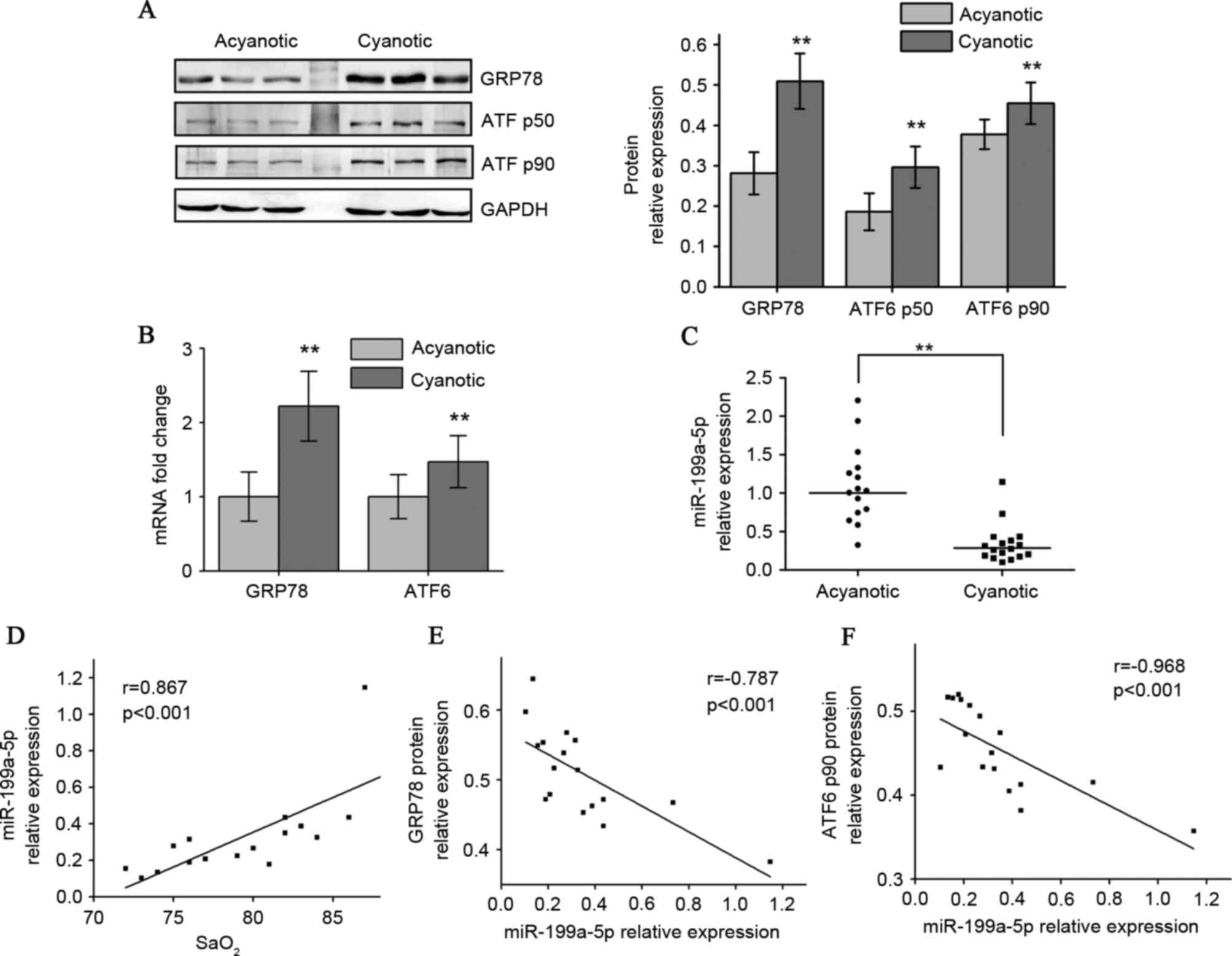
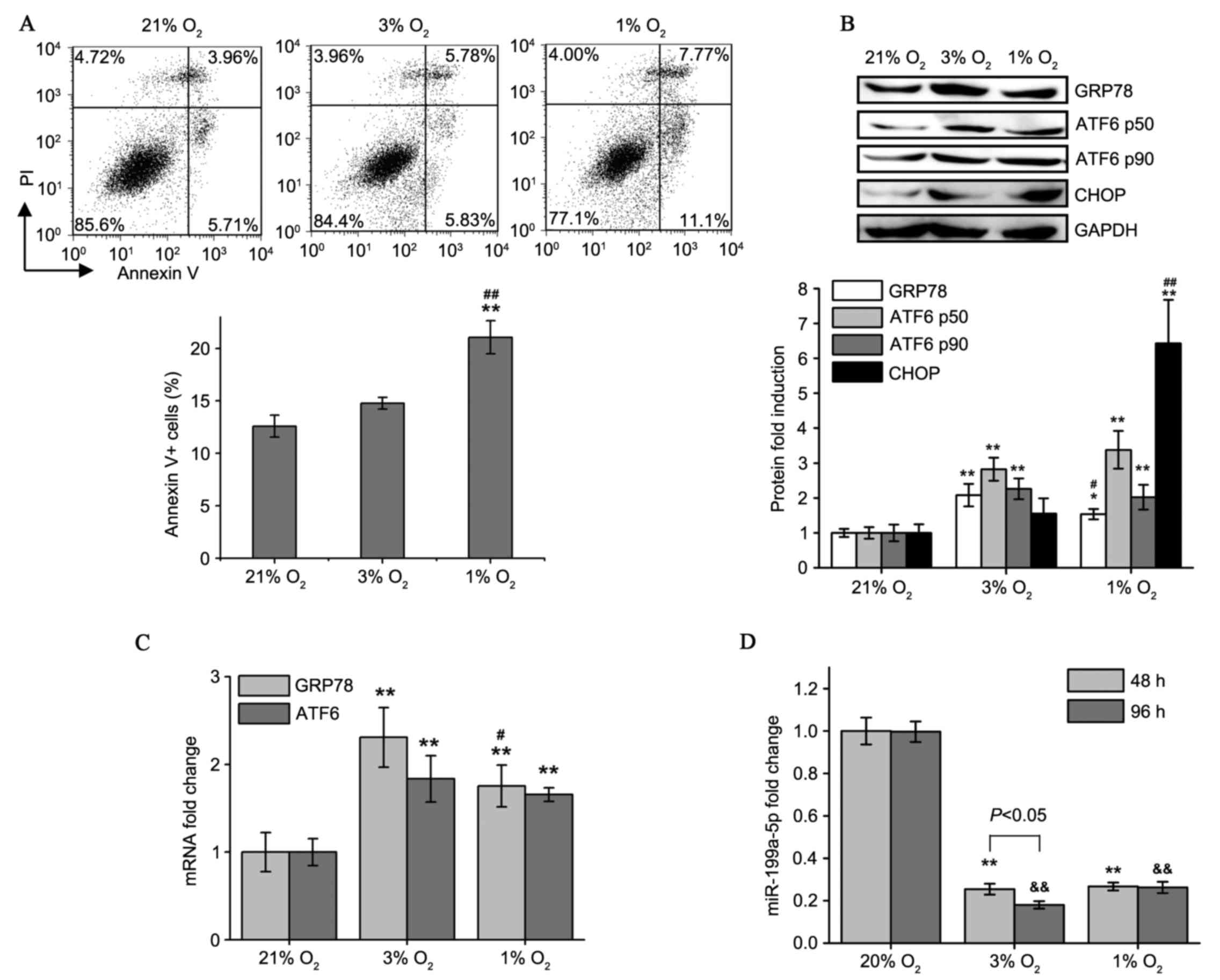
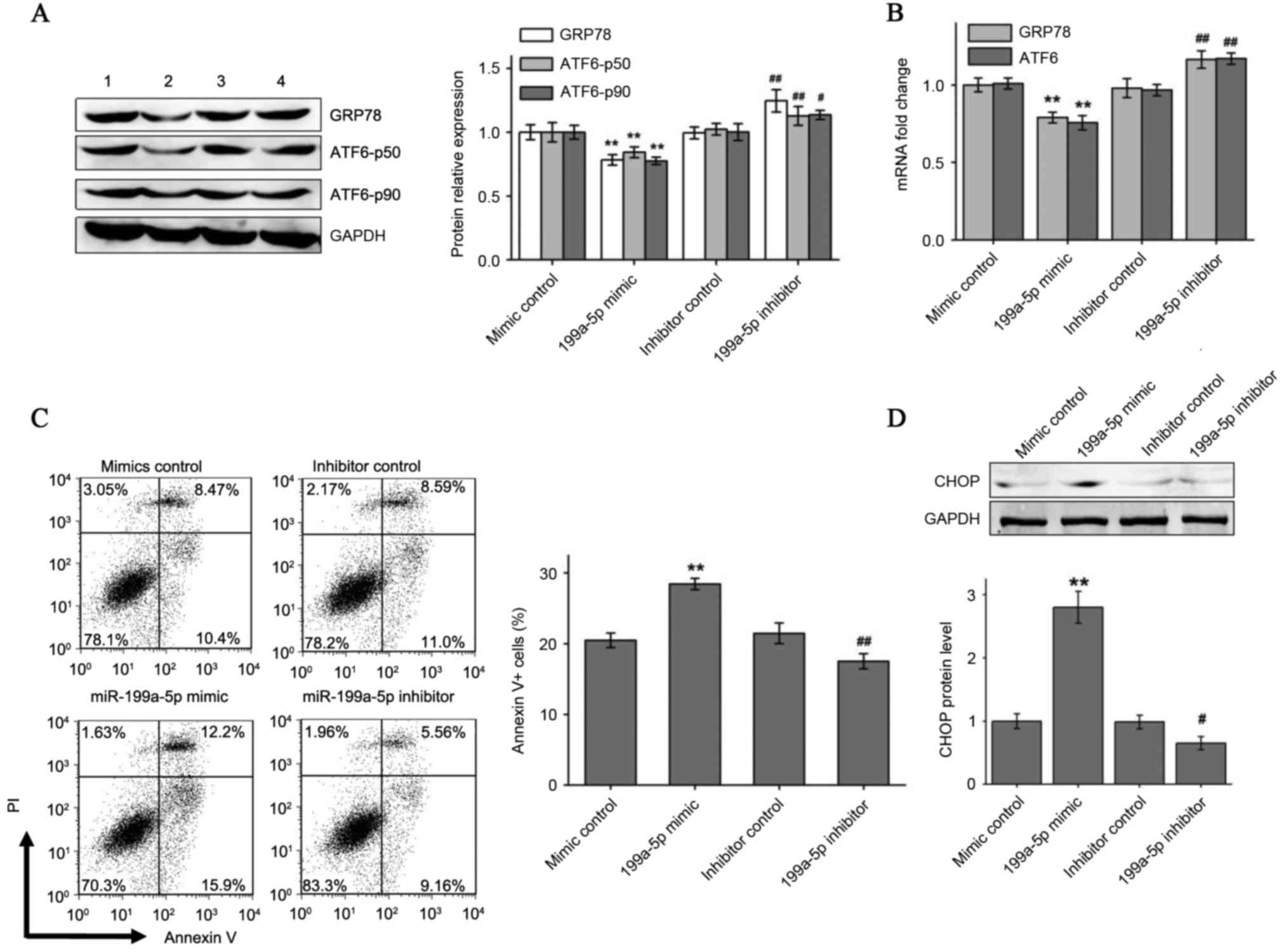
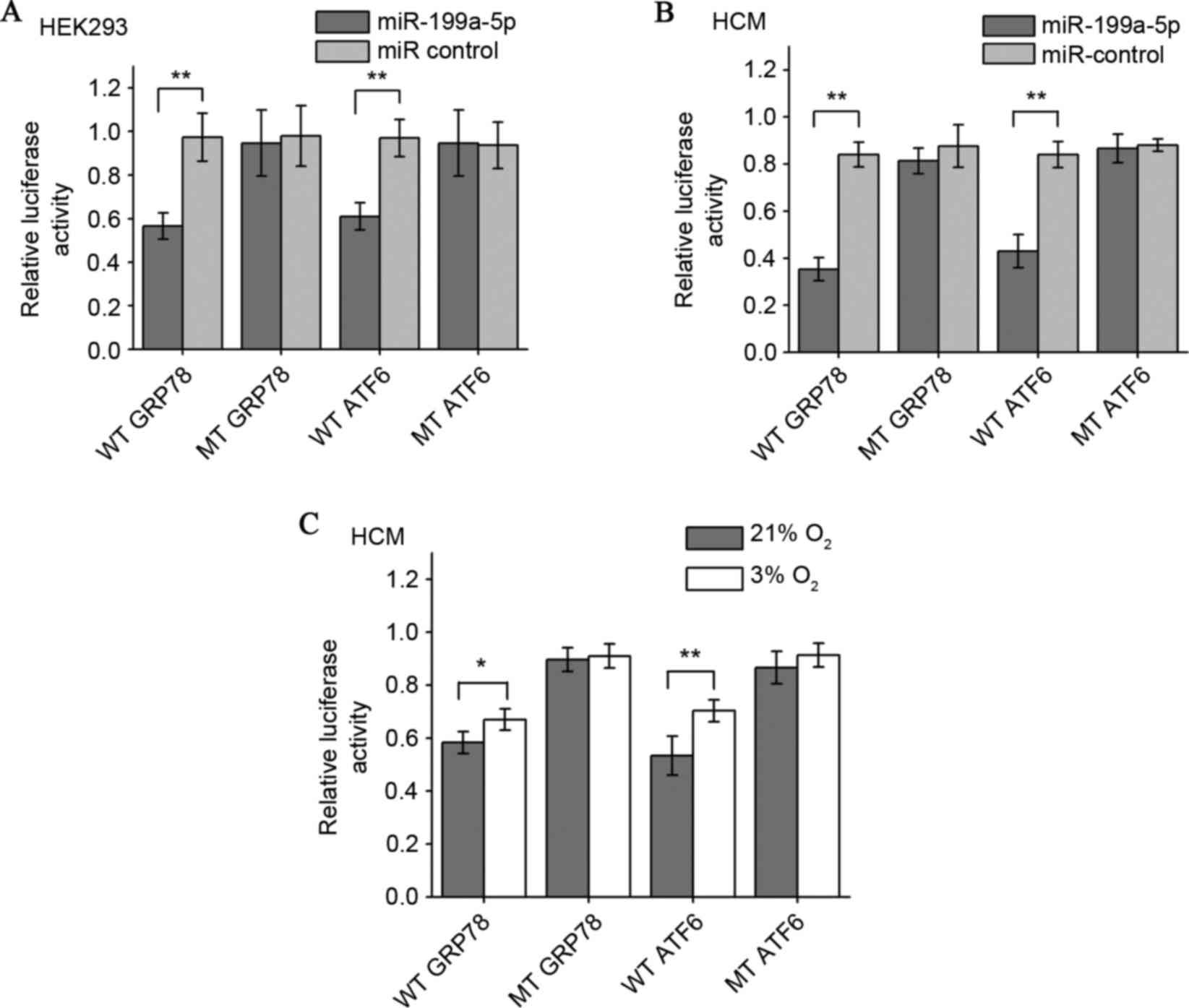
|
1
|
van der Bom T, Zomer AC, Zwinderman AH,
Meijboom FJ, Bouma BJ and Mulder BJ: The changing epidemiology of
congenital heart disease. Nat Rev Cardiol. 8:50–60. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miyague NI, Cardoso SM, Meyer F, Ultramari
FT, Araújo FH, Rozkowisk I and Toschi AP: Epidemiological study of
congenital heart defects in children and adolescents. Analysis of
4,538 cases. Arq Bras Cardiol. 80:269–278. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oechslin E: Management of adults with
cyanotic congenital heart disease. Heart. 101:485–494. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lou Y, Wang Z, Xu Y, Zhou P, Cao J, Li Y,
