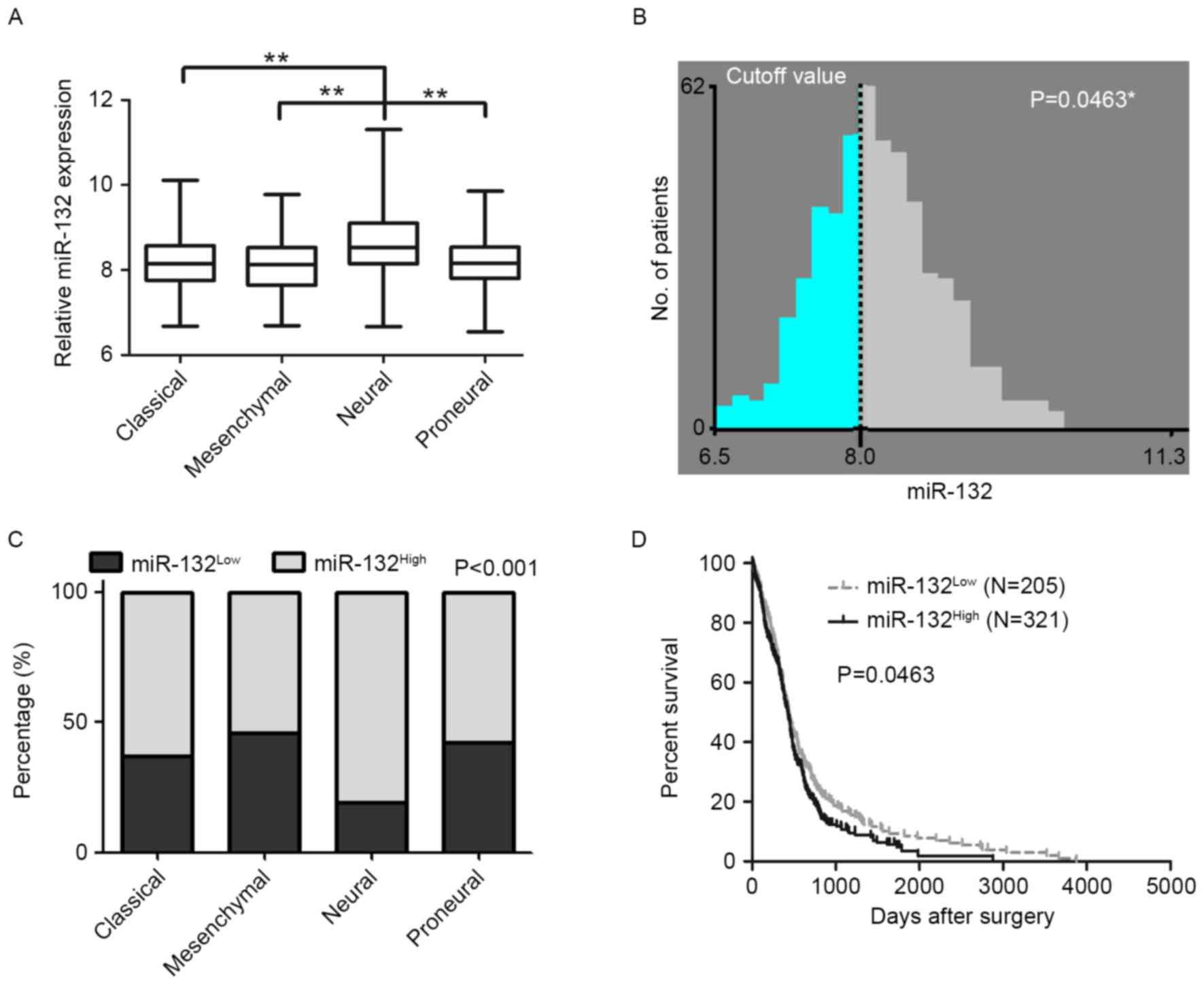
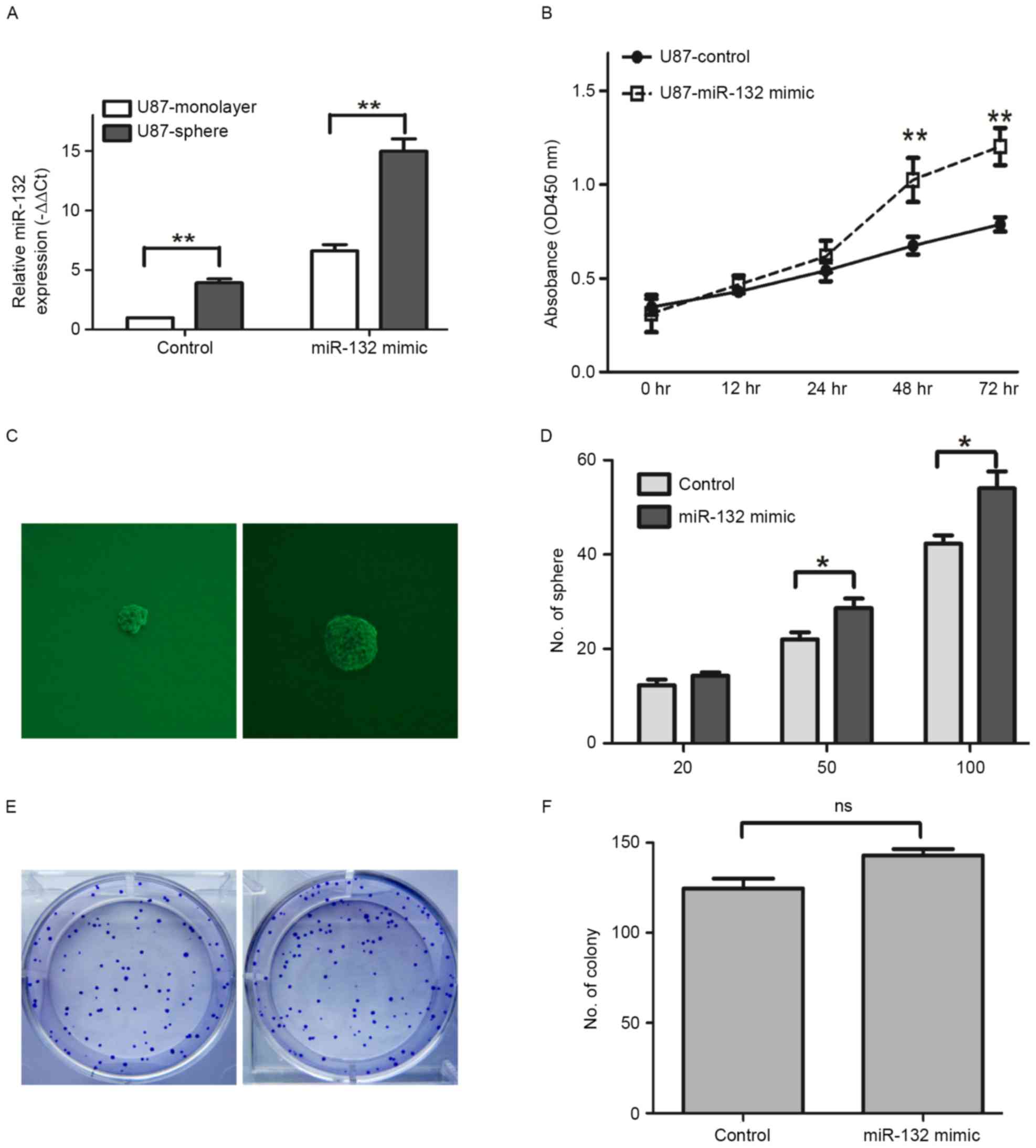
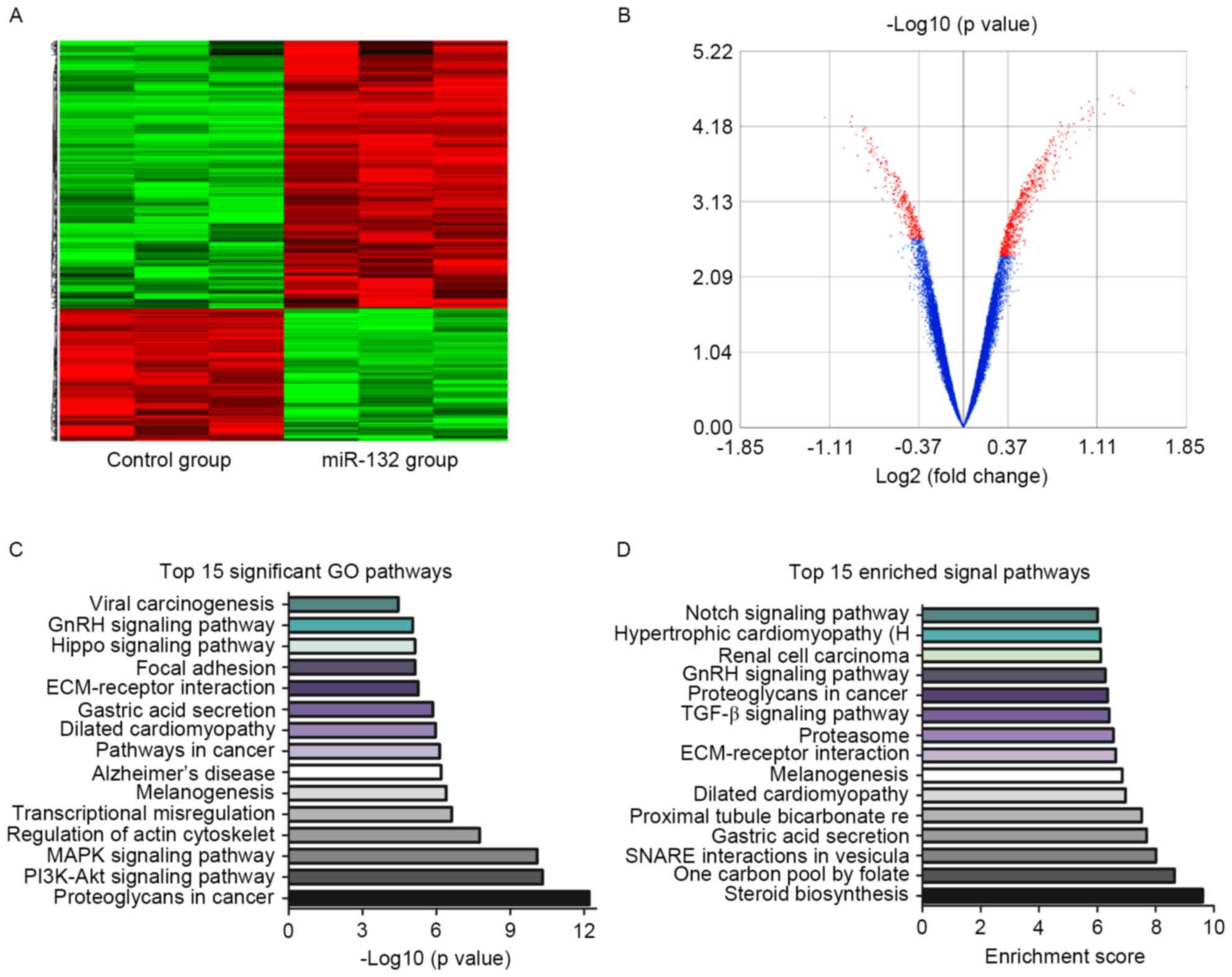
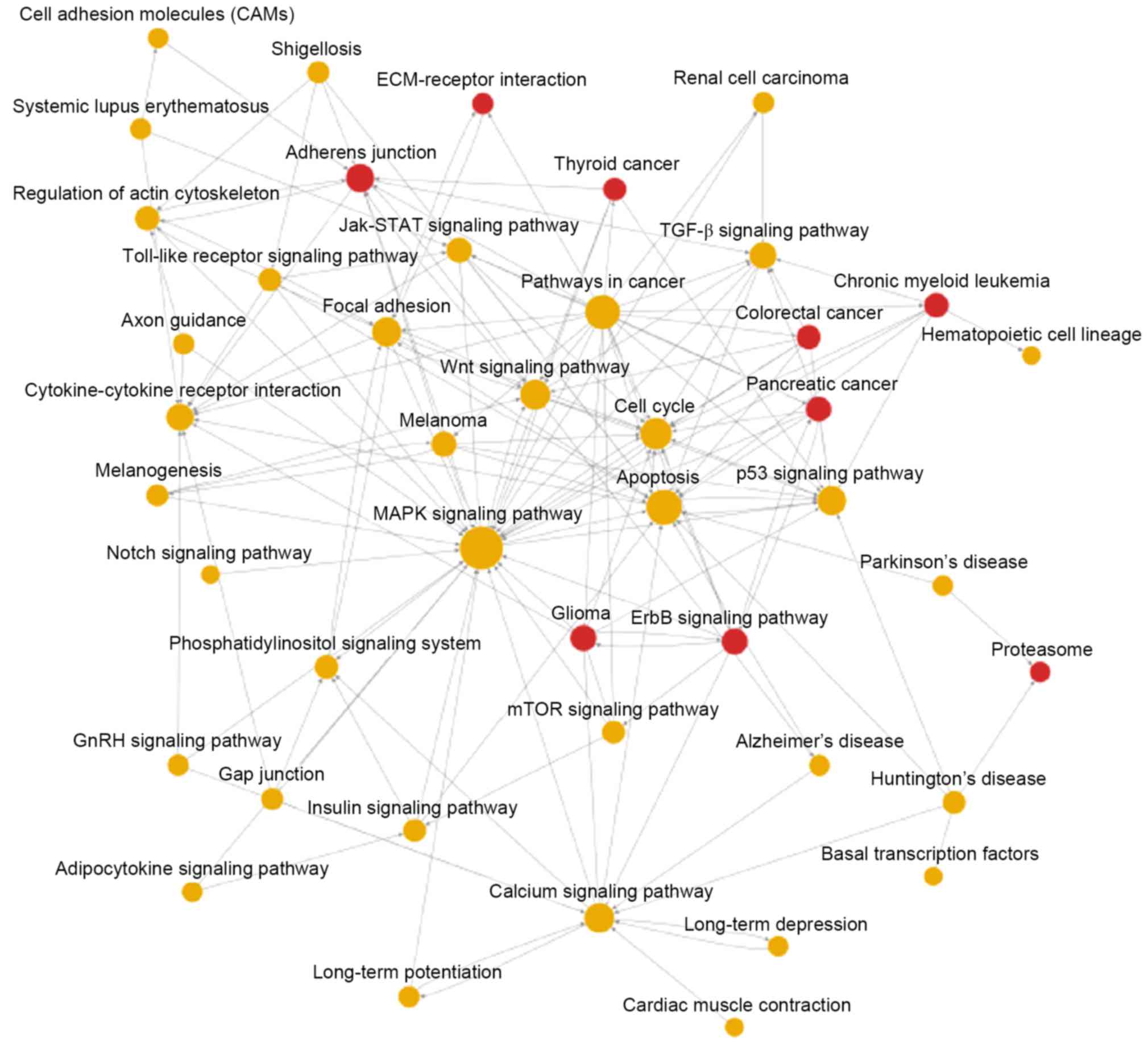
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berindan-Neagoe I, Pdel C Monroig,
Pasculli B and Calin GA: MicroRNAome genome: A treasure for cancer
diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:311–336. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl J Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lei CJ, Li L, Gao X, Zhang J, Pan QY, Long
HC, Chen CZ, Ren DF and Zheng G: hsa-miR-132 inhibits proliferation
