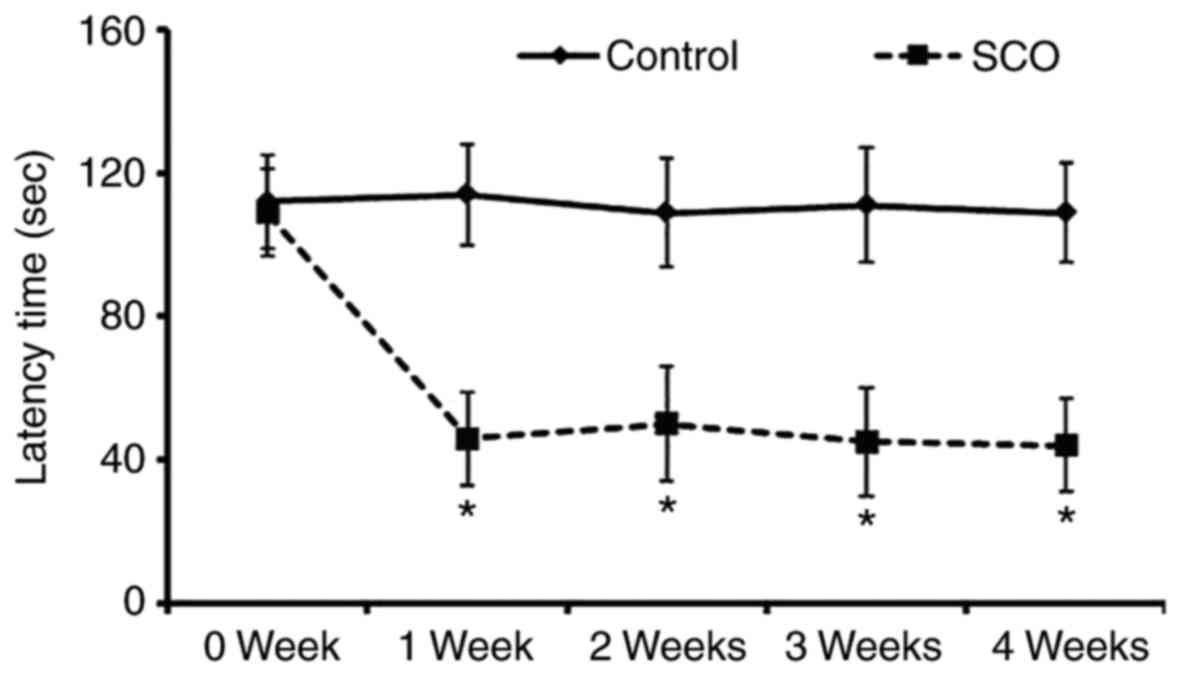
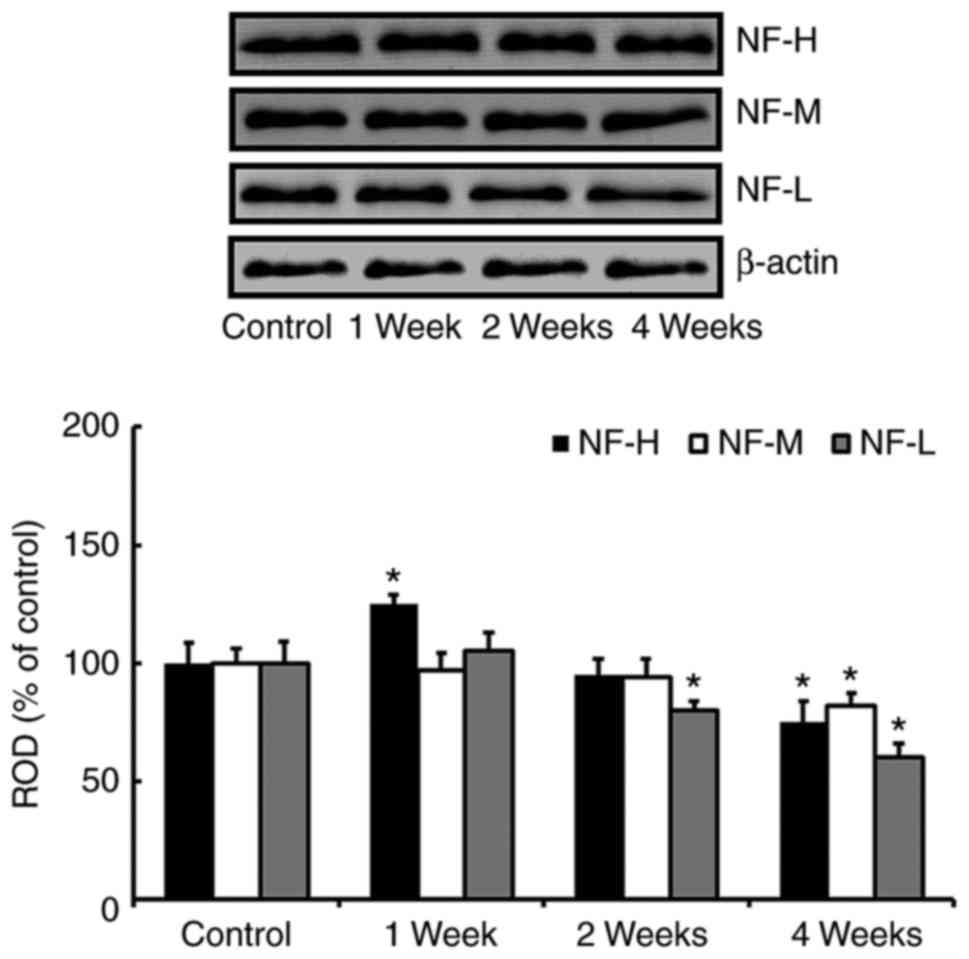
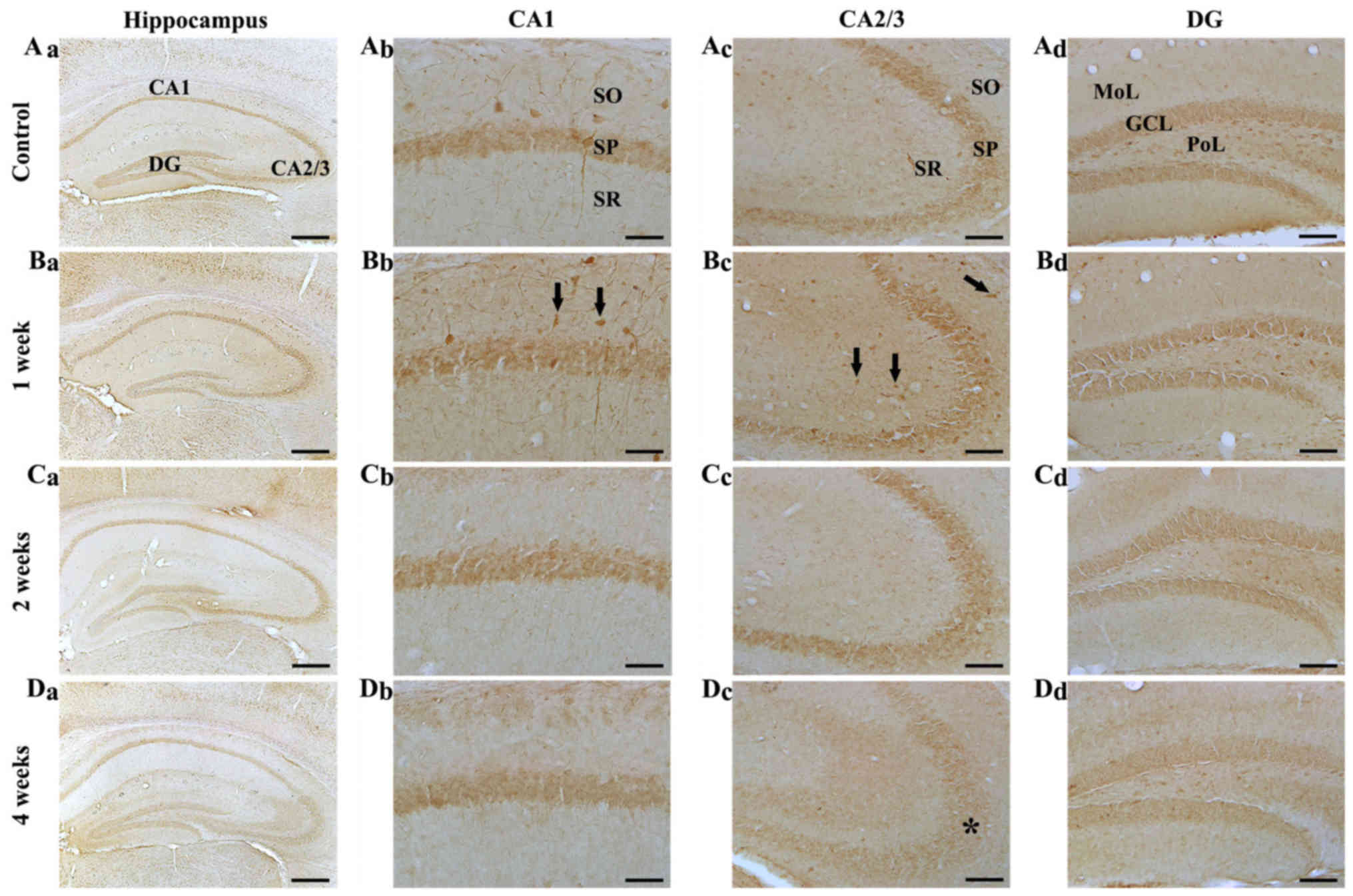
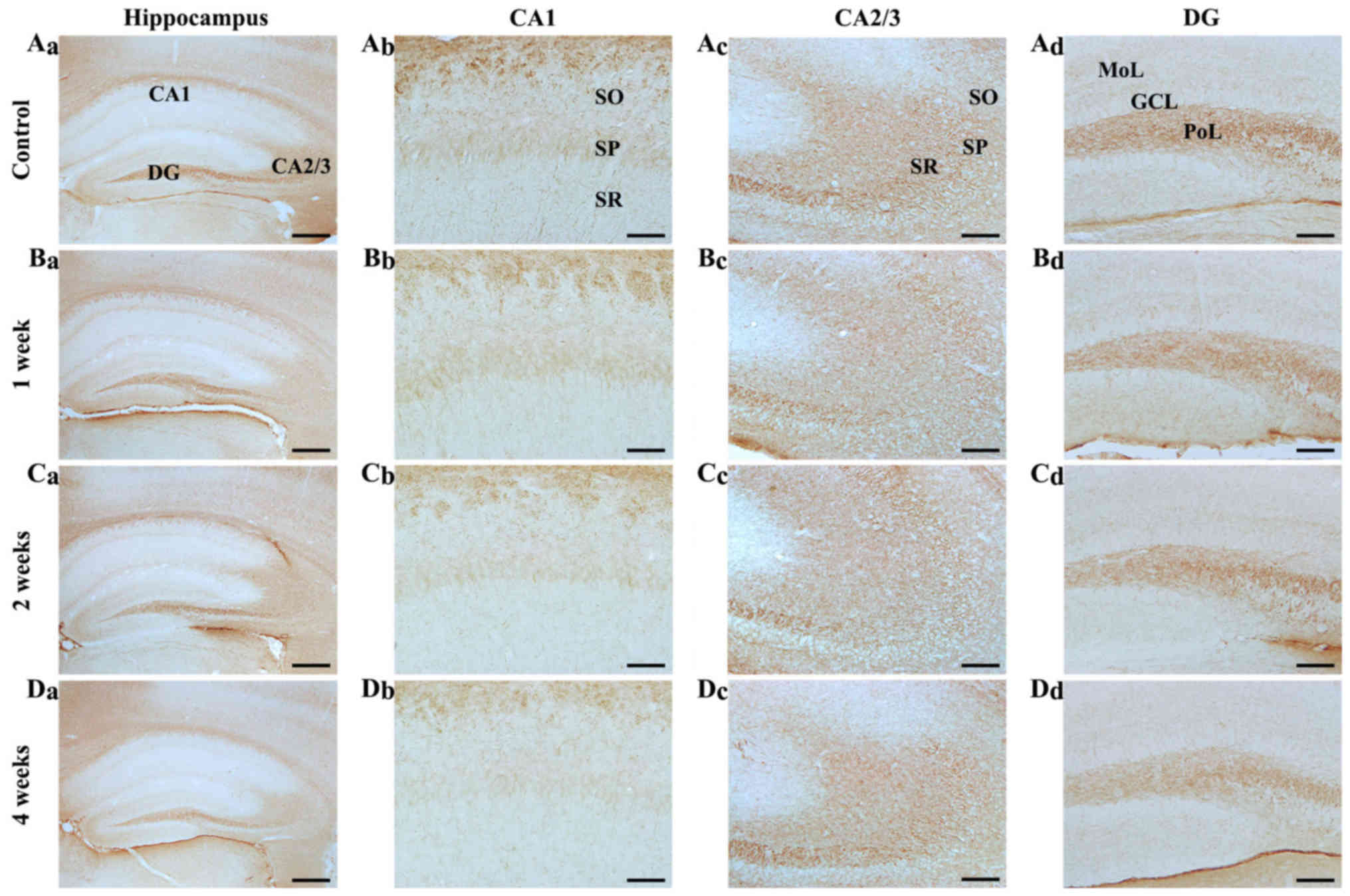
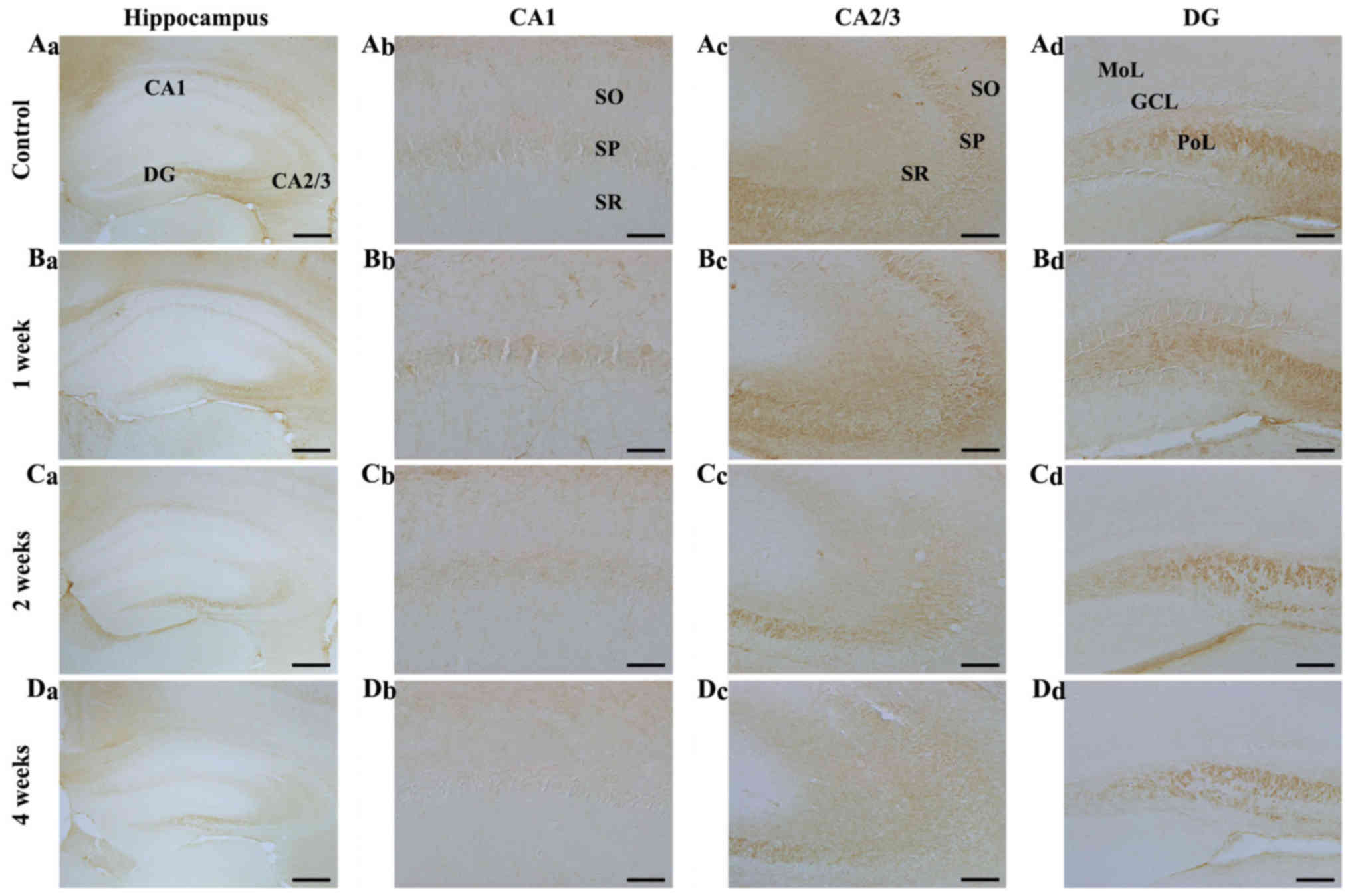
|
1
|
Bartus RT, Dean RL III, Beer B and Lippa
AS: The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction.
Science. 217:408–414. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhou MM, Xue Y, Sun SH, Wen M, Li ZJ, Xu
J, Wang JF, Yanagita T, Wang YM and Xue CH: Effects of different
fatty acids composition of phosphatidylcholine on brain function of
