|
1
|
World Health Organization (WHO), . 2017,
https://www.who.int/cancer/en/April
10–2017
|
|
2
|
Schirrmacher V: Fifty years of clinical
application of Newcastle disease virus: Time to celebrate!
Biomedicines. 4:E162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Russell SJ, Peng KW and Bell JC: Oncolytic
virotherapy. Nat Biotechnol. 30:658–670. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O and Zitvogel
L: Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol.
31:51–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guo ZS, Liu Z and Bartlett DL: Oncolytic
immunotherapy: Dying the right way is a key to eliciting potent
antitumor immunity. Front Oncol. 4:742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mayo MA: Virus taxonomy-Houston 2002. Arch
Virol. 147:1071–1076. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Alexander DJ: Newcastle disease and other
avian paramyxoviruses. Rev Sci Tech. 19:443–462. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Czeglédi A, Ujvári D, Somogyi E, Wehmann
E, Werner O and Lomniczi B: Third genome size category of avian
paramyxovirus serotype 1 (Newcastle disease virus) and evolutionary
implications. Virus Res. 120:36–48. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Morrison T, McQuain C, Sergel T, McGinnes
L and Reitter J: The role of the amino terminus of F1 of the
Newcastle disease virus fusion protein in cleavage and fusion.
Virology. 193:997–1000. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Panda A, Huang Z, Elankumaran S, Rockemann
DD and Samal SK: Role of fusion protein cleavage site in the
virulence of Newcastle disease virus. Microb Pathog. 36:1–10. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ahlert T and Schirrmacher V: Isolation of
a human melanoma adapted Newcastle disease virus mutant with highly
selective replication patterns. Cancer Res. 50:5962–5968.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Elankumaran S, Rockemann D and Samal SK:
Newcastle disease virus exerts oncolysis by both intrinsic and
extrinsic caspase-dependent pathways of cell death. J Virol.
80:7522–7534. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kumar R, Tiwari AK, Chaturvedi U, Kumar
GR, Sahoo AP, Rajmani RS, Saxena L, Saxena S, Tiwari S and Kumar S:
Velogenic Newcastle disease virus as an oncolytic virotherapeutics:
In vitro characterization. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 167:2005–2022.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gallucci S and Matzinger P: Danger
signals: SOS to the immune system. Curr Opin Immunol. 13:114–119.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zeng J, Fournier P and Schirrmacher V:
Induction of interferon-alpha and tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in human blood mononuclear cells by
hemagglutinin-neuraminidase but not F protein of Newcastle disease
virus. Virology. 297:19–30. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fournier P, Zeng J and Schirrmacher V: Two
ways to induce innate immune responses in human PBMCs: Paracrine
stimulation of IFN-α responses by viral protein or dsRNA. Int J
Oncol. 23:673–680. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lam HY, Yusoff K, Yeap SK, Subramani T,
Abd-Aziz S, Omar AR and Alitheen NB: Immunomodulatory effects of
Newcastle disease virus AF2240 strain on human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells. Int J Med Sci. 11:1240–1247. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zorn U, Dallmann I, Grosse J, Kirchner H,
Poliwoda H and Atzpodien J: Induction of cytokines and cytotoxicity
against tumor cells by Νewcastle disease virus. Cancer Biother.
9:225–235. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schirrmacher V, Bai L, Umansky V, Yu L,
Xing Y and Qian Z: Newcastle disease virus activates macrophages
for anti-tumor activity. Int J Oncol. 16:363–373. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Janke M, Peeters B, de Leeuw O, Moorman R,
Arnold A, Fournier P and Schirrmacher V: Recombinant Newcastle
disease virus (NDV) with inserted gene coding for GM-CSF as a new
vector for cancer immunogene therapy. Gene Ther. 14:1639–1649.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Janke M, Peeters B, Zhao H, de Leeuw O,
Moorman R, Arnold A, Ziouta Y, Fournier P and Schirrmacher V:
Activation of human T cells by a tumor vaccine infected with
recombinant Newcastle disease virus producing IL-2. Int J Oncol.
