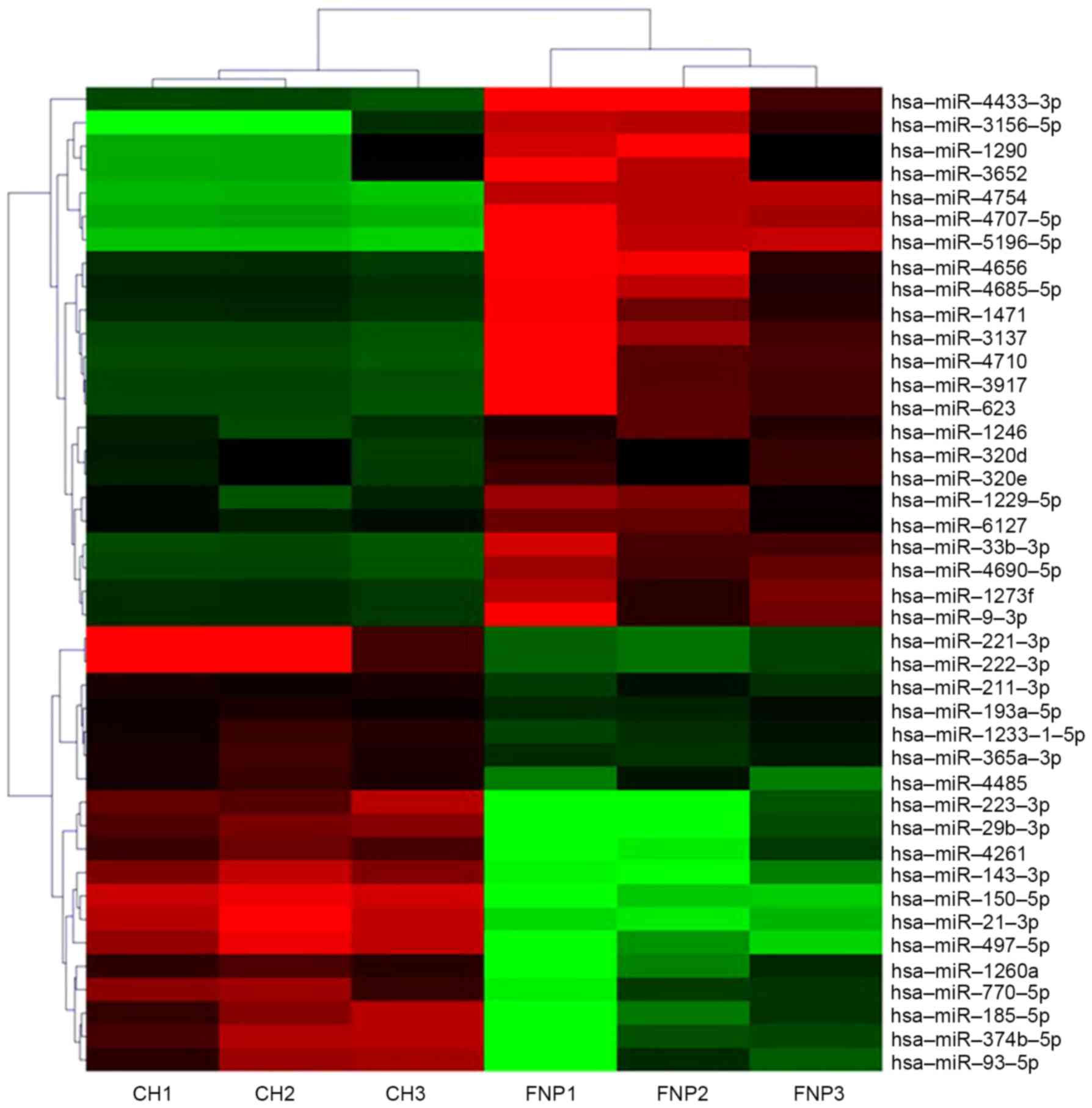
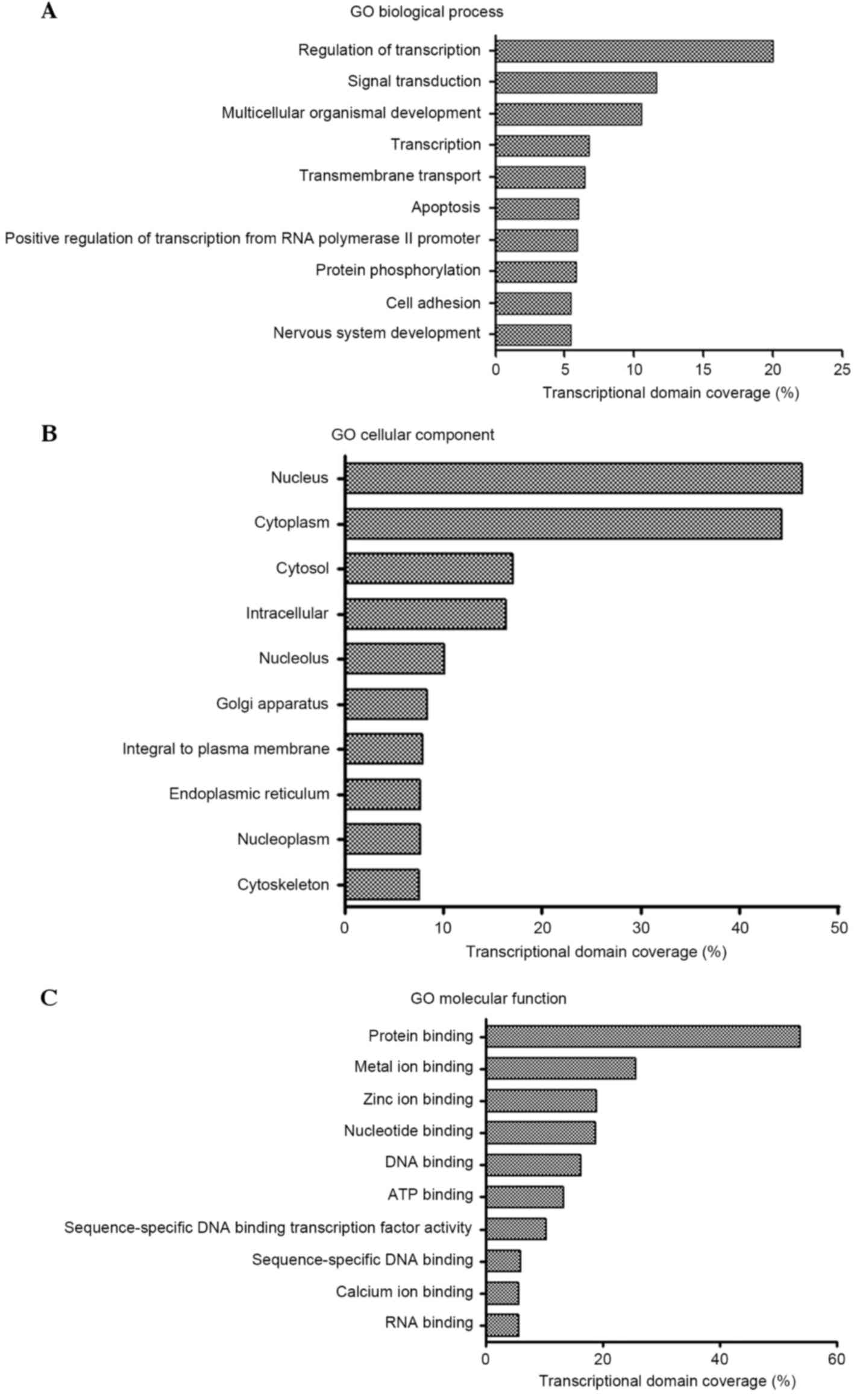
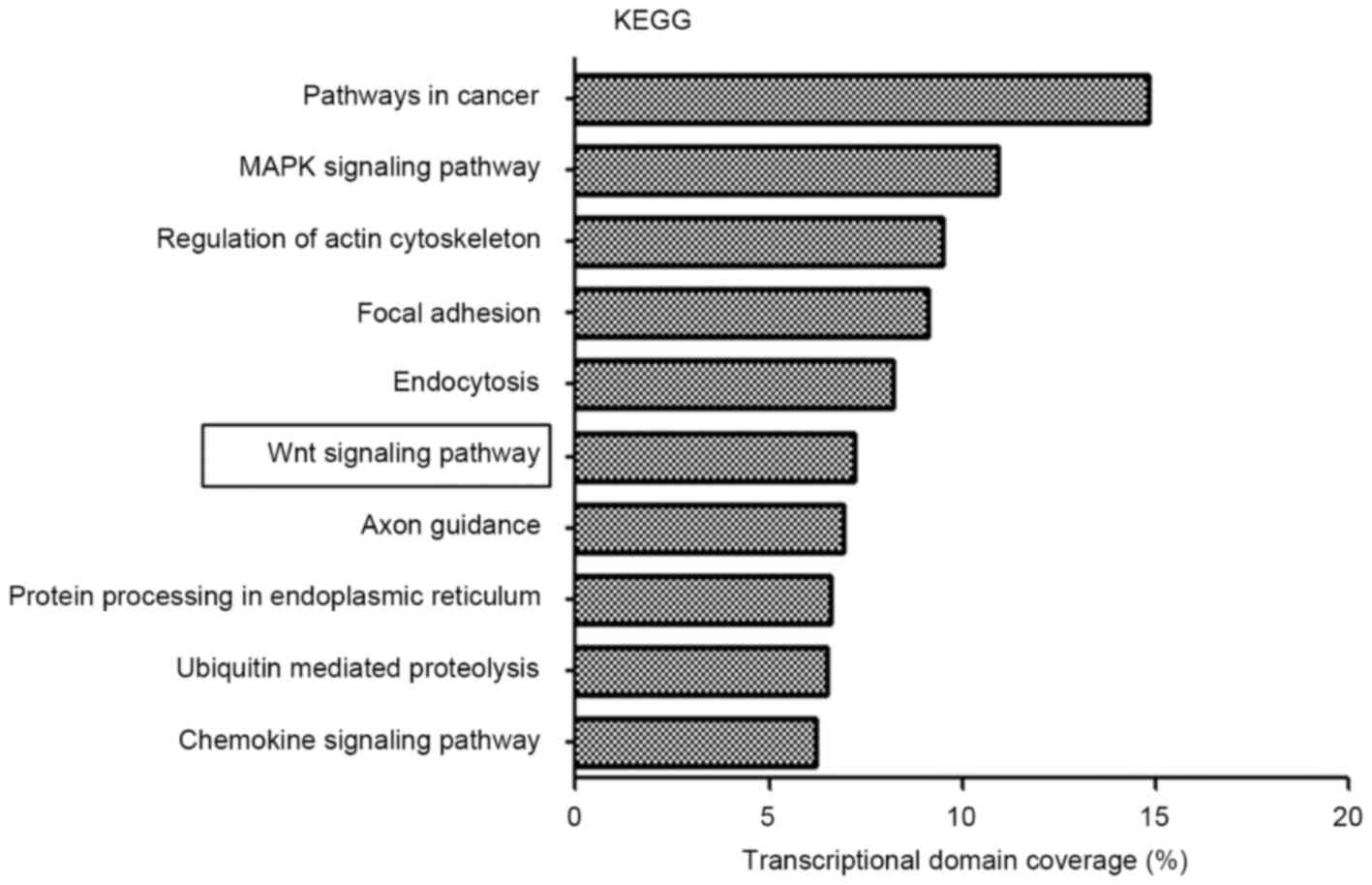
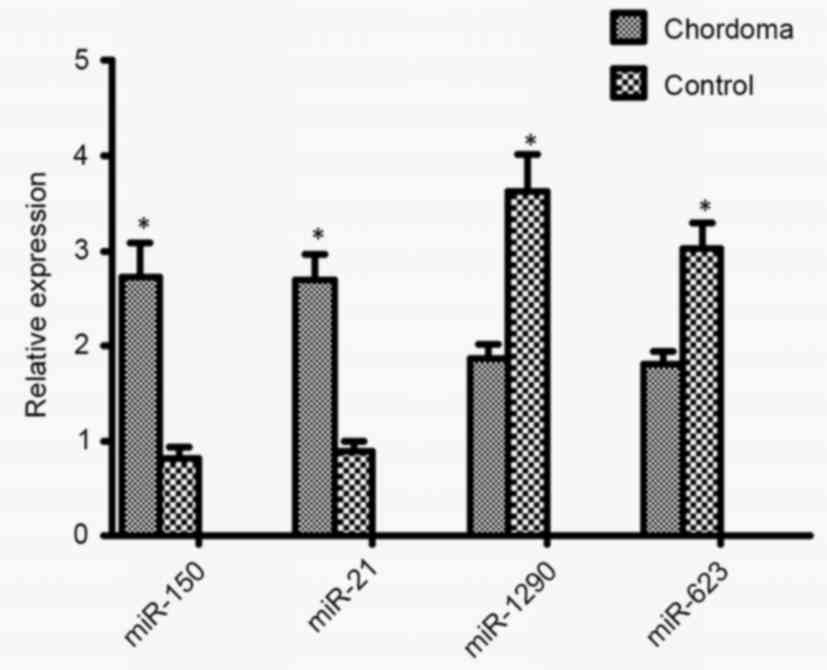
|
1
|
Casali PG, Stacchiotti S, Sangalli C, Olmi
P and Gronchi A: Chordoma. Curr Opin Oncol. 19:367–370. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McMaster ML, Goldstein AM, Bromley CM,
Ishibe N and Parry DM: Chordoma: Incidence and survival patterns in
the United States, 1973–1995. Cancer Causes Control. 12:1–11. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fuchs B, Dickey ID, Yaszemski MJ, Inwards
CY and Sim FH: Operative management of sacral chordoma. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 87:2211–2216. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sciubba DM, Cheng JJ, Petteys RJ, Weber
KL, Frassica DA and Gokaslan ZL: Chordoma of the sacrum and
vertebral bodies. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 17:708–717. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chugh R, Tawbi H, Lucas DR, Biermann JS,
Schuetze SM and Baker LH: Chordoma: The nonsarcoma primary bone
tumor. Oncologist. 12:1344–1350. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lujambio A and Lowe SW: The microcosmos of
cancer. Nature. 482:347–355. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kong YW, Ferland-McCollough D, Jackson TJ
and Bushell M: microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol.
