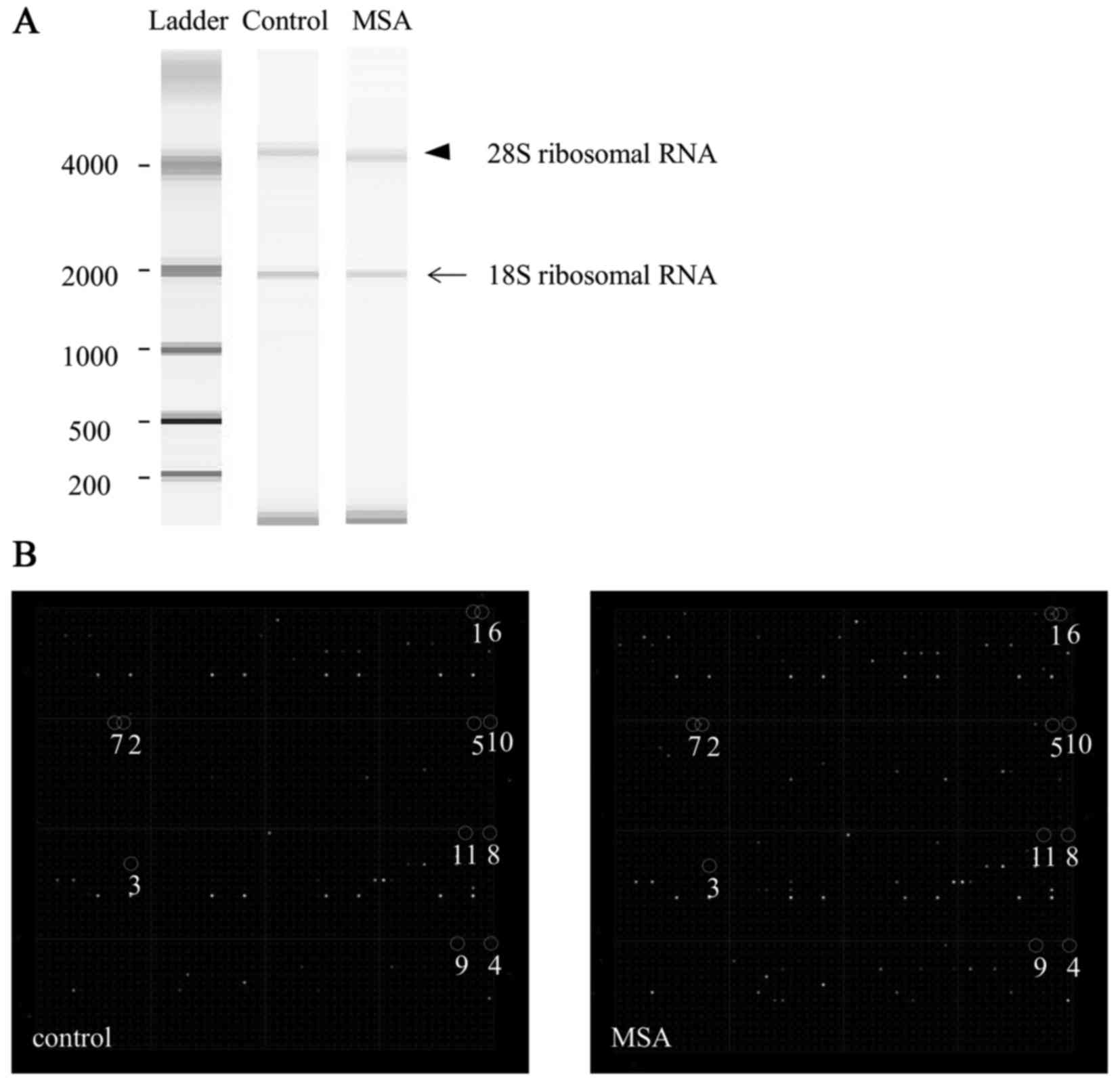
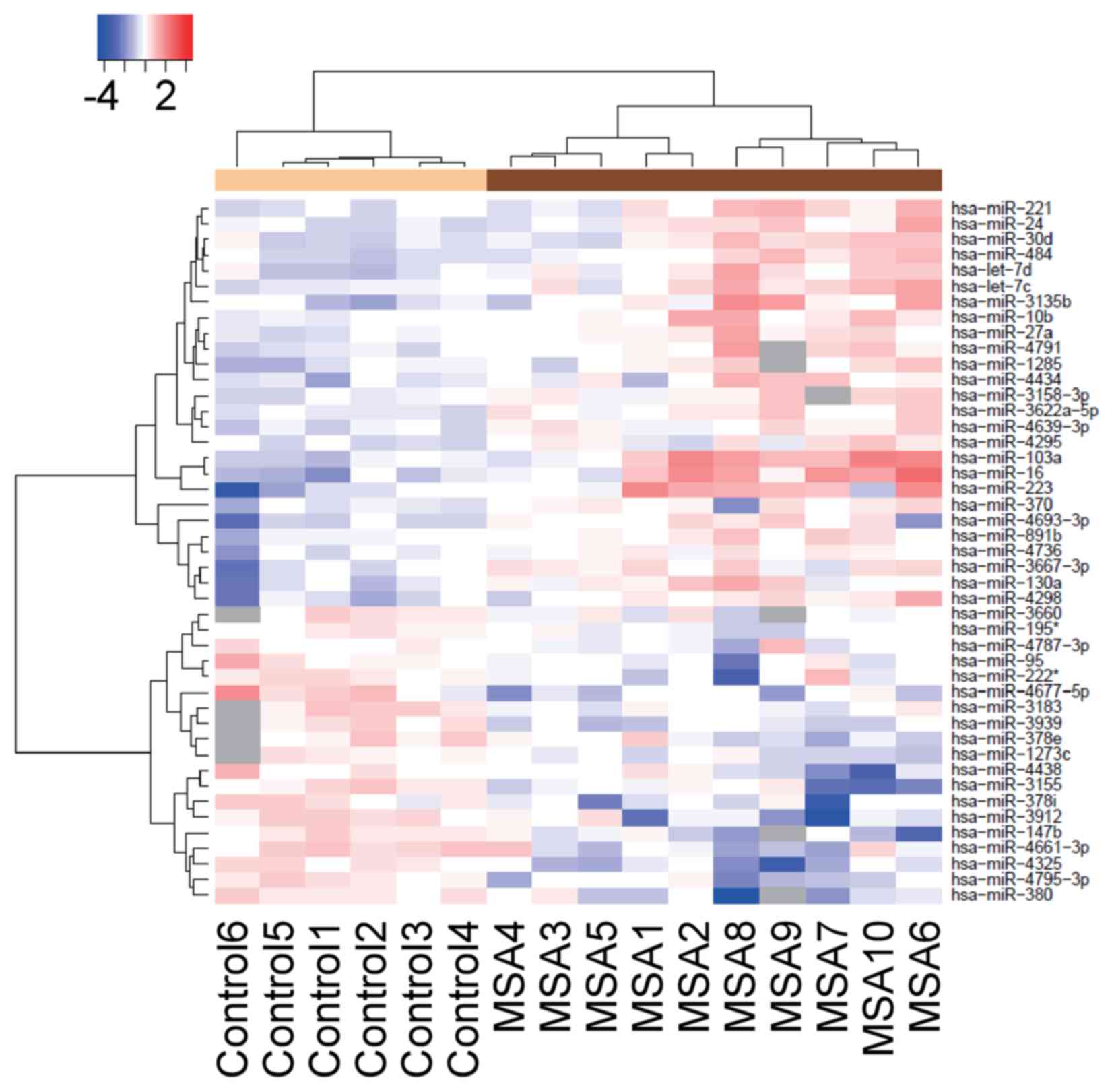
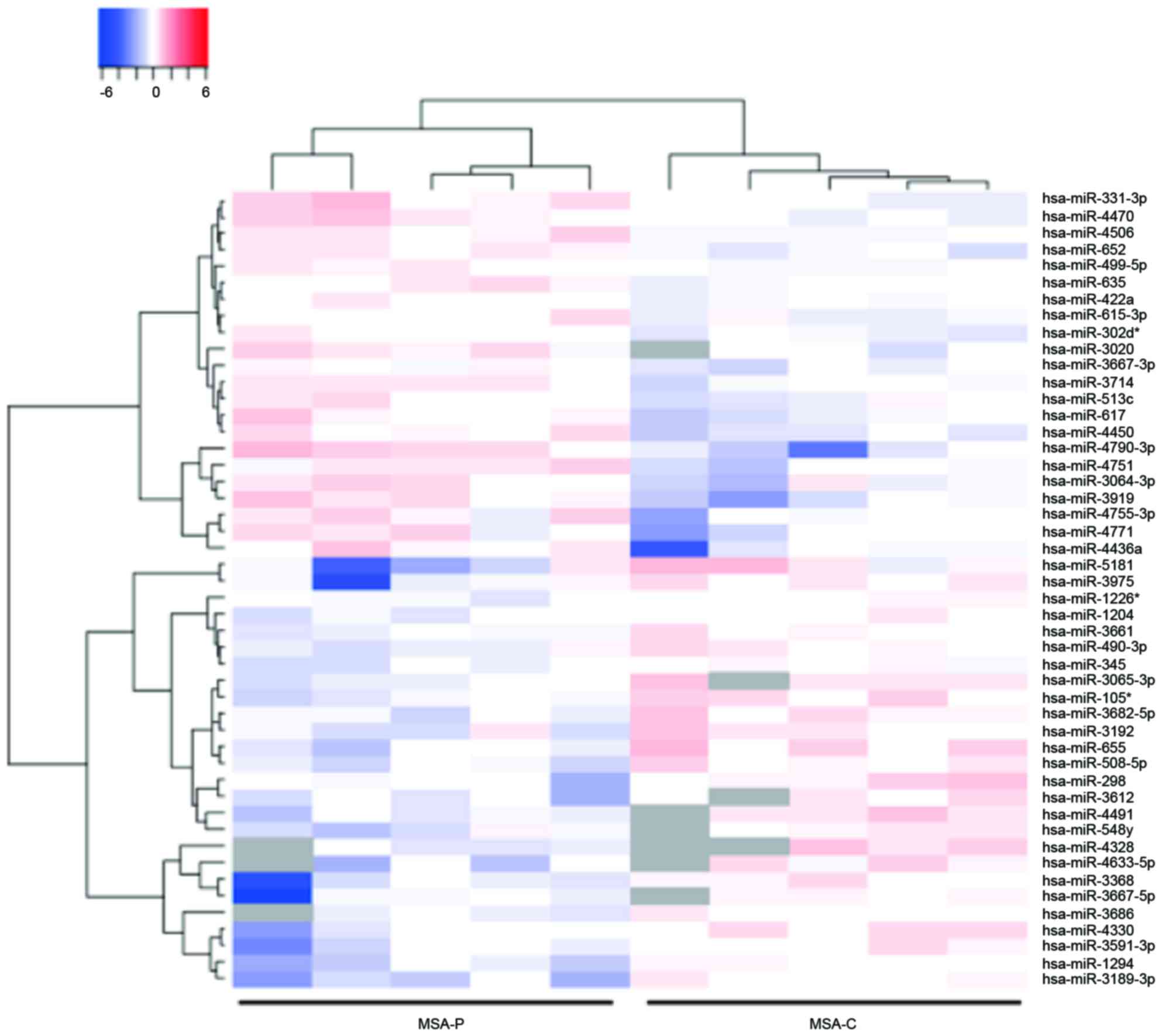
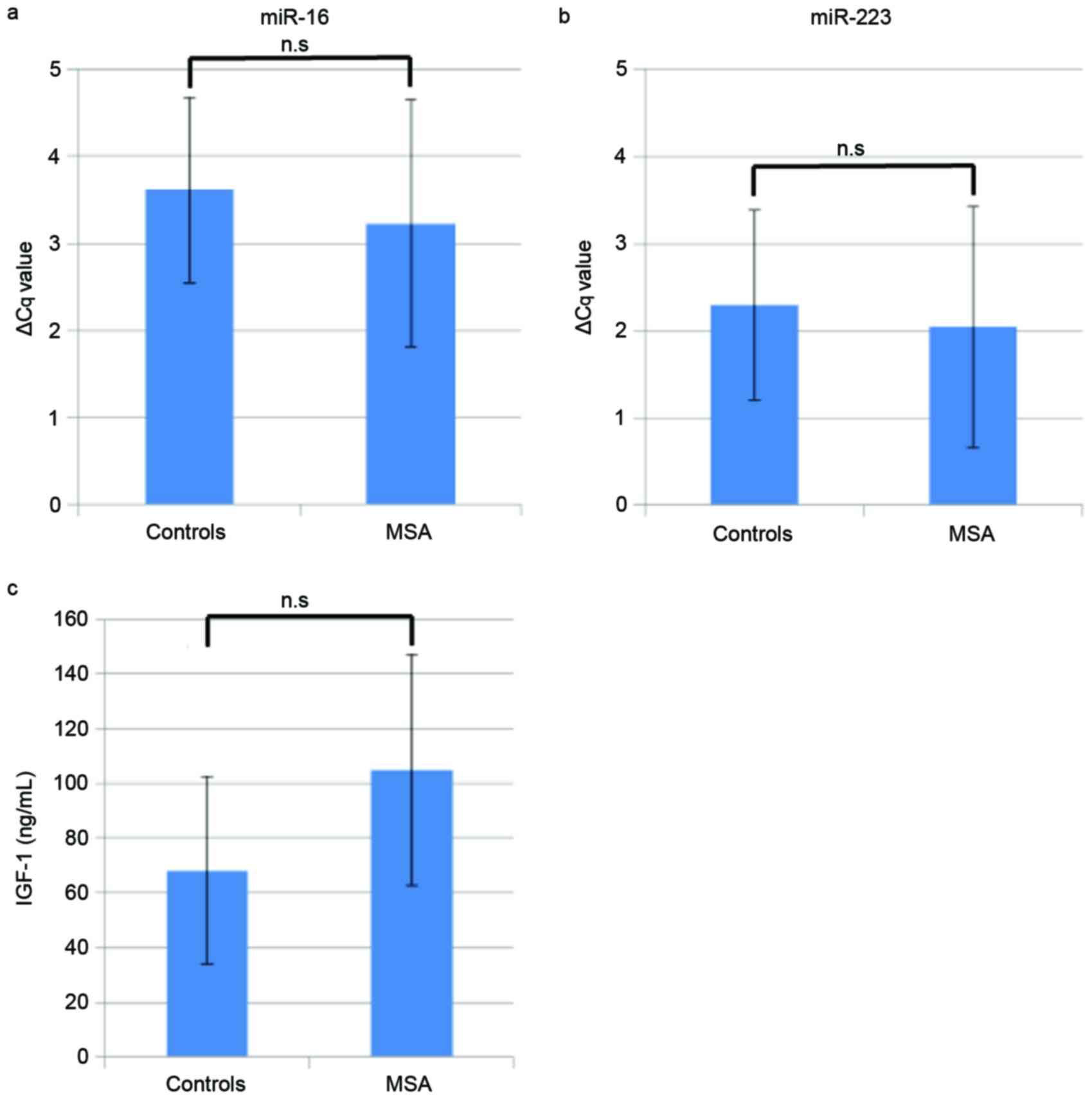
|
1
|
Stefanova N, Bücke P, Duerr S and Wenning
GK: Multiple system atrophy: An update. Lancet Neurol. 8:1172–1178.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Joutsa J, Gardberg M, Röyttä M and
Kaasinen V: Diagnostic accuracy of parkinsonism syndromes by
general neurologists. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 20:840–844. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jellinger KA: Neuropathology of multiple
system atrophy: New thoughts about pathogenesis. Mov Disord.
29:1720–1741. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stefanova N, Kaufmann WA, Humpel C, Poewe
W and Wenning GK: Systemic proteasome inhibition triggers
