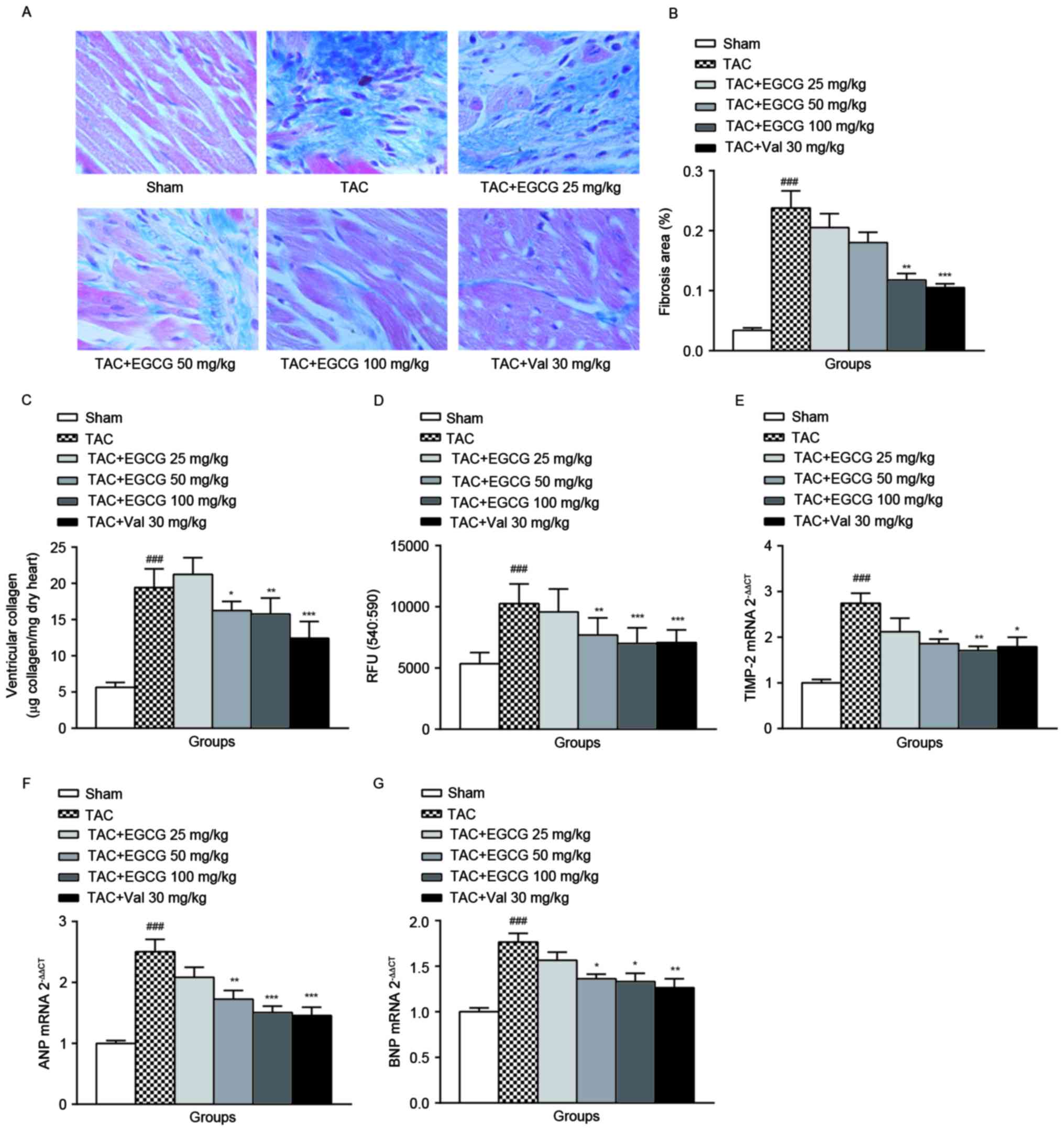
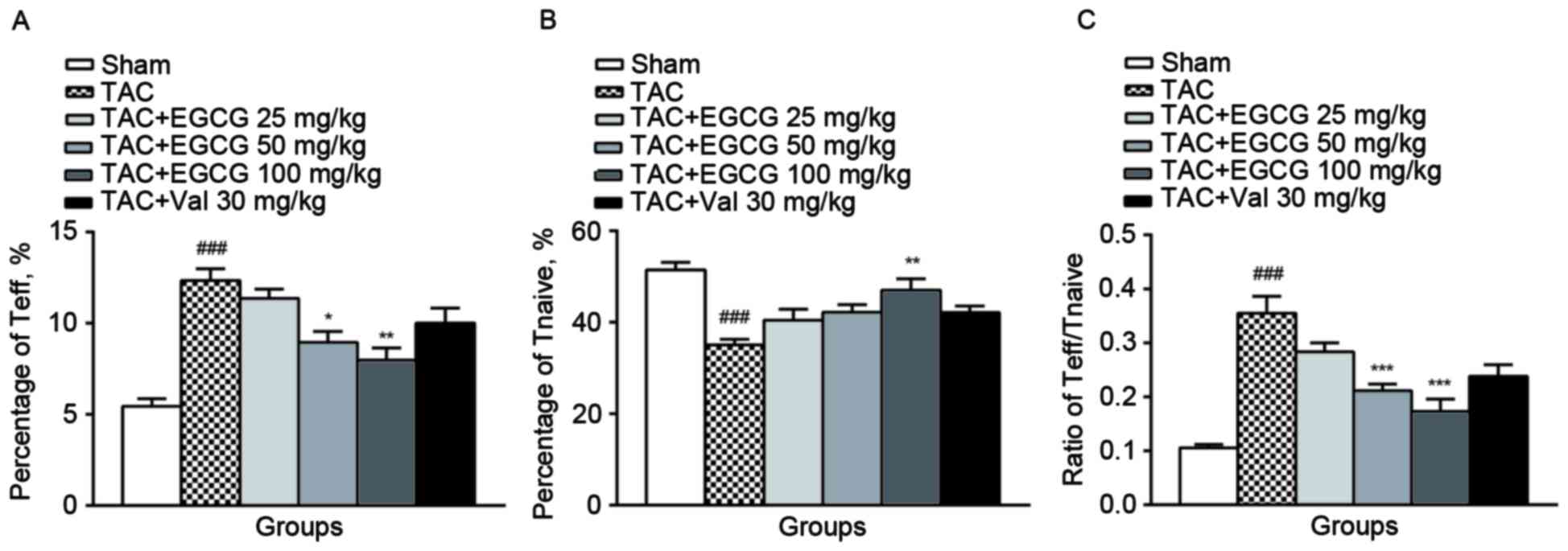
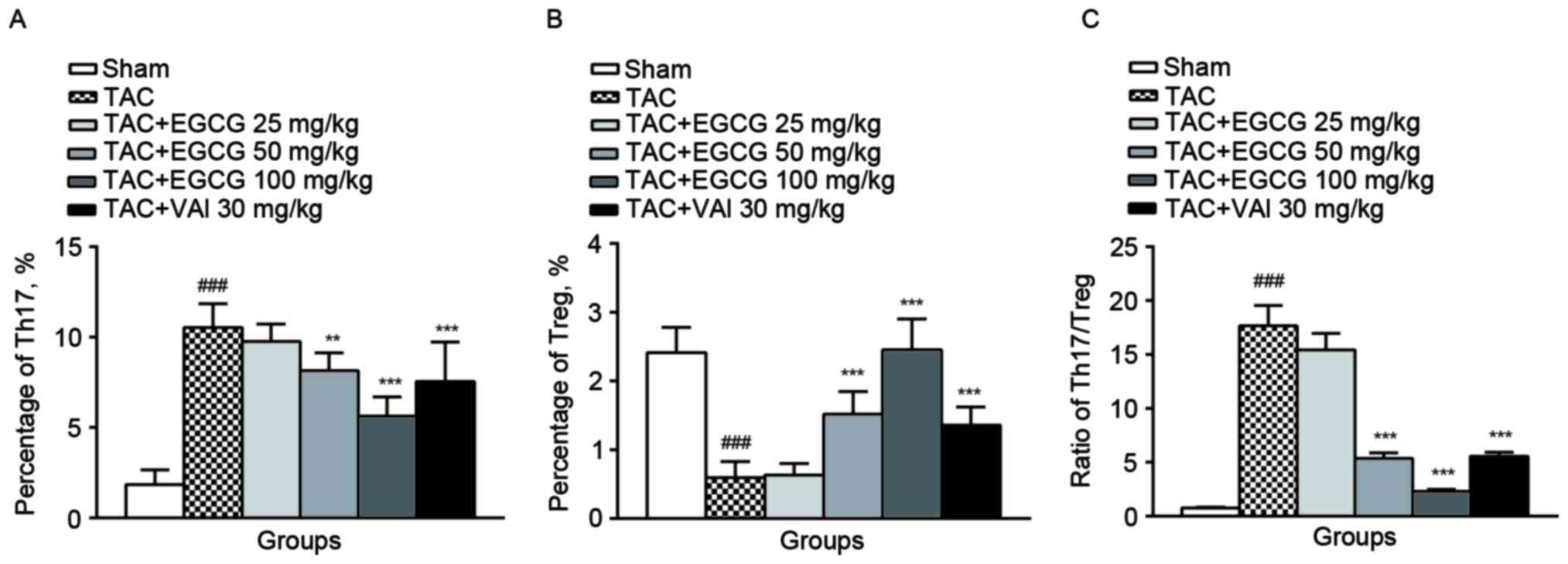
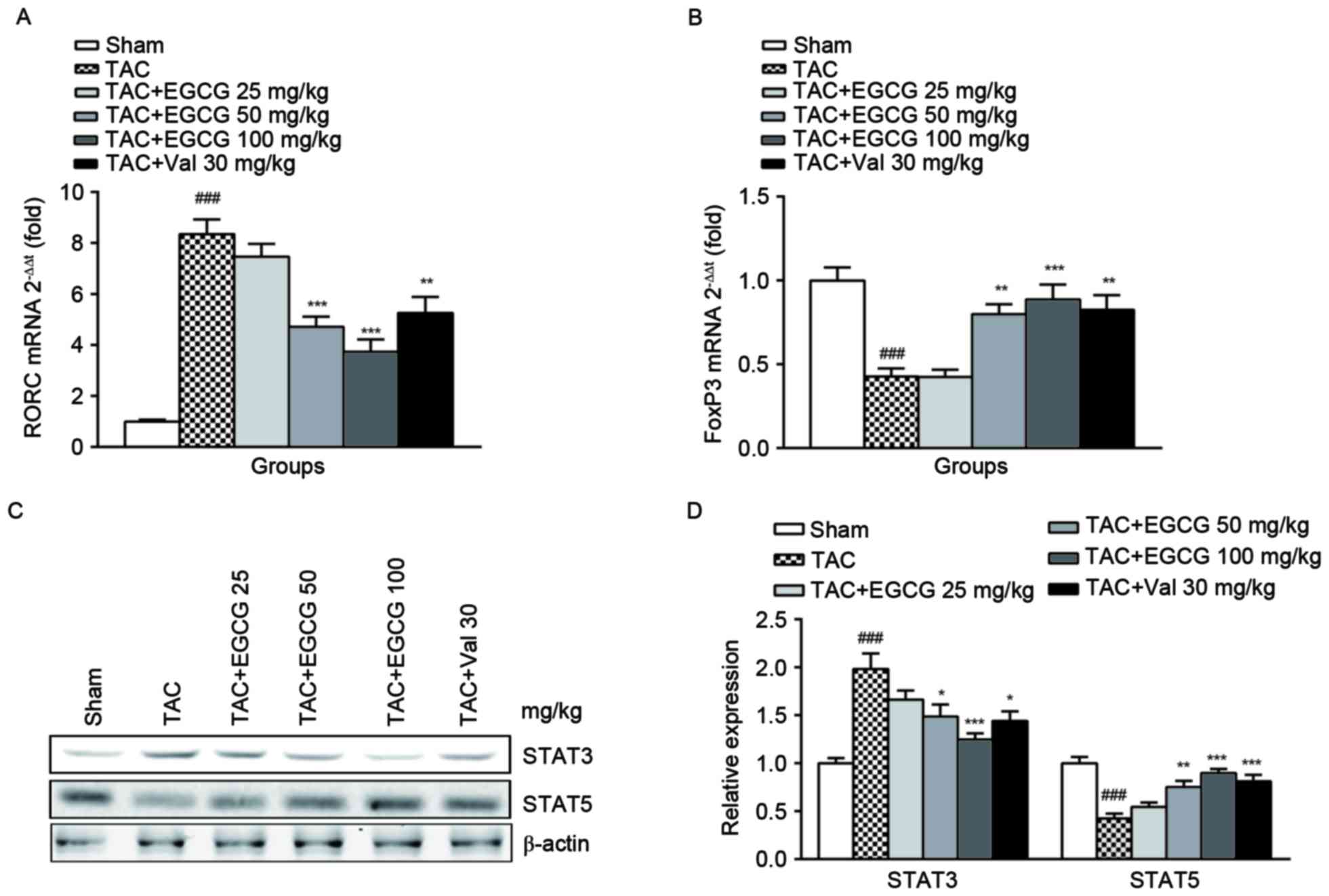
|
1
|
Morita H and Komuro I: Periostin isoforms
and cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction: Is the dispute
settled? Hypertension. 67:504–505. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu X, Pang J, Chen Y, Bucala R, Zhang Y
and Ren J: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) deficiency
exacerbates aging-induced cardiac remodeling and dysfunction
despite improved inflammation: Role of autophagy regulation. Sci
Rep. 6:224882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Melendez GC, McLarty JL, Levick SP, Du Y,
Janicki JS and Brower GL: Interleukin 6 mediates myocardial
fibrosis, concentric hypertrophy, and diastolic dysfunction in
rats. Hypertension. 56:225–231. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu W, Li J, Tian W, Xu T and Zhang Z:
Chronic alcohol consumption induces cardiac remodeling in mice from
Th1 or Th2 background. Exp Mol Pathol. 91:761–767. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kwon WY, Cha HN, Heo JY, Choi JH, Jang BI,
Lee IK and Park SY: Interleukin-10 deficiency aggravates
angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling in mice. Life Sci.
