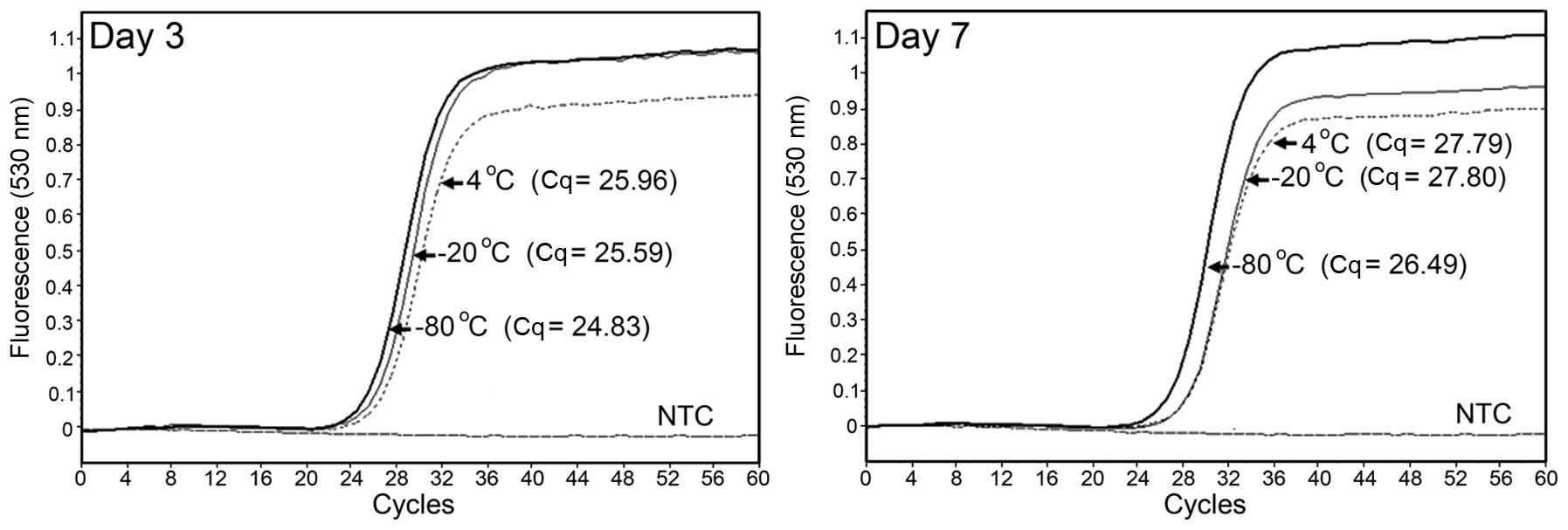
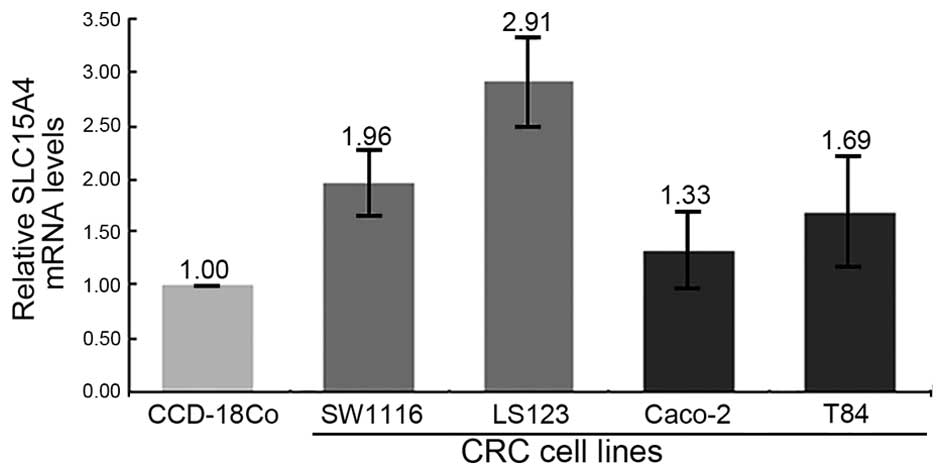
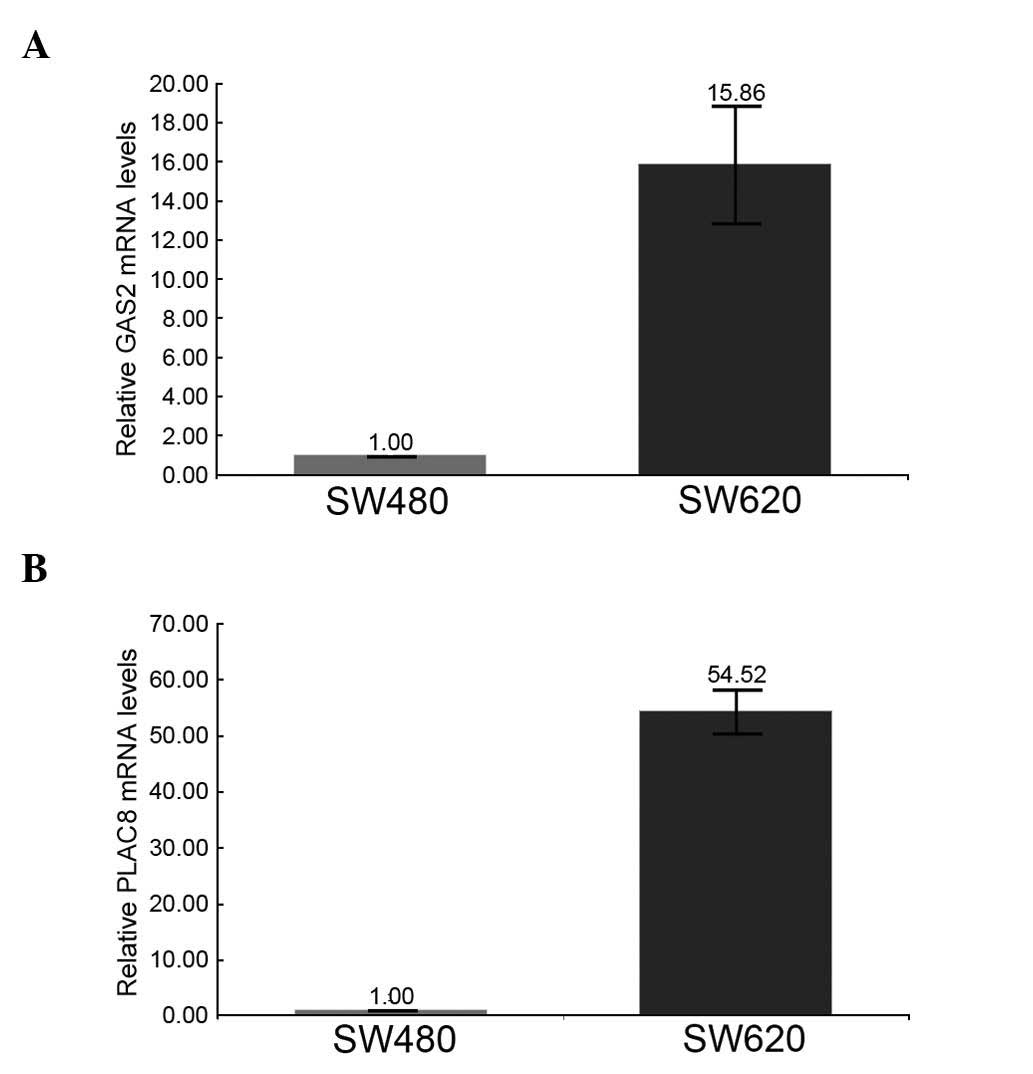
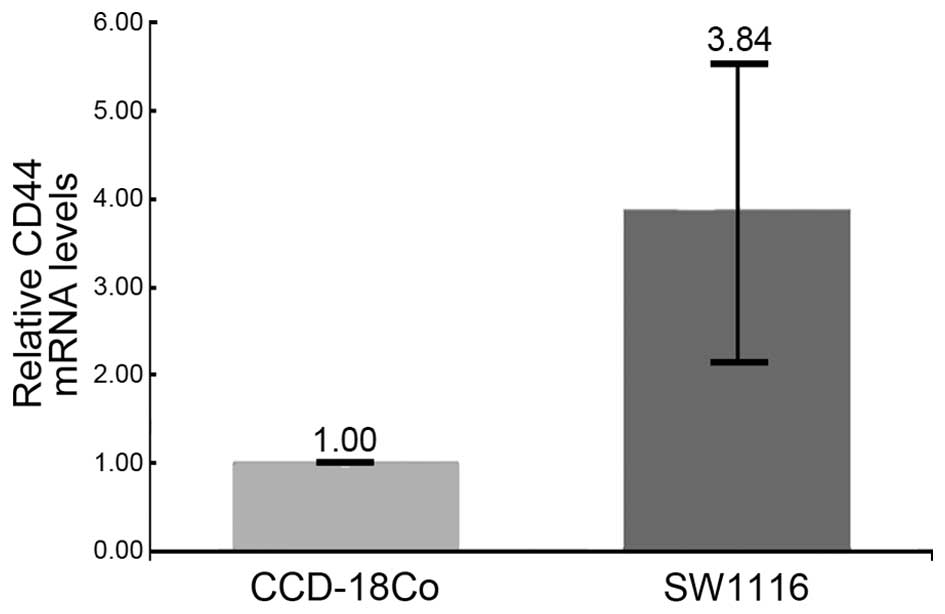
|
1
|
Vogelstein B, Fearon ER, Hamilton SR, Kern
SE, Preisinger AC, Leppert M, Nakamura Y, White R, Smits AM and Bos
JL: Genetic alterations during colorectal-tumor development. J Engl
Med. 319:525–532. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jass JR: Colorectal cancer: A multipathway
disease. Crit Rev Oncog. 12:273–287. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ
and Bushell M: microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol.
13:e249–e258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
You JS and Jones PA: Cancer genetics and
epigenetics: Two sides of the same coin? Cancer Cell. 22:9–20.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA and Ward E:
Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:366–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chun P and Wainberg ZA: Adjuvant
Chemotherapy for Stage II Colon Cancer: The role of molecular
markers in choosing therapy. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 3:191–196.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsuyama T, Ishikawa T, Mogushi K,
Yoshida T, Iida S, Uetake H, Mizushima H, Tanaka H and Sugihara K:
MUC12 mRNA expression is an independent marker of prognosis in
stage II and stage III colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer.
127:2292–2299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kimura Y, Sumiyoshi M and Baba K:
Antitumor activities of synthetic and natural stilbenes through
antiangiogenic action. Cancer Sci. 99:2083–2096. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Watine JC and Bunting PS: Mass colorectal
cancer screening: Methodological quality of practice guidelines is
not related to their content validity. Clinical Biochem.
41:459–466. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Soreide K, Berg M, Skudal BS and Nedreboe
BS: Advances in the understanding and treatment of colorectal
cancer. Discov Med. 12:393–404. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sinicrope FA, Shi Q, Smyrk TC, et al:
Molecular markers identify subtypes of stage III colon cancer
associated with patient outcomes. Gastroenterology. 148:88–99.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsuda T, Chiu HM, Sano Y, Fujii T, Ono A
and Saito Y: Surveillance colonoscopy after endoscopic treatment
for colorectal neoplasia: From the standpoint of the Asia-Pacific
region. Digestive Endoscopy. 28:342–347. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blázquez C, Geelen MJ, Velasco G and
Guzmán M: The AMP-activated protein kinase prevents ceramide
synthesis de novo and apoptosis in astrocytes. FEBS Lett.
