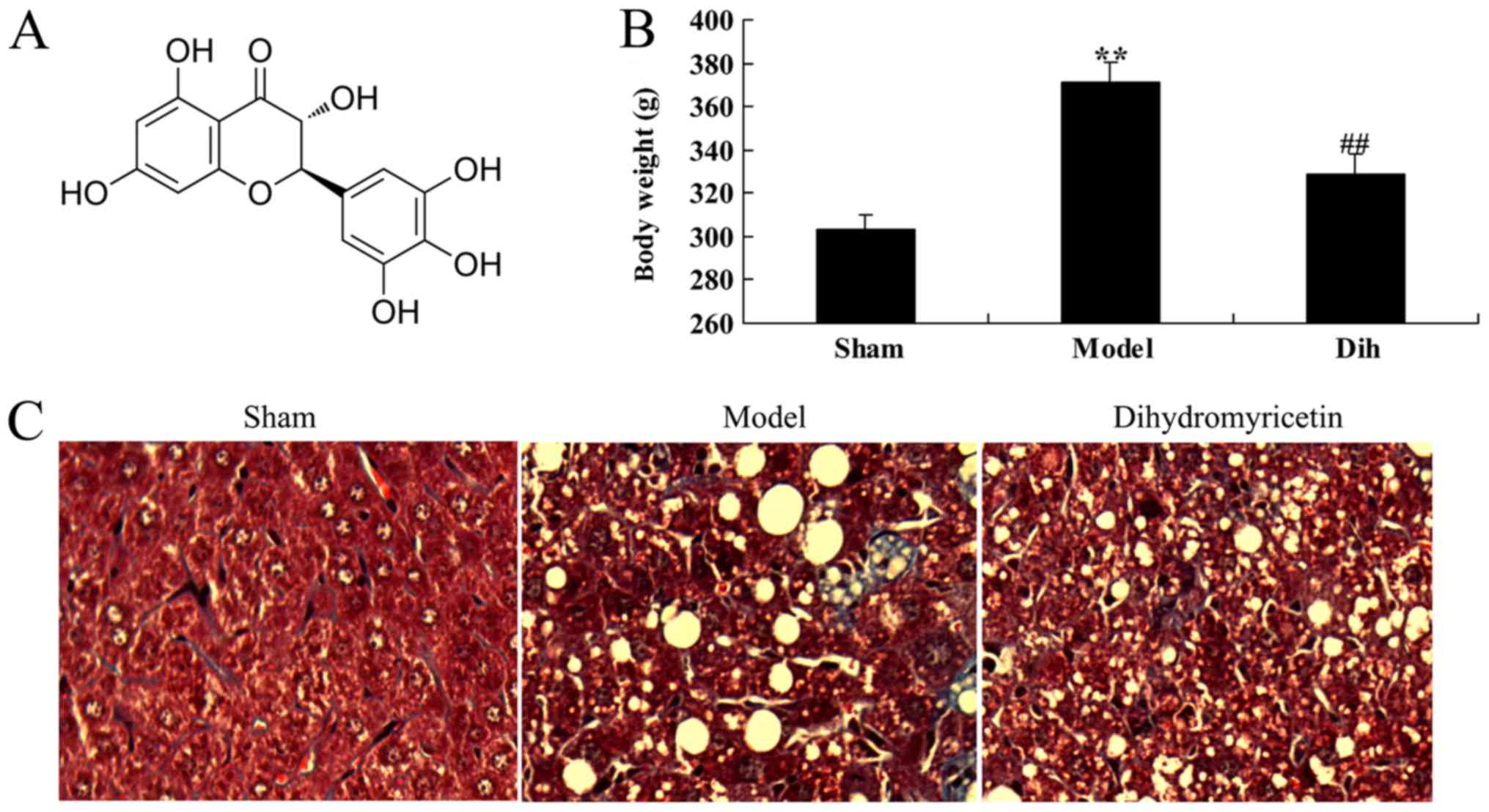
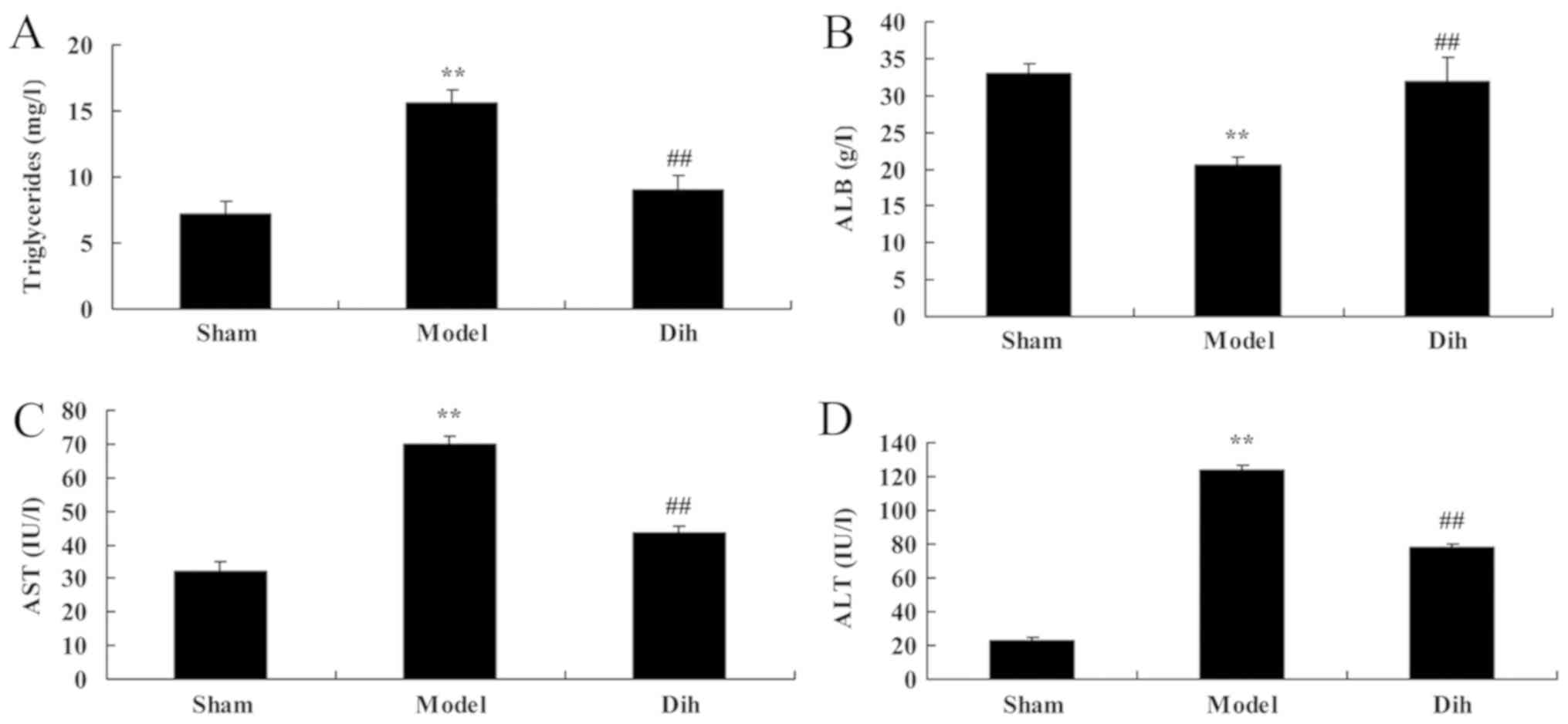
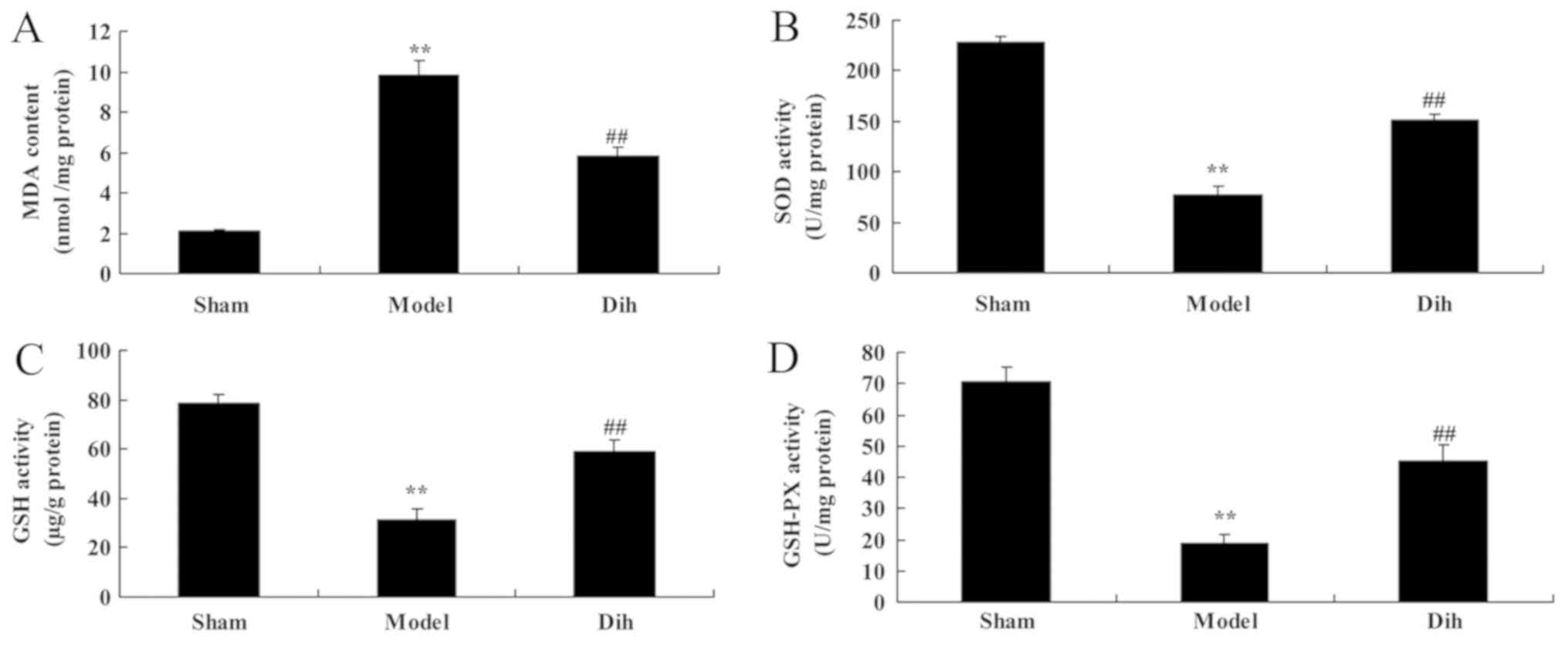
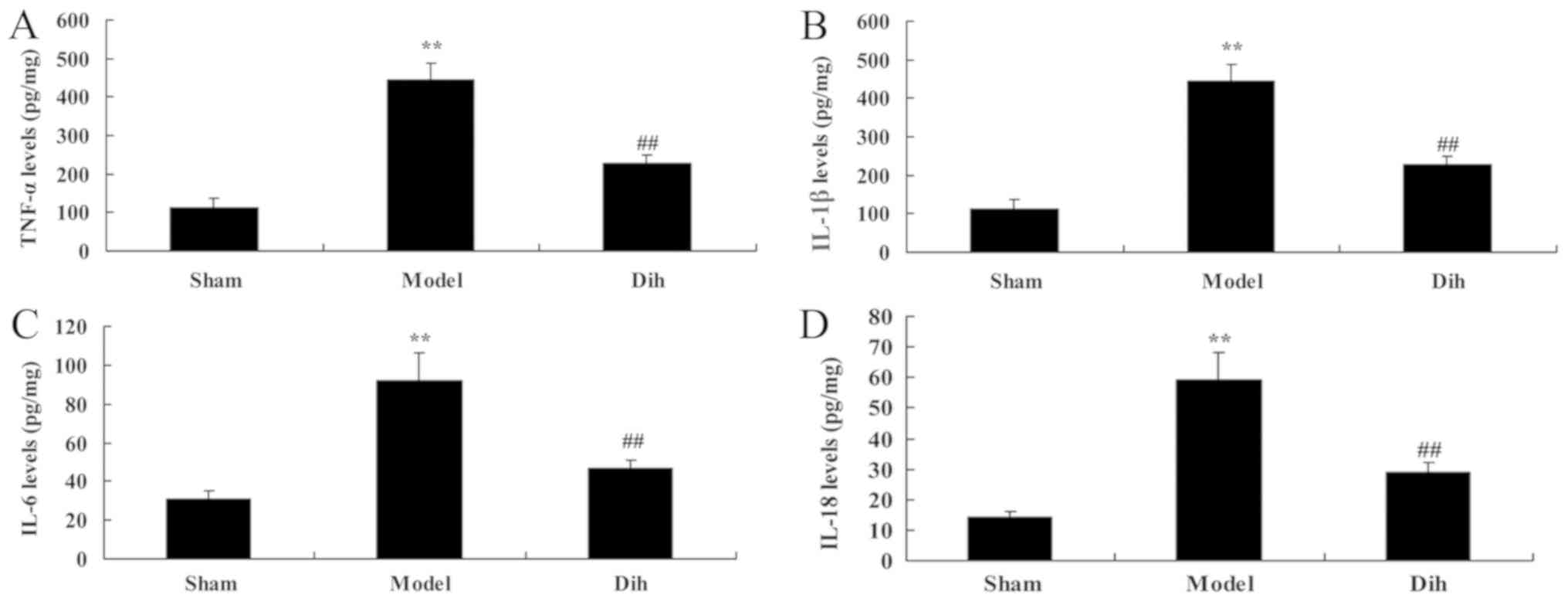
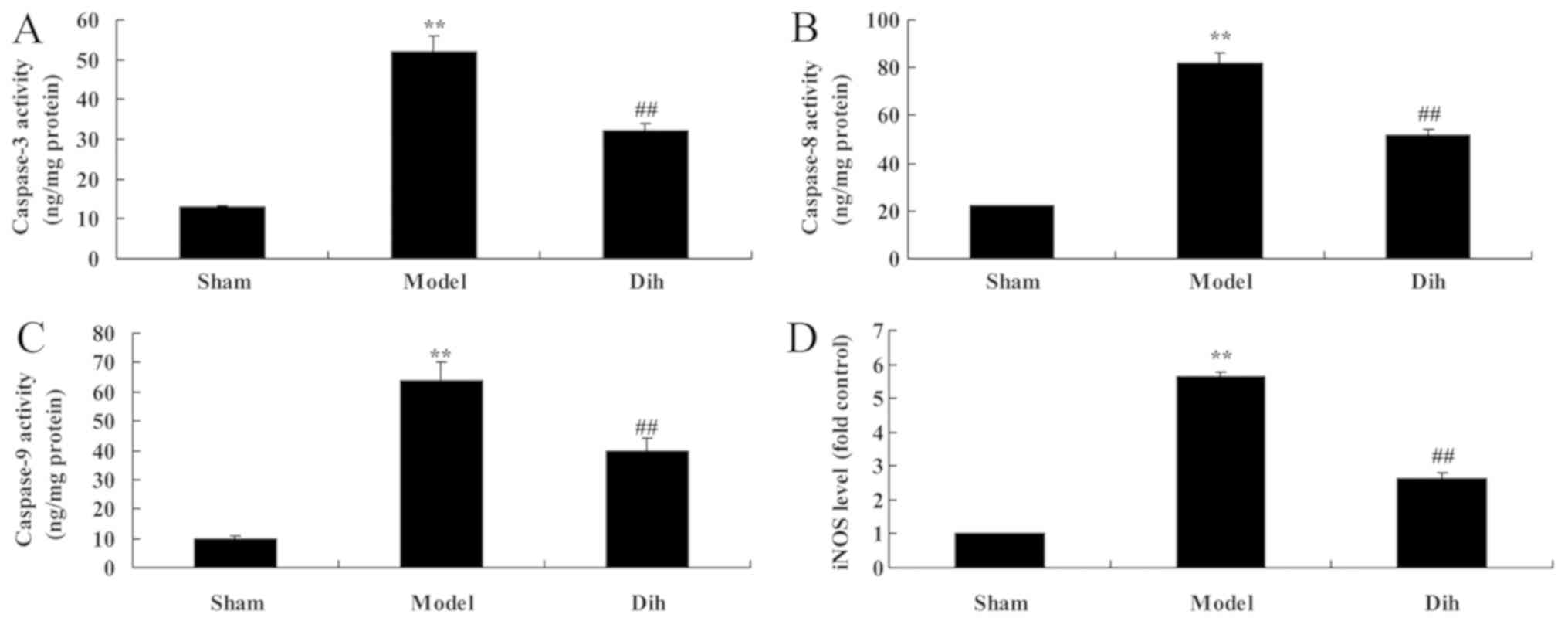
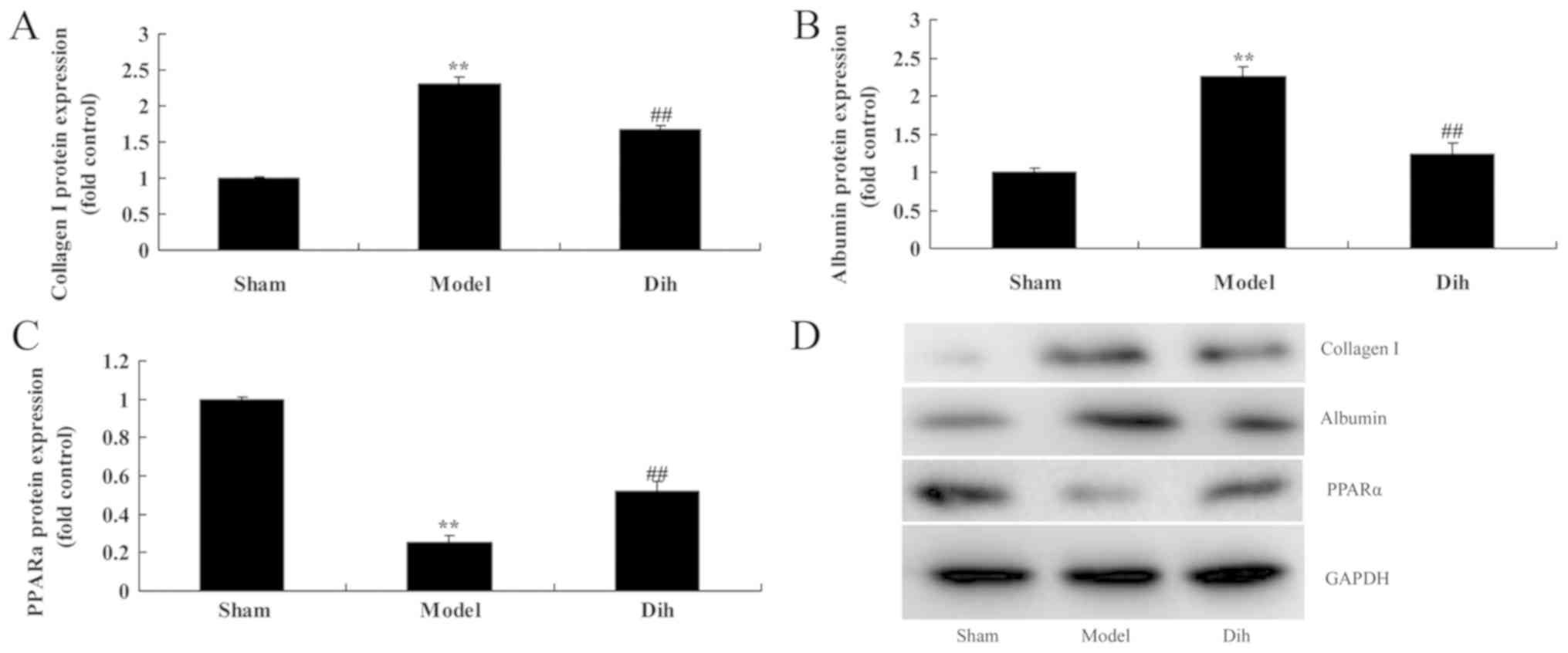