dementia mice induced by scopolamine. Lipids Health Dis.
15:1352016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Lee B, Sur B, Shim J, Hahm DH and Lee H:
Acupuncture stimulation improves scopolamine-induced cognitive
impairment via activation of cholinergic system and regulation of
BDNF and CREB expressions in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14:3382014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Park JH, Choi HY, Cho JH, Kim IH, Lee TK,
Lee JC, Won MH, Chen BH, Shin BN, Ahn JH, et al: Effects of chronic
scopolamine treatment on cognitive impairments and myelin basic
protein expression in the mouse hippocampus. J Mol Neurosci.
59:579–589. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Yoo DY, Choi JH, Kim W, Nam SM, Jung HY,
Kim JH, Won MH, Yoon YS and Hwang IK: Effects of luteolin on
spatial memory, cell proliferation and neuroblast differentiation
in the hippocampal dentate gyrus in a scopolamine-induced amnesia
model. Neurol Res. 35:813–820. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ahmed T and Gilani AH: Inhibitory effect
of curcuminoids on acetylcholinesterase activity and attenuation of
scopolamine-induced amnesia may explain medicinal use of turmeric
in Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 91:554–559. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Klinkenberg I and Blokland A: The validity
of scopolamine as a pharmacological model for cognitive impairment:
A review of animal behavioral studies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
34:1307–1350. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lian W, Fang J, Xu L, Zhou W, Kang, Xiong
W, Jia H, Liu AL and Du GH: DL0410 ameliorates memory and cognitive
impairments induced by scopolamine via increasing cholinergic
neurotransmission in mice. Molecules. 22:pii: E410. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hami J, Kheradmand H and Haghir H: Sex
differences and laterality of insulin receptor distribution in
developing rat hippocampus: An immunohistochemical study. J Mol
Neurosci. 54:100–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Huang W, Cao J, Liu X, Meng F, Li M, Chen
B and Zhang J: AMPK plays a dual role in regulation of CREB/BDNF
pathway in mouse primary hippocampal cells. J Mol Neurosci.
