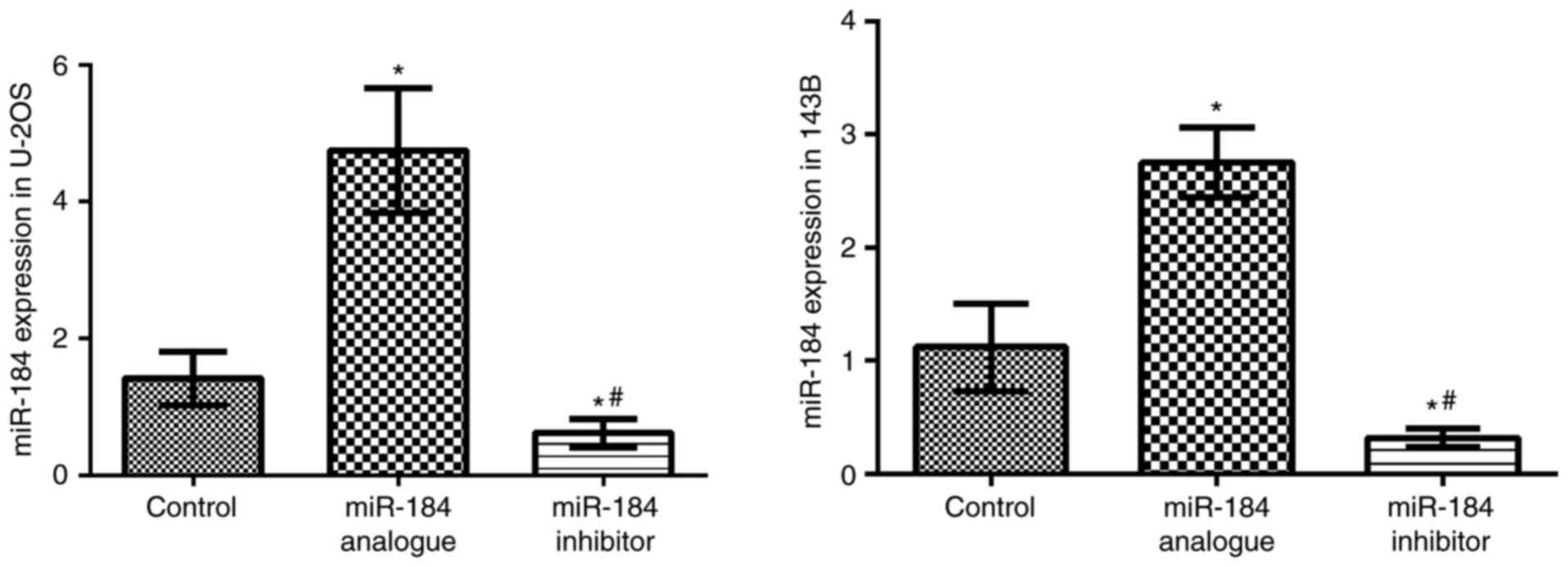
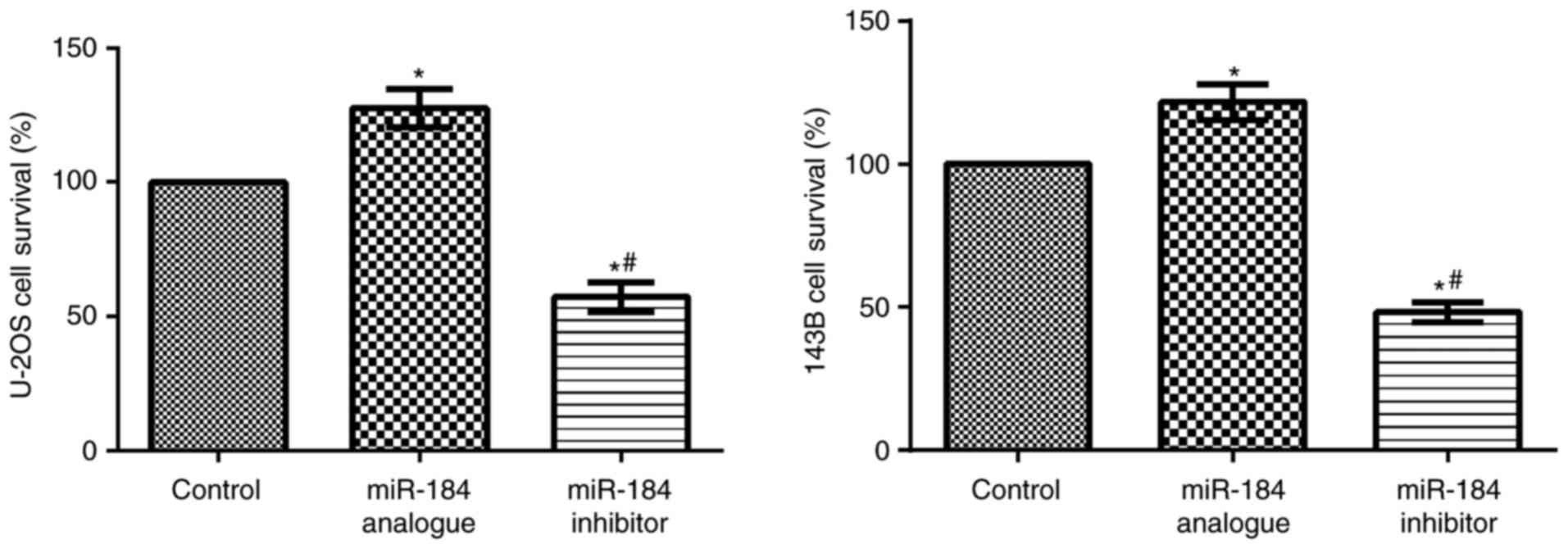
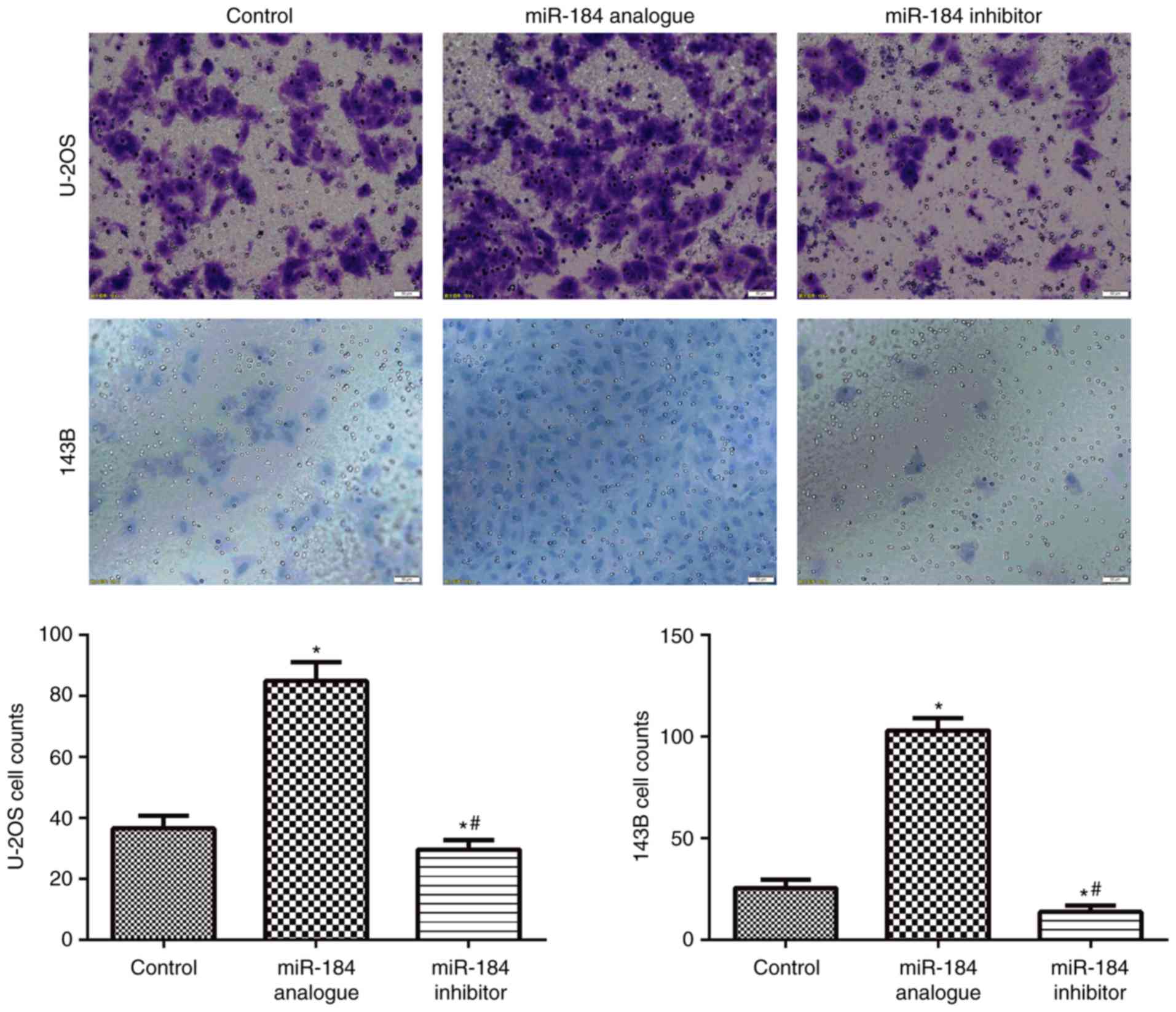