33:823–832. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Absalón AE, Mariano-Matías A,
Vásquez-Márquez A, Morales-Garzón A, Cortés-Espinosa DV,
Ortega-García R and Lucio-Decanini E: Complete genome sequence of a
velogenic Newcastle disease virus isolated in Mexico. Virus Genes.
45:304–310. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
López-Terrada D, Cheung SW, Finegold MJ
and Knowles BB: Hep G2 is a hepatoblastoma-derived cell line. Hum
Pathol. 40:1512–1515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Garzón-Morales JA, Lucio-Decanini E,
Cortes-Espinosa DV and Absalón-Constantino AE: Newcastle disease
virus and the use thereof as a vaccine US Patent 2013/0315956 A1.
Filing date: November 18, 2011. Publication date. November
28–2013
|
|
25
|
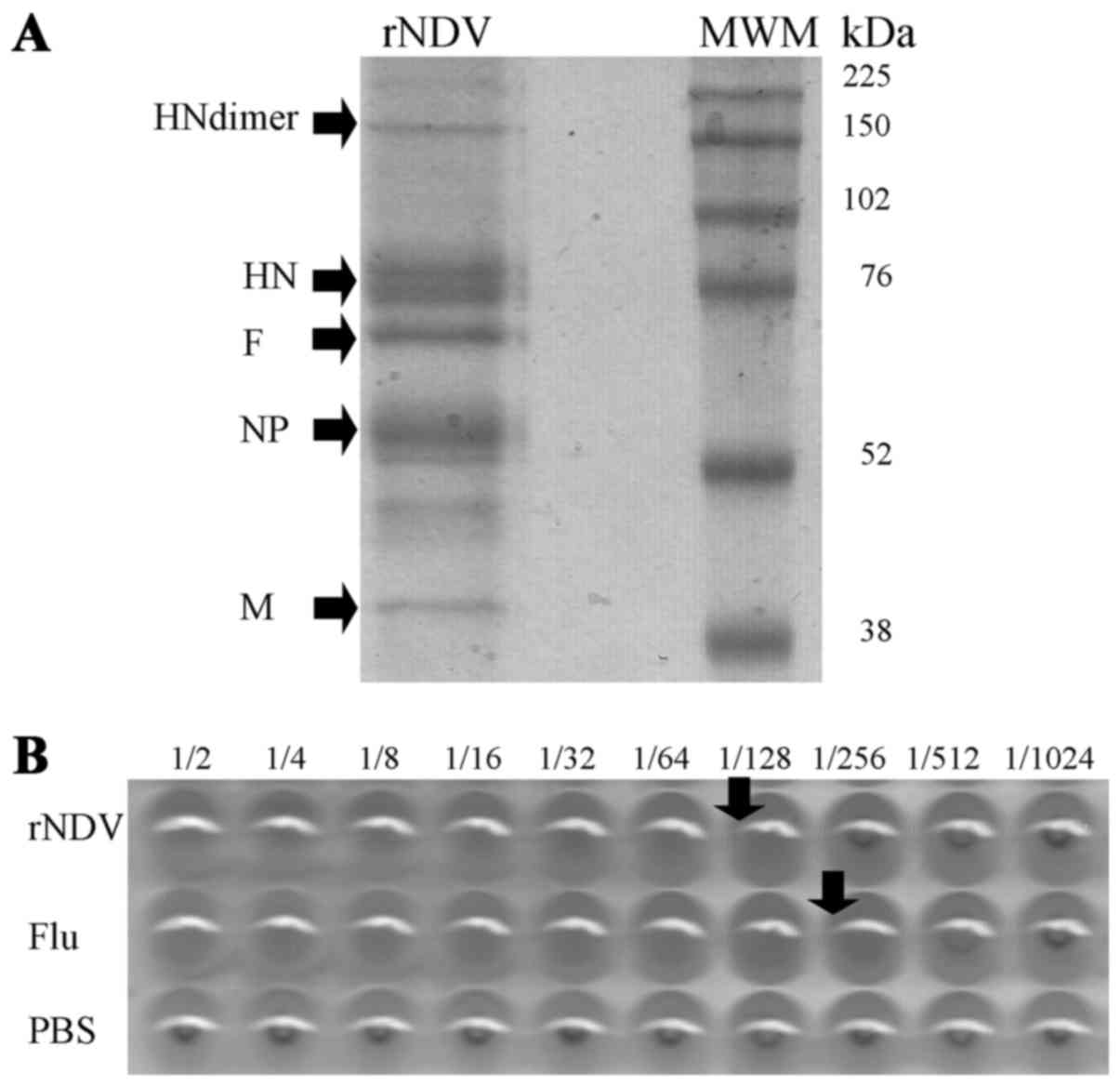
Gallagher SR: Unit 7.3. SDS-polyacrylamide
gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). Curr Protoc Essent Lab Tech.
