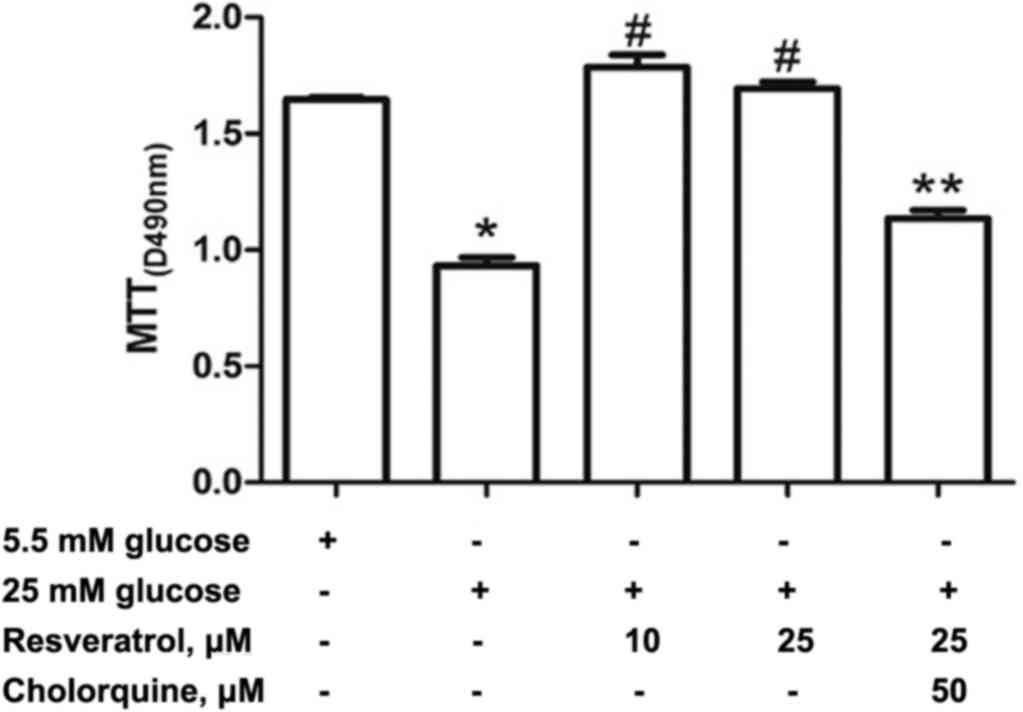
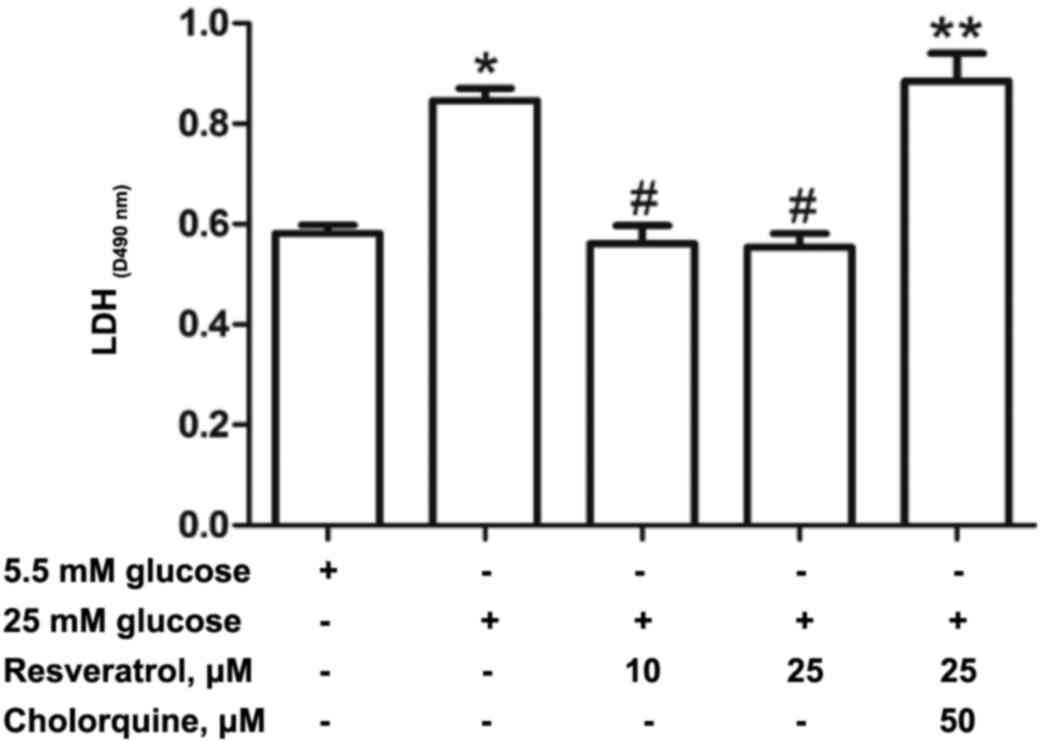
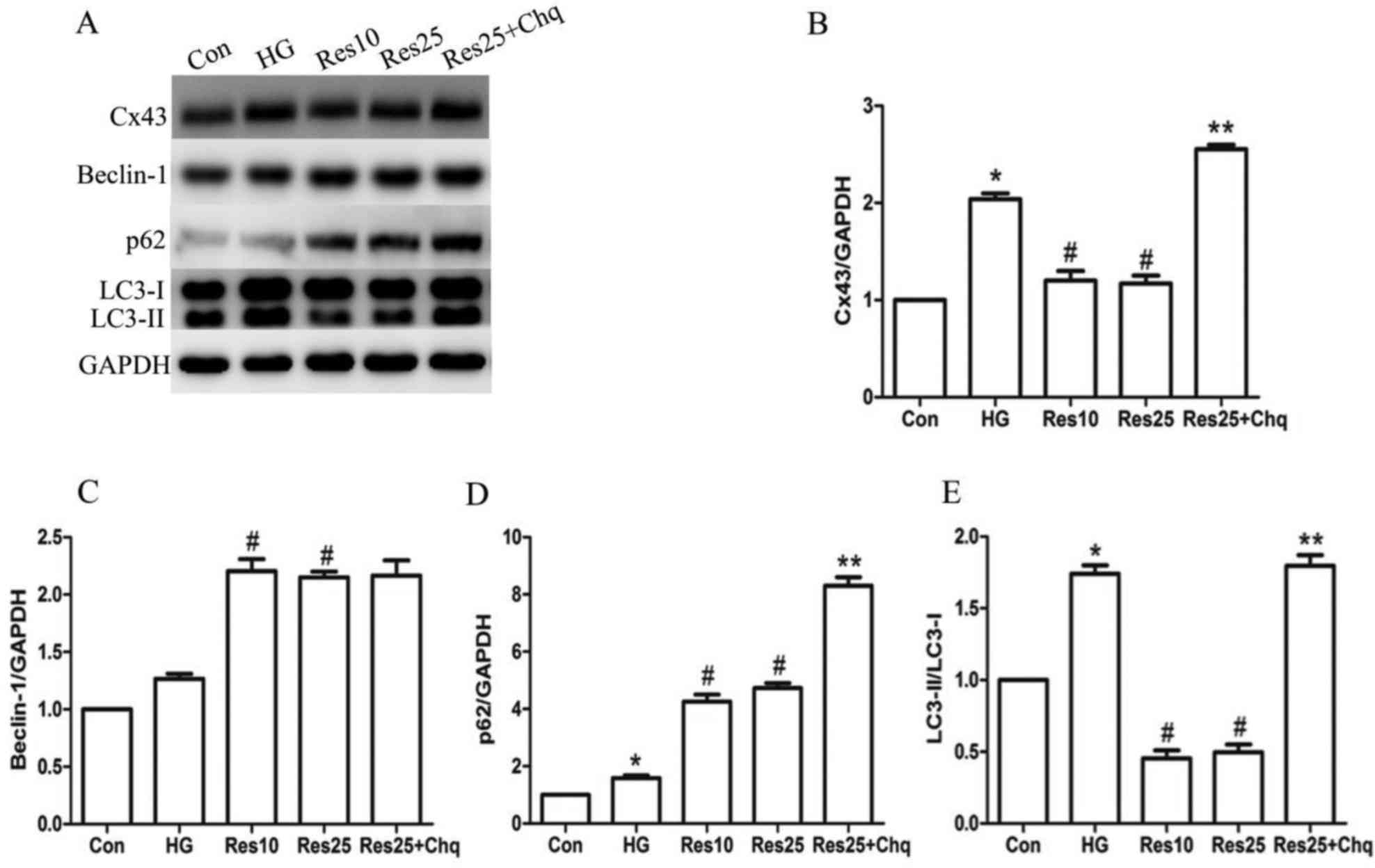
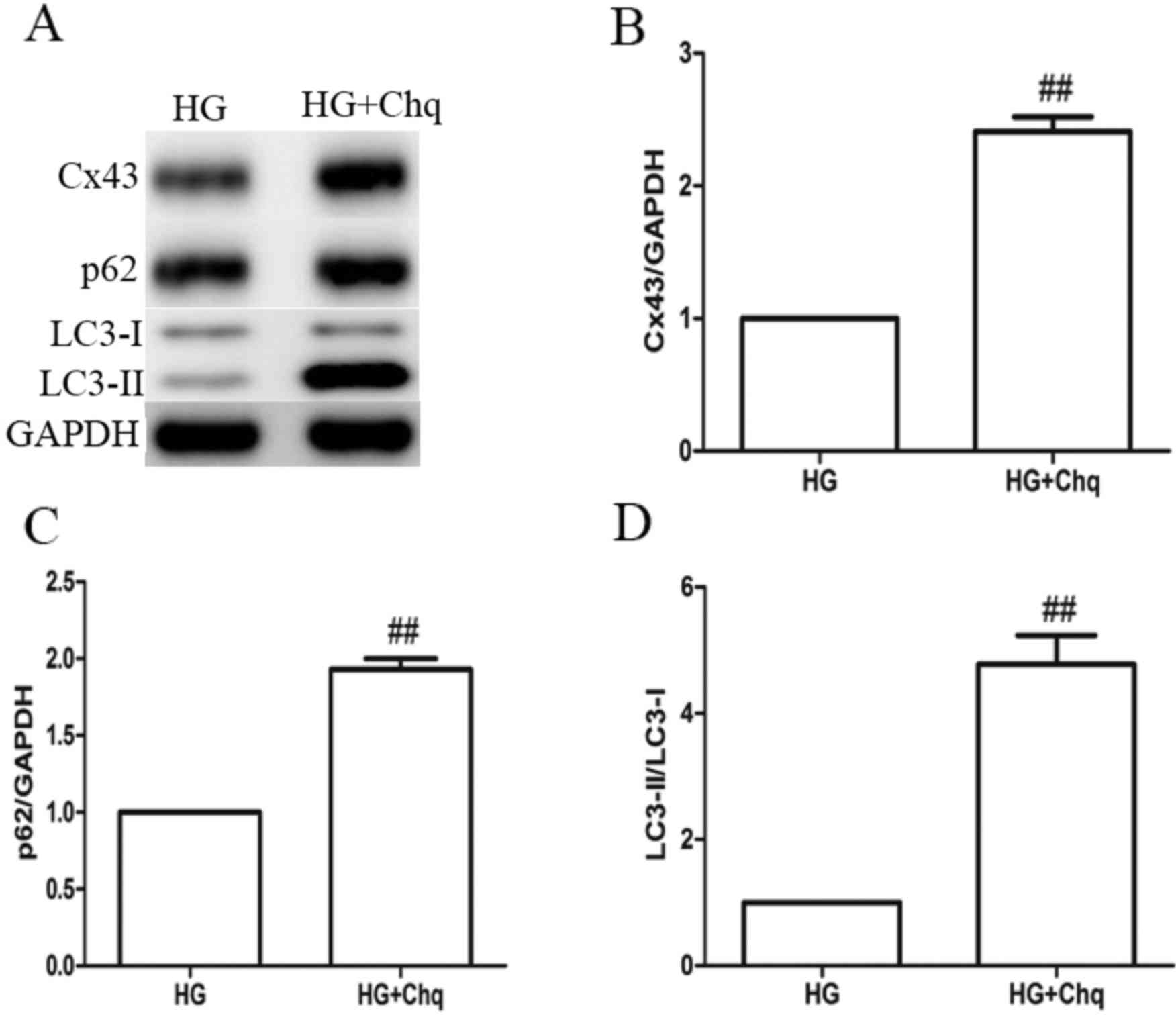