56:782–788. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kong Y, Bai PS, Sun H and Nan KJ:
Expression of the newly identified gene CAC1 in the hippocampus of
Alzheimer's disease patients. J Mol Neurosci. 47:207–218. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhao L, Sun C, Xiong L, Yang Y, Gao Y,
Wang L, Zuo H, Xu X, Dong J, Zhou H and Peng R: MicroRNAs: Novel
mechanism involved in the pathogenesis of microwave exposure on
rats' hippocampus. J Mol Neurosci. 53:222–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Terry AV Jr, Callahan PM, Hall B and
Webster SJ: Alzheimer's disease and age-related memory decline
(preclinical). Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 99:190–210. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Gold PE: Acetylcholine modulation of
neural systems involved in learning and memory. Neurobiol Learn
Mem. 80:194–210. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hasselmo ME: The role of acetylcholine in
learning and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 16:710–715. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Lippa AS, Critchett DJ, Ehlert F, Yamamura
HI, Enna SJ and Bartus RT: Age-related alterations in
neurotransmitter receptors: An electrophysiological and biochemical
analysis. Neurobiol Aging. 2:3–8. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vijayan VK: Cholinergic enzymes in the
cerebellum and the hippocampus of the senescent mouse. Exp
Gerontol. 12:7–11. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nixon RA and Sihag RK: Neurofilament
phosphorylation: A new look at regulation and function. Trends
Neurosci. 14:501–506. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E and
Hyman BT: Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 1:a0061892011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Dong DL, Xu ZS, Chevrier MR, Cotter RJ,
Cleveland DW and Hart GW: Glycosylation of mammalian
neurofilaments. Localization of multiple O-linked
N-acetylglucosamine moieties on neurofilament polypeptides L and M.
J Biol Chem. 268:16679–16687. 1993.
|
|
21
|
Sánchez I, Hassinger L, Sihag RK,
Cleveland DW, Mohan P and Nixon RA: Local control of neurofilament
accumulation during radial growth of myelinating axons in vivo.
Selective role of site-specific phosphorylation. J Cell Biol.
151:1013–1024. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Yabe JT, Chan WK, Chylinski TM, Lee S,
Pimenta AF and Shea TB: The predominant form in which neurofilament
subunits undergo axonal transport varies during axonal initiation,
elongation, and maturation. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 48:61–83.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hayes RL, Yang K, Whitson JS and
Postmantur R: Cytoskeletal derangements following central nervous
system injury: Modulation by neurotrophic gene transfection. J
Neurotrauma. 12:933–941. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tu PH, Elder G, Lazzarini RA, Nelson D,
Trojanowski JQ and Lee VM: Overexpression of the human NFM subunit
in transgenic mice modifies the level of endogenous NFL and the
phosphorylation state of NFH subunits. J Cell Biol. 129:1629–1640.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Al-Chalabi A and Miller CC: Neurofilaments
and neurological disease. Bioessays. 25:346–355. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Julien JP: Neurofilament functions in
health and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 9:554–560. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Perrot R, Berges R, Bocquet A and Eyer J:
Review of the multiple aspects of neurofilament functions, and
their possible contribution to neurodegeneration. Mol Neurobiol.
38:27–65. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Vickers JC, Kirkcaldie MT, Phipps A and
King AE: Alterations in neurofilaments and the transformation of
the cytoskeleton in axons may provide insight into the aberrant
neuronal changes of Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Bull.