neurodegeneration in a transgenic mouse model expressing human
α-synuclein under oligodendrocyte promoter: Implications for
multiple system atrophy. Acta Neuropathol. 124:51–65. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Salta E and De Strooper B: Non-coding RNAs
with essential roles in neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol.
11:189–200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cloutier F, Marrero A, O'Connell C and
Morin P Jr: MicroRNAs as potential circulating biomarkers for
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Mol Neurosci. 56:102–112. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pellecchia MT, Pivonello R, Longo K,
Manfredi M, Tessitore A, Amboni M, Pivonello C, Rocco M, Cozzolino
A, Colao A and Barone P: Multiple system atrophy is associated with
changes in peripheral insulin-like growth factor system. Mov
Disord. 25:2621–2626. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Numao A, Suzuki K, Miyamoto M, Miyamoto T
and Hirata K: Clinical correlates of serum insulin-like growth
factor-1 in patients with Parkinson's disease, multiple system
atrophy and progressive supranuclear palsy. Parkinsonism Relat
Disord. 20:212–216. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jia CY, Li HH, Zhu XC, Dong YW, Fu D, Zhao
QL, Wu W and Wu XZ: MiR-223 suppresses cell proliferation by
targeting IGF-1R. PLoS One. 6:e270082011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu S, Peng W, Li X, Weng J, Zhang X, Guo
J, Huang D, Rong Q and Chen S: miR-1827 inhibits osteogenic
differentiation by targeting IGF1 in MSMSCs. Sci Rep. 7:461362017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ,
Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ, Wood NW, Colosimo C, Dürr A, Fowler CJ,
et al: Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple
system atrophy. Neurology. 71:670–676. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vallelunga A, Ragusa M, Di Mauro S,
Iannitti T, Pilleri M, Biundo R, Weis L, Di Pietro C, De Iuliis A,
Nicoletti A, et al: Identification of circulating microRNAs for the
differential diagnosis of Parkinson's disease and multiple system
atrophy. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:1562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee ST, Chu K, Jung KH, Ban JJ, Im WS, Jo
HY, Park JH, Lim JY, Shin JW, Moon J, et al: Altered expression of
miR-202 in cerebellum of multiple-system atrophy. Mol Neurobiol.