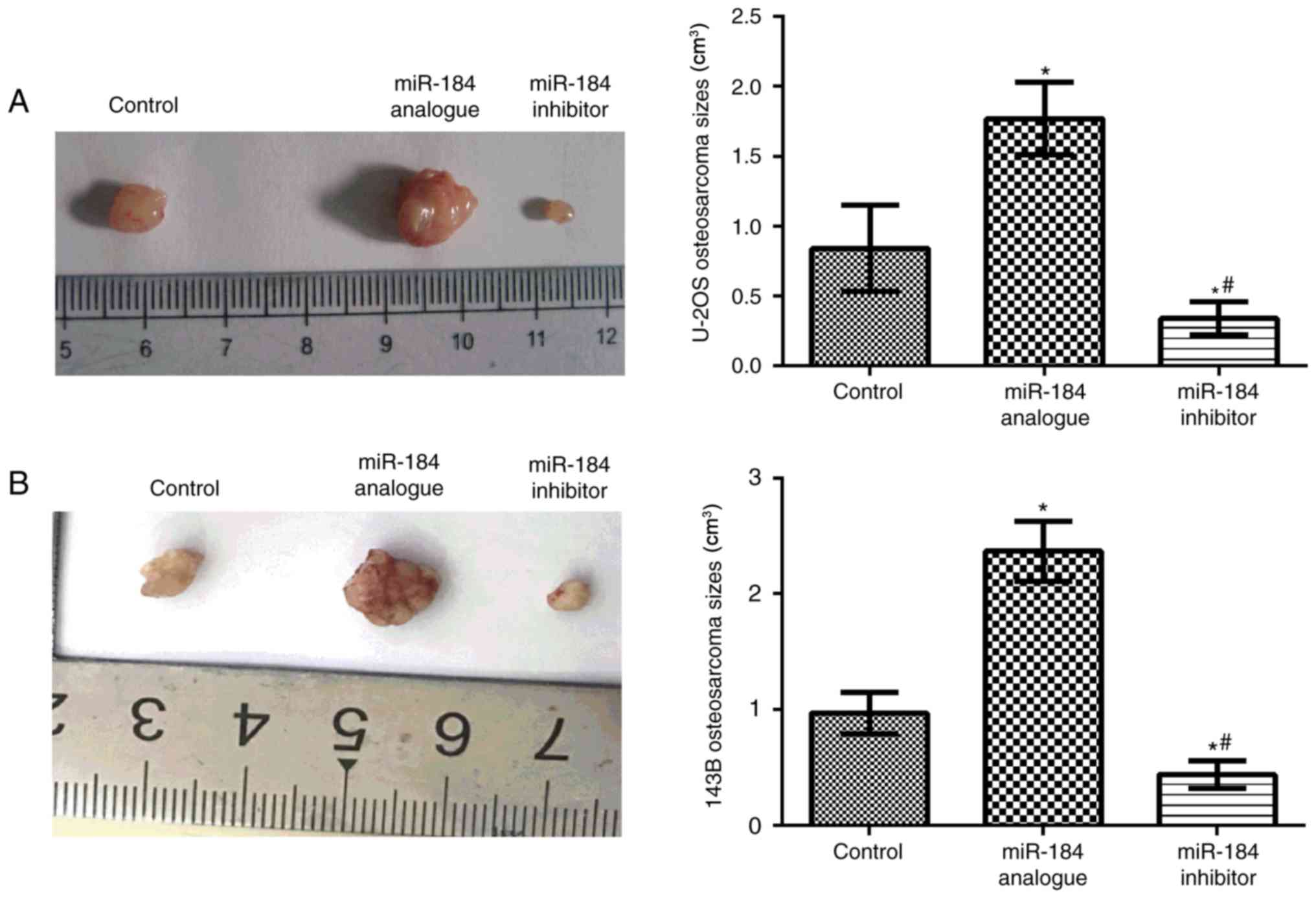
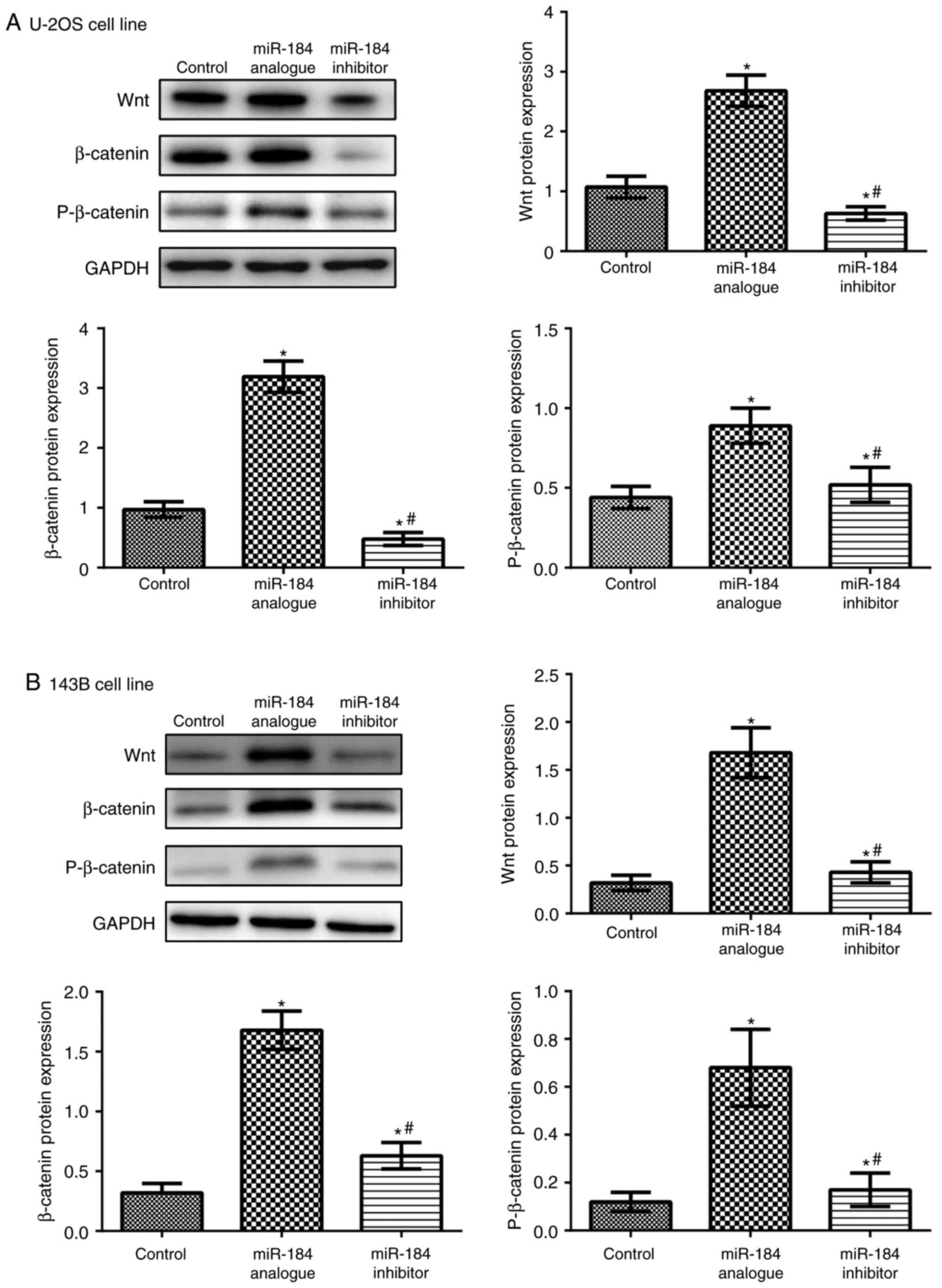