2012:1–28. 2011.
|
|
26
|
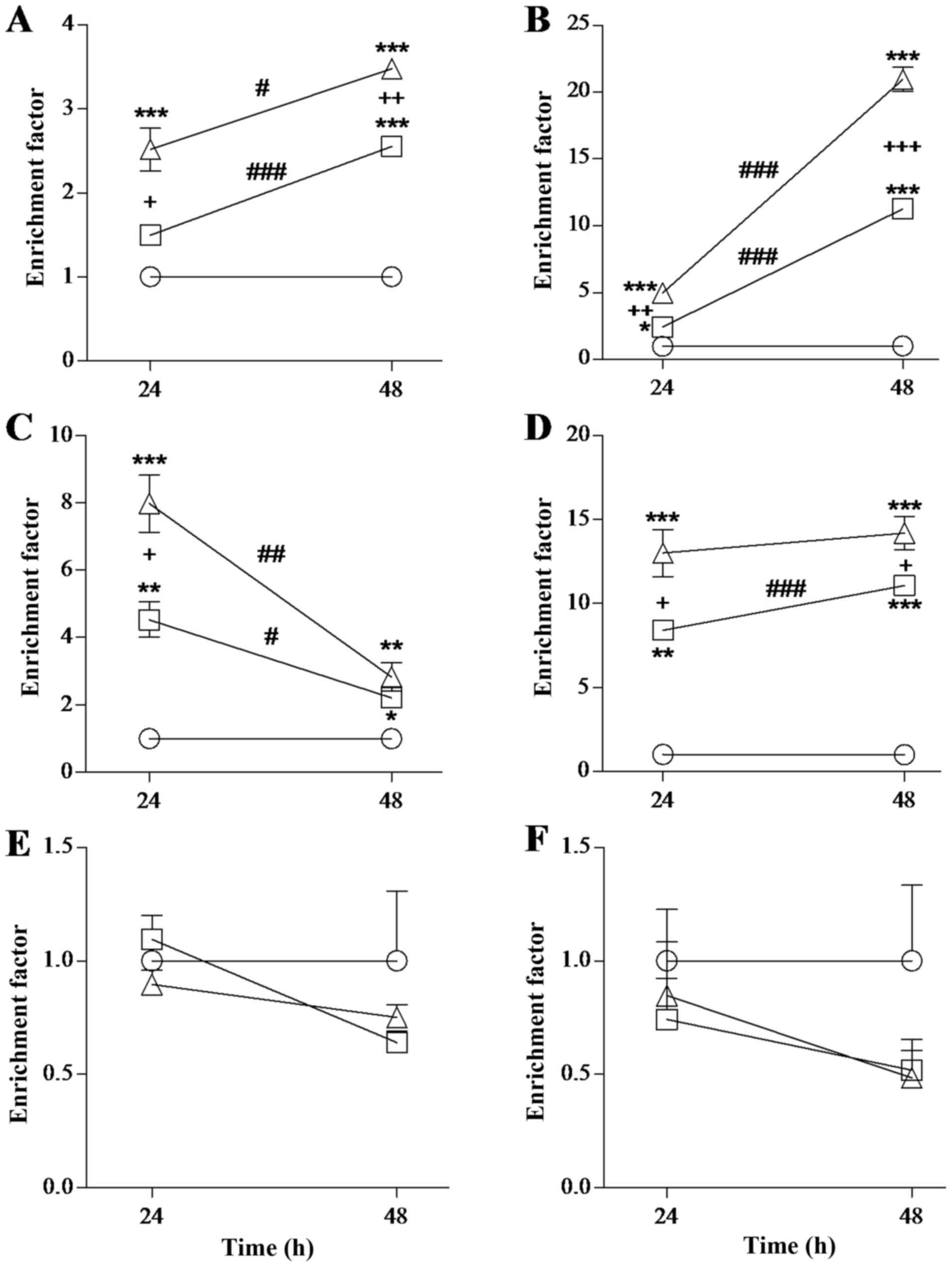
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zamarin D and Palese P: Oncolytic
Newcastle disease virus for cancer therapy: Old challenges and new
directions. Future Microbiol. 7:347–367. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rani S, Gogoi P and Kumar S: Spectrum of
Newcastle disease virus stability in gradients of temperature and
pH. Biologicals. 42:351–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alabsi AM, Bakar SA, Ali R, Omar AR, Bejo
MH, Ideris A and Ali AM: Effects of Newcastle disease virus strains
AF2240 and V4-UPM on cytolysis and apoptosis of leukemia cell
lines. Int J Mol Sci. 12:8645–8660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lv Z, Zhang TY, Yin JC, Wang H, Sun T,
Chen LQ, Bai FL, Wu W, Ren GP and Li DS: Enhancement of anti-tumor
activity of Newcastle disease virus by the synergistic effect of
cytosine deaminase. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:7489–7496. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang K, Li Y, Zhu Q, Xu J, Wang Y, Deng
W, Liu Q, Zhang G and Meng S: Pharmacological modulation of
autophagy enhances Newcastle disease virus-mediated oncolysis in
drug-resistant lung cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 14:5512014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rajmani RS, Gupta SK, Singh PK, Gandham
RK, Sahoo AP, Chaturvedi U and Tiwari AK: HN protein of Newcastle
disease virus sensitizes HeLa cells to TNF-α-induced apoptosis by
downregulating NF-κB expression. Arch Virol. 161:2395–2405. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ni J, Galani IE, Cerwenka A, Schirrmacher