489:149–153. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Belletti B, Nicoloso MS, Schiappacassi M,
Chimienti E, Berton S, Lovat F, Colombatti A and Baldassarre G:
p27(kip1) functional regulation in human cancer: A potential target
for therapeutic designs. Curr Med Chem. 12:1589–1605. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang SH, Lin JK, Lai CR, Chen CC, Li AF,
Liang WY and Jiang JK: Risk factors for peritoneal dissemination of
colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 87:167–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang CJ, Yang SH, Lee CL, Cheng YC, Tai
SY and Chien CC: Ribosomal protein S27-like in colorectal cancer: A
candidate for predicting prognoses. PLoS One. 8:e670432013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH,
Levin TR, Lavin P, Lidgard GP, Ahlquist DA and Berger BM:
Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N
Engl J Med. 370:1287–1297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ng JM and Yu J: Promoter hypermethylation
of tumour suppressor genes as potential biomarkers in colorectal
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16:2472–2496. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Giusti L, Iacconi P, Da Valle Y, Ciregia
F, Ventroni T, Donadio E, Giannaccini G, Chiarugi M, Torregrossa L,
Proietti A, et al: A proteomic profile of washing fluid from the
colorectal tract to search for potential biomarkers of colon
cancer. Mol Biosyst. 8:1088–1099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Young GP and Bosch LJ: Fecal tests: From
blood to molecular markers. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep. 7:62–70.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang CJ, Chien CC, Yang SH, Chang CC, Sun
HL, Cheng YC, Liu CC, Lin SC and Lin CM: Faecal ribosomal protein
L19 is a genetic prognostic factor for survival in colorectal
cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 12:1936–1943. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takai T, Kanaoka S, Yoshida K, Hamaya Y,
Ikuma M, Miura N, Sugimura H, Kajimura M and Hishida A: Fecal
cyclooxygenase 2 plus matrix metalloproteinase 7 mRNA assays as a
marker for colorectal cancer screening. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 18:1888–1893. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hamaya Y, Yoshida K, Takai T, Ikuma M,
Hishida A and Kanaoka S: Factors that contribute to faecal
cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA expression in subjects with colorectal
cancer. Br J Cancer. 102:916–921. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang SH, Huang CJ, Lee CL, Liu CC, Chien
CC and Chen SH: Fecal RNA detection of cytokeratin 19 and ribosomal
protein L19 for colorectal cancer. Hepatogastroenterology.
57:710–715. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Steele RJ, Kostourou I, McClements P,
Watling C, Libby G, Weller D, Brewster DH, Black R, Carey FA and
Fraser C: Effect of repeated invitations on uptake of colorectal
cancer screening using faecal occult blood testing: Analysis of
prevalence and incidence screening. BMJ. 341:c55312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tonus C, Sellinger M, Koss K and Neupert
G: Faecal pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 for colorectal cancer
screening: A meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:4004–4011.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Raspe E, Decraene C and Berx G: Gene
expression profiling to dissect the complexity of cancer biology:
Pitfalls and promise. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:250–260. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bernal G: Use of RNA isolated from feces
as a promising tool for the early detection of colorectal cancer.
Int J Biol Markers. 27:e82–e89. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shi M, Beauchamp RD and Zhang B: A
network-based gene expression signature informs prognosis and
treatment for colorectal cancer patients. PLoS One. 7:e412922012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chien CC, Chang CC, Yang SH, Chen SH, et
al: A homologue of the drosophila headcase protein is a novel tumor
marker for early-stage colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 15:919–926.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang SH, Chien CC, Chen CW, Li SY and
Huang CJ: Potential of faecal RNA in diagnosing colorectal cancer.
Cancer Lett. 226:55–63. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang CC, Yang SH, Chien CC, Chen SH, Pan
S, Lee CL, Lin CM, Sun HL, Huang CC, Wu YY, et al: Clinical meaning
of age-related expression of fecal cytokeratin 19 in colorectal
malignancy. BMC cancer. 9:3762009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kato I, Badsha KZ, Land S, Nechvatal JM,
Matherly LH, Tarca AL, Majumdar AP, Basson MD and Ram JL: DNA/RNA
markers for colorectal cancer risk in preserved stool specimens: A
pilot study. Tumori. 95:753–761. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang RN, Yang SH, Chang CC, Chien CC, Pan
S and Huang CJ: Upregulation of fecal cytokeratin 19 is associated
with prognosis in older colorectal cancer patients. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 14:703–708. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liebig C, Agarwal N, Ayala GE, Verstovsek
G, Tuszynski GP and Albo D: Angiocidin inhibitory peptides decrease
tumor burden in a murine colon cancer model. J Surg Res.