126:324–333. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Siedler DG, Chuah MI, Kirkcaldie MT,
Vickers JC and King AE: Diffuse axonal injury in brain trauma:
Insights from alterations in neurofilaments. Front Cell Neurosci.
8:4292014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Wang ZH, Wu YY, Tang H, Tan L,
Wang X, Gao XY, Xiong YS, Liu D, Wang JZ and Zhu LQ: Melatonin
attenuates scopolamine-induced memory/synaptic disorder by rescuing
EPACs/miR-124/Egr1 pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 47:373–381. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yan BC, Park JH, Chen BH, Cho JH, Kim IH,
Ahn JH, Lee JC, Hwang IK, Cho JH, Lee YL, et al: Long-term
administration of scopolamine interferes with nerve cell
proliferation, differentiation and migration in adult mouse
hippocampal dentate gyrus, but it does not induce cell death.
Neural Regen Res. 9:1731–1739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Lee JC, Park JH, Ahn JH, Kim IH, Cho JH,
Choi JH, Yoo KY, Lee CH, Hwang IK, Cho JH, et al: NNew GABAergic
neurogenesis in the hippocampal CA1 region of a gerbil model of
long-term survival after transient cerebral ischemic injury. Brain
Pathol. 26:581–592. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Park JH, Lee CH, Yoo KY, Choi JH, Hwang
IK, Lee JY, Kang IJ and Won MH: FoxO3a immunoreactivity is markedly
decreased in the dentate gyrus, not the hippocampus proper, of the
aged gerbil. Exp Gerontol. 46:836–840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Blokland A: Scopolamine-induced deficits
in cognitive performance: A review of animal studies. Scopolamine
Rev. 1:1–76. 2005.
|
|
35
|
Ebert U and Kirch W: Scopolamine model of
dementia: Electroencephalogram findings and cognitive performance.
Eur J Clin Invest. 28:944–949. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shi Z, Chen L, Li S, Chen S, Sun X, Sun L,
Li Y, Zeng J, He Y and Liu X: Chronic scopolamine-injection-induced
cognitive deficit on reward-directed instrumental learning in rat
is associated with CREB signaling activity in the cerebral cortex
and dorsal hippocampus. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 230:245–260.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Romanski LM and LeDoux JE: Information
cascade from primary auditory cortex to the amygdala:
Corticocortical and corticoamygdaloid projections of temporal
cortex in the rat. Cereb Cortex. 3:515–532. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
D'Hooge R and De Deyn PP: Applications of
the Morris water maze in the study of learning and memory. Brain
Res Brain Res Rev. 36:60–90. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Morris R: Developments of a water-maze
procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci
Methods. 11:47–60. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fletcher DA and Mullins RD: Cell mechanics
and the cytoskeleton. Nature. 463:485–492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
41
|
Norgren N, Rosengren L and Stigbrand T:
Elevated neurofilament levels in neurological diseases. Brain Res.
987:25–31. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Gotow T: Neurofilaments in health and
disease. Med Electron Microsc. 33:173–199. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Fournier AJ, Rajbhandari L, Shrestha S,
Venkatesan A and Ramesh KT: In vitro and in situ visualization of
cytoskeletal deformation under load: traumatic axonal injury. FASEB
J. 28:5277–5287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Leifer D and Kowall NW:
Immunohistochemical patterns of selective cellular vulnerability in
human cerebral ischemia. J Neurol Sci. 119:217–228. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Posmantur RM, Newcomb JK, Kampfl A and
Hayes RL: Light and confocal microscopic studies of evolutionary
changes in neurofilament proteins following cortical impact injury
in the rat. Exp Neurol. 161:15–26. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Reinés A, Cereseto M, Ferrero A, Bonavita
C and Wikinski S: Neuronal cytoskeletal alterations in an
experimental model of depression. Neuroscience. 129:529–538. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Sanna MD, Ghelardini C and Galeotti N:
Effect of amitriptyline treatment on neurofilament-H protein in an
experimental model of depression. Brain Res Bull. 128:1–6. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|