of hepatic carcinoma cells by targeting YAP. Cell Biochem Funct.
33:326–333. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li W, Zhang J, Chen T, Yin P, Yang J and
Cao Y: miR-132 upregulation promotes gastric cancer cell growth
through suppression of FoxO1 translation. Tumour Biol. Aug
23–2015.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
8
|
Mokutani Y, Uemura M, Munakata K, Okuzaki
D, Haraguchi N, Takahashi H, Nishimura J, Hata T, Murata K,
Takemasa I, et al: Down-Regulation of microRNA-132 is associated
with poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 23 Suppl
5:S599–S608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tavolaro S, Colombo T, Chiaretti S,
Peragine N, Fulci V, Ricciardi MR, Messina M, Bonina S, Brugnoletti
F, Marinelli M, et al: Increased chronic lymphocytic leukemia
proliferation upon IgM stimulation is sustained by the upregulation
of miR-132 and miR-212. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 54:222–234. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA and
Maniatis T: The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation
by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol
Cell. 27:435–448. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Magill ST, Cambronne XA, Luikart BW, Lioy
DT, Leighton BH, Westbrook GL, Mandel G, Goodman RH, et al:
microRNA-132 regulates dendritic growth and arborization of newborn
neurons in the adult hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:20382–20387. 2010; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawashima H, Numakawa T, Kumamaru E,
Adachi N, Mizuno H, Ninomiya M, Kunugi H and Hashido K:
Glucocorticoid attenuates brain-derived neurotrophic
factor-dependent upregulation of glutamate receptors via the
suppression of microRNA-132 expression. Neuroscience.