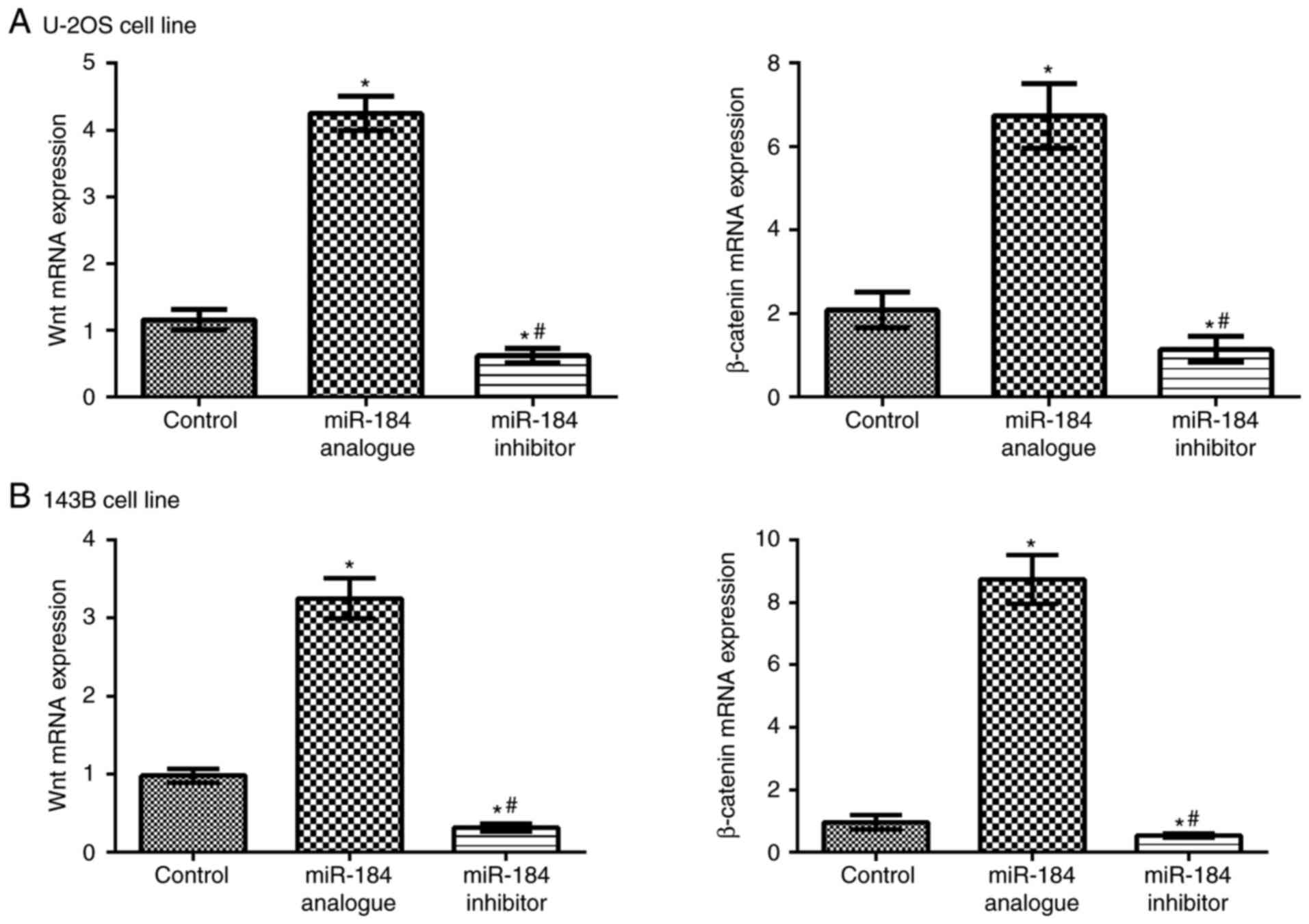
|
1
|
Unni KK: Osteosarcoma of bone. J Orthop
Sci. 3:287–294. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Longhi A, Ferrari S, Bacci G and Specchia
S: Long-term follow-up of patients with doxorubicin-induced cardiac
toxicity after chemotherapy for osteosarcoma. Anticancer Drugs.
