|
1
|
Peek RM Jr and Blaser MJ: Helicobacter
pylori and gastrointestinal tract adenocarcinomas. Nat Rev Cancer.
2:28–37. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wadhwa R, Song S, Lee JS, Yao Y, Wei Q and
Ajani JA: Gastric cancer-molecular and clinical dimensions. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 10:643–655. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Akhavan-Niaki H and Samadani AA: Molecular
insight in gastric cancer induction: An overview of cancer stemness
genes. Cell Biochem Biophys. 68:463–473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Correa P, Camargo MC, Piazuelo MB, et al:
The biology of gastric cancers. Springer Ebooks; 2008
|
|
6
|
Figueiredo C, Garcia-Gonzalez MA and
Machado JC: Molecular pathogenesis of gastric cancer. Helicobacter.
18:(Suppl 1). S28–S33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Conteduca V, Sansonno D, Lauletta G, Russi
S, Ingravallo G and Dammacco F: H. pylori infection and gastric
cancer: State of the art (review). Int J Oncol. 42:5–18.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamashita K, Sakuramoto S, Nemoto M,
Shibata T, Mieno H, Katada N, Kikuchi S and Watanabe M: Trend in
gastric cancer: 35 years of surgical experience in Japan. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:3390–3397. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Xu J, Shi Z, Shen X, Luo T, Bi J
and Nie M: Clinicopathologic characteristics and prognostic of
gastric cancer in young patients. Scand J Gastroenterol.
51:1043–1049. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee S, Baek M, Yang H, Bang YJ, Kim WH, Ha
JH, Kim DK and Jeoung DI: Identification of genes differentially
expressed between gastric cancers and normal gastric mucosa with
cDNA microarrays. Cancer Lett. 184:197–206. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meyerson M, Gabriel S and Getz G: Advances
in understanding cancer genomes through second-generation
sequencing. Nat Rev Genet. 11:685–696. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mardis ER: A decade's perspective on DNA
sequencing technology. Nature. 470:198–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S,
Cimmino A, Petrocca F, Visone R, Iorio M, Roldo C, Ferracin M, et
al: A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines
cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, Shimizu M,
Taccioli C, Rossi S, Alder H, Liu CG, Oue N, Yasui W, et al:
Relation between microRNA expression and progression and prognosis
of gastric cancer: A microRNA expression analysis. Lancet Oncol.
11:136–146. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Z, Gerstein M and Snyder M: RNA-Seq:
A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat Rev Genet. 10:57–63.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kahvejian A, Quackenbush J and Thompson
JF: What would you do if you could sequence everything? Nat
Biotechnol. 26:1125–1133. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang SN, Sun HH, Jin YM, Piao LZ, Jin DH,
Lin ZH and Shen XH: Identification of differentially expressed
genes in gastric cancer by high density cDNA microarray. Cancer
Genet. 205:147–155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hippo Y, Taniguchi H, Tsutsumi S, Machida
N, Chong JM, Fukayama M, Kodama T and Aburatani H: Global gene
expression analysis of gastric cancer by oligonucleotide
microarrays. Cancer Res. 62:233–240. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheadle C, Vawter MP, Freed WJ and Becker
KG: Analysis of microarray data using Z score transformation. J Mol
Diagn. 5:73–81. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trapnell C, Pachter L and Salzberg SL:
TopHat: Discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics.
25:1105–1111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tabas-Madrid D, Nogales-Cadenas R and
Pascual-Montano A: GeneCodis3: A non-redundant and modular
enrichment analysis tool for functional genomics. Nucleic Acids
Res. 40:W478–W483. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bornstein P, Kyriakides TR, Yang Z,
Armstrong LC and Birk DE: Thrombospondin 2 modulates collagen
fibrillogenesis and angiogenesis. J Investig Dermatol Symp Proc.