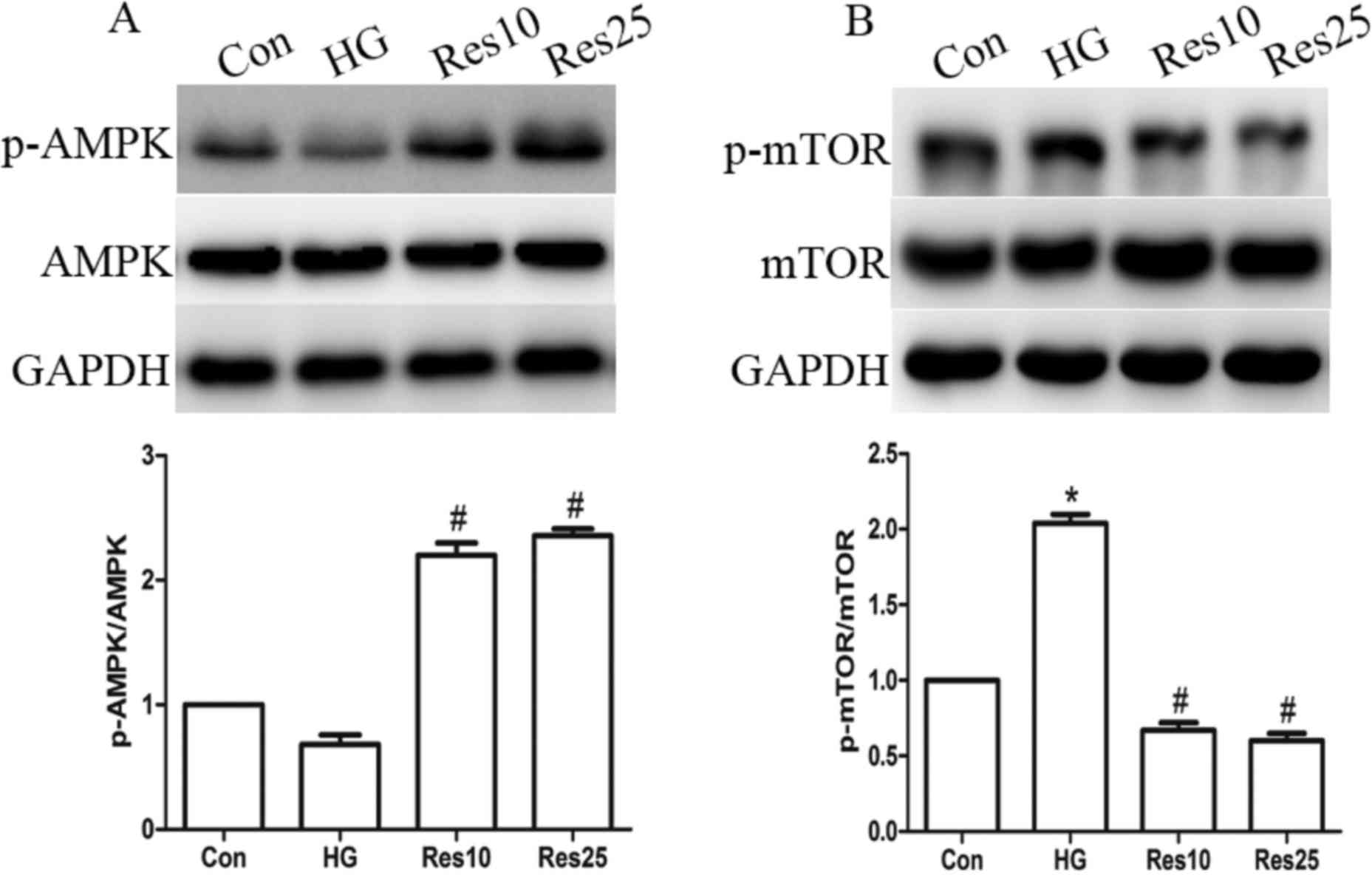
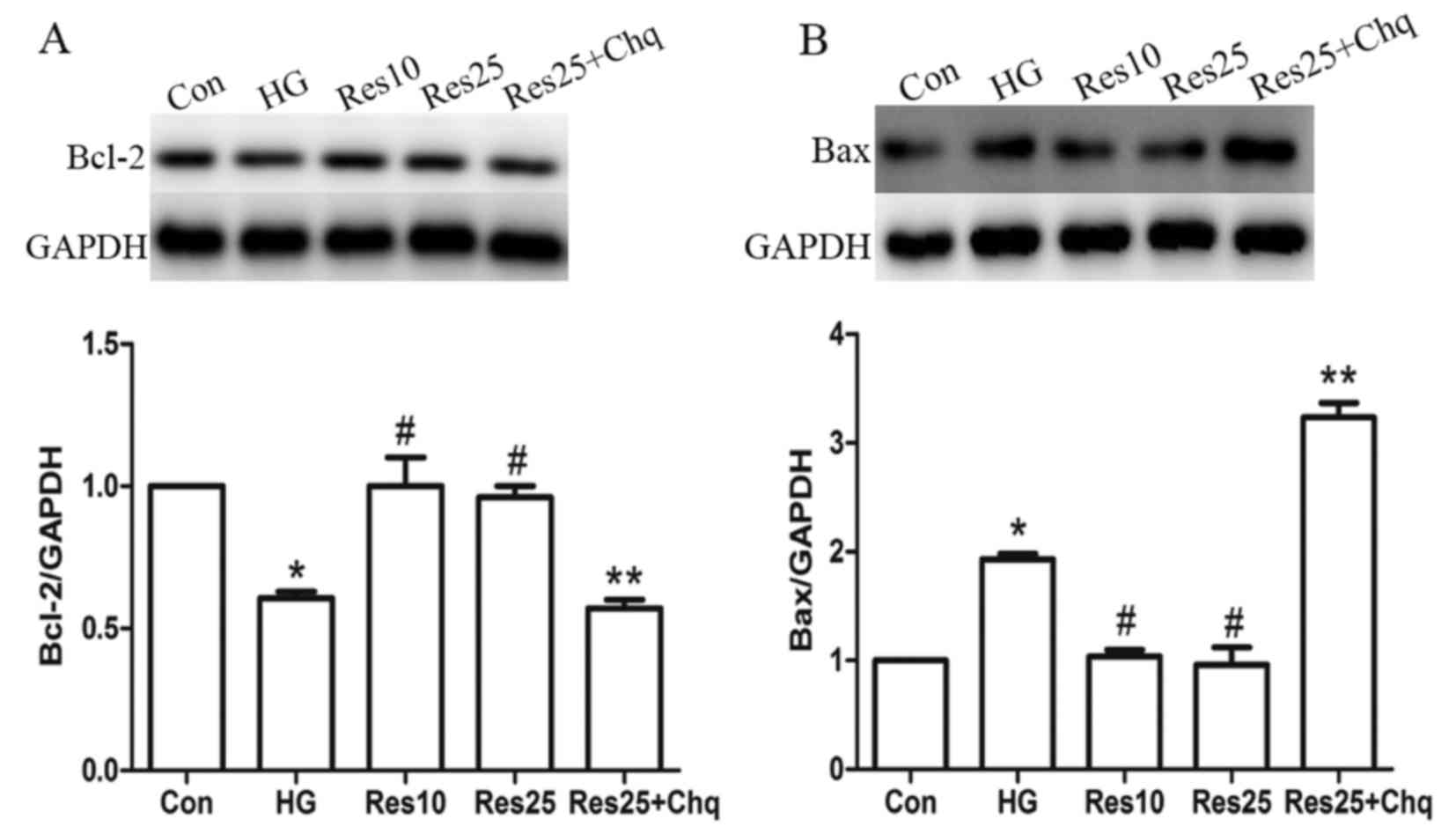
|
1
|
He C, Zhu H, Li H, Zou MH and Xie Z:
Dissociation of Bcl-2-Beclin1 complex by activated AMPK enhances
cardiac autophagy and protects against cardiomyocyte apoptosis in
diabetes. Diabetes. 62:1270–1281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie Z, Lau K, Eby B, Lozano P, He C,
Pennington B, Li H, Rathi S, Dong Y, Tian R, et al: Improvement of
cardiac functions by chronic metformin treatment is associated with
enhanced cardiac autophagy in diabetic OVE26 mice. Diabetes.