18:737–744. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Meyers PA, Schwartz CL, Krailo MD, Healey
JH, Bernstein ML, Betcher D, Ferguson WS, Gebhardt MC, Goorin AM,
Harris M, et al: Osteosarcoma: The addition of muramyl tripeptide
to chemotherapy improves overall survival-a report from the
Children's Oncology Group. J Clin Oncol. 26:633–638. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hameed M and Dorfman H: Primary malignant
bone tumors-recent developments. Semin Diagn Pathol. 28:86–101.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mirabello L, Troisi RJ and Savage SA:
Osteosarcoma incidence and survival rates from 1973 to 2004: Data
from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results program.
Cancer. 115:1531–1543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Diao C, Xi Y and Xiao T: Identification
and analysis of key genes in osteosarcoma using bioinformatics.
Oncol Lett. 15:2789–2794. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Y, Sun W, Ma X, Hao Y, Liu G, Hu X,
Shang H, Wu P, Zhao Z and Liu W: Logistic regression analysis for
the identification of the metastasis-associated signaling pathways
of osteosarcoma. Int J Mol Med. 41:1233–1244. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miao J, Wu S, Peng Z, Tania M and Zhang C:
MicroRNAs in osteosarcoma: Diagnostic and therapeutic aspects.
Tumour Biol. 34:2093–2098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu JQ, Zhang WB, Wan R and Yang YQ:
MicroRNA-32 inhibits osteosarcoma cell proliferation and invasion
by targeting Sox9. Tumour Biol. 35:9847–9853. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan K, Gao J, Yang T, Ma Q, Qiu X, Fan Q
and Ma B: MicroRNA-34a inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
7:e337782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang K, Zhang C, Liu L and Zhou J: A key
role of microRNA-29b in suppression of osteosarcoma cell
proliferation and migration via modulation of VEGF. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 7:5701–5708. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li E, Zhang J, Yuan T and Ma B: MiR-145
inhibits osteosarcoma cells proliferation and invasion by targeting
ROCK1. Tumour Biol. 35:7645–7650. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han K, Zhao T, Chen X, Bian N, Yang T, Ma
Q, Cai C, Fan Q, Zhou Y and Ma B: microRNA-194 suppresses
osteosarcoma cell proliferation and metastasis in vitro and
in vivo by targeting CDH2 and IGF1R. Int J Oncol.
45:1437–1449. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pan W, Wang H, Jianwei R and Ye Z:
MicroRNA-27a promotes proliferation, migration and invasion by
targeting MAP2K4 in human osteosarcoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem.
33:402–412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen L, Chen XD and Zhang YH: MicroRNA-128
promotes proliferation in osteosarcoma cells by downregulating
PTEN. Tumour Biol. 35:2069–2074. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su Z, Chen D, Li Y, Zhang E, Yu Z, Chen T,
Jiang Z, Ni L, Yang S, Gui Y, et al: microRNA-184 functions as
tumor suppressor in renal cell carcinoma. Exp Ther Med. 9:961–966.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu G, Liu J, Wu Z, Wu X and Yao X:
MicroRNA-184 inhibits cell proliferation and metastasis in human
colorectal cancer by directly targeting IGF-1R. Oncol Lett.
