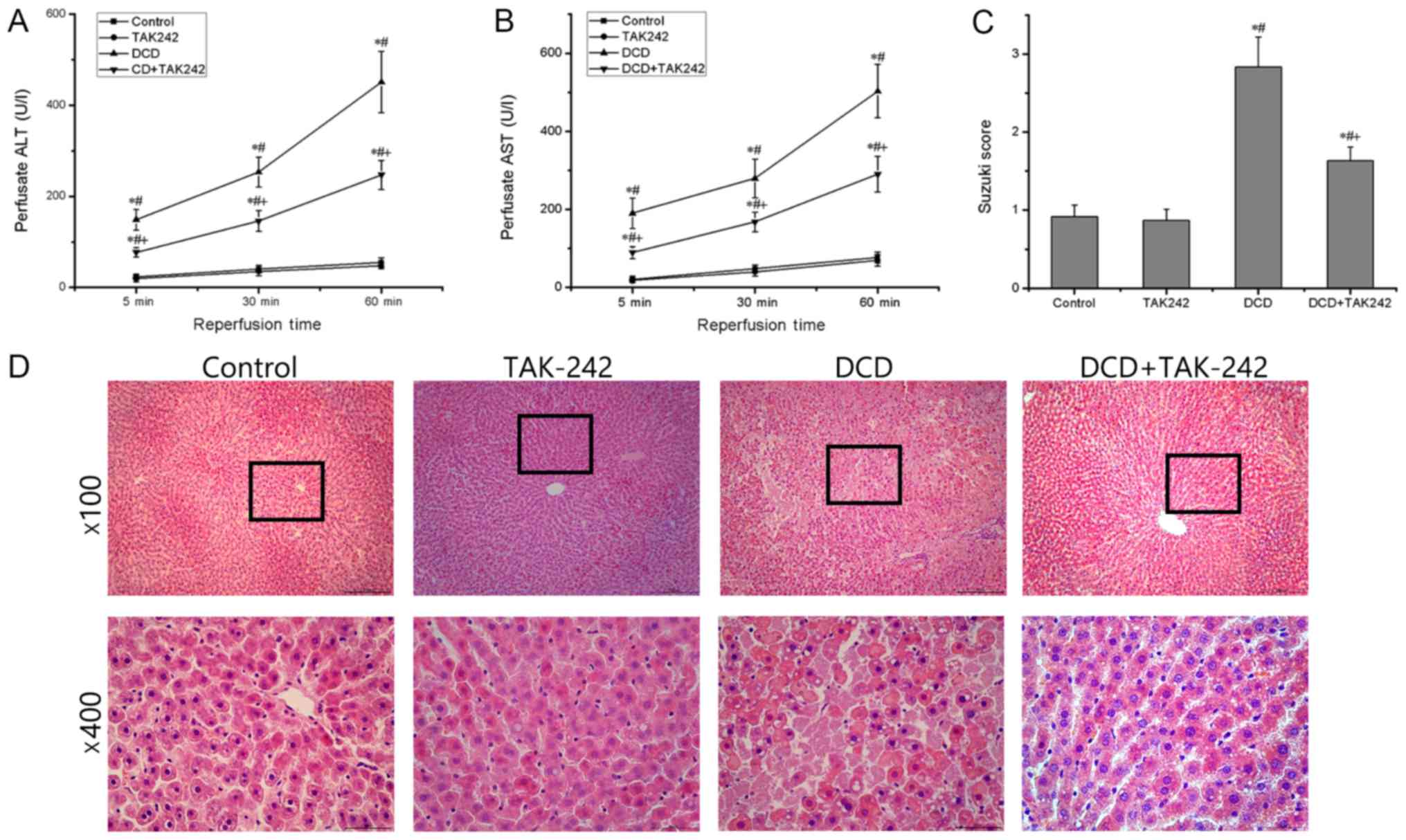
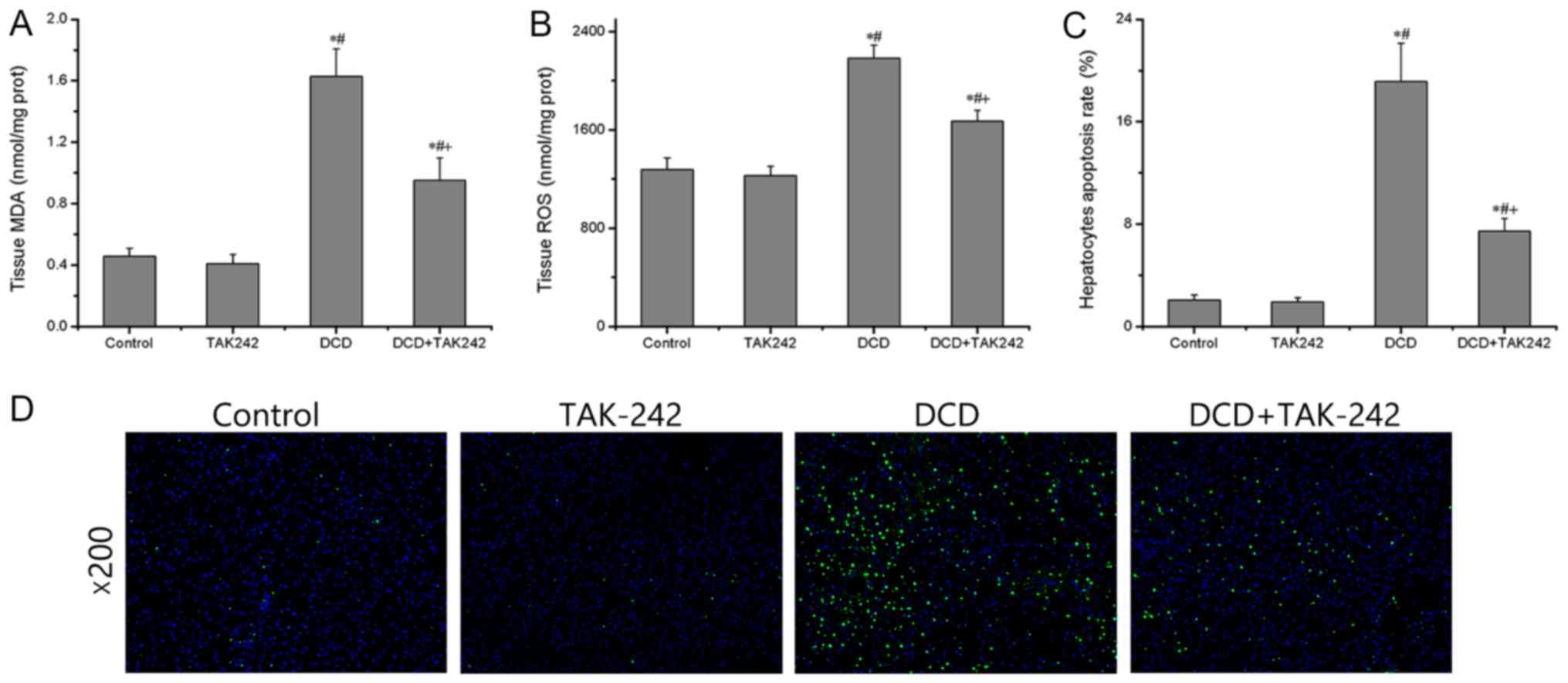
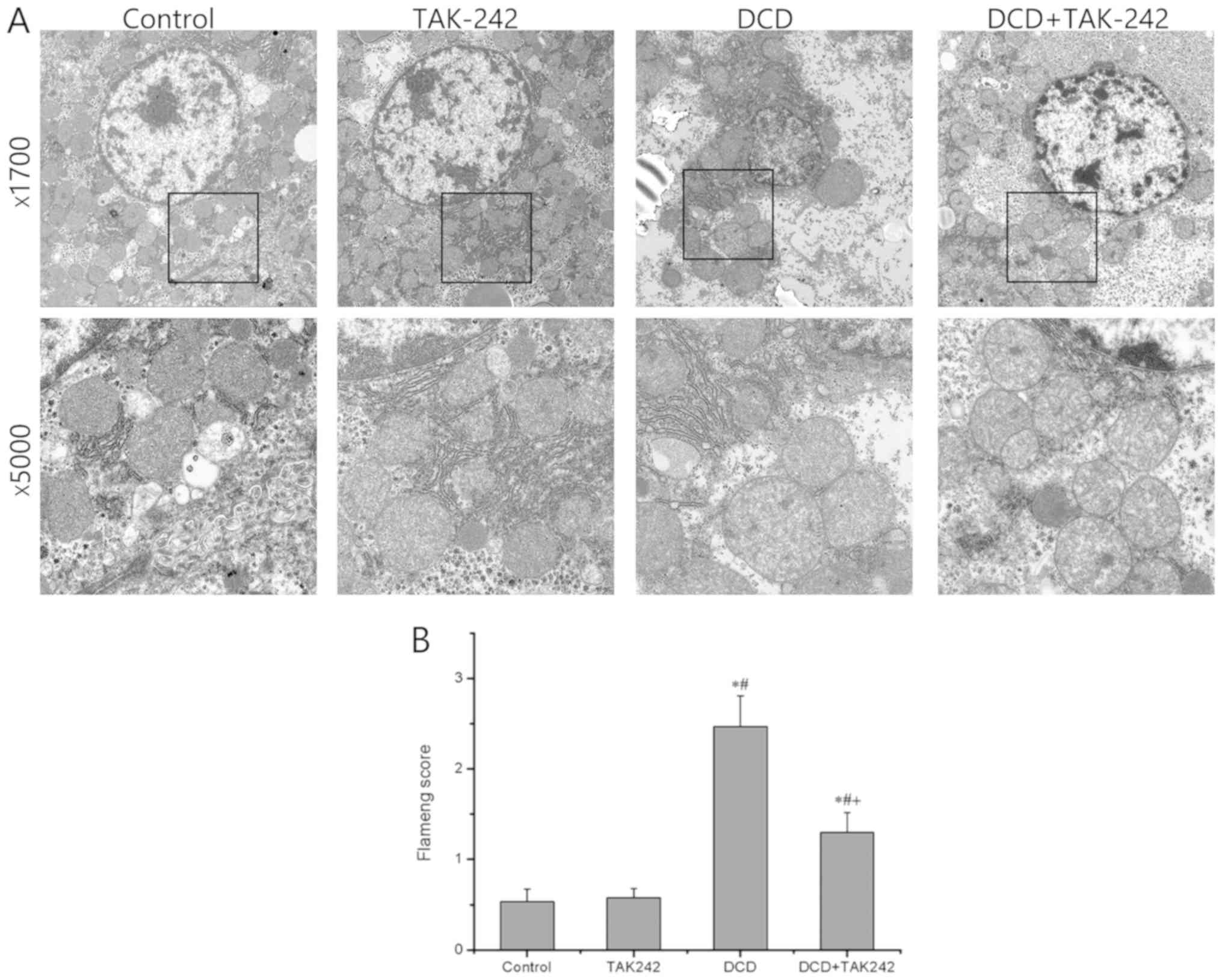
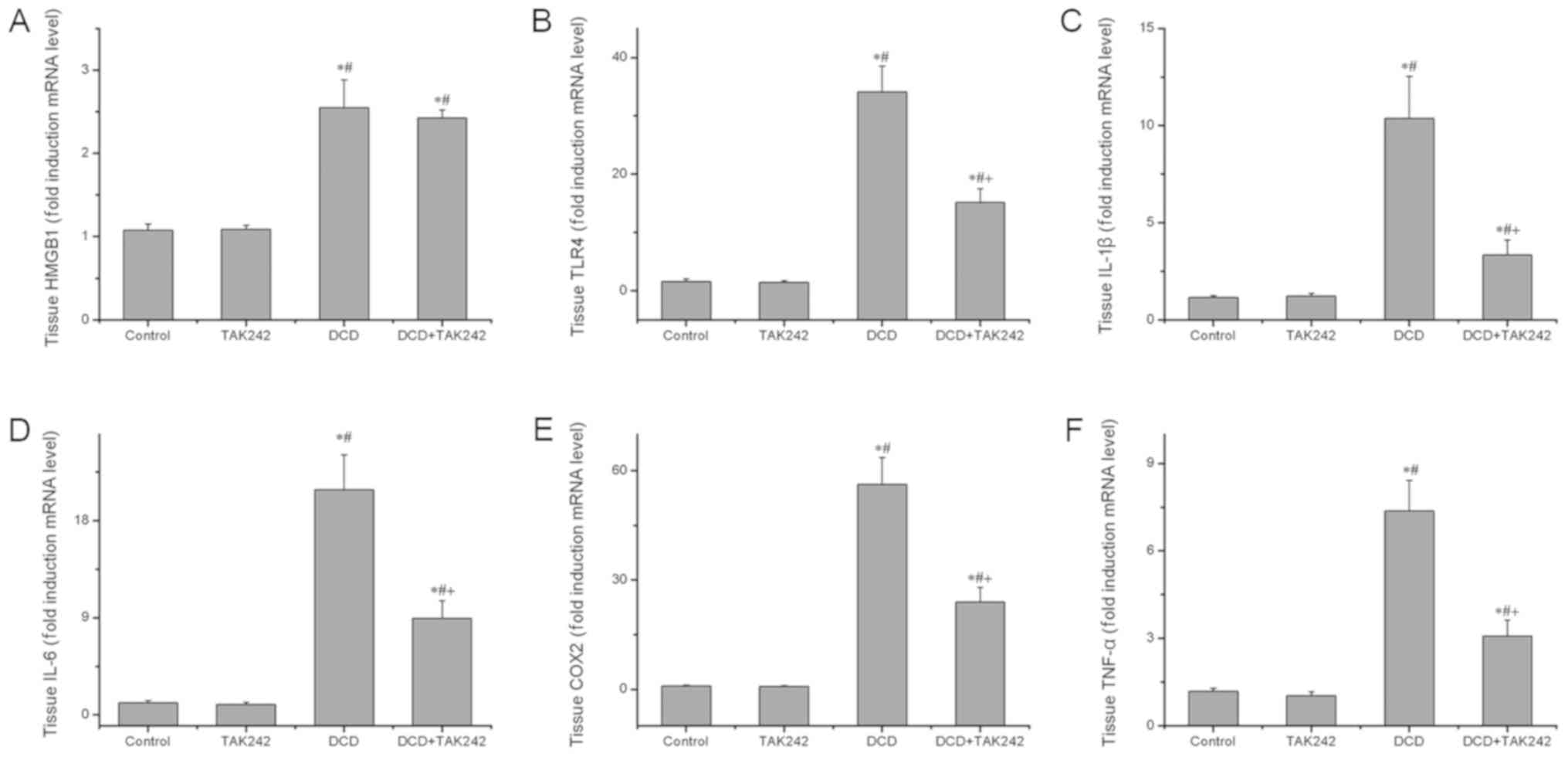
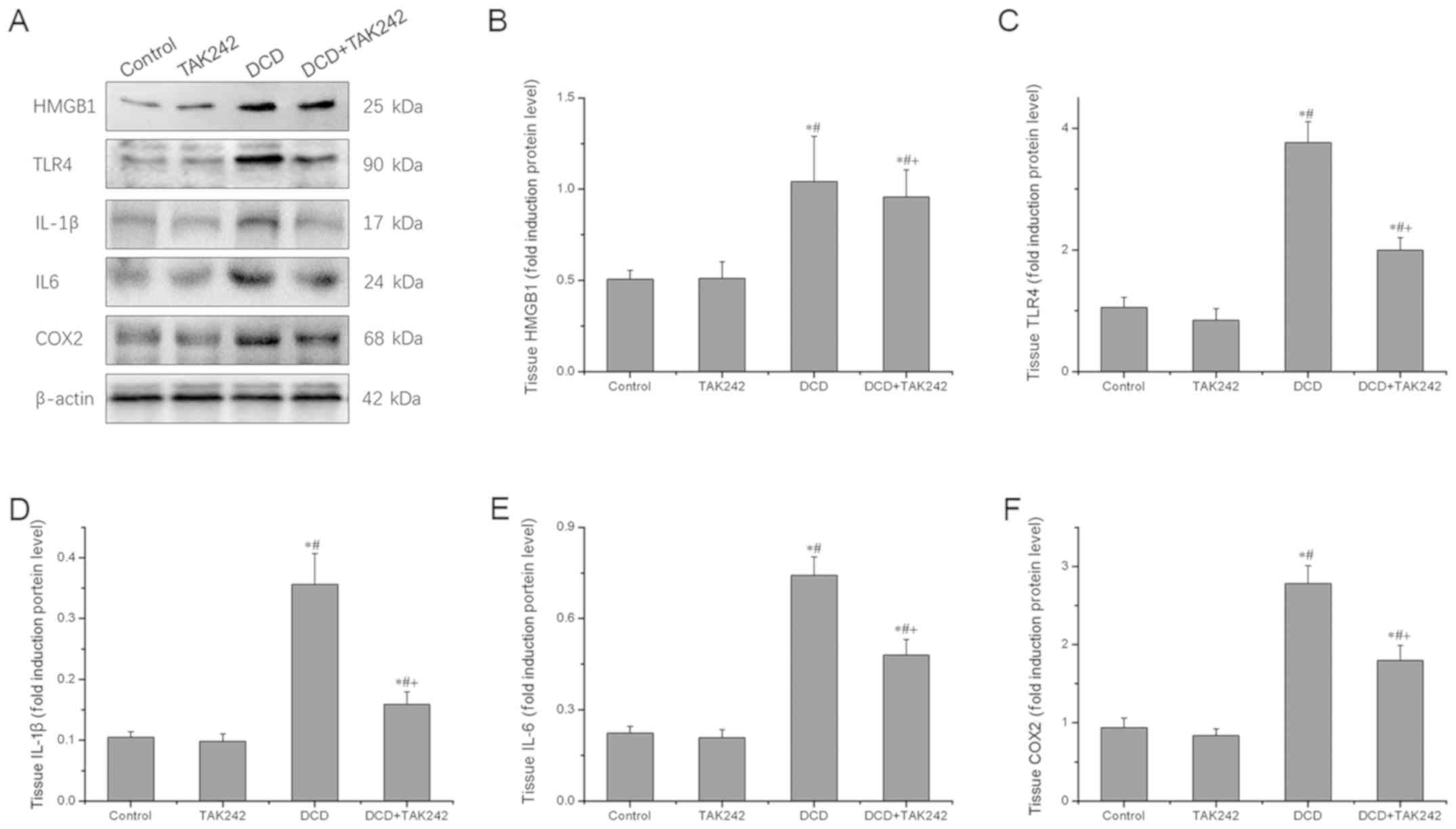
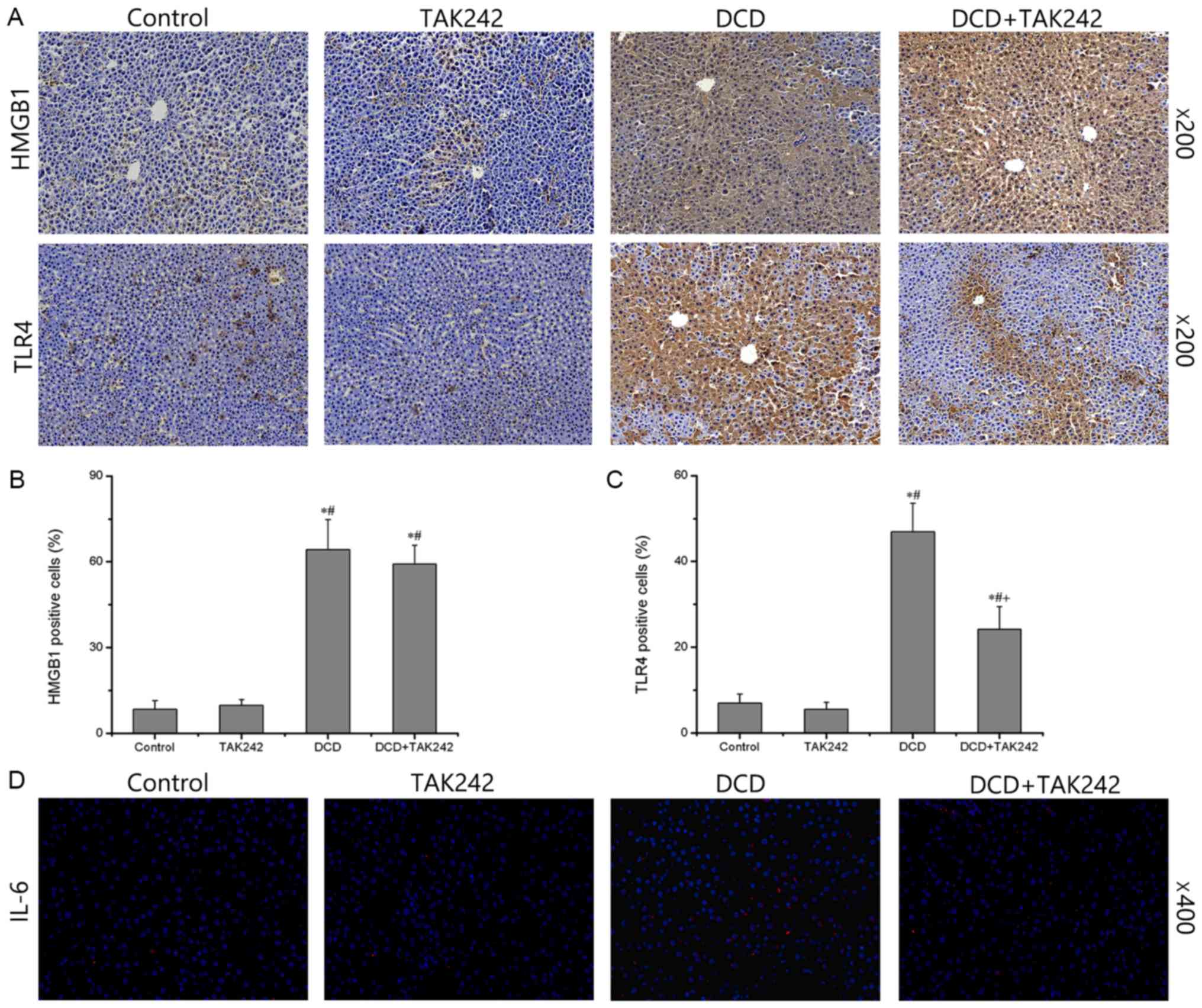
|
1
|
Ortega-Deballon I, Hornby L and Shemie SD:
Protocols for uncontrolled donation after circulatory death: A
systematic review of international guidelines, practices and
transplant outcomes. Crit Care. 19:2682015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bendorf A, Kelly PJ, Kerridge IH,
McCaughan GW, Myerson B, Stewart C and Pussell BA: An international
comparison of the effect of policy shifts to organ donation