60:1770–1778. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martins-Marques T, Catarino S, Marques C,
Pereira P and Girão H: To beat or not to beat: Degradation of Cx43
imposes the heart rhythm. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:476–481. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rohr S: Role of gap junctions in the
propagation of the cardiac action potential. Cardiovasc Res.
62:309–322. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vozzi C, Dupont E, Coppen SR, Yeh HI and
Severs NJ: Chamber-related differences in connexin expression in
the human heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 31:991–1003. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou P, Zhang SM, Wang QL, Wu Q, Chen M
and Pei JM: Anti-arrhythmic effect of verapamil is accompanied by
preservation of cx43 protein in rat heart. PLoS One. 8:e715672013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rutledge CA, Ng FS, Sulkin MS, Greener ID,
Sergeyenko AM, Liu H, Gemel J, Beyer EC, Sovari AA, Efimov IR and
Dudley SC: c-Src kinase inhibition reduces arrhythmia inducibility
and connexin43 dysregulation after myocardial infarction. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 63:928–934. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hesketh GG, Shah MH, Halperin VL, Cooke
CA, Akar FG, Yen TE, Kass DA, Machamer CE, Van Eyk JE and Tomaselli
GF: Ultrastructure and regulation of lateralized connexin43 in the
failing heart. Circ Res. 106:1153–1163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang W, Zhao G, Hu X, Wang M, Li H, Ye Y,
Du Q, Yao J, Bao Z, Hong W, et al: Aliskiren-attenuated myocardium
apoptosis via regulation of autophagy and connexin-43 in aged
spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1247–1256.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lin H, Ogawa K, Imanaga I and Tribulova N:
Remodeling of connexin 43 in the diabetic rat heart. Mol Cell
Biochem. 290:69–78. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Howarth FC, Nowotny N, Zilahi E, El Haj MA
and Lei M: Altered expression of gap junction connexin proteins may
partly underlie heart rhythm disturbances in the
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rat heart. Mol Cell Biochem.
305:145–151. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Howarth FC, Chandler NJ, Kharche S, Tellez
JO, Greener ID, Yamanushi TT, Billeter R, Boyett MR, Zhang H and
Dobrzynski H: Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on
connexin43 mRNA and protein expression in ventricular muscle. Mol
Cell Biochem. 319:105–114. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fong JT, Kells RM, Gumpert AM, Marzillier
JY, Davidson MW and Falk MM: Internalized gap junctions are
degraded by autophagy. Autophagy. 8:794–811. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martins-Marques T, Catarino S, Zuzarte M,
Marques C, Matafome P, Pereira P and Girão H: Ischaemia-induced
autophagy leads to degradation of gap junction protein connexin43
in cardiomyocytes. Biochem J. 467:231–245. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei H, Liu L and Chen Q: Selective removal
of mitochondria via mitophagy: Distinct pathways for different
mitochondrial stresses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:2784–2790. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Matsui Y, Takagi H, Qu X, Abdellatif M,
Sakoda H, Asano T, Levine B and Sadoshima J: Distinct roles of
autophagy in the heart during ischemia and reperfusion: Roles of
AMP-activated protein kinase and Beclin 1 in mediating autophagy.