146:214–221. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yu Q, Vazquez R, Zabadi S, Watson RR and
Larson DF: T-lymphocytes mediate left ventricular fibrillar
collagen cross-linking and diastolic dysfunction in mice. Matrix
Biol. 29:511–518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang CS, Chen G and Wu Q: Recent
scientific studies of a traditional chinese medicine, tea, on
prevention of chronic diseases. J Tradit Complement Med. 4:17–23.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu S, Xu ZL, Sun L, Liu Y, Li CC, Li HM,
Zhang W, Li CJ and Qin W: (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces
apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells via PTEN. Mol Med Rep.
14:599–605. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zeng X and Tan X:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate and zinc provide anti-apoptotic
protection against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in H9c2 rat cardiac
myoblast cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:1850–1856. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tang J, Zheng JS, Fang L, Jin Y, Cai W and
Li D: Tea consumption and mortality of all cancers, CVD and all
causes: A meta-analysis of eighteen prospective cohort studies. Br
J Nutr. 114:673–683. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xuan F and Jian J: Epigallocatechin
gallate exerts protective effects against myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury through the PI3K/Akt pathway-mediated
inhibition of apoptosis and the restoration of the autophagic flux.
Int J Mol Med. 38:328–336. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tian C, Huang Q, Yang L, Légaré S,
Angileri F, Yang H, Li X, Min X, Zhang C, Xu C, et al: Green tea
consumption is associated with reduced incident CHD and improved
CHD-related biomarkers in the Dongfeng-Tongji cohort. Sci Rep.
6:243532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai Y, He SQ, Hong HQ, Cai YP, Zhao L and
Zhang M: High doses of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate from green
tea induces cardiac fibrosis in mice. Biotechnol Lett.
37:2371–2377. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han YS, Lan L, Chu J, Kang WQ and Ge ZM:
Epigallocatechin gallate attenuated the activation of rat cardiac
fibroblasts induced by angiotensin II via regulating β-arrestin1.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 31:338–346. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim YH, Won YS, Yang X, Kumazoe M,
Yamashita S, Hara A, Takagaki A, Goto K, Nanjo F and Tachibana H:
Green tea catechin metabolites exert immunoregulatory effects on
CD4 (+) T cell and natural killer cell activities. J Agric Food
Chem. 64:3591–3597. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li X, Zhang L and Liang J: Unraveling the
expression profiles of long noncoding RNAs in rat cardiac
hypertrophy and functions of lncRNA BC088254 in cardiac hypertrophy
induced by transverse aortic constriction. Cardiology. 134:84–98.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo K, Lan CZ, Yu TT, Huang LL, Wang XH,
Pan C and Gao S: Effects of Xin-Ji-Er-Kang formula on 2K1C-induced
hypertension and cardiovascular remodeling in rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 155:1227–1235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wen Y, Zeng Z, Gui C, Li L and Li W:
Changes in the expression of Th17 cell-associated cytokines in the
development of rheumatic heart disease. Cardiovasc Pathol.