14:3215–3222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang YB, Zhao XH, Li G, Zheng JH and Qiu
W: MicroRNA-184 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of
human colon cancer SW480 and HCT116 cells by downregulating C-MYC
and BCL-2. J Cell Biochem. 119:1702–1715. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liang XG, Meng WT, Hu LJ, Li L, Xing H,
Xie G, Wang AQ and Jia YQ: MicroRNA-184 modulates human central
nervous system lymphoma cells growth and invasion by targeting
iASPP. J Cell Biochem. 118:2645–2653. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao B, Gao K, Li L, Huang Z and Lin L:
miR-184 functions as an oncogenic regulator in hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC). Biomed Pharmacother. 68:143–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yin GR, Wang Q, Zhang XB and Wang SJ:
Regulatory role of microRNA184 in osteosarcoma cells. Genet Mol
Res. 14:14246–14252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rapp J, Jaromi L, Kvell K, Miskei G and
Pongracz JE: WNT signaling-lung cancer is no exception. Respir Res.
18:1672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bryja V, Gradl D, Schambony A, Arenas E
and Schulte G: Beta-arrestin is a necessary component of
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:6690–6695. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Seki Y, Yamamoto H, Ngan CY, Yasui M,
Tomita N, Kitani K, Takemasa I, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N, et
al: Construction of a novel DNA decoy that inhibits the oncogenic
beta-catenin/T-cell factor pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:985–994.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lustig B and Behrens J: The Wnt signaling
pathway and its role in tumor development. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
129:199–221. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rubin EM, Guo Y, Tu K, Xie J, Zi X and
Hoang BH: Wnt inhibitory factor 1 decreases tumorigenesis and
metastasis in osteosarcoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:731–741. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
An JH, Yang JY, Ahn BY, Cho SW, Jung JY,
Cho HY, Cho YM, Kim SW, Park KS, Kim SY, et al: Enhanced
mitochondrial biogenesis contributes to Wnt induced osteoblastic
differentiation of C3H10T1/2 cells. Bone. 47:140–150. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cai Y, Mohseny AB, Karperien M, Hogendoorn
PC, Zhou G and Cleton-Jansen AM: Inactive Wnt/beta-catenin pathway
in conventional high-grade osteosarcoma. J Pathol. 220:24–33. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun X, He Y, Huang C, Ma TT and Li J:
Distinctive microRNA signature associated of neoplasms with the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Signal. 25:2805–2811. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Euhus DM, Hudd C, LaRegina MC and Johnson
FE: Tumor measurement in the nude mouse. J Surg Oncol. 31:229–234.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lindsey BA, Markel JE and Kleinerman ES:
Osteosarcoma overview. Rheumatol Ther. 4:25–43. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Durfee RA, Mohammed M and Luu HH: Review
of osteosarcoma and current management. Rheumatol Ther. 3:221–243.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang J, Yan YG, Wang C, Zhang SJ, Yu XH
and Wang WJ: MicroRNAs in osteosarcoma. Clin Chim Acta. 444:9–17.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang J and Zhang W: New molecular insights
into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:398–406.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lauvrak SU, Munthe E, Kresse SH, Stratford
EW, Namløs HM, Meza-Zepeda LA and Myklebost O: Functional
characterisation of osteosarcoma cell lines and identification of
mRNAs and miRNAs associated with aggressive cancer phenotypes. Br J
Cancer. 109:2228–2236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lin BC, Huang D, Yu CQ, Mou Y, Liu YH,
Zhang DW and Shi FJ: MicroRNA-184 modulates doxorubicin resistance
in osteosarcoma cells by targeting BCL2L1. Med Sci Monit.
22:1761–1765. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang X, Ding H, Han Y, Sun D, Wang H and
Zhai XU: The significance of microRNA-184 on JAK2/STAT3 signaling
pathway in the formation mechanism of glioblastoma. Oncol Lett.
10:3510–3514. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ueno K, Hirata H, Hinoda Y and Dahiya R:
Frizzled homolog proteins, microRNAs and Wnt signaling in cancer.
Int J Cancer. 132:1731–1740. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Schepeler T: Emerging roles of microRNAs
in the Wnt signaling network. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:357–371. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li H, Xiang H, Ge W, Wang H, Wang T and
Xiong M: Expression and functional perspectives of miR-184 in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:12313–12318. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Feng R and Dong L: Inhibitory effect of
miR-184 on the potential of proliferation and invasion in human
glioma and breast cancer cells in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:9376–9382. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|