Circ Res. 100:914–922. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lichtenstein A, Minogue PJ, Beyer EC and
Berthoud VM: Autophagy: A pathway that contributes to connexin
degradation. J Cell Sci. 124:910–920. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Tsujimoto
A, Mikami A, Ogino A, Watanabe T, Morishita K, Okada H, Kawasaki M,
et al: Autophagic adaptations in diabetic cardiomyopathy differ
between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Autophagy. 11:1146–1160. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Palanivel R, Rai E, Park M, Gabor
TV, Scheid MP, Xu A and Sweeney G: Adiponectin stimulates autophagy
and reduces oxidative stress to enhance insulin sensitivity during
high-fat diet feeding in mice. Diabetes. 64:36–48. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang B, Yang Q, Sun YY, Xing YF, Wang YB,
Lu XT, Bai WW, Liu XQ and Zhao YX: Resveratrol-enhanced autophagic
flux ameliorates myocardial oxidative stress injury in diabetic
mice. J Cell Mol Med. 18:1599–1611. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gurusamy N, Lekli I, Mukherjee S, Ray D,
Ahsan MK, Gherghiceanu M, Popescu LM and Das DK: Cardioprotection
by resveratrol: A novel mechanism via autophagy involving the
mTORC2 pathway. Cardiovasc Res. 86:103–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kanamori H, Takemura G, Goto K, Tsujimoto
A, Ogino A, Takeyama T, Kawaguchi T, Watanabe T, Morishita K,
Kawasaki M, et al: Resveratrol reverses remodeling in hearts with
large, old myocardial infarctions through enhanced
autophagy-activating AMP kinase pathway. Am J Pathol. 182:701–713.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo R and Ren J: Deficiency in AMPK
attenuates ethanol-induced cardiac contractile dysfunction through
inhibition of autophagosome formation. Cardiovasc Res. 94:480–491.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A,
Bruun JA, Outzen H, Øvervatn A, Bjørkøy G and Johansen T:
p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of
ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem.
282:24131–24145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Arozena A Acevedo, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD,
Adeli K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays
for monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang R, Liu YY, Liu XY, Jia SW, Zhao J,
Cui D and Wang L: Resveratrol protects neurons and the myocardium
by reducing oxidative stress and ameliorating mitochondria damage
in a cerebral ischemia rat model. Cell Physiol Biochem. 34:854–864.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vilar S, Quezada E, Santana L, Uriarte E,
Yánez M, Fraiz N, Alcaide C, Cano E and Orallo F: Design,
synthesis, and vasorelaxant and platelet antiaggregatory activities
of coumarin-resveratrol hybrids. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 16:257–261.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu PL, Chong IW, Lee YC, Tsai JR, Wang
HM, Hsieh CC, Kuo HF, Liu WL, Chen YH and Chen HL:
Anti-inflammatory effects of resveratrol on
Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-induced alveolar epithelial cell dysfunction.
J Agric Food Chem. 63:9480–9487. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ghaly HA, Boyle PM, Vigmond EJ, Shimoni Y
and Nygren A: Simulations of reduced conduction reserve in the
diabetic rat heart: Response to uncoupling and reduced
excitability. Ann Biomed Eng. 38:1415–1425. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Okruhlicova L, Tribulova N, Misejkova M,
Kucka M, Stetka R, Slezak J and Manoach M: Gap junction remodelling
is involved in the susceptibility of diabetic rats to
hypokalemia-induced ventricular fibrillation. Acta Histochem.
104:387–391. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Santos-Almeida FM, Girão H, da Silva CA,
Salgado HC and Fazan R Jr: Cholinergic stimulation with
pyridostigmine protects myocardial infarcted rats against
ischemic-induced arrhythmias and preserves connexin43 protein. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 308:H101–H107. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Greener ID, Sasano T, Wan X, Igarashi T,
Strom M, Rosenbaum DS and Donahue JK: Connexin43 gene transfer
reduces ventricular tachycardia susceptibility after myocardial
infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 60:1103–1110. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fernandes R, Girão H and Pereira P: High
glucose down-regulates intercellular communication in retinal
endothelial cells by enhancing degradation of connexin 43 by a
proteasome-dependent mechanism. J Biol Chem. 279:27219–27224. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu L, Zhao Y, Fan Y, Wang M, Xu S and Fu
G: Epigallocatechin-3 gallate, a green tea catechin, attenuated the
downregulation of the cardiac gap junction induced by high glucose
in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Cell physiol Biochem. 26:403–412.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kanno S, Kovacs A, Yamada KA and Saffitz
JE: Connexin43 as a determinant of myocardial infarct size
following coronary occlusion in mice. J Am Coll Cardiol.
41:681–686. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Colosetti P, Puissant A, Robert G, Luciano
F, Jacquel A, Gounon P, Cassuto JP and Auberger P: Autophagy is an
important event for megakaryocytic differentiation of the chronic
myelogenous leukemia K562 cell line. Autophagy. 5:1092–1098. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng Q, Su H, Ranek MJ and Wang X:
Autophagy and p62 in cardiac proteinopathy. Circ Res. 109:296–308.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|