V and Fournier P: Antitumor vaccination by Newcastle disease virus
hemagglutinin-neuraminidase plasmid DNA application: Changes in
tumor microenvironment and activation of innate anti-tumor
immunity. Vaccine. 29:1185–1193. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Donnelly OG, Errington-mais F, Steele L,
Hadac E, Scott K, Peach H, Phillips RM, Bond J, Harrington K, Vile
R, et al: Measles virus causes immunogenic cell death in human
melanoma. Gene Ther. 20:7–15. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zamarin D, Holmgaard RB, Subudhi SK, Park
JS, Mansour M, Palese P, Merghoub T, Wolchok JD and Allison JP:
Localized oncolytic virotherapy overcomes systemic tumor resistance
to immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med.
6:226–232. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Seal BS, King DJ and Sellers HS: The avian
response to Newcastle disease virus. Dev Comp Immunol. 24:257–268.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Miller PJ, King DJ, Afonso CL and Suarez
DL: Antigenic differences among Newcastle disease virus strains of
different genotypes used in vaccine formulation affect viral
shedding after a virulent challenge. Vaccine. 25:7238–7246. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Balkwill FR, Lee A, Aldam G, Moodie E,
Thomas JA, Tavernier J and Fiers W: Human tumor xenografts treated
with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alone or in
combination with interferons. Cancer Res. 46:3990–3993.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Talmadge JE, Phillips H, Schneider M, Rowe
T, Pennington R, Bowersox O and Lenz B: Immunomodulatory properties
of recombinant murine and human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res.