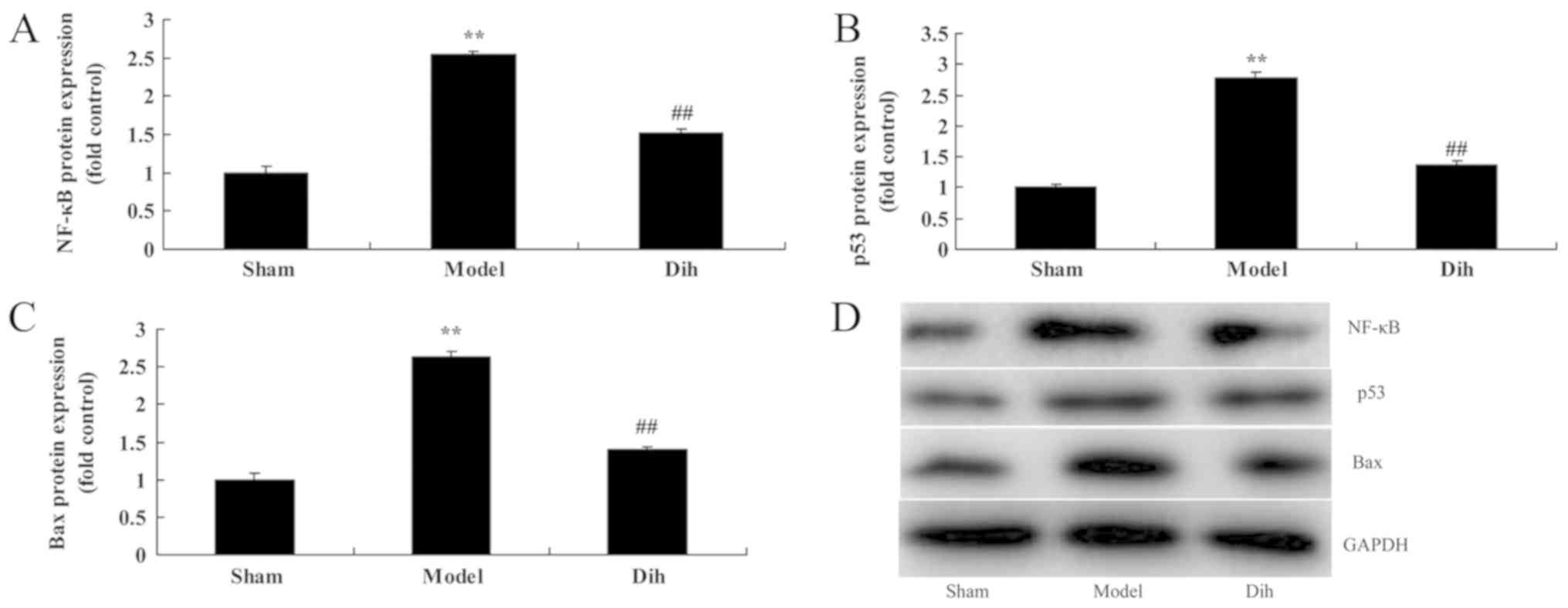
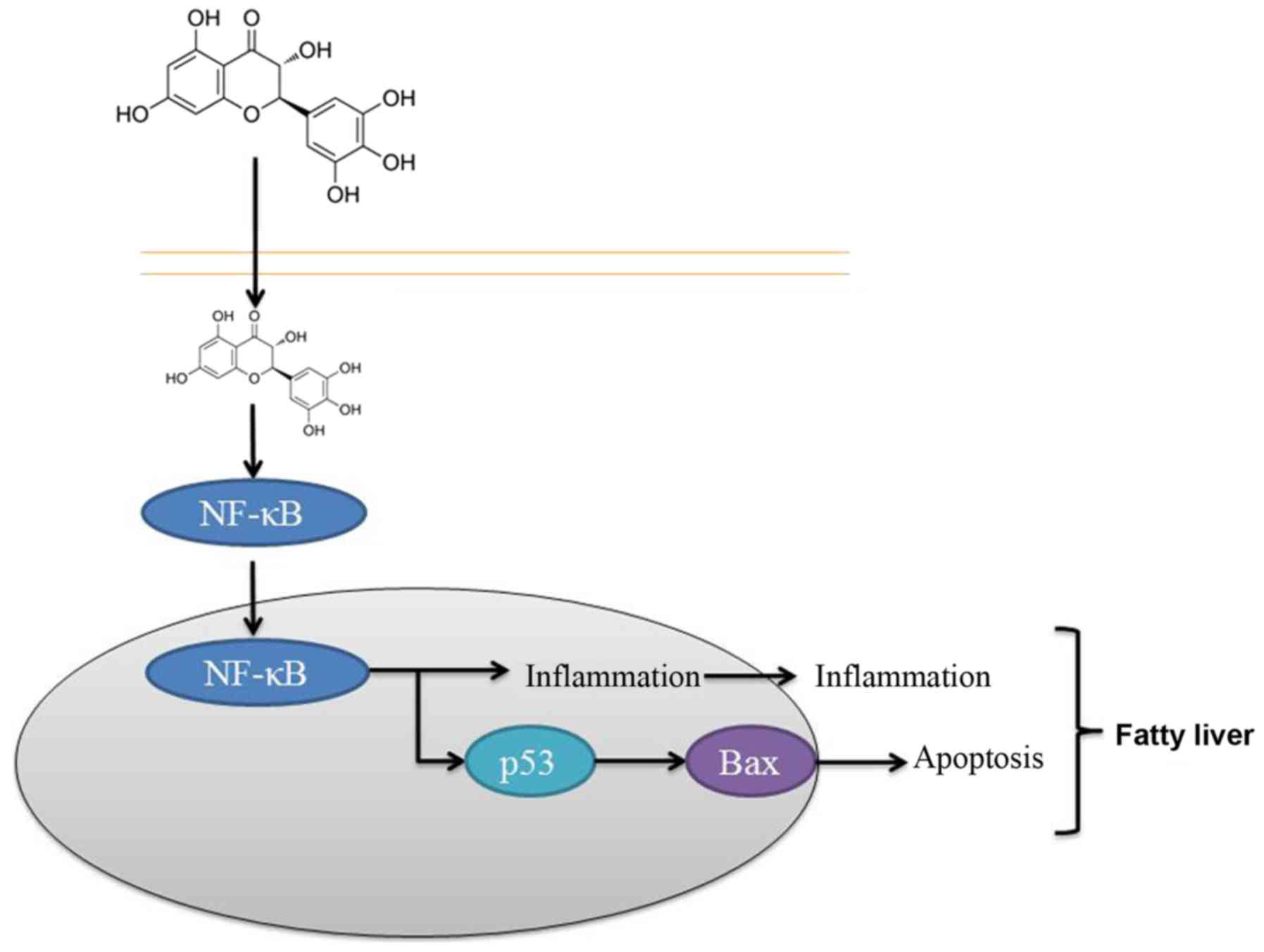
|
1
|
Song Q, Liu L, Yu J, Zhang J, Xu M, Sun L,
Luo H, Feng Z and Meng G: Dihydromyricetin attenuated Ang II
induced cardiac fibroblasts proliferation related to inhibitory of
oxidative stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 807:159–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Huang H, Hu M, Zhao R, Li P and Li M:
Dihydromyricetin suppresses the proliferation of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells by inducing G2/M arrest through the
Chk1/Chk2/Cdc25C pathway. Oncol Rep. 30:2467–2475. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rotman Y: Similarity between studies of
dihydromyricetin and reservatrol for NAFLD. Pharmacol Res.
100:3352015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Houghton D, Thoma C, Hallsworth K, Cassidy
S, Hardy T, Burt AD, Tiniakos D, Hollingsworth KG, Taylor R, Day
CP, et al: Exercise reduces liver lipids and visceral adiposity in
patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in a randomized
controlled trial. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:96–102.e3. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alexander KS, Zakai NA, Lidofsky SD,
Callas PW, Judd SE, Tracy RP and Cushman M: Non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease, liver biomarkers and stroke risk: The reasons for
geographic and racial differences in stroke cohort. PLoS One.