5:61–66. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O'Rourke KM, Laherty CD and Dixit VM:
Thrombospondin 1 and thrombospondin 2 are expressed as both homo-
and heterotrimers. J Biol Chem. 267:24921–24924. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsai SC, Valkov N, Yang WM, Gump J,
Sullivan D and Seto E: Histone deacetylase interacts directly with
DNA topoisomerase II. Nat Genet. 26:349–353. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Acampora D, D'Esposito M, Faiella A,
Pannese M, Migliaccio E, Morelli F, Stornaiuolo A, Nigro V, Simeone
A and Boncinelli E: The human HOX gene family. Nucleic Acids Res.
17:10385–10402. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hewitt JE, Gordon MM, Taggart RT, Mohandas
TK and Alpers DH: Human gastric intrinsic factor: Characterization
of cDNA and genomic clones and localization to human chromosome 11.
Genomics. 10:432–440. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
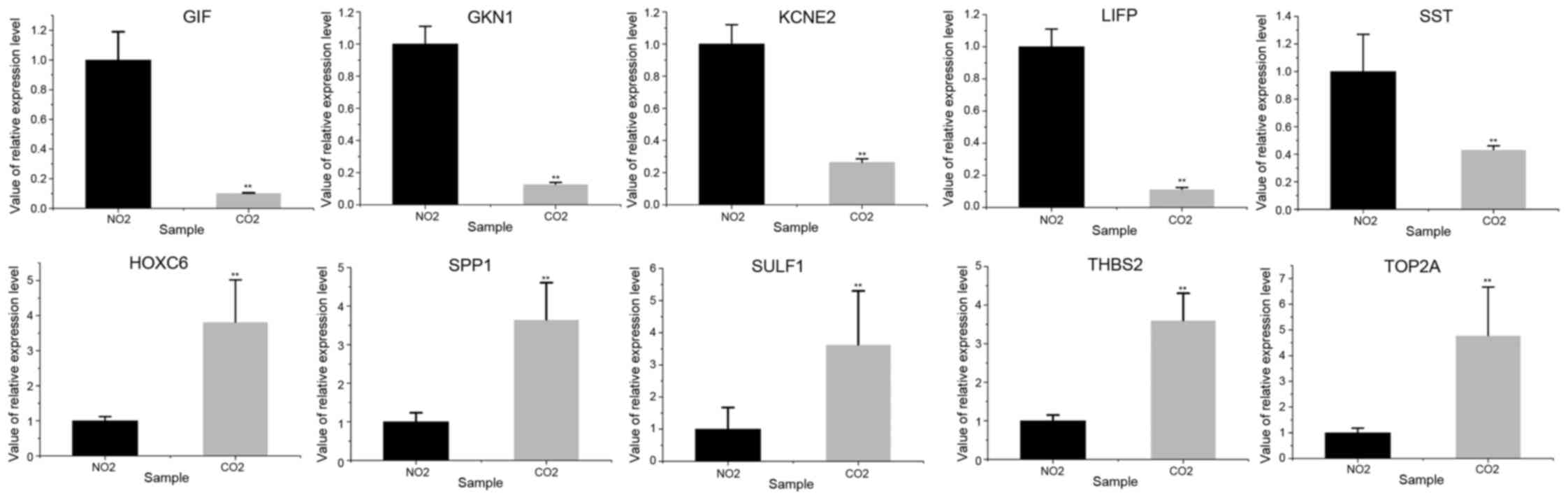
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)). Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fox A, Taylor D and Slonim DK: High
throughput interaction data reveals degree conservation of hub
proteins. Pac Symp Biocomput. 391–402. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lavi O, Skinner J and Gottesman MM:
Network features suggest new hepatocellular carcinoma treatment
strategies. BMC Syst Biol. 8:882014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tay ST, Leong SH, Yu K, Aggarwal A, Tan
SY, Lee CH, Wong K, Visvanathan J, Lim D, Wong WK, et al: A
combined comparative genomic hybridization and expression
microarray analysis of gastric cancer reveals novel molecular
subtypes. Cancer Res. 63:3309–3316. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu CM, Lee YS, Wang TH, Lee LY, Kong WH,
Chen ES, Wei ML, Liang Y and Hwang TL: Identification of
differential gene expression between intestinal and diffuse gastric
cancer using cDNA microarray. Oncol Rep. 15:57–64. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dang Y, Wang YC and Huang QJ: Microarray
and next-generation sequencing to analyse gastric cancer. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 15:8033–8039. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Song B, Du J, Deng N, Ren JC and Shu ZB:
Comparative analysis of gene expression profiles of gastric cardia
adenocarcinoma and gastric non-cardia adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett.