following cardiocirculatory death (DCD) on donation rates after
brain death (DBD) and transplantation rates. PLoS One.
8:e620102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jay C, Ladner D, Wang E, Lyuksemburg V,
Kang R, Chang Y, Feinglass J, Holl JL, Abecassis M and Skaro AI: A
comprehensive risk assessment of mortality following donation after
cardiac death liver transplant-an analysis of the national
registry. J Hepatol. 55:808–813. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dageforde LA, Feurer ID, Pinson CW and
Moore DE: Is liver transplantation using organs donated after
cardiac death cost-effective or does it decrease waitlist death by
increasing recipient death? HPB (Oxford). 15:182–189. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nastos C, Kalimeris K, Papoutsidakis N,
Tasoulis MK, Lykoudis PM, Theodoraki K, Nastou D, Smyrniotis V and
Arkadopoulos N: Global consequences of liver ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:9069652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhai Y, Petrowsky H, Hong JC, Busuttil RW
and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: Ischaemia-reperfusion injury in liver
transplantation-from bench to bedside. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 10:79–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhai Y, Busuttil RW and Kupiec-Weglinski
JW: Liver ischemia and reperfusion injury: New insights into
mechanisms of innate-adaptive immune-mediated tissue inflammation.
Am J Transplant. 11:1563–1569. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Deoliveira ML, Jassem W, Valente R,
Khorsandi SE, Santori G, Prachalias A, Srinivasan P, Rela M and
Heaton N: Biliary complications after liver transplantation using
grafts from donors after cardiac death: Results from a matched
control study in a single large volume center. Ann Surg.
254:716–723. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS
release. Physiol Rev. 94:909–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chouchani ET, Pell VR, Gaude E,
Aksentijević D, Sundier SY, Robb EL, Logan A, Nadtochiy SM, Ord
ENJ, Smith AC, et al: Ischaemic accumulation of succinate controls
reperfusion injury through mitochondrial ROS. Nature. 515:431–435.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szabo G and Petrasek J: Inflammasome
activation and function in liver disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 12:387–400. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quesnelle KM, Bystrom PV and
Toledo-Pereyra LH: Molecular responses to ischemia and reperfusion
in the liver. Arch Toxicol. 89:651–657. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu L, Zhou H, Ni M, Wang X, Busuttil R,
Kupiec-Weglinski J and Zhai Y: Innate immune regulations and liver
ischemia reperfusion injury. Transplantation. 100:2601–2610. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Theodoraki K, Karmaniolou I, Tympa A,
Tasoulis MK, Nastos C, Vassiliou I, Arkadopoulos N and Smyrniotis
V: Beyond preconditioning: Postconditioning as an alternative
technique in the prevention of liver ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:82359212016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bejaoui M, Pantazi E, Folch-Puy E,
Baptista PM, García-Gil A, Adam R and Roselló-Catafau J: Emerging
concepts in liver graft preservation. World J Gastroenterol.