48:544–550. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
van der Veen AH, de Wilt JH, Eggermont AM,
van Tiel ST, Seynhaeve ALB and ten Hagen TL: TNF-alpha augments
intratumoural concentrations of doxorubicin in TNF-alpha-based
isolated limb perfusion in rat sarcoma models and enhances
anti-tumour effects. Br J Cancer. 82:973–980. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Seynhaeve AL, Hoving S, Schipper D,
Vermeulen CE, De Wiel-Ambagtsheer GA, VanTiel ST, Eggermont AM and
Ten Hagen TL: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha mediates homogeneous
distribution of liposomes in murine melanoma that contributes to a
better tumor response. Cancer Res. 67:9455–9462. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
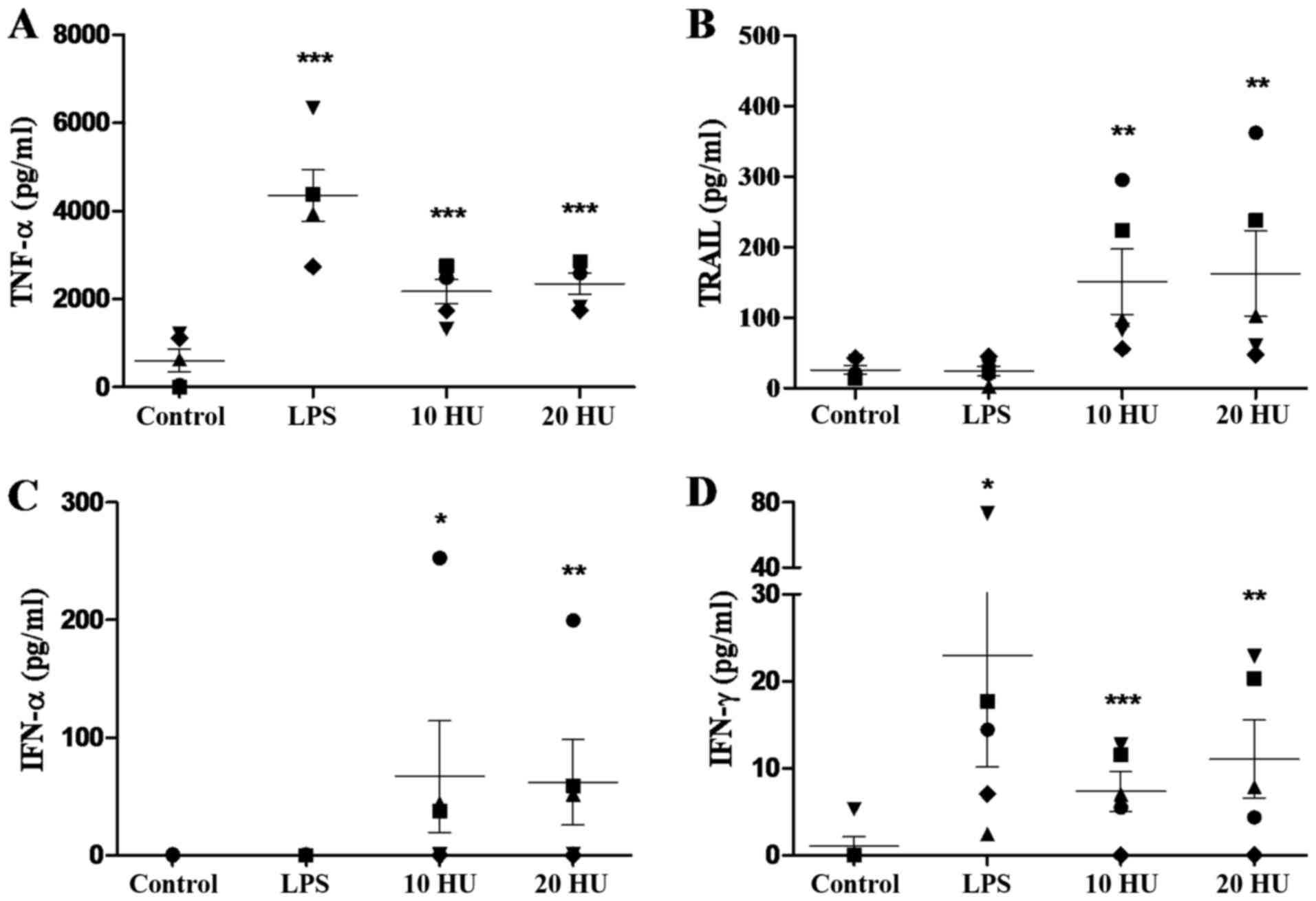
Lorence RM, Rood PA and Kelley KW:
Newcastle disease virus as an antineoplastic agent: Induction of
tumor necrosis factor-alpha and augmentation of its cytotoxicity. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 80:1305–1312. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ahmed I, Ahmad U, Keong YY, Manna NA and
Othman F: Induction of nitric oxide and TNF-α in Newcastle disease
virus (NDV) AF2240 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages and their
cytotoxic activity on MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line. J Cancer
Sci Ther. 6:478–482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Pecora AL, Rizvi N, Cohen GI, Meropol NJ,
Sterman D, Marshall JL, Goldberg S, Gross P, O'Neil JD, Groene WS,
et al: Phase I trial of intravenous administration of PV701, an
oncolytic virus, in patients with advanced solid cancers. J Clin
Oncol. 20:2251–2266. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S,
Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, Blackie C, Chang L, McMurtrey AE, Hebert
A, et al: Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2
ligand. J Clin Invest. 104:155–162. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Washburn B, Weigand MA, Grosse-Wilde A,
Janke M, Stahl H, Rieser E, Sprick MR, Schirrmacher V and Walczak
H: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand mediates tumoricidal
activity of human monocytes stimulated by Newcastle disease virus.
J Immunol. 170:1814–1821. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Song DZ, Liang Y, Xiao Q, Yin J, Gong JL,
Lai ZP, Zhang ZF, Gao LX and Fan XH: TRAIL is involved in the
tumoricidal activity of mouse natural killer cells stimulated by
Newcastle disease virus in vitro. Anat Rec (Hoboken).