142:320–326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu CY, Lee WH, Wang JY, Chiang H, Chang
JL, Tsai WC, Sheu LF and Jin JS: Tissue microarray-determined
expression profiles of cyclooxygenase-2 in colorectal
adenocarcinoma: Association with clinicopathological parameters.
Chin J Physiol. 49:298–304. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Altangerel O, Cao S, Meng J, et al:
Chronic neutrophilic leukemia with overexpression of EVI-1, and
concurrent CSF3R and SETBP1 mutations: A case report. Oncology
letters. 10:1694–1700. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hellemans J, Mortier G, De Paepe A,
Speleman F and Vandesompele J: qBase relative quantification
framework and software for management and automated analysis of
real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome biology. 8:R192007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tien LT, Chien CC, Yang SH, Lin CM, Wu YY
and Huang CJ: p53-Dependent Expression of Ribosomal Protein
S27-Like in Colorectal Cancer. Fu Jen J Med. 8:11–17. 2010.
|
|
40
|
Christensen J, El-Gebali S, Natoli M,
Sengstag T, Delorenzi M, Bentz S, Bouzourene H, Rumbo M, Felsani A,
Siissalo S, et al: Defining new criteria for selection of
cell-based intestinal models using publicly available databases.
BMC genomics. 13:2742012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wu CC, Tsai FM, Shyu RY, Tsai YM, Wang CH
and Jiang SY: G protein-coupled receptor kinase 5 mediates
Tazarotene-induced gene 1-induced growth suppression of human colon
cancer cells. BMC cancer. 11:1752011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Godar S, Ince TA, Bell GW, Feldser D,
Donaher JL, Bergh J, Liu A, Miu K, Watnick RS, Reinhardt F, et al:
Growth-inhibitory and tumor-suppressive functions of p53 depend on
its repression of CD44 expression. Cell. 134:62–73. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Elzagheid A, Emaetig F, Buhmeida A, Laato
M, El-Faitori O, Syrjänen K, Collan Y and Pyrhönen S: Loss of MUC2
expression predicts disease recurrence and poor outcome in
colorectal carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 34:621–628. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Herszenyi L, Hritz I, Lakatos G, Varga MZ
and Tulassay Z: The behavior of matrix metalloproteinases and their
inhibitors in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13240–13263.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lu Y, Jingyan G, Baorong S, Peng J, Xu Y
and Cai S: Expression of EGFR, Her2 predict lymph node metastasis
(LNM)-associated metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark.
11:219–226. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Schetter AJ, et al:
Identification of a metastasis-specific MicroRNA signature in human
colorectal cancer. J Nat Can Ins. 107:2015.
|
|
47
|
Bordonaro M and Lazarova DL: Determination
of the Role of CBP- and p300-Mediated Wnt Signaling on Colonic
Cells. JMIR Res Prot. 5:e662016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Huang CJ, Lee CL, Yang SH, et al:
Upregulation of the growth arrest-specific-2 in recurrent
colorectal cancers, and its susceptibility to chemotherapy in a
model cell system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1862:1345–1353. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Miyake M, Takemasa I, Matoba R, Tanino M,
Niijima S, Ikeda M, Yamamoto H, Sekimoto M, Kuhara S, Okayama T, et
al: Heterogeneity of colorectal cancers and extraction of
discriminator gene signatures for personalized prediction of
prognosis. Int J Oncol. 39:781–789. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sudoyo AW: Biomolecular markers as
determinants of patients selection for adjuvant chemotherapy of
sporadic colorectal cancers. Acta Med Indones. 42:45–50.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Carroll MR, Seaman HE and Halloran SP:
Tests and investigations for colorectal cancer screening. Clinical
Biochem. 47:921–939. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Pox C: Colon cancer screening: Which
non-invasive filter tests? Dig Dis. 1:(Suppl 1). S56–S59. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Miller S and Steele S: Novel molecular
screening approaches in colorectal cancer. J Surg Oncol.