21:396–407. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Radojkovic M, Stojanovic M, Stanojevic G,
Radojkovic D, Gligorijevic J, Ilic I and Stojanovic N: Ischemic
preconditioning vs adenosine vs prostaglandin E1 for protection
against liver ischemia/reperfusion injury. Brazilian J Med Biol
Res. 50:e61852017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mergental H, Perera MT, Laing RW, Muiesan
P, Isaac JR, Smith A, Stephenson BT, Cilliers H, Neil DA, Hübscher
SG, et al: Transplantation of declined liver allografts following
normothermic ex-situ evaluation. Am J Transplant. 16:3235–3245.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sha T, Sunamoto M, Kitazaki T, Sato J, Ii
M and Iizawa Y: Therapeutic effects of TAK-242, a novel selective
Toll-like receptor 4 signal transduction inhibitor, in mouse
endotoxin shock model. Eur J Pharmacol. 571:231–239. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li M, Wang ZN, Yang LF, Yan Y, Cai LM, Li
YT, Qiao YK and Chen ZG: TLR4 antagonist suppresses airway
remodeling in asthma by inhibiting the T-helper 2 response. Exp
Ther Med. 14:2911–2916. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Committee for the Update of the Guide for
the care and use of Laboratory Animals, Institute for Laboratory
Animal Research, Division on Earth and Life Studies et al, . Guide
For the care and use of laboratory animals eighth edition
[EB/OL].
|
|
21
|
Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Zhang M, Zhao J, Ma X,
Huang T, Pang H, Li J and Song J: Inhibition of TLR4
signalling-induced inflammation attenuates secondary injury after
diffuse axonal injury in rats. Mediators Inflamm. 2016:47069152016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yokoi T, Yokoyama Y, Kokuryo T, Yamaguchi
J and Nagino M: Inhibition of Toll-like receptor 4 ameliorates
experimental postischemic injury in the cholestatic liver through
inhibition of high-mobility group box protein b1 (HMGB1) signaling.
Surgery. 163:270–276. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schlegel A, Graf R, Clavien PA and
Dutkowski P: Hypothermic oxygenated perfusion (HOPE) protects from
biliary injury in a rodent model of DCD liver transplantation. J
Hepatol. 59:984–991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Z, Zhang X, Xiao Q, Ye S, Lai CH, Luo
J, Huang X, Wang W, Zeng C, Zhong Z, et al: Pretreatment donors
after circulatory death with simvastatin alleviates liver ischemia
reperfusion injury through a KLF2-dependent mechanism in rat. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2017:38619142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Suzuki S, Toledo-Pereyra LH, Rodriguez FJ
and Cejalvo D: Neutrophil infiltration as an important factor in
liver ischemia and reperfusion injury. Modulating effects of FK506
and cyclosporine. Transplantation. 55:1265–1272. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Flameng W, Borgers M, Daenen W and
Stalpaert G: Ultrastructural and cytochemical correlates of
myocardial protection by cardiac hypothermia in man. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 79:413–424. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mateo R, Cho Y, Singh G, Stapfer M,
Donovan J, Kahn J, Fong TL, Sher L, Jabbour N, Aswad S, et al: Risk
factors for graft survival after liver transplantation from
donation after cardiac death donors: An analysis of OPTN/UNOS data.
Am J Transplant. 6:791–796. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion-from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–401.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nace GW, Huang H, Klune JR, Eid RE,
Rosborough BR, Korff S, Li S, Shapiro RA, Stolz DB, Sodhi CP, et
al: Cellular specific role of toll-like receptor 4 in hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Hepatology. 58:374–387. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Takashima K, Matsunaga N, Yoshimatsu M,
Hazeki K, Kaisho T, Uekata M, Hazeki O, Akira S, Iizawa Y and Ii M:
Analysis of binding site for the novel small-molecule TLR4 signal
transduction inhibitor TAK242 and its therapeutic effect on mouse
sepsis model. Br J Pharmacol. 157:1250–1262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Granger DN and Kvietys PR: Reperfusion
injury and reactive oxygen species: The evolution of a concept.
