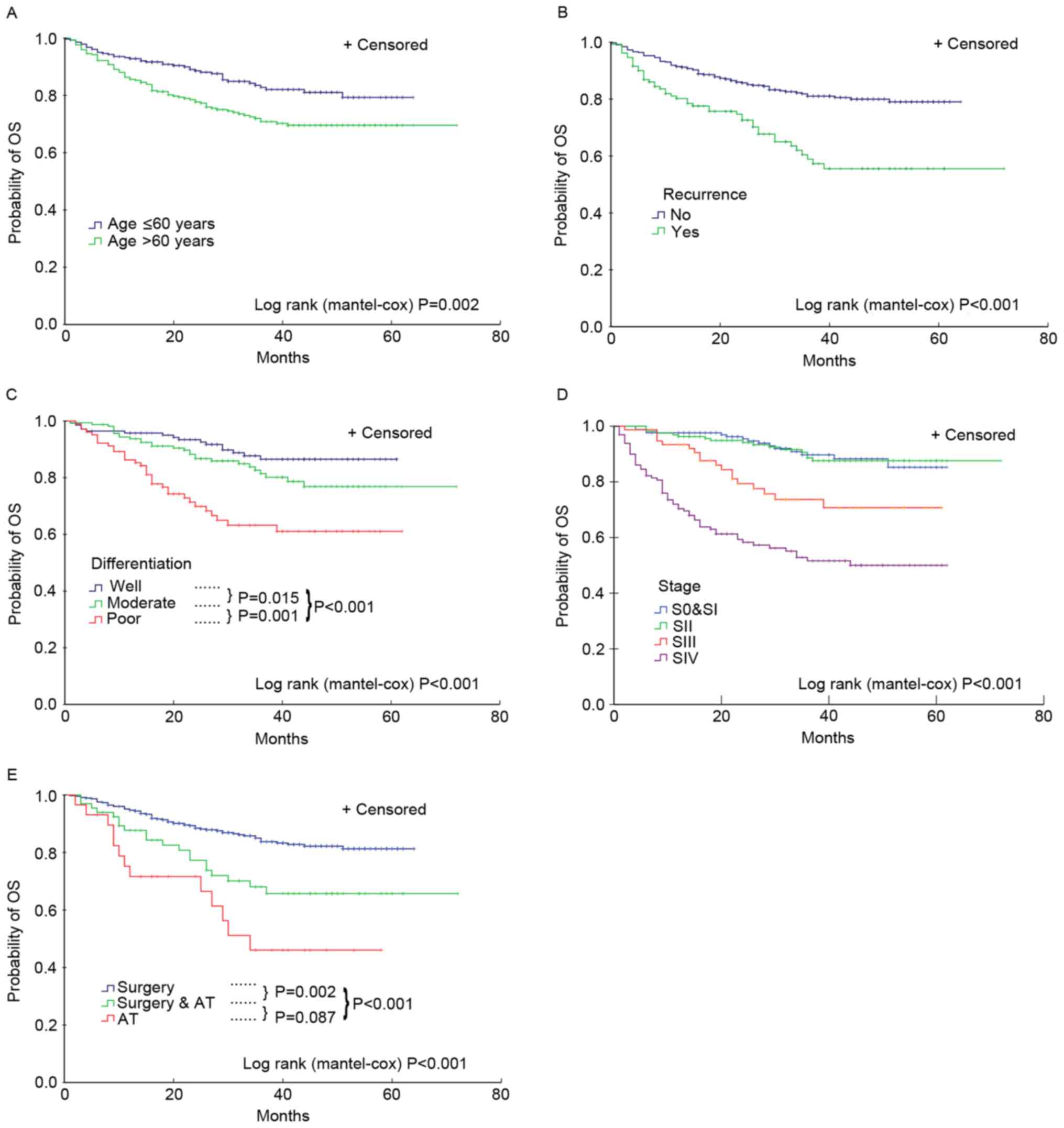
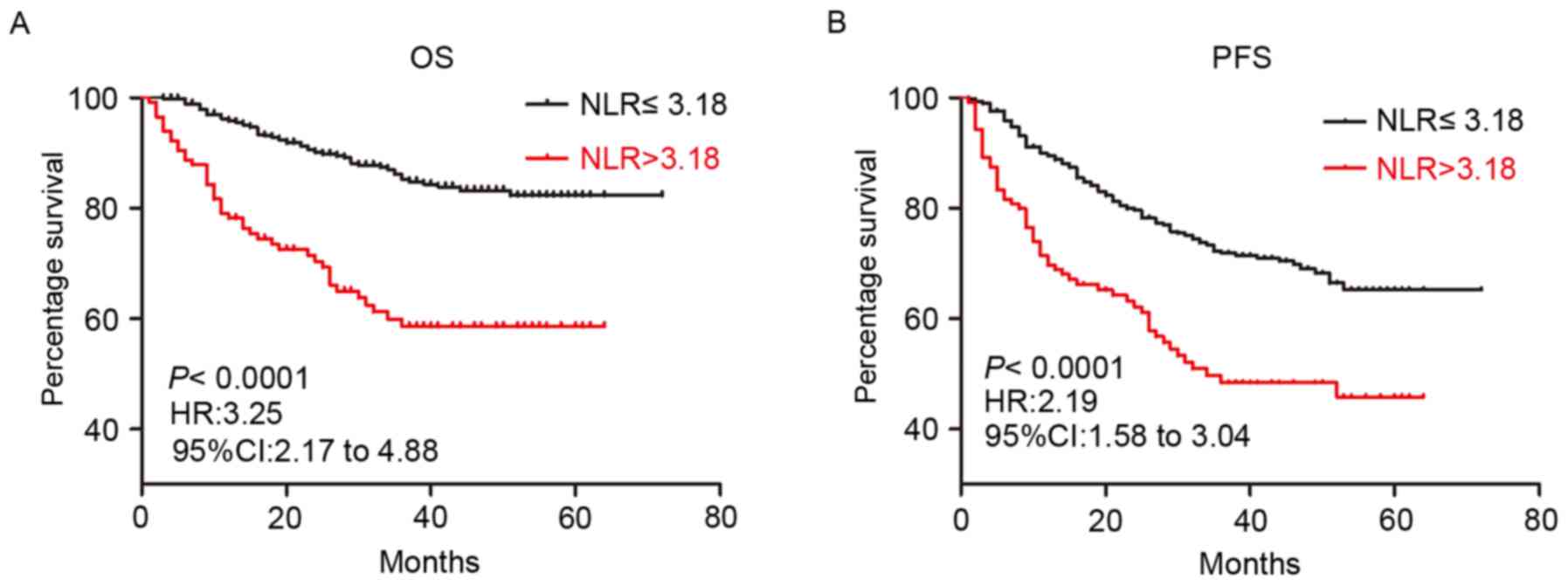
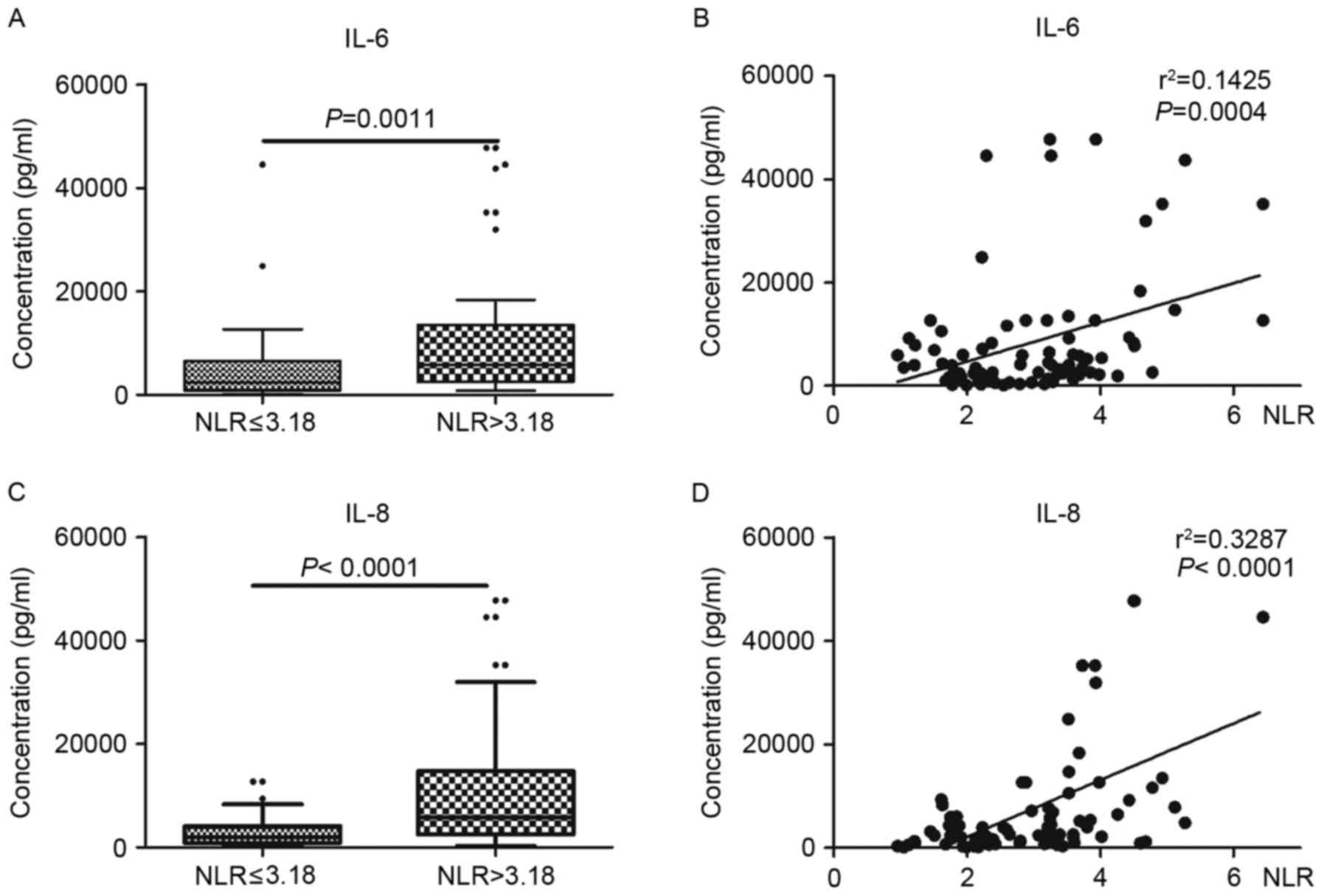
|
1
|
Cahlon O, Lee N, Le QT, Kaplan MJ and
Colevas AD: Cancer of the larynx. https://clinicalgate.com/cancer-of-the-larynx/April
9–2015
|
|
2
|
American Cancer Society, . What are the
key statistics about laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancers.
https://www.cancer.org/cancer/laryngeal-and-hypopharyngeal-cancer/about/key-statistics.htmlJanuary
5–2017
|
|
3
|
Barzan L, Talamini R, Franchin G, Vaccher
E, Politi D, Minatel E and Gobitti C: Changes in presentation and
survival of head and neck carcinomas in Northeastern Italy,
1975–1998. Cancer. 95:540–552. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Woodard TD, Oplatek A and Petruzzelli GJ:
Life after total laryngectomy: A measure of long-term survival,
function, and quality of life. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
133:526–532. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ji W, Guan C and Pan Z: Analysis of
curative effects on laryngeal carcinoma patients in the northeast
region of China. Acta Otolaryngol. 128:574–577. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hermanns T, Bhindi B, Wei Y, Yu J, Noon
