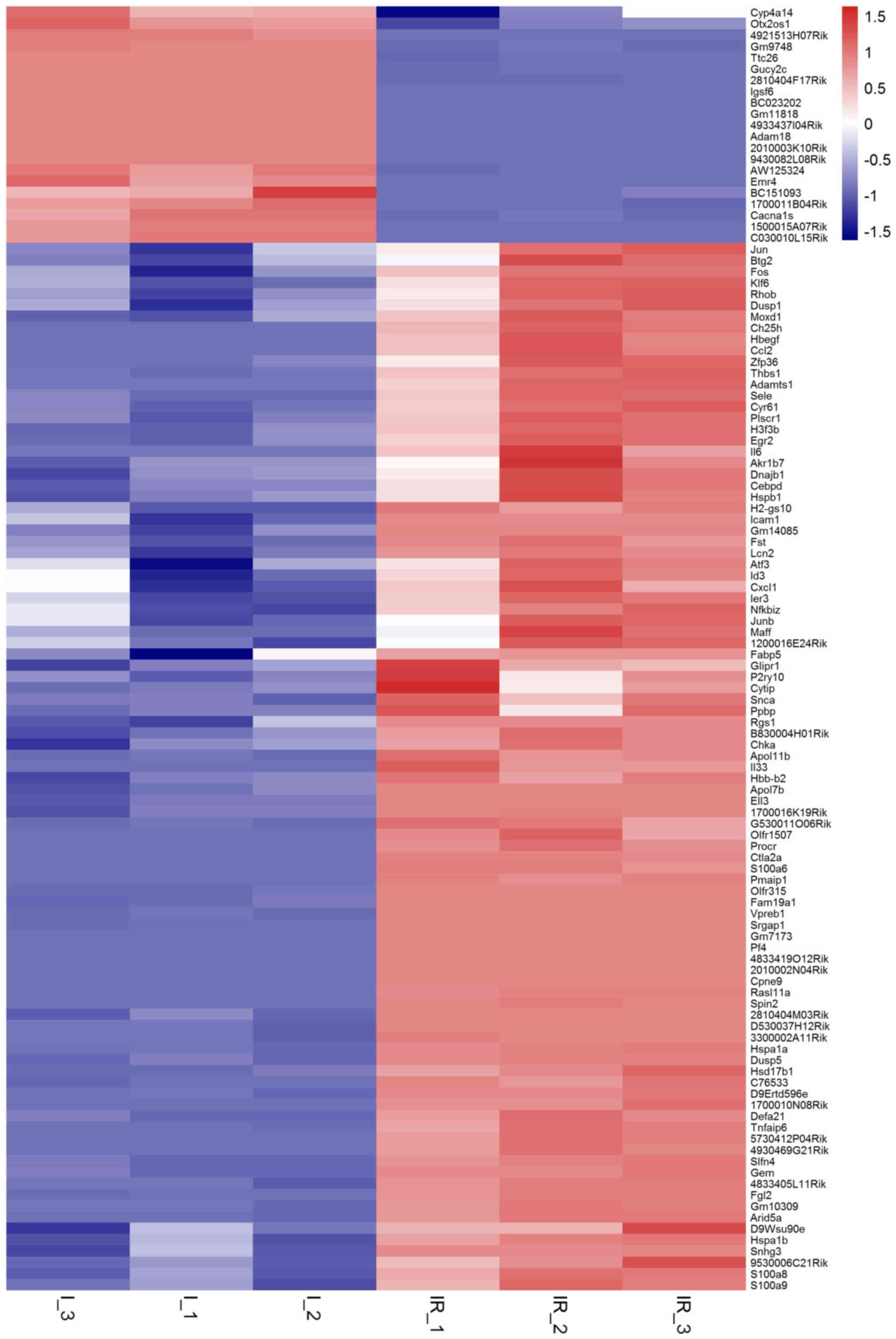
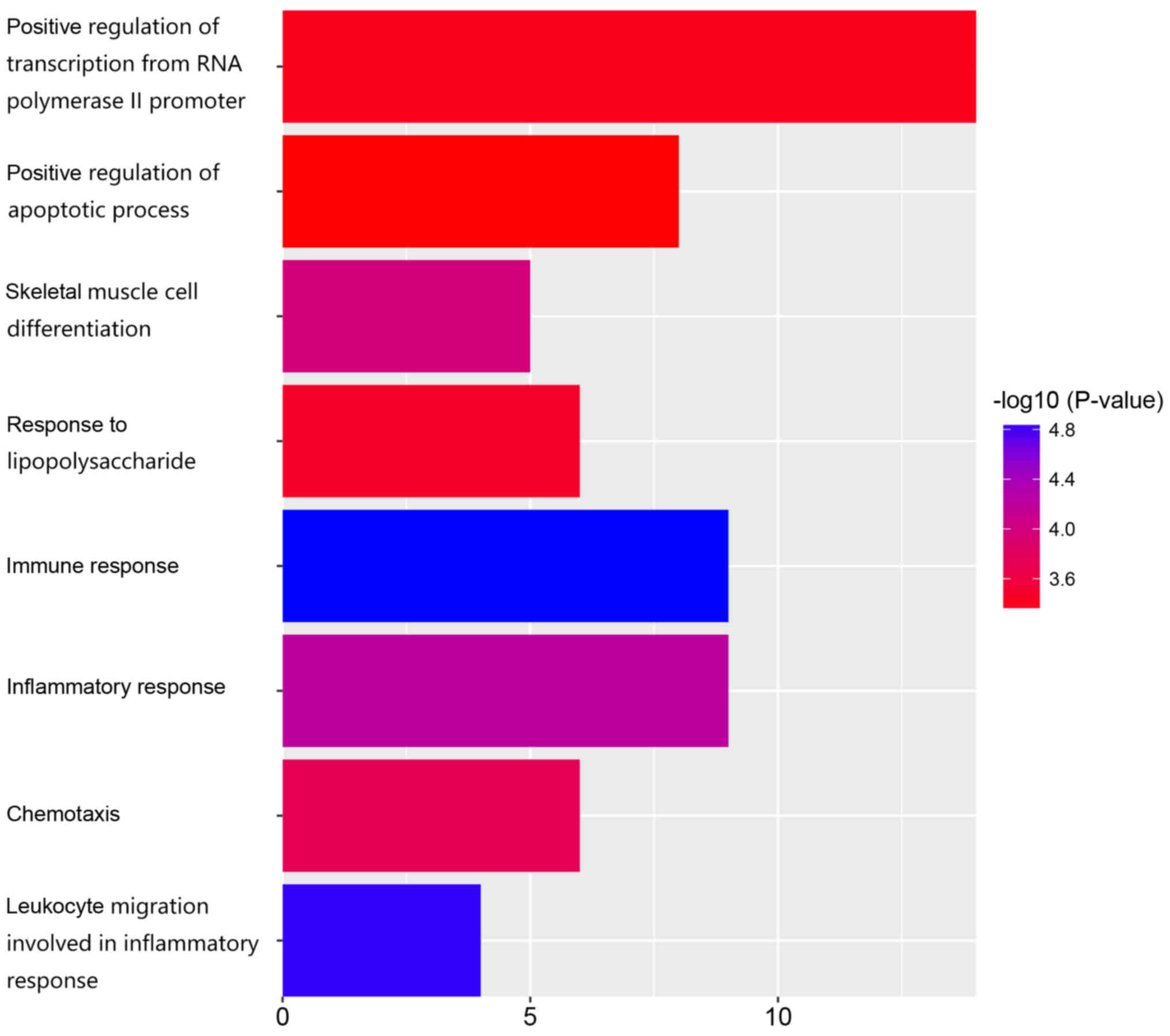
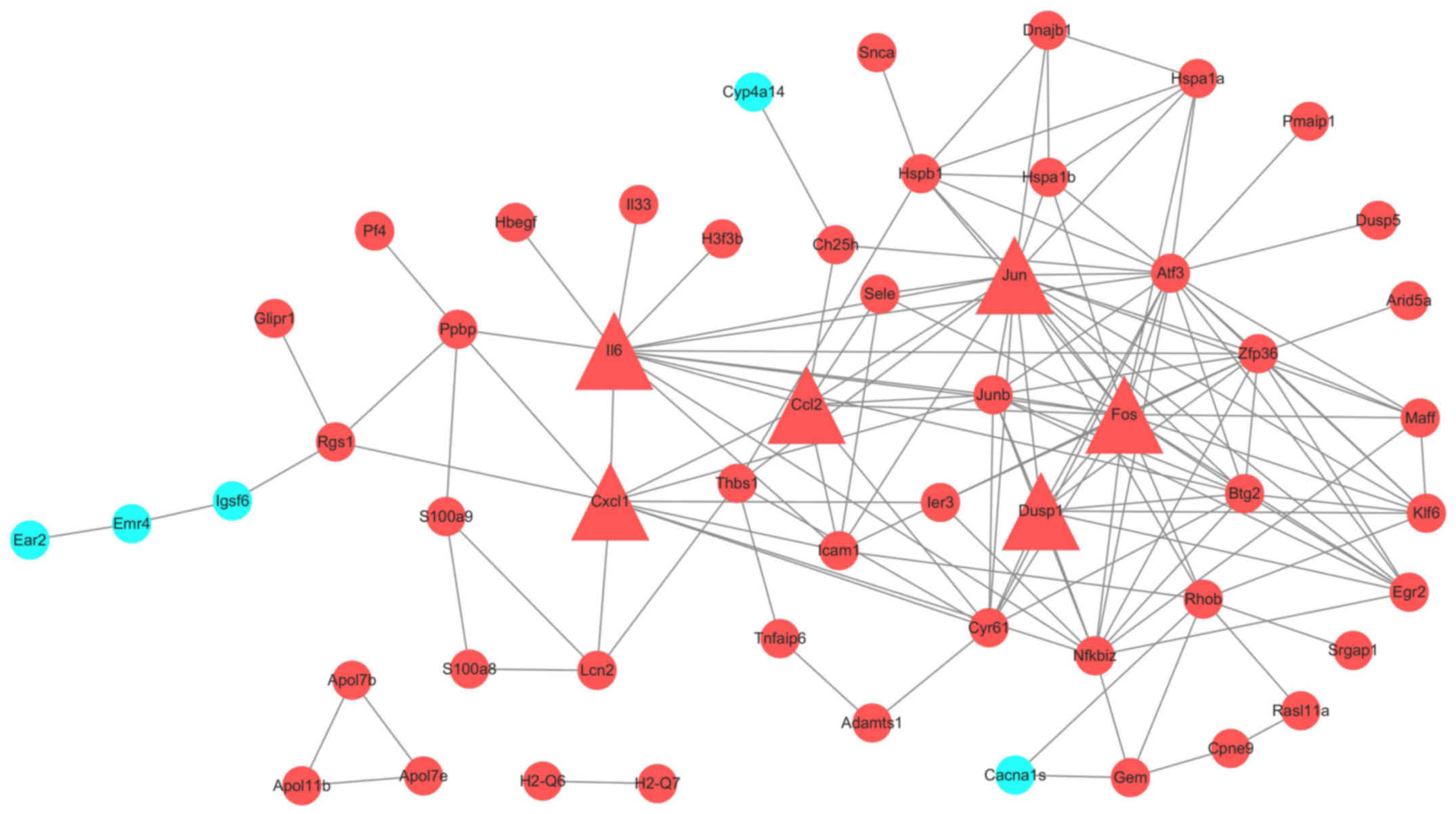
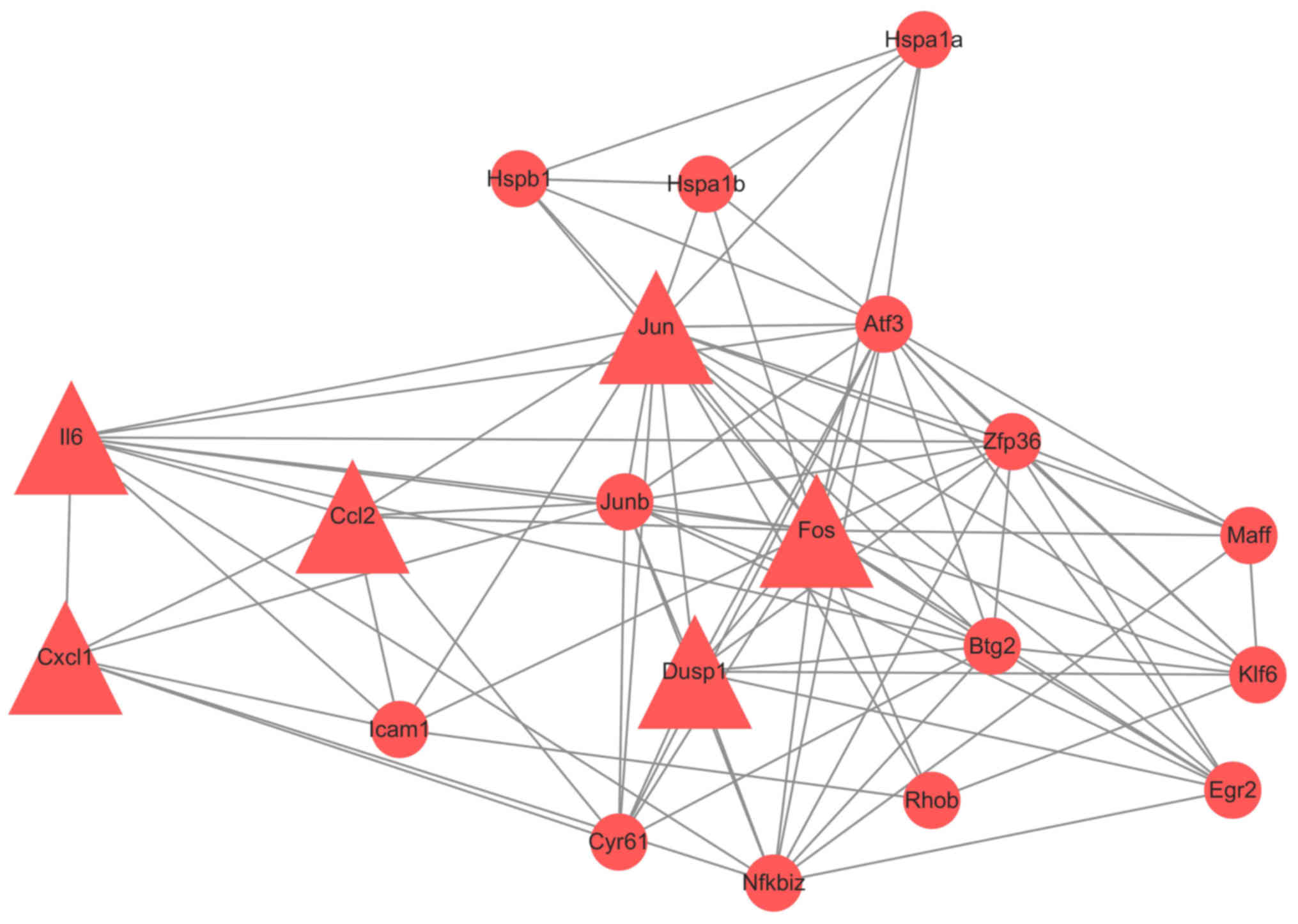
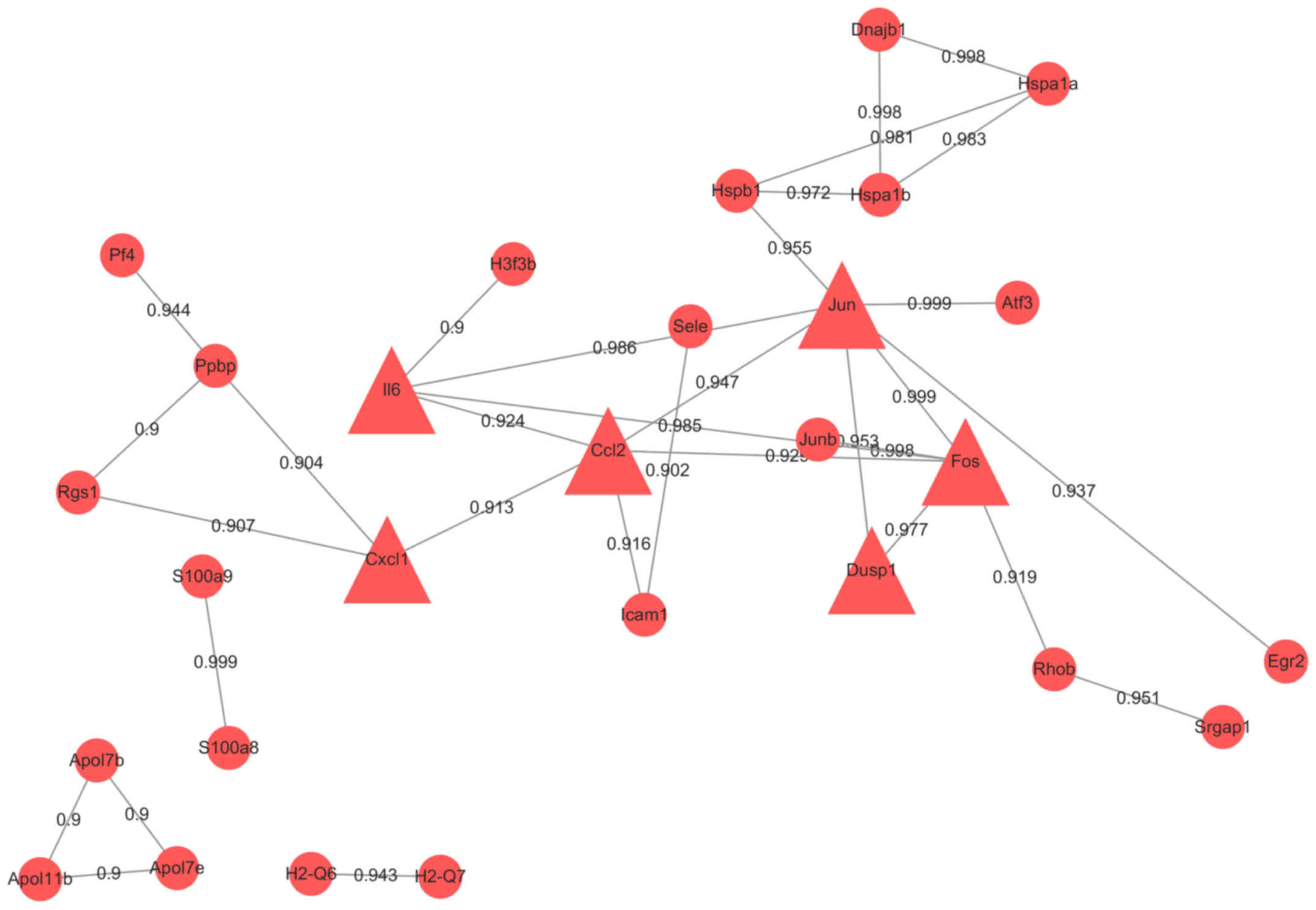
|
1
|
Li Y, Yang Y, Feng Y, Yan J, Fan C, Jiang
S and Qu Y: A review of melatonin in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury and clinical liver disease. Ann Med. 46:503–511. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhai Y, Petrowsky H, Hong JC, Busuttil RW