13:e249–e258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Duan Z, Choy E, Nielsen GP, Rosenberg A,
Iafrate J, Yang C, Schwab J, Mankin H, Xavier R and Hornicek FJ:
Differential expression of microRNA (miRNA) in chordoma reveals a
role for miRNA-1 in Met expression. J Orthop Res. 28:746–752.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bayrak OF, Gulluoglu S, Aydemir E, Ture U,
Acar H, Atalay B, Demir Z, Sevli S, Creighton CJ, Ittmann M, et al:
MicroRNA expression profiling reveals the potential function of
microRNA-31 in chordomas. J Neurooncol. 115:143–151. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Schiff D, Park D and Abounader R:
MicroRNA-608 and microRNA-34a regulate chordoma malignancy by
targeting EGFR, Bcl-xL and MET. PLoS One. 9:e915462014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vujovic S, Henderson S, Presneau N, Odell
E, Jacques TS, Tirabosco R, Boshoff C and Flanagan AM: Brachyury, a
crucial regulator of notochordal development, is a novel biomarker
for chordomas. J Pathol. 209:157–165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen J, Shi Q, Lu J, Wang DL, Zou TM, Yang
HL and Zhu GQ: Histological study of chordomaorigin from fetal
notochordal cell rests. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 38:2165–2170. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ziyan W, Shuhua Y, Xiufang W and Xiaoyun
L: MicroRNA-21 is involved in osteosarcoma cell invasion and
migration. Med Oncol. 28:1469–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang C, Liu K, Li T, Fang J, Ding Y, Sun
L, Tu T, Jiang X, Du S, Hu J, et al: miR-21: A gene of dual
regulation in breast cancer. Int J Oncol. 48:161–172. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Basati G, Razavi Emami A, Abdi S and
Mirzaei A: Elevated level of microRNA-21 in the serum of patients
with colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 31:2052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Long C, Jiang L, Wei F, Ma C, Zhou H, Yang
S, Liu X and Liu Z: Integrated miRNA-mRNA analysis revealing the
potential roles of miRNAs in chordomas. PLoS One. 8:e666762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tamborini E, Virdis E, Negri T, Orsenigo
M, Brich S, Conca E, Gronchi A, Stacchiotti S, Manenti G, Casali
PG, et al: Analysis of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and
downstream pathways in chordomas. Neuro Oncol. 12:776–789. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang K, Chen H, Zhang B, Sun J, Lu J,
Chen K and Yang H: Overexpression of Raf-1 and ERK1/2 in sacral
chordoma and association with tumor recurrence. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:608–614. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tian J, He H and Lei G: Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in bone cancers. Tumour Biol. 35:9439–9445. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song JL, Nigam P, Tektas SS and Selva E:
microRNA regulation of Wnt signaling pathways in development and
disease. Cell Signal. 27:1380–1391. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li G, Wang Y, Liu Y, Su Z, Liu C, Ren S,
Deng T, Huang D, Tian Y and Qiu Y: miR-185-3p regulates
nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by targeting WNT2B in
vitro. Cancer Sci. 105:1560–1568. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu M, Lang N, Chen X, Tang Q, Liu S,
Huang J, Zheng Y and Bi F: miR-185 targets RhoA and Cdc42
expression and inhibits the proliferation potential of human
colorectal cells. Cancer Lett. 301:151–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fu P, Du F, Yao M, Lv K and Liu Y:
MicroRNA-185 inhibits proliferation by targeting c-Met in human
breast cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 8:1879–1883. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|