Chen Y, Sun J and Fu L: Resveratrol prevents doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity in H9c2 cells through the inhibition of endoplasmic
reticulum stress and the activation of the Sirt1 pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 36:873–880. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schönenberger MJ and Kovacs WJ: Hypoxia
signaling pathways: Modulators of oxygen-related organelles. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 3:422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu XL and Gao DS: Endoplasmic reticulum
proteins quality control and the unfolded protein response: The
regulative mechanism of organisms against stress injuries.
Biofactors. 40:569–585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jian Z, Li JB, Ma RY, Chen L, Wang XF and
Xiao YB: Pivotal role of activating transcription factor 6α in
myocardial adaptation to chronic hypoxia. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:972–979. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Glembotski CC: Roles for ATF6 and the
sarco/endoplasmic reticulum protein quality control system in the
heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 71:11–15. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thuerauf DJ, Marcinko M, Gude N, Rubio M,
Sussman MA and Glembotski CC: Activation of the unfolded protein
response in infarcted mouse heart and hypoxic cultured cardiac
myocytes. Circ Res. 99:275–282. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou J, Dong X, Zhou Q, Wang H, Qian Y,
Tian W, Ma D and Li X: microRNA expression profiling of heart
tissue during fetal development. Int J Mol Med. 33:1250–1260.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Azzouzi HE, Leptidis S, Doevendans PA and
De Windt LJ: HypoxamiRs: Regulators of cardiac hypoxia and energy
metabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 26:502–508. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maurel M and Chevet E: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress signaling: The microRNA connection. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 304:C1117–C1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Topkara VK and Mann DL: Role of microRNAs
in cardiac remodeling and heart failure. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.