and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: Ischaemia-reperfusion injury in liver
transplantation-from bench to bedside. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 10:79–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Papadopoulos D, Siempis T, Theodorakou E
and Tsoulfas G: Hepatic ischemia and reperfusion injury and trauma:
Current concepts. Arch Trauma Res. 2:63–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanaka Y, Maher JM, Chen C and Klaassen
CD: Hepatic ischemia-reperfusion induces renal heme oxygenase-1 via
NF-E2-related factor 2 in rats and mice. Mol Pharmacol. 71:817–825.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee SM, Park MJ, Cho TS and Clemens MG:
Hepatic injury and lipid peroxidation during ischemia and
reperfusion. Shock. 13:279–284. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calkins CM, Bensard DD, Moore EE, McIntyre
RC, Silliman CC, Biffl W, Harken AH, Partrick DA and Offner PJ: The
injured child is resistant to multiple organ failure: A different
inflammatory response? J Trauma. 53:1058–1063. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Okaya T, Blanchard J, Schuster R, Kuboki
S, Husted T, Caldwell CC, Zingarelli B, Wong H, Solomkin JS and
Lentsch AB: Age-dependent responses to hepatic ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Shock. 24:421–427. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huber N, Sakai N, Eismann T, Shin T,
Kuboki S, Blanchard J, Schuster R, Edwards MJ, Wong HR and Lentsch
AB: Age-related decrease in proteasome expression contributes to
defective nuclear factor-kappaB activation during hepatic
ischemia/reperfusion. Hepatology. 49:1718–1728. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jaeschke H and Woolbright BL: Current
strategies to minimize hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by
targeting reactive oxygen species. Transplant Rev (Orlando).