165:1301–1311. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shaked I, Meerson A, Wolf Y, Avni R,
Greenberg D, Gilboa-Geffen A and Soreq H: MicroRNA-132 potentiates
cholinergic anti-inflammatory signaling by targeting
acetylcholinesterase. Immunity. 31:965–973. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miller BH, Zeier Z, Xi L, Lanz TA, Deng S,
Strathmann J, Willoughby D, Kenny PJ, Elsworth JD, Lawrence MS, et
al: MicroRNA-132 dysregulation in schizophrenia has implications
for both neurodevelopment and adult brain function. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:3125–3130. 2012; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee ST, Chu K, Im WS, Yoon HJ, Im JY, Park
JE, Park KH, Jung KH, Lee SK, Kim M and Roh JK: Altered microRNA
regulation in Huntington's disease models. Exp Neurol. 227:172–179.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Q, Liao F, Wu H, Cai T, Yang L, Wang
ZF and Zou R: Upregulation of miR-132 expression in glioma and its
clinical significance. Tumour Biol. 35:12299–12304. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ruan J, Lou S, Dai Q, Mao D, Ji J and Sun
X: Tumor suppressor miR-181c attenuates proliferation, invasion,
and self-renewal abilities in glioblastoma. Neuroreport. 26:66–73.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Setty M, Helmy K, Khan AA, Silber J, Arvey
A, Neezen F, Agius P, Huse JT, Holland EC and Leslie CS: Inferring
transcriptional and microRNA-mediated regulatory programs in
glioblastoma. Mol Syst Biol. 8:6052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
An F, Zhan Q, Xia M, Jiang L, Lu G, Huang
M, Guo J and Liu S: From moderately severe to severe
hypertriglyceridemia induced acute pancreatitis: Circulating miRNAs
play role as potential biomarkers. PLoS One. 9:e1110582014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk - database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V,
Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP, et al:
Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes
of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1,
EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 17:98–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang H, Li XT, Wu C, Wu ZW, Li YY, Yang
TQ, Chen GL, Xie XS, Huang YL, Du ZW and Zhou YX: miR-132 can
inhibit glioma cells invasion and migration by target MMP16 in
vitro. Onco Targets Ther. 8:3211–3218. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Z, Chen Y, Fu Y, Yang Y, Zhang Y,
Chen Y and Li D: Meta-analysis of differentially expressed genes in
osteosarcoma based on gene expression data. BMC Med Genet.
15:802014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian H, Hou L, Xiong YM, Huang JX, Zhang
WH, Pan YY and Song XR: miR-132 targeting E2F5 suppresses cell
proliferation, invasion, migration in ovarian cancer cells. Am J
Transl Res. 8:1492–1501. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest
WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, et
al: Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis,
delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in
neurogenesis. Cancer Cell. 9:157–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zagore LL, Grabinski SE, Sweet TJ,
Hannigan MM, Sramkoski RM, Li Q and Licatalosi DD: RNA binding
protein Ptbp2 is essential for male germ cell development. Mol Cell
Biol. 35:4030–4042. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fang D, Yang H, Lin J, Teng Y, Jiang Y,
Chen J and Li Y: 17β-estradiol regulates cell proliferation, colony
formation, migration, invasion and promotes apoptosis by
upregulating miR-9 and thus degrades MALAT-1 in osteosarcoma cell
MG-63 in an estrogen receptor-independent manner. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 457:500–506. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng S, Gray EE, Chawla G, Porse BT,
O'Dell TJ and Black DL: PSD-95 is post-transcriptionally repressed
during early neural development by PTBP1 and PTBP2. Nat Neurosci.
15:381–388. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cheung HC, Hai T, Zhu W, Baggerly KA,
Tsavachidis S, Krahe R and Cote GJ: Splicing factors PTBP1 and
PTBP2 promote proliferation and migration of glioma cell lines.
Brain. 132:2277–2288. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Han W, Wang L, Yin B and Peng X:
Characterization of a novel posttranslational modification in
polypyrimidine tract-binding proteins by SUMO1. BMB Rep.
47:233–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|