13:e01941532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim W, Kim BG, Lee JS, Lee CK, Yeon JE,
Chang MS, Kim JH, Kim H, Yi S, Lee J, et al: Randomised clinical
trial: The efficacy and safety of oltipraz, a liver X receptor
alpha-inhibitory dithiolethione in patients with non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 45:1073–1083. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li L, Hai J, Li Z, Zhang Y, Peng H, Li K
and Weng X: Resveratrol modulates autophagy and NF-κB activity in a
murine model for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food
Chem Toxicol. 63:166–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bu W and Luo T: miR-1297 promotes cell
proliferation of non-small cell lung cancer cells: Involving in
PTEN/Akt/Skp2 signaling pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 36:976–982. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chan DC, Watts GF, Gan S, Wong AT, Ooi EM
and Barrett PH: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as the transducer
of hepatic oversecretion of very-low-density
lipoprotein-apolipoprotein B-100 in obesity. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 30:1043–1050. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kalinowski P, Paluszkiewicz R,
Ziarkiewicz-Wroblewska B, Wróblewski T, Remiszewski P, Grodzicki M
and Krawczyk M: Liver function in patients with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease randomized to Roux-en-Y gastric bypass versus sleeve
gastrectomy: A secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial.
Ann Surg. 266:738–745. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gonzalez-Manan D, D'Espessailles A, Dossi
CG, San Martin M, Mancilla RA and Tapia GS: Rosa mosqueta oil
prevents oxidative stress and inflammation through the upregulation
of PPAR-α and NRF2 in C57BL/6J rat fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr.
147:579–588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mukai T, Egawa M, Takeuchi T, Yamashita H
and Kusudo T: Silencing of FABP1 ameliorates hepatic steatosis,
inflammation, and oxidative stress in rat with nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. FEBS Open Bio. 7:1009–1016. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sharifi N, Amani R, Hajiani E and
Cheraghian B: Does vitamin D improve liver enzymes, oxidative
stress, and inflammatory biomarkers in adults with non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease? A randomized clinical trial. Endocrine.
47:70–80. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou Y, Ding YL, Zhang JL, Zhang P, Wang
JQ and Li ZH: Alpinetin improved high fat diet-induced
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through improving
oxidative stress, inflammatory response and lipid metabolism.
Biomed Pharmacother. 97:1397–1408. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen Y, Lv L, Pi H, Qin W, Chen J, Guo D,
Lin J, Chi X, Jiang Z, Yang H and Jiang Y: Dihydromyricetin
protects against liver ischemia/reperfusion induced apoptosis via
activation of FOXO3a-mediated autophagy. Oncotarget. 7:76508–76522.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Willy JA, Young SK, Stevens JL, Masuoka HC
and Wek RC: CHOP links endoplasmic reticulum stress to NF-κB
activation in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Mol
Biol Cell. 26:2190–2204. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shankar E, Zhang A, Franco D and Gupta S:
Betulinic acid-mediated apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
involves p53 and nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κB) Pathways.
Molecules. 22(pii): E2642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Tan X, Yang D, Lu J, Liu B,
Baiyun R and Zhang Z: Dietary luteolin attenuates chronic liver
injury induced by mercuric chloride via the Nrf2/NF-κB/P53
signaling pathway in rats. Oncotarget. 8:40982–40993.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou DZ, Sun HY, Yue JQ, Peng Y, Chen YM
and Zhong ZJ: Dihydromyricetin induces apoptosis and cytoprotective
autophagy through ROS-NF-κB signalling in human melanoma cells.
Free Radic Res. 51:517–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim JY, Song EH, Lee HJ, Oh YK, Choi KH,
Yu DY, Park SI, Seong JK and Kim WH: HBx-induced hepatic steatosis
and apoptosis are regulated by TNFR1- and NF-kappaB-dependent
pathways. J Mol Biol. 397:917–931. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maraslioglu M, Weber R, Korff S, Blattner
C, Nauck C, Henrich D, Jobin C, Marzi I and Lehnert M: Activation
of NF-κB after chronic ethanol intake and haemorrhagic
shock/resuscitation in rat. Br J Pharmacol. 170:506–518. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|