25:171–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee DS, Chen JH, Lundy DJ, Liu CH, Hwang
SM, Pabon L, Shieh RC, Chen CC, Wu SN, Yan YT, et al: Defined
MicroRNAs induce aspects of maturation in mouse and human
embryonic-stem-cell-derived cardiomyocytes. Cell Rep. 12:1960–1967.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song XW, Li Q, Lin L, Wang XC, Li DF, Wang
GK, Ren AJ, Wang YR, Qin YW, Yuan WJ and Jing Q: MicroRNAs are
dynamically regulated in hypertrophic hearts, and miR-199a is
essential for the maintenance of cell size in cardiomyocytes. J
Cell Physiol. 225:437–443. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xing Y, Liu Z, Yang G, Gao D and Niu X:
MicroRNA expression profiles in rats with selenium deficiency and
the possible role of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in cardiac
dysfunction. Int J Mol Med. 35:143–152. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ding G, Huang G, Liu HD, Liang HX, Ni YF,
Ding ZH, Ni GY and Hua HW: MiR-199a suppresses the hypoxia-induced
proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells through targeting
HIF1α. Mol Cell Biochem. 384:173–180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rane S, He M, Sayed D, Vashistha H,
Malhotra A, Sadoshima J, Vatner DE, Vatner SF and Abdellatif M:
Downregulation of miR-199a derepresses hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha and Sirtuin 1 and recapitulates hypoxia
preconditioning in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res. 104:879–886. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Su SF, Chang YW, Andreu-Vieyra C, Fang JY,
Yang Z, Han B, Lee AS and Liang G: miR-30d, miR-181a and
miR-199a-5p cooperatively suppress the endoplasmic reticulum
chaperone and signaling regulator GRP78 in cancer. Oncogene.
32:4694–4701. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hassan T, Carroll TP, Buckley PG, Cummins
R, O'Neill SJ, McElvaney NG and Greene CM: miR-199a-5p silencing
regulates the unfolded protein response in chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease and α1-antitrypsin deficiency. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 189:263–273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang Y, Ridzon D, Wong L and Chen C:
Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal human
tissues. BMC Genomics. 8:1662007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nam JW, Rissland OS, Koppstein D,
Abreu-Goodger C, Jan CH, Agarwal V, Yildirim MA, Rodriguez A and
Bartel DP: Global analyses of the effect of different cellular
contexts on microRNA targeting. Mol Cell. 53:1031–1043. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dai BH, Geng L, Wang Y, Sui CJ, Xie F,
Shen RX, Shen WF and Yang JM: microRNA-199a-5p protects hepatocytes
from bile acid-induced sustained endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e6042013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Namba T, Ishihara T, Tanaka K, Hoshino T
and Mizushima T: Transcriptional activation of ATF6 by endoplasmic
reticulum stressors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 355:543–548. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chang SC, Erwin AE and Lee AS:
Glucose-regulated protein (GRP94 and GRP78) genes share common
regulatory domains and are coordinately regulated by common
trans-acting factors. Mol Cell Biol. 9:2153–2162. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dai L, Lou W, Zhu J, Zhou X and Di W:
miR-199a inhibits the angiogenic potential of endometrial stromal
cells under hypoxia by targeting HIF-1α/VEGF pathway. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:4735–4744. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo H, Ingolia NT, Weissman JS and Bartel
DP: Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA
levels. Nature. 466:835–840. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nallamshetty S, Chan SY and Loscalzo J:
Hypoxia: A master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity.
Free Radic Biol Med. 64:20–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Haghikia A, Missol-Kolka E, Tsikas D,
Venturini L, Brundiers S, Castoldi M, Muckenthaler MU, Eder M,
Stapel B, Thum T, et al: Signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3-mediated regulation of miR-199a-5p links
cardiomyocyte and endothelial cell function in the heart: A key
role for ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes. Eur Heart J. 32:1287–1297.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gu Q, Kong Y, Yu ZB, Bai L and Xiao YB:
Hypoxia-induced SOCS3 is limiting STAT3 phosphorylation and NF-κB
activation in congenital heart disease. Biochimie. 93:909–920.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|