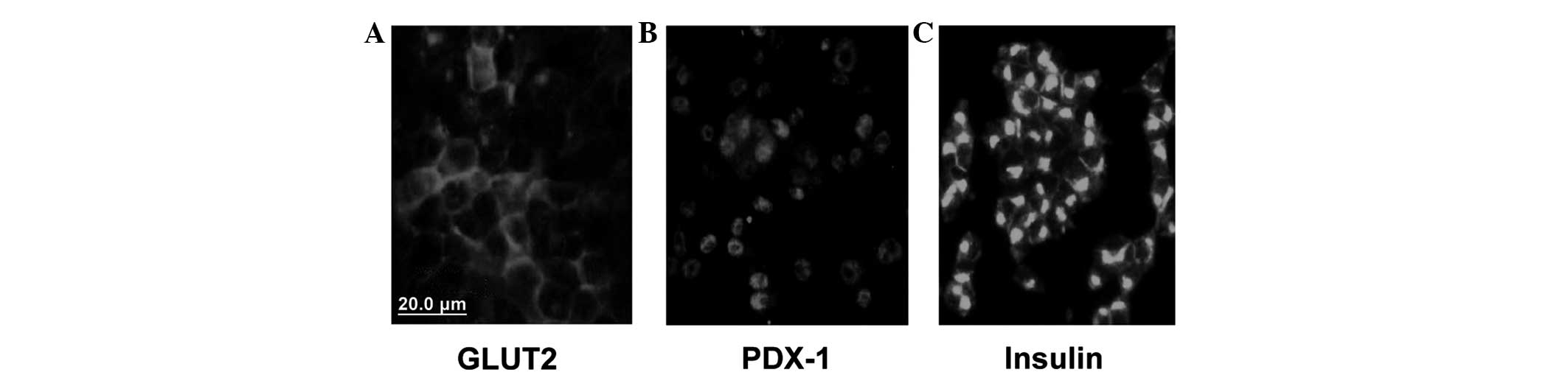
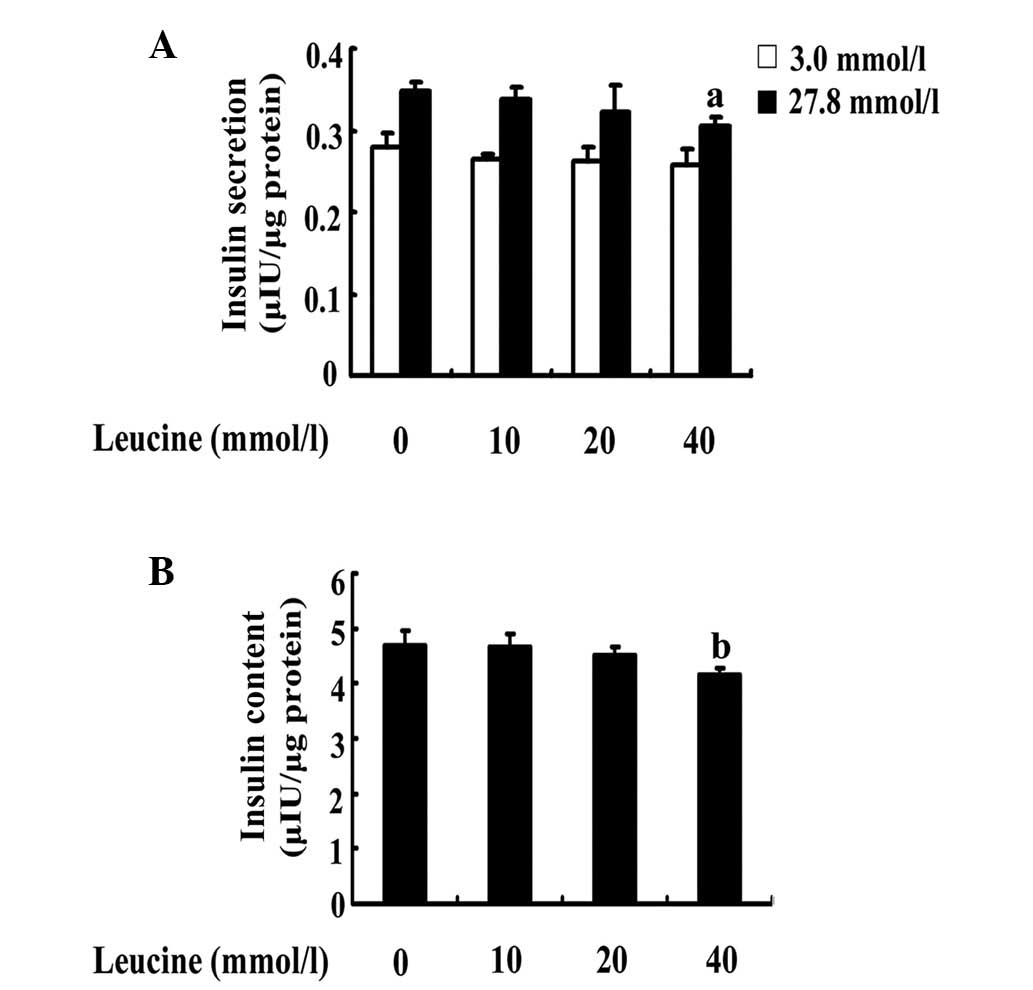
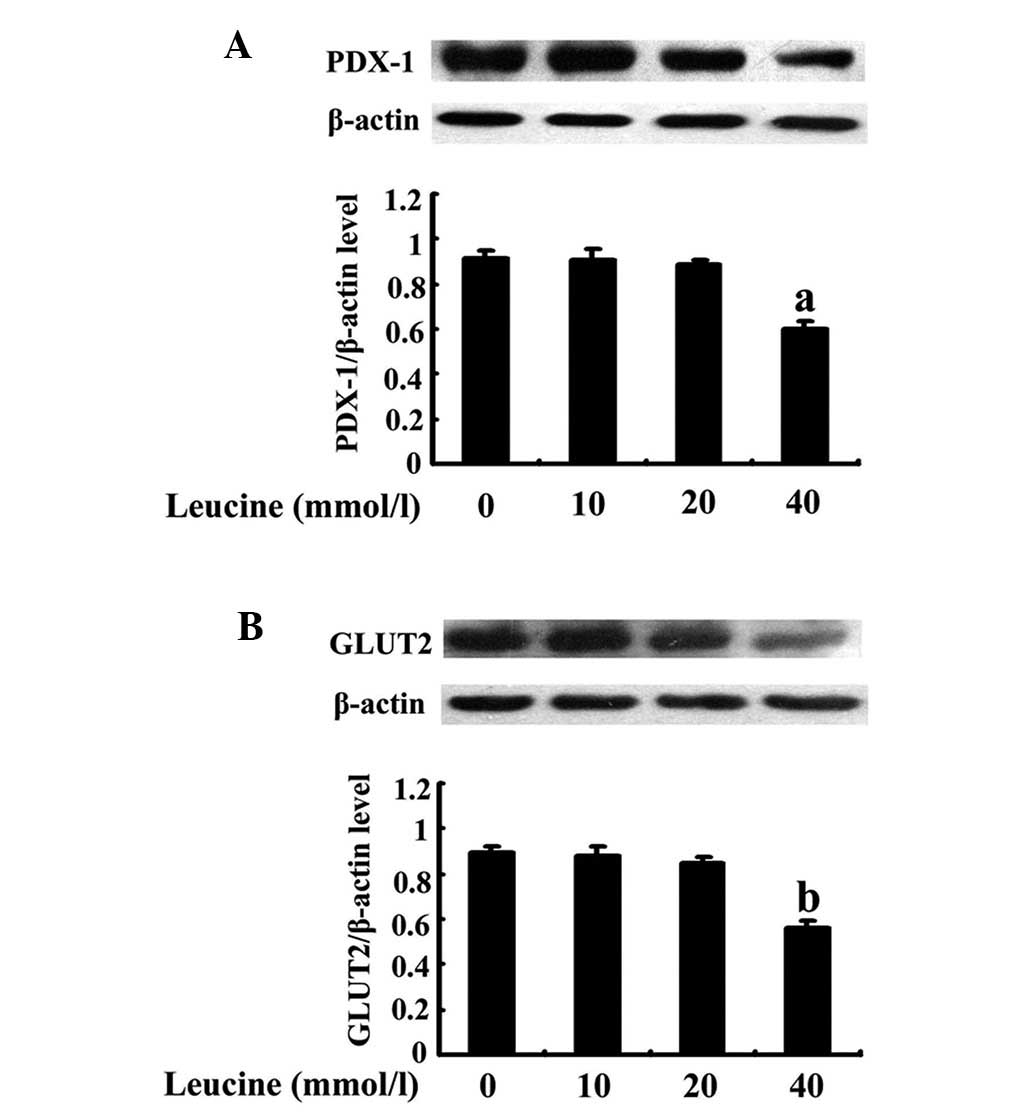
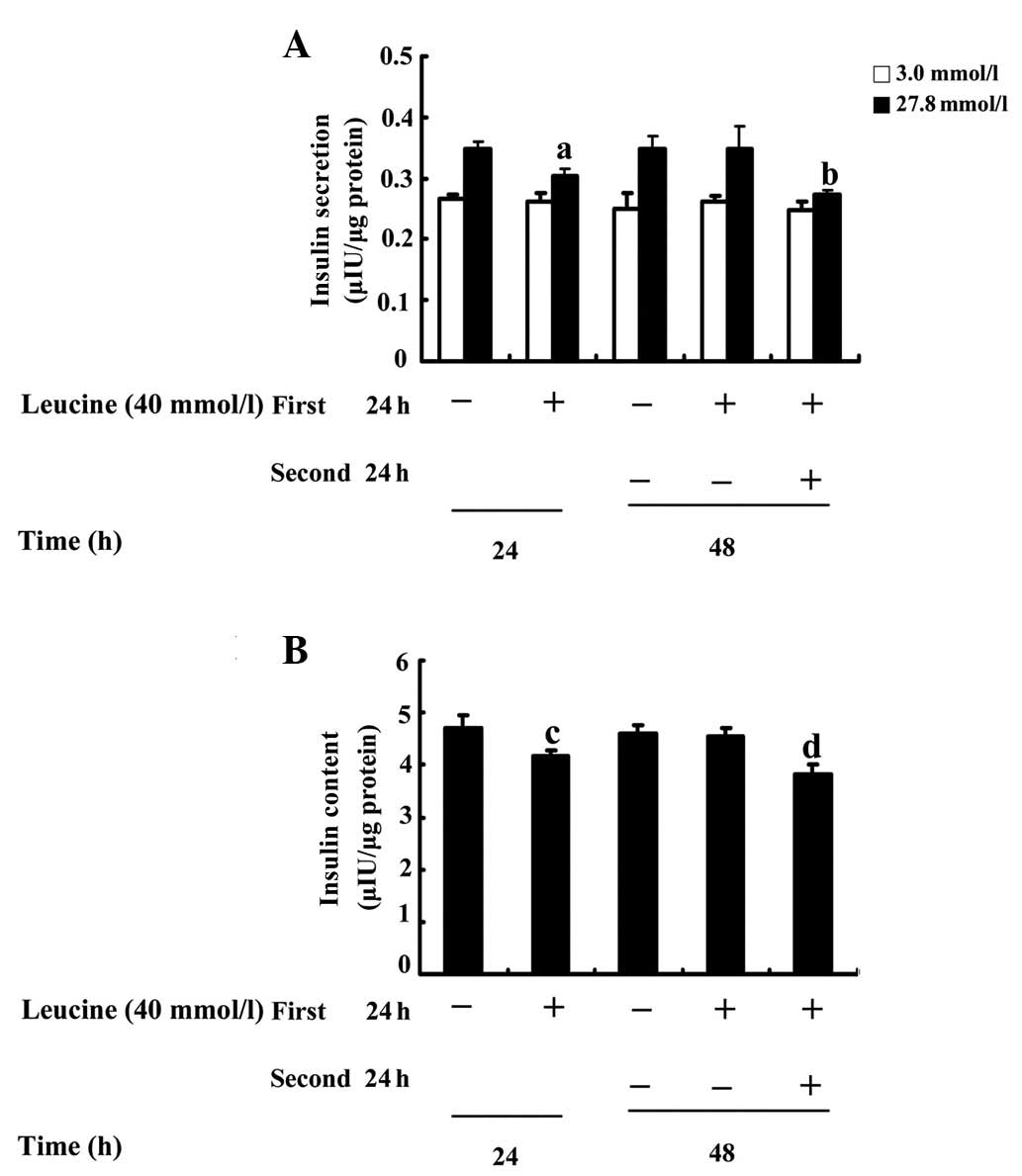
|
1
|
DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC and Ferrannini
E: Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care.
15:318–368. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Porte D Jr and Kahn SE: beta-cell
dysfunction and failure in type 2 diabetes: potential mechanisms.
Diabetes. 50(Suppl 1): S160–S163. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun Y, Zhang L, Gu HF, et al: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha regulates the expression of
pancreatic/duodenal homeobox-1 in rat insulinoma (INS-1) cells and
ameliorates glucose-induced insulin secretion impaired by
palmitate. Endocrinology. 149:662–671. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Van de Casteele M, Kefas BA, Cai Y, et al:
Prolonged culture in low glucose induces apoptosis of rat
pancreatic beta-cells through induction of c-myc. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 312:937–944. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Unger RH and Zhou YT: Lipotoxicity of
beta-cells in obesity and in other causes of fatty acid spillover.