12:3866–3874. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cui J, Chen Y, Chou WC, Sun L, Chen L, Suo
J, Ni Z, Zhang M, Kong X, Hoffman LL, et al: An integrated
transcriptomic and computational analysis for biomarker
identification in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:1197–1207.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bertucci F, Salas S, Eysteries S, Nasser
V, Finetti P, Ginestier C, Charafe-Jauffret E, Loriod B, Bachelart
L, Montfort J, et al: Gene expression profiling of colon cancer by
DNA microarrays and correlation with histoclinical parameters.
Oncogene. 23:1377–1391. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Koslowski M, Sahin U, Mitnacht-Kraus R,
Seitz G, Huber C and Türeci O: A placenta-specific gene ectopically
activated in many human cancers is essentially involved in
malignant cell processes. Cancer Res. 67:9528–9534. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bonome T, Lee JY, Park DC, Radonovich M,
Pise-Masison C, Brady J, Gardner GJ, Hao K, Wong WH, Barrett JC, et
al: Expression profiling of serous low malignant potential,
low-grade and high-grade tumors of the ovary. Cancer Res.
65:10602–10612. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Avdulov S, Li S, Michalek V, Burrichter D,
Peterson M, Perlman DM, Manivel JC, Sonenberg N, Yee D, Bitterman
PB and Polunovsky VA: Activation of translation complex eIF4F is
essential for the genesis and maintenance of the malignant
phenotype in human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Cell.
5:553–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gao J, Sai N, Wang C, Sheng X, Shao Q,
Zhou C, Shi Y, Sun S, Qu X and Zhu C: Overexpression of
chromokinesin KIF4 inhibits proliferation of human gastric
carcinoma cells both in vitro and in vivo. Tumor Biol. 32:53–61.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Nishita Y, Yoshida I, Sado T and Takagi N:
Genomic imprinting and chromosomal localization of the human MEST
gene. Genomics. 36:539–542. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lunardi D, Abelli L, Panti C, Marsili L,
Fossi MC and Mancia A: Transcriptomic analysis of bottlenose
dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) skin biopsies to assess the effects of
emerging contaminants. Mar Environ Res. 114:74–79. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hartl D, He CH, Koller B, Da Silva CA,
Homer R, Lee CG and Elias JA: Acidic mammalian chitinase is
secreted via an ADAM17/epidermal growth factor receptor-dependent
pathway and stimulates chemokine production by pulmonary epithelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 283:33472–33482. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Żurawska-Płaksej E, Ługowska A, Hetmańczyk
K, Knapik-Kordecka M and Piwowar A: Neutrophils as a source of
chitinases and chitinase-like proteins in type 2 diabetes. PLoS
One. 10:e01417302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gooday GW, Brydon LJ and Chappell LH:
Chitinase in female onchocerca gibsoni and its inhibition by
allosamidin. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 29:223–225. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kamata T: Roles of Nox1 and other Nox
isoforms in cancer development. Cancer Sci. 100:1382–1388. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nair NG, Blessantoli M and Vennila JJ:
Gene expression in gastric cancer for Singapore and UK population:
An Insilico comparative approach. Res J Recent Sci. 3:2014.
|
|
48
|
Taniwaki M, Takano A, Ishikawa N, Yasui W,
Inai K, Nishimura H, Tsuchiya E, Kohno N, Nakamura Y and Daigo Y:
Activation of KIF4A as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic
target for lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:6624–6631. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|