105:459–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bhardwaj RK, Herrera-Ruiz D, Eltoukhy N,
Saad M and Knipp GT: The functional evaluation of human
peptide/histidine transporter 1 (hPHT1) in transiently transfected
COS-7 cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 27:533–542. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kobayashi T, Shimabukuro-Demoto S,
Yoshida-Sugitani R, Furuyama-Tanaka K, Karyu H, et al: The
histidine transporter SLC15A4 coordinates mTOR-dependent
inflammatory responses and pathogenic antibody production.
Immunity. 41:375–388. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sasawatari S, Okamura T, Kasumi E,
Tanaka-Furuyama K, Yanobu-Takanashi R, Shirasawa S, Kato N and
Toyama-Sorimachi N: The solute carrier family 15A4 regulates TLR9
and NOD1 functions in the innate immune system and promotes colitis
in mice. Gastroenterology. 140:1513–1525. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ye Q, Zheng Y, Fan S, Qin Z, Li N, Tang A,
Ai F, Zhang X, Bian Y, Dang W, et al: Lactoferrin deficiency
promotes colitis-associated colorectal dysplasia in mice. PLoS One.
9:e1032982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Rao G, Wang H, Li B, Huang L, Xue D, et
al: Reciprocal interactions between tumor-associated macrophages
and CD44 positive cancer cells via osteopontin/CD44 promote
tumorigenicity in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:785–797.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Perez A, Neskey DM, Wen J, Pereira L,
Reategui EP, Goodwin WJ, Carraway KL and Franzmann EJ: CD44
interacts with EGFR and promotes head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma initiation and progression. Oral Oncol. 49:306–313. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Yu S, Cai X, Wu C, Wu L, Wang Y, Liu Y, et
al: Adhesion glycoprotein CD44 functions as an upstream regulator
of a network connecting ERK, AKT and Hippo-YAP pathways in cancer
progression. Oncotarget. 6:2951–2965. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Sawai M, Yashiro M, Nishiguchi Y, Ohira M
and Hirakawa K: Growth-inhibitory effects of the ketone body,
monoacetoacetin, on human gastric cancer cells with succinyl-CoA:
3-oxoacid CoA-transferase (SCOT) deficiency. Anticancer Res.
24:2213–2217. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Lin Z,
Whitaker-Menezes D, Howell A, Sotgia F and Lisanti MP: Ketone body
utilization drives tumor growth and metastasis. Cell cycle.
11:3964–3971. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Saraon P, Cretu D, Musrap N, Karagiannis
GS, Batruch I, Drabovich AP, van der Kwast T, Mizokami A, Morrissey
C, Jarvi K and Diamandis EP: Quantitative proteomics reveals that
enzymes of the ketogenic pathway are associated with prostate
cancer progression. Mol Cell Proteomics. 12:1589–1601. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mourtada-Maarabouni M, Watson D, Munir M,
Farzaneh F and Williams GT: Apoptosis suppression by candidate
oncogene PLAC8 is reversed in other cell types. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 13:80–91. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li C, Ma H, Wang Y, Cao Z, Graves-Deal R,
Powell AE, Starchenko A, Ayers GD, Washington MK, Kamath V, et al:
Excess PLAC8 promotes an unconventional ERK2-dependent EMT in colon
cancer. J Clin Invest. 124:2172–2187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Coghlin C and Murray GI: Biomarkers of
colorectal cancer: Recent advances and future challenges.
Proteomics Clin Appl. 9:64–71. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Okuno K, Yasutomi M, Nishimura N, Arakawa
T, Shiomi M, Hida J, Ueda K and Minami K: Gene expression analysis
in colorectal cancer using practical DNA array filter. Dis Colon
Rectum. 44:295–299. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Kim HJ, Yu MH, Kim H, Byun J and Lee C:
Noninvasive molecular biomarkers for the detection of colorectal
cancer. BMB Rep. 41:685–692. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zoratto F, Rossi L, Verrico M, Papa A,
Basso E, Zullo A, Tomao L, Romiti A, Lo Russo G and Tomao S: Focus
on genetic and epigenetic events of colorectal cancer pathogenesis:
Implications for molecular diagnosis. Tumour Biol. 35:6195–6206.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|