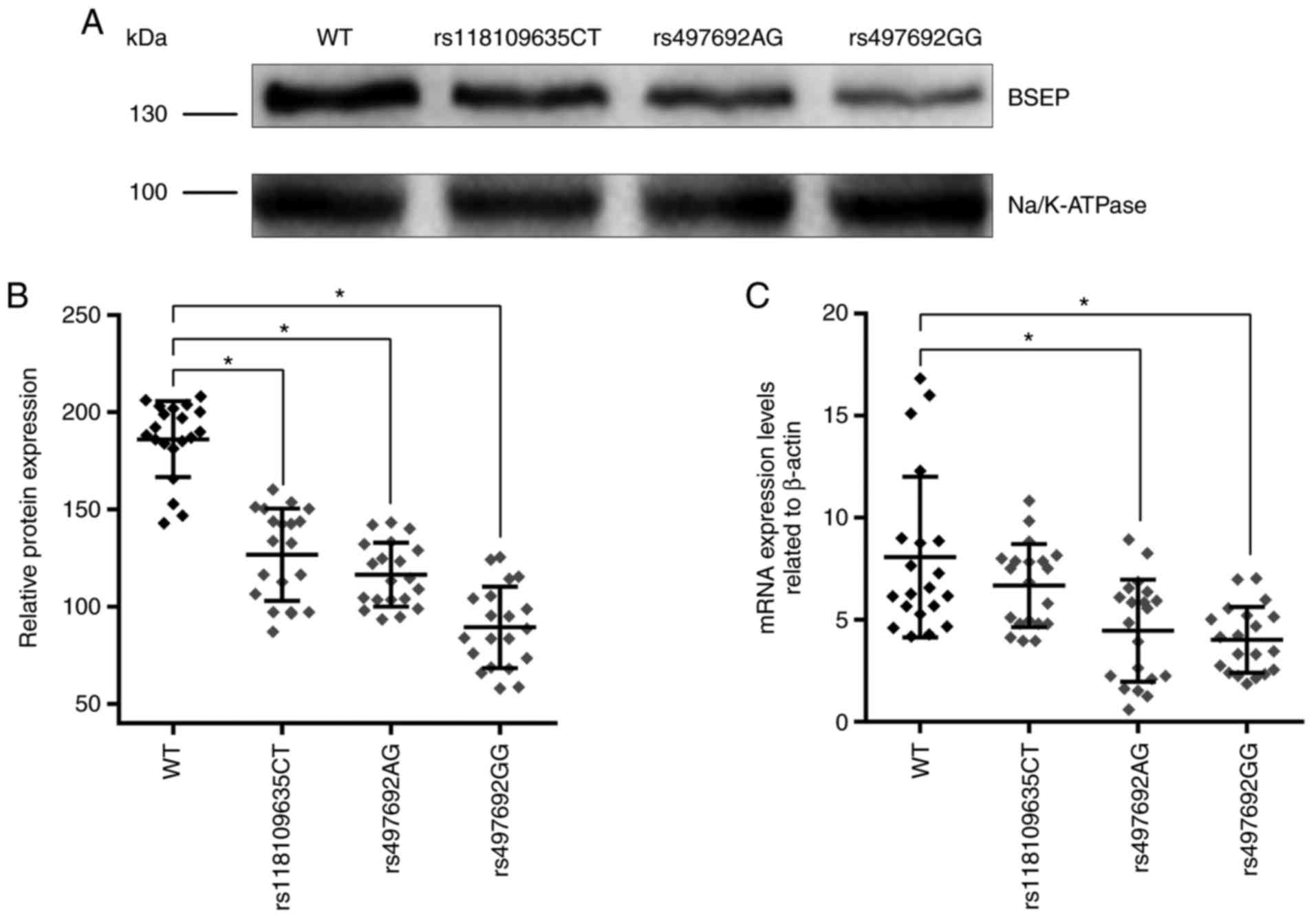
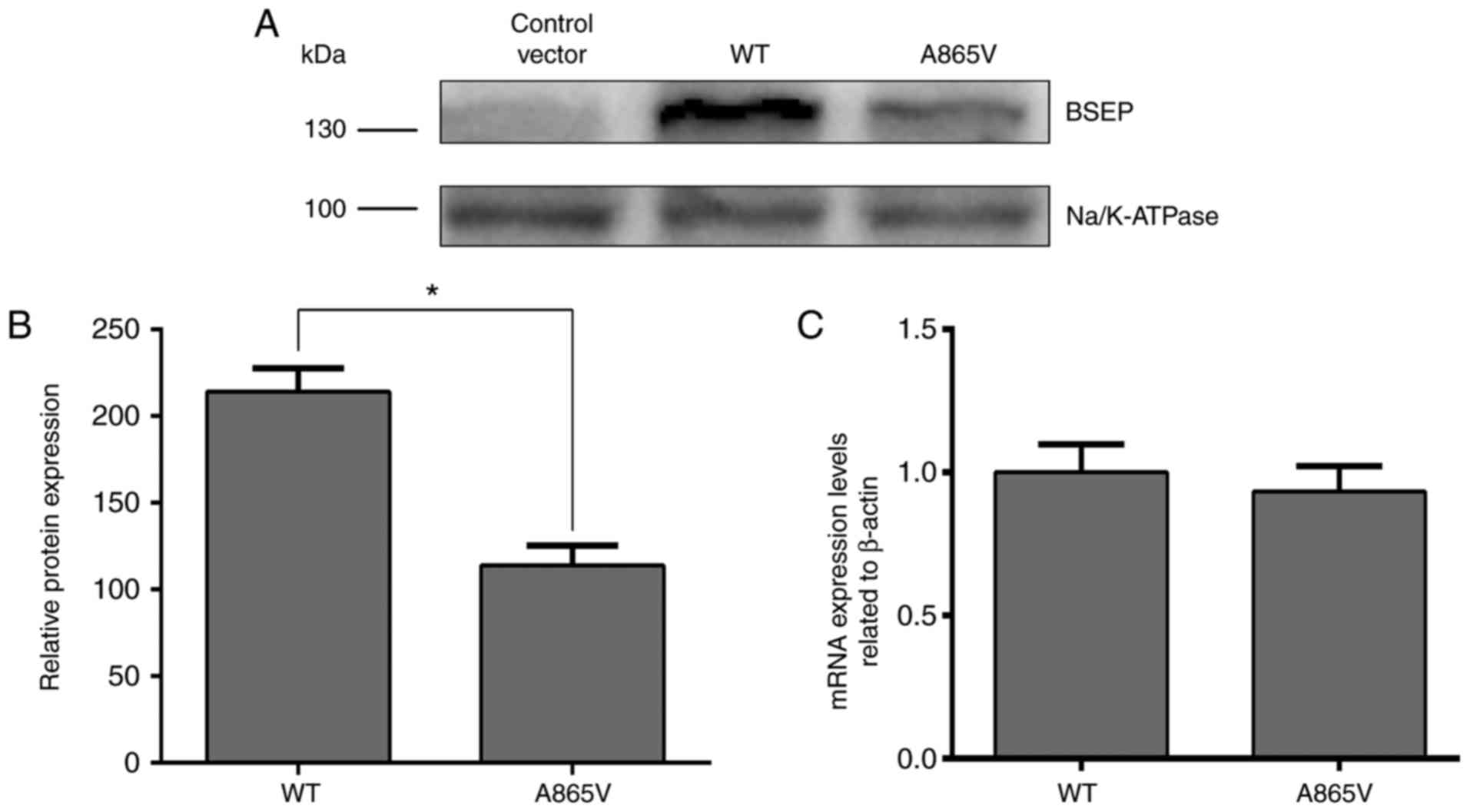
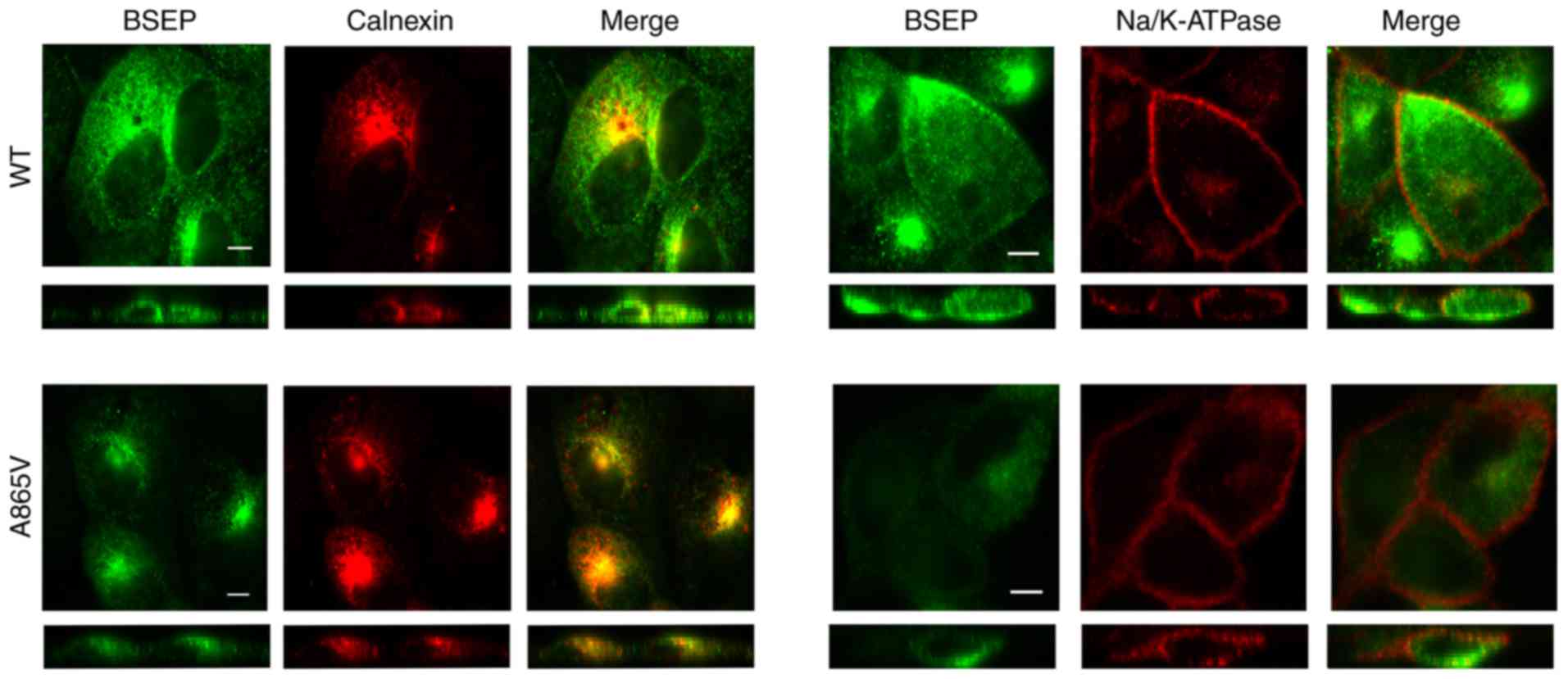
|
1
|
Clemente G, De Rose AM, Murri R, Ardito F,
Nuzzo G and Giuliante F: Liver resection for primary intrahepatic
stones: Focus on postoperative infectious complications. World J
Surg. 40:433–439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li SQ, Hua YP, Shen SL, Hu WJ, Peng BG and
Liang LJ: Segmental bile duct-targeted liver resection for
right-sided intrahepatic stones. Medicine (Baltimore).
94:e11582015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Catena M, Aldrighetti L, Finazzi R, Arzu
G, Arru M, Pulitanò C and Ferla G: Treatment of non-endemic
hepatolithiasis in a Western country. The role of hepatic
resection. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 88:383–389. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nakayama F, Soloway RD, Nakama T, Miyazaki
K, Ichimiya H, Sheen PC, Ker CG, Ong GB, Choi TK, Boey J, et al:
Hepatolithiasis in East Asia. Retrospective study. Dig Dis Sci.
