trial group. Lancet. 353:1568–1573.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moreland LW, Baumgartner SW, Schiff MH,
Tindall EA, Fleischmann RM, Weaver AL, Ettlinger RE, Cohen S,
Koopman WJ, Mohler K, et al: Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with
a recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75)-Fc fusion
protein. N Engl J Med. 337:141–147. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nader N, Chrousos GP and Kino T:
Interactions of the circadian CLOCK system and the HPA axis. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 21:277–286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kowanko IC, Knapp MS, Pownall R and
Swannell AJ: Domiciliary self-measurement in the rheumatoid
arthritis and the demonstration of circadian rhythmicity. Ann Rheum
Dis. 41:453–455. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cutolo M and Straub RH: Circadian rhythms
in arthritis: Hormonal effects on the immune/inflammatory reaction.
Autoimmu Rev. 7:223–228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane
DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS,
et al: The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria
for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
31:315–324. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Forbes EE, Dahl RE, Almeida JR, Ferrell
RE, Nimgaonkar VL, Mansour H, Sciarrillo SR, Holm SM, Rodriguez EE
and Phillips ML: PER2 rs2304672 polymorphism moderates
circadian-relevant reward circuitry activity in adolescents. Biol
Psychiatry. 71:451–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee HJ, Kim L, Kang SG, Yoon HK, Choi JE,
Park YM, Kim SJ and Kripke DF: PER2 variation is associated with
diurnal preference in a Korean young population. Behav Genet.
41:273–277. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim HK, Lee WY, Kwon JT, Sohn DR, Hong SJ
and Kim HJ: Association of ultraviolet radiation
resistance-associated gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis.
Biomed Rep. 2:117–121. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kwak Y, Lundkvist GB, Brask J, Davidson A,
Menaker M, Kristensson K and Block GD: Interferon-gamma alters
electrical activity and clock gene expression in suprachiasmatic
nucleus neurons. J Biol Rhythms. 23:150–159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Davis MC, Zautra AJ, Younger J, Motivala
SJ, Attrep J and Irwin MR: Chronic stress and regulation of
cellular markers of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis:
Implications for fatigue. Brain Behav Immun. 22:24–32. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Takane H, Ohdo S, Baba R, Koyanagi S,
Yukawa E and Higuchi S: Relationship between 24-hour rhythm in
antiviral effect of interferon-beta and interferon-alpha/beta
receptor expression in mice. Jpn J Pharmacol. 90:304–312. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hayashi M, Shimba S and Tezuka M:
Characterization of the molecular clock in mouse peritoneal
macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:621–626. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arjona A and Sarkar DK: The circadian gene
mPer2 regulates the daily rhythm of IFN-gamma. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 26:645–649. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu J, Malkani G, Shi X, Meyer M,
Cunningham-Runddles S, Ma X and Sun ZS: The circadian clock Period
2 gene regulates gamma interferon production of NK cells in host
response to lipopolysaccharide-induced endotoxic shock. Infect
Immun. 74:4750–4756. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Keller M, Mazuch J, Abraham U, Eom GD,
Herzog ED, Volk HD, Kramer A and Maier B: A circadian clock in
macrophages controls inflammatory immune responses. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:21407–21412. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hashiramoto A, Yamane T, Tsumiyama K,
Yoshida K, Komai K, Yamada H, Yamazaki F, Doi M, Okamura H and
Shiozawa S: Mammalian clock gene Cryptochrome regulates arthritis
via proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 184:1560–1565.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yoshida K, Hashimoto T, Sakai Y and
Hashiramoto A: Involvement of the circadian rhythm and inflammatory
cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol
Res. 2014:2824952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|