Diabetes. 50(Suppl 1): S118–S121. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ling Z and Pipeleers DG: Prolonged
exposure of human beta cells to elevated glucose levels results in
sustained cellular activation leading to a loss of glucose
regulation. J Clin Invest. 98:2805–2812. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Briaud I, Harmon JS, Kelpe CL, Segu VB and
Poitout V: Lipotoxicity of the pancreatic beta-cell is associated
with glucose-dependent esterification of fatty acids into neutral
lipids. Diabetes. 50:315–321. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Robertson RP, Harmon J, Tran PO and
Poitout V: Beta-cell glucose toxicity, lipotoxicity, and chronic
oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 53(Suppl 1):
S119–S124. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Anello M, Ucciardello V, Piro S, et al:
Chronic exposure to high leucine impairs glucose-induced insulin
release by lowering the ATP-to-ADP ratio. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 281:E1082–E1087. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang J, Wong RK, Park M, et al: Leucine
regulation of glucokinase and ATP synthase sensitizes
glucose-induced insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cells.
Diabetes. 55:193–201. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang J, Wong RK, Wang X, et al: Leucine
culture reveals that ATP synthase functions as a fuel sensor in
pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem. 279:53915–53923. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kaneto H, Miyatsuka T, Fujitani Y, et al:
Role of PDX-1 and MafA as a potential therapeutic target for
diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 77(Suppl 1): S127–S137. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fernandes A, King LC, Guz Y, Stein R,
Wright CV and Teitelman G: Differentiation of new insulin-producing
cells is induced by injury in adult pancreatic islets.
Endocrinology. 138:1750–1762. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Offield MF, Jetton TL, Labosky PA, et al:
PDX-1 is required for pancreatic outgrowth and differentiation of
the rostral duodenum. Development. 122:983–995. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Waeber G, Thompson N, Nicod P and Bonny C:
Transcriptional activation of the GLUT2 gene by the
IPF-1/STF-1/IDX-1 homeobox factor. Mol Endocrinol. 10:1327–1334.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marshak S, Totary H, Cerasi E and Melloul
D: Purification of the beta-cell glucose-sensitive factor that
transactivates the insulin gene differentially in normal and
transformed islet cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:15057–15062.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Iype T, Francis J, Garmey JC, et al:
Mechanism of insulin gene regulation by the pancreatic
transcription factor Pdx-1: application of pre-mRNA analysis and
chromatin immunoprecipitation to assess formation of functional
transcriptional complexes. J Biol Chem. 280:16798–16807. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Melloul D, Marshak S and Cerasi E:
Regulation of insulin gene transcription. Diabetologia. 45:309–326.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jonsson J, Carlsson L, Edlund T and Edlund
H: Insulin-promoter-factor 1 is required for pancreas development
in mice. Nature. 371:606–609. 1994. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kushner JA, Ye J, Schubert M, et al: Pdx1
restores beta cell function in Irs2 knockout mice. J Clin Invest.
109:1193–1201. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gremlich S, Bonny C, Waeber G and Thorens
B: Fatty acids decrease IDX-1 expression in rat pancreatic islets
and reduce GLUT2, glucokinase, insulin, and somatostatin levels. J
Biol Chem. 272:30261–30269. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leahy JL, Cooper HE, Deal DA and Weir GC:
Chronic hyperglycemia is associated with impaired glucose influence
on insulin secretion. A study in normal rats using chronic in vivo
glucose infusions. J Clin Invest. 77:908–915. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xiao CQ, Deng HM and Huang Y: Effects of
supraphysiologic concentration glucose on pancreatic duodenal
homeobox-1 expression and insulin secretion in rats. Chin Med J
(Engl). 120:1020–1023. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lennernäs H, Nilsson D, Aquilonius SM,
Ahrenstedt O, Knutson L and Paalzow LK: The effect of L-leucine on
the absorption of levodopa, studied by regional jejunal perfusion
in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 35:243–250. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ganapathy V and Radhakrishnan AN:
Interaction of amino acids with glycl-L-leucine hydrolysis and
transport in monkey small intestine. Clin Sci (Lond). 57:521–527.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rideau N and Simon J: L-leucine or its
keto acid potentiate but do not initiate insulin release in
chicken. Am J Physiol. 257:E15–E19. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang X, Sun N, Wang L, et al:
AMP-activated protein kinase and pancreatic/duodenal homeobox-1
involved in insulin secretion under high leucine exposure in rat
insulinoma beta-cells. J Cell Mol Med. 13:758–770. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|