24:382–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang B, Wang QT, Song SS, Wu YJ, Ma YK,
Zhang LL, Chen JY, Wu HX, Jiang L and Wei W: Combined use of
etanercept and MTX restores CD4*/CD8* ratio and Tregs in spleen and
thymus in collagen-induced arthritis. Inflamm Res. 61:1229–1239.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen J, Feng X and Huang Q: Modulation of
T-Bet and GATA-3 expression in experimental autoimmune thyroiditis
rats through ginsenoside treatment. Endocr Res. 41:28–33. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang QT, Zhang LL, Wu HX and Wei W: The
expression change of β-arrestins in fibroblast-like synoviocytes
from rats with collagen-induced arthritis and the effect of total
glucosides of paeony. J Ethnopharmacol. 133:511–516. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Terrazas C, Varikuti S, Kimble J, Moretti
E, Boyaka PN and Satoskar AR: IL-17A promotes susceptibility during
experimental visceral leishmaniasis caused by Leishmania donovani.
FASEB J. 30:1135–1143. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lee YJ, Hyung KE, Yoo JS, Jang YW, Kim SJ,
Lee DI, Lee SJ, Park SY, Jeong JH and Hwang KW: Effects of exposure
to extremely low-frequency electromagnetic fields on the
differentiation of Th17 T cells and regulatory T cells. Gen Physiol
Biophys. 35:487–495. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stellato C, Gubin MM, Magee JD, Fang X,
Fan J, Tartar DM, Chen J, Dahm GM, Calaluce R, Mori F, et al:
Coordinate regulation of GATA-3 and Th2 cytokine gene expression by
the RNA-binding protein HuR. J Immunol. 187:441–449. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moore-Morris T, Guimarães-Camboa N, Yutzey
KE, Pucéat M and Evans SM: Cardiac fibroblasts: From development to
heart failure. J Mol Med (Berl). 93:823–830. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Badenhorst D, Maseko M, Tsotetsi OJ,
Naidoo A, Brooksbank R, Norton GR and Woodiwiss AJ: Cross-linking
influences the impact of quantitative changes in myocardial
collagen on cardiac stiffness and remodelling in hypertension in
rats. Cardiovasc Res. 57:632–641. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu Q, Horak K and Larson DF: Role of T
lymphocytes in hypertension-induced cardiac extracellular matrix
remodeling. Hypertension. 48:98–104. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nogueira LG, Santos RH, Fiorelli AI,
Mairena EC, Benvenuti LA, Bocchi EA, Stolf NA, Kalil J and
Cunha-Neto E: Myocardial gene expression of T-bet, GATA-3, Ror-γt,
FoxP3, and hallmark cytokines in chronic Chagas disease
cardiomyopathy: An essentially unopposed TH1-type response.
Mediators Inflamm. 2014:9143262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shao J, Nangaku M, Miyata T, Inagi R,
Yamada K, Kurokawa K and Fujita T: Imbalance of T-cell subsets in
angiotensin II-infused hypertensive rats with kidney injury.
Hypertension. 42:31–38. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jung YW, Kim HG, Perry CJ and Kaech SM:
CCR7 expression alters memory CD8 T-cell homeostasis by regulating
occupancy in IL-7- and IL-15-dependent niches. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 113:8278–8283. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cappuzzello C, Di Vito L, Melchionna R,
Melillo G, Silvestri L, Cesareo E, Crea F, Liuzzo G, Facchiano A,
Capogrossi MC and Napolitano M: Increase of plasma IL-9 and
decrease of plasma IL-5, IL-7 and IFN-γ in patients with chronic
heart failure. J Transl Med. 9:282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Machino-Ohtsuka T, Tajiri K, Kimura T,
Sakai S, Sato A, Yoshida T, Hiroe M, Yasutomi Y, Aonuma K and
Imanaka-Yoshida K: Tenascin-C aggravates autoimmune myocarditis via
dendritic cell activation and Th17 cell differentiation. J Am Heart
Assoc. 3:e0010522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lim SM, Kang GD, Jeong JJ, Choi HS and Kim
DH: Neomangiferin modulates the Th17/Treg balance and ameliorates
colitis in mice. Phytomedicine. 23:131–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cai Y, Yu SS, Chen TT, Gao S, Geng B, Yu
Y, Ye JT and Liu PQ: EGCG inhibits CTGF expression via blocking
NF-κB activation in cardiac fibroblast. Phytomedicine. 20:106–113.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dooley A, Bruckdorfer KR and Abraham DJ:
Modulation of fibrosis in systemic sclerosis by nitric oxide and
antioxidants. Cardiol Res Pract. 2012:5219582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|