51:180–186. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ubhi K, Rockenstein E, Kragh C, Inglis C,
Spencer B, Michael S, Mante M, Adame A, Galasko D and Masliah E:
Widespread microRNA dysregulation in multiple system
atrophy-disease-related alteration in miR-96. Eur J Neurosci.
39:1026–1041. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schafferer S, Khurana R, Refolo V, Venezia
S, Sturm E, Piatti P, Hechenberger C, Hackl H, Kessler R, Willi M,
et al: Changes in the miRNA-mRNA regulatory network precede motor
symptoms in a mouse model of multiple system atrophy: Clinical
implications. PLoS One. 11:e01507052016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang E, Liu R and Chu Y: miRNA-15a/16: As
tumor suppressors and more. Future Oncol. 11:2351–2363. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang Z and Cheng Y: miR-16-1 promotes the
aberrant α-synuclein accumulation in Parkinson disease via
targeting heat shock protein 70. ScientificWorldJournal.
2014:9383482014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kawamoto Y, Akiguchi I, Shirakashi Y,
Honjo Y, Tomimoto H, Takahashi R and Budka H: Accumulation of Hsc70
and Hsp70 in glial cytoplasmic inclusions in patients with multiple
system atrophy. Brain Res. 1136:219–227. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan B, Chen Y, Song H, Xu Y, Wang R and
Chen L: Mir-24-3p downregulation contributes to VP16-DDP resistance
in small-cell lung cancer by targeting ATG4A. Oncotarget.
6:317–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Comincini S, Allavena G, Palumbo S, Morini
M, Durando F, Angeletti F, Pirtoli L and Miracco C: microRNA-17
regulates the expression of ATG7 and modulates the autophagy
process, improving the sensitivity to temozolomide and low-dose
ionizing radiation treatments in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer
Biol Ther. 14:574–586. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun KT, Chen MY, Tu MG, Wang IK, Chang SS
and Li CY: MicroRNA-20a regulates autophagy related protein-ATG16L1
in hypoxia-induced osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 73:145–153.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu H, Wang F, Hu S, Yin C, Li X, Zhao S,
Wang J and Yan X: MiR-20a and miR-106b negatively regulate
autophagy induced by leucine deprivation via suppression of ULK1
expression in C2C12 myoblasts. Cell Signal. 24:2179–2186. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Wang N, Liu P, Chen Q, Situ H, Xie
T, Zhang J, Peng C, Lin Y and Chen J: MicroRNA-25 regulates
chemoresistance-associated autophagy in breast cancer cells, a
process modulated by the natural autophagy inducer
isoliquiritigenin. Oncotarget. 5:7013–7026. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang X, Zhong X, Tanyi JL, Shen J, Xu C,
Gao P, Zheng TM, DeMichele A and Zhang L: mir-30d regulates
multiple genes in the autophagy pathway and impairs autophagy
process in human cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
431:617–622. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Yang WQ, Zhu H, Qian YY, Zhou L,
Ren YJ, Ren XC, Zhang L, Liu XP, Liu CG, et al: Regulation of
autophagy by miR-30d impacts sensitivity of anaplastic thyroid
carcinoma to cisplatin. Biochem Pharmacol. 87:562–570. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Song L, Su M, Wang S, Zou Y, Wang X, Wang
Y, Cui H, Zhao P, Hui R and Wang J: MiR-451 is decreased in
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and regulates autophagy by targeting
TSC1. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2266–2274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tanji K, Odagiri S, Maruyama A, Mori F,
Kakita A, Takahashi H and Wakabayashi K: Alteration of
autophagosomal proteins in the brain of multiple system atrophy.
Neurobiol Dis. 49:190–198. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Haneklaus M, Gerlic M, O'Neill LA and
Masters SL: miR-223: Infection, inflammation and cancer. J Intern
Med. 274:215–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Boyerinas B, Park SM, Hau A, Murmann AE
and Peter ME: The role of let-7 in cell differentiation and cancer.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:F19–F36. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lehmann SM, Krüger C, Park B, Derkow K,
Rosenberger K, Baumgart J, Trimbuch T, Eom G, Hinz M, Kaul D, et
al: An unconventional role for miRNA: Let-7 activates Toll-like
receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration. Nat Neurosci. 15:827–835.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|