31:21–26. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pan S, Li X, Jiang P, Jiang Y, Shuai L, He
Y and Li Z: Variations of ABCB4 and ABCB11 genes are associated
with primary intrahepatic stones. Mol Med Rep. 11:434–446. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meng ZW, Han SH, Zhu JH, Zhou LY and Chen
YL: Risk factors for cholangiocarcinoma after initial hepatectomy
for intrahepatic stones. World J Surg. 41:835–843. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cetta FM: Bile infection documented as
initial event in the pathogenesis of brown pigment biliary stones.
Hepatology. 6:482–489. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sakpal SV, Babel N and Chamberlain RS:
Surgical management of hepatolithiasis. HPB (Oxford). 11:194–202.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tazuma S: Gallstone disease: Epidemiology,
pathogenesis, and classification of biliary stones (common bile
duct and intrahepatic). Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
20:1075–1083. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meier Y, Pauli-Magnus C, Zanger UM, Klein
K, Schaeffeler E, Nussler AK, Nussler N, Eichelbaum M, Meier PJ and
Stieger B: Interindividual variability of canalicular
ATP-binding-cassette (ABC)-transporter expression in human liver.
Hepatology. 44:62–74. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kubitz R, Dröge C, Kluge S, Stindt J and
Häussinger D: Genetic variations of bile salt transporters. Drug
Discov Today Technol. 12:e55–e67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kubitz R, Dröge C, Stindt J, Weissenberger
K and Häussinger D: The bile salt export pump (BSEP) in health and
disease. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 36:536–553. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen R, Wang J, Tang S, Zhang Y, Lv X, Wu
S, Yang Z, Xia Y, Chen D and Zhan S: Role of polymorphic bile salt
export pump (BSEP, ABCB11) transporters in anti-tuberculosis
drug-induced liver injury in a Chinese cohort. Sci Rep.