Redox Biol. 6:524–551. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Papanicolaou KN, Phillippo MM and Walsh K:
Mitofusins and the mitochondrial permeability transition: The
potential downside of mitochondrial fusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 303:H243–H255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Baines CP and Molkentin JD: Adenine
nucleotide translocase-1 induces cardiomyocyte death through
upregulation of the pro-apoptotic protein Bax. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
46:969–977. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luedde T, Kaplowitz N and Schwabe RF: Cell
death and cell death responses in liver disease: Mechanisms and
clinical relevance. Gastroenterology. 147:765–783.e4. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen L, Ren F, Zhang H, Wen T, Piao Z,
Zhou L, Zheng S, Zhang J, Chen Y, Han Y, et al: Inhibition of
glycogen synthase kinase 3β ameliorates D-GalN/LPS-induced liver
injury by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress-triggered
apoptosis. PLoS One. 7:e452022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hamada T, Duarte S, Tsuchihashi S,
Busuttil RW and Coito AJ: Inducible nitric oxide synthase
deficiency impairs matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity and disrupts
leukocyte migration in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. Am J
Pathol. 174:2265–2277. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tian Y, Wang J, Wang W, Ding Y, Sun Z,
Zhang Q, Wang Y, Xie H, Yan S and Zheng S: Mesenchymal stem cells
improve mouse non-heart-beating liver graft survival by inhibiting
Kupffer cell apoptosis via TLR4-ERK1/2-Fas/FasL-caspase3 pathway
regulation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 7:1572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Konishi T, Schuster RM and Lentsch AB:
Liver repair and regeneration after ischemia-reperfusion injury is
associated with prolonged fibrosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 316:G323–G331. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Marrone G, Shah VH and Gracia-Sancho J:
Sinusoidal communication in liver fibrosis and regeneration. J
Hepatol. 65:608–617. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Barton GM and Kagan JC: A cell biological
view of Toll-like receptor function: Regulation through
compartmentalization. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:535–542. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhai Y, Shen XD, O'Connell R, Gao F,
Lassman C, Busuttil RW, Cheng G and Kupiec-Weglinski JW: Cutting
edge: TLR4 activation mediates liver ischemia/reperfusion
inflammatory response via ifn regulatory factor 3-dependent
MyD88-independent pathway. J Immunol. 12:7115–7119. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wittebole X, Castanares-Zapatero D and
Laterre PF: Toll-like receptor 4 modulation as a strategy to treat
sepsis. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:5683962010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
de Mingo Á, de Gregorio E, Moles A,
Tarrats N, Tutusaus A, Colell A, Fernandez-Checa JC, Morales A and
Marí M: Cysteine cathepsins control hepatic NF-κB-dependent
inflammation via sirtuin-1 regulation. Cell Death Dis. 7:e24642016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tsung A, Klune JR, Zhang X, Jeyabalan G,
Cao Z, Peng X, Stolz DB, Geller DA, Rosengart MR and Billiar TR:
HMGB1 release induced by liver ischemia involves Toll-like receptor
4-dependent reactive oxygen species production and calcium-mediated
signaling. J Exp Med. 204:2913–2923. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao G, Fu C, Wang L, Zhu L, Yan Y, Xiang
Y, Zheng F, Gong F, Chen S and Chen G: Down-regulation of nuclear
HMGB1 reduces ischemia-induced HMGB1 translocation and release and
protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury. Sci Rep.
7:462722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang GY, Lu D, Duan SF, Gao YR, Liu SY,
Hong Y, Dong PZ, Chen YG, Li T, Wang DY, et al: Hydrogen Sulfide
alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced diaphragm dysfunction in rats
by reducing apoptosis and inflammation through ROS/MAPK and
TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:96478092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang L, Li N, Lin D and Zang Y: Curcumin
protects against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion induced injury
through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Oncotarget. 8:65414–65420.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yu Y, Tang D and Kang R: Oxidative
stress-mediated HMGB1 biology. Front Physiol. 6:932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang H, Wang H, Chavan SS and Andersson U:
High mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1): The prototypical
endogenous danger molecule. Mol Med. 21 (Suppl):S6–S12. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|