26:103–114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abu-Amara M, Yang SY, Seifalian A,
Davidson B and Fuller B: The nitric oxide pathway-evidence and
mechanisms for protection against liver ischaemia reperfusion
injury. Liver Int. 32:531–543. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zaouali MA, Boncompagni E, Reiter RJ,
Bejaoui M, Freitas I, Pantazi E, Folch-Puy E, Abdennebi HB,
Garcia-Gil FA and Roselló-Catafau J: AMPK involvement in
endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy modulation after fatty
liver graft preservation: A role for melatonin and trimetazidine
cocktail. J Pineal Res. 55:65–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eltzschig HK and Collard CD: Vascular
ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Br Med Bull. 70:71–86. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai J, Perkumas KM, Qin X, Hauser MA,
Stamer WD and Liu Y: Expression profiling of human schlemm's canal
endothelial cells from eyes with and without glaucoma. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:6747–6753. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:(Database
issue). D109–D114. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bechara C, Chai H, Lin PH, Yao Q and Chen
C: Growth related oncogene-alpha (GRO-alpha): Roles in
atherosclerosis, angiogenesis and other inflammatory conditions.
Med Sci Monit. 13:RA87–RA90. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gomez-Rodriguez V, Orbe J,
Martinez-Aguilar E, Rodriguez JA, Fernandez-Alonso L, Serneels J,
Bobadilla M, Perez-Ruiz A, Collantes M, Mazzone M, et al:
Functional MMP-10 is required for efficient tissue repair after
experimental hind limb ischemia. FASEB J. 29:960–972. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jazwa A, Stepniewski J, Zamykal M,
Jagodzinska J, Meloni M, Emanueli C, Jozkowicz A and Dulak J:
Pre-emptive hypoxia-regulated HO-1 gene therapy improves
post-ischaemic limb perfusion and tissue regeneration in mice.
Cardiovasc Res. 97:115–124. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ahuja N, Andres-Hernando A, Altmann C,
Bhargava R, Bacalja J, Webb RG, He Z, Edelstein CL and Faubel S:
Circulating IL-6 mediates lung injury via CXCL1 production after
acute kidney injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
303:F864–F872. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stewart RK, Dangi A, Huang C, Murase N,
Kimura S, Stolz DB, Wilson GC, Lentsch AB and Gandhi CR: A novel
mouse model of depletion of stellate cells clarifies their role in
ischemia/reperfusion- and endotoxin-induced acute liver injury. J
Hepatol. 60:298–305. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang J, Xu P, Song P, Wang H, Zhang Y, Hu
Q, Wang G, Zhang S, Yu Q, Billiar TR, et al: CCL2-CCR2 signaling
promotes hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Surg Res.
202:352–362. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Heil M, Ziegelhoeffer T, Wagner S,
Fernández B, Helisch A, Martin S, Tribulova S, Kuziel WA, Bachmann
G and Schaper W: Collateral artery growth (arteriogenesis) after
experimental arterial occlusion is impaired in mice lacking
CC-chemokine receptor-2. Circ Res. 94:671–677. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Contreras-Shannon V, Ochoa O, Reyes-Reyna
SM, Sun D, Michalek JE, Kuziel WA, McManus LM and Shireman PK: Fat
accumulation with altered inflammation and regeneration in skeletal
muscle of CCR2-/−mice following ischemic injury. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 292:C953–C967. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cochain C, Rodero MP, Vilar J, Récalde A,
Richart AL, Loinard C, Zouggari Y, Guérin C, Duriez M, Combadière
B, et al: Regulation of monocyte subset systemic levels by distinct
chemokine receptors controls post-ischaemic neovascularization.
Cardiovasc Res. 88:186–195. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang W, Rojas M, Lilly B, Tsai NT,
Lemtalsi T, Liou GI, Caldwell RW and Caldwell RB: NAD(P)H
oxidase-dependent regulation of CCL2 production during retinal
inflammation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:3033–3040. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Adamski MG, Li Y, Wagner E, Yu H,
Seales-Bailey C, Soper SA, Murphy M and Baird AE: Expression
profile based gene clusters for ischemic stroke detection.
Genomics. 104:163–169. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kapoor S, Berishvili E, Bandi S and Gupta
S: Ischemic preconditioning affects long-term cell fate through DNA
damage-related molecular signaling and altered proliferation. Am J
Pathol. 184:2779–2790. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oyaizu T, Fung SY, Shiozaki A, Guan Z,
Zhang Q, dos Santos CC, Han B, Mura M, Keshavjee S and Liu M: Src
tyrosine kinase inhibition prevents pulmonary
ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury. Intensive Care Med.
38:894–905. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|