6:277502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chai J, He Y, Cai SY, Jiang Z, Wang H, Li
Q, Chen L, Peng Z, He X, Wu X, et al: Elevated hepatic multidrug
resistance-associated protein 3/ATP-binding cassette subfamily C 3
expression in human obstructive cholestasis is mediated through
tumor necrosis factor alpha and c-Jun NH2-terminal
kinase/stress-activated protein kinase-signaling pathway.
Hepatology. 55:1485–1494. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Beausejour Y, Alvarez F, Beaulieu M and
Bilodeau M: Description of two new ABCB11 mutations responsible for
type 2 benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis in a
French-Canadian family. Can J Gastroenterol. 25:311–314. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hayashi H, Naoi S, Hirose Y, Matsuzaka Y,
Tanikawa K, Igarashi K, Nagasaka H, Kage M, Inui A and Kusuhara H:
Successful treatment with 4-phenylbutyrate in a patient with benign
recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 2 refractory to biliary
drainage and bilirubin absorption. Hepatol Res. 46:192–200. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hayashi H, Takada T, Suzuki H, Akita H and
Sugiyama Y: Two common PFIC2 mutations are associated with the
impaired membrane trafficking of BSEP/ABCB11. Hepatology.
41:916–924. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Waisbourd-Zinman O, Surrey LF, Schwartz
AE, Russo PA and Wen J: A Rare BSEP mutation associated with a mild
form of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2. Ann
Hepatol. 16:465–468. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Keitel V, Burdelski M, Warskulat U,
Kühlkamp T, Keppler D, Häussinger D and Kubitz R: Expression and
localization of hepatobiliary transport proteins in progressive
familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatology. 41:1160–1172. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Anzivino C, Odoardi MR, Meschiari E,
Baldelli E, Facchinetti F, Neri I, Ruggiero G, Zampino R,
Bertolotti M, Loria P and Carulli L: ABCB4 and ABCB11 mutations in
intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in an Italian population. Dig
Liver Dis. 45:226–232. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Keitel V, Vogt C, Häussinger D and Kubitz
R: Combined mutations of canalicular transporter proteins cause
severe intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gastroenterology.
131:624–629. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lim TY, Coltart I, Foskett P, Thompson R,
Strautnieks S, Penna L, Williamson C, Miquel R and Heneghan MA:
Donor transmitted mutation of the ABCB11 gene and ensuing
intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy in a liver transplant
recipient. Liver Transpl. 23:1229–1232. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lam P, Pearson CL, Soroka CJ, Xu S,
Mennone A and Boyer JL: Levels of plasma membrane expression in
progressive and benign mutations of the bile salt export pump
(Bsep/Abcb11) correlate with severity of cholestatic diseases. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 293:C1709–C1716. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Z, Chen K, Jiang P, Zhang X, Li X and
Li Z: CD44v/CD44s expression patterns are associated with the
survival of pancreatic carcinoma patients. Diagn Pathol. 9:792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gordo-Gilart R, Andueza S, Hierro L,
Martínez-Fernández P, D'Agostino D, Jara P and Alvarez L:
Functional analysis of ABCB4 mutations relates clinical outcomes of
progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 3 to the degree
of MDR3 floppase activity. Gut. 64:147–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang R, Chen HL, Liu L, Sheps JA, Phillips
MJ and Ling V: Compensatory role of P-glycoproteins in knockout
mice lacking the bile salt export pump. Hepatology. 50:948–956.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu G, He P, Liu Z, Chen Q, Zheng B and
Zhang Q: Diagnosis of ABCB11 gene mutations in children with
intrahepatic cholestasis using high resolution melting analysis and
direct sequencing. Mol Med Rep. 10:1264–1274. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park JS, Ko JS, Seo JK, Moon JS and Park
SS: Clinical and ABCB11 profiles in Korean infants with progressive
familial intrahepatic cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol.
22:4901–4907. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tai Y, Xie Y and Tang CW: Compound
heterozygous mutations of ABCB11 responsible for benign recurrent
intrahepatic cholestasis. J Dig Dis. 16:299–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Byrne JA, Strautnieks SS, Ihrke G, Pagani
F, Knisely AS, Linton KJ, Mieli-Vergani G and Thompson RJ: Missense
mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms in ABCB11 impair bile
salt export pump processing and function or disrupt pre-messenger
RNA splicing. Hepatology. 49:553–567. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hayashi H and Sugiyama Y: 4-phenylbutyrate
enhances the cell surface expression and the transport capacity of
wild-type and mutated bile salt export pumps. Hepatology.
45:1506–1516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|