296:1552–1560. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Vidalain PO, Azocar O, Lamouille B, Astier
A, Rabourdin-Combe C and Servet-Delprat C: Measles virus induces
functional TRAIL production by human dendritic cells. J Virol.
74:556–559. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chaperot L, Blum A, Manches O, Lui G,
Angel J, Molens JP and Plumas J: Virus or TLR agonists induce
TRAIL-mediated cytotoxic activity of plasmacytoid dendritic cells.
J Immunol. 176:248–255. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ehrlich S, Infante-Duarte C, Seeger B and
Zipp F: Regulation of soluble and surface-bound TRAIL in human T
cells, B cells and monocytes. Cytokine. 24:244–253. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Griffith TS, Wiley SR, Kubin MZ, Sedger
LM, Maliszewski CR and Fanger NA: Monocyte-mediated tumoricidal
activity via the tumor necrosis factor-related cytokine, TRAIL. J
Exp Med. 189:1343–1354. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fanger NA, Maliszewski CR, Schooley K and
Griffith TS: Human dendritic cells mediate cellular apoptosis via
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). J
Exp Med. 190:1155–1164. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Löseke S, Grage-Griebenow E, Wagner A,
Gehlhar K and Bufe A: Differential expression of IFN-alpha subtypes
in human PBMC: Evaluation of novel real-time PCR assays. J Immunol
Methods. 276:207–222. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Goodbourn S, Didcock L and Randall RE:
Interferons: Cell signalling, immune modulation, antiviral response
and virus countermeasure. J Gen Virol. 81:2341–2364. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Onoguchi K, Yoneyama M, Takemura A, Akira
S, Taniguchi T, Namiki H and Fujita T: Viral infections activate
types I and III interferon genes through a common mechanism. J Biol
Chem. 282:7576–7581. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ivashkiv LB and Donlin LT: Regulation of
type I interferon responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:36–49. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T and Hume
DA: Interferon-gamma: An overview of signals, mechanisms and
functions. J Leukoc Biol. 75:163–189. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Parker BS, Rautela J and Hertzog PJ:
Antitumour actions of interferons: Implications for cancer therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 16:131–144. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|