AP, Richard PO, Bhatt JR, Almatar A, Jewett MA, Fleshner NE, et al:
Pre-treatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as predictor of
adverse outcomes in patients undergoing radical cystectomy for
urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Br J Cancer. 111:444–451.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Canna K, McArdle PA, McMillan DC, McNicol
AM, Smith GW, McKee RF and McArdle CS: The relationship between
tumour T-lymphocyte infiltration, the systemic inflammatory
response and survival in patients undergoing curative resection for
colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 92:651–654. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Roxburgh CS, Salmond JM, Horgan PG, Oien
KA and McMillan DC: Comparison of the prognostic value of
inflammation-based pathologic and biochemical criteria in patients
undergoing potentially curative resection for colorectal cancer.
Ann Surg. 249:788–793. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guthrie GJ, Charles KA, Roxburgh CS,
Horgan PG, McMillan DC and Clarke SJ: The systemic
inflammation-based neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio: Experience in
patients with cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 88:218–230. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Smith RA, Bosonnet L, Ghaneh P, Sutton R,
Evans J, Healey P, Garvey C, Hughes M, Raraty M, Campbell F and
Neoptolemos JP: The platelet-lymphocyte ratio improves the
predictive value of serum CA19-9 levels in determining patient
selection for staging laparoscopy in suspected periampullary
cancer. Surgery. 143:658–666. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ying HQ, Deng QW, He BS, Pan YQ, Wang F,
Sun HL, Chen J, Liu X and Wang SK: The prognostic value of
preoperative NLR, d-NLR, PLR and LMR for predicting clinical
outcome in surgical colorectal cancer patients. Med Oncol.
31:3052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xue TC, Zhang L, Xie XY, Ge NL, Li LX,
Zhang BH, Ye SL and Ren ZG: Prognostic significance of the
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in primary liver cancer: A
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e960722014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei Y, Jiang YZ and Qian WH: Prognostic
role of NLR in urinary cancers: A meta-analysis. PLoS One.
9:e920792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roxburgh CS and McMillan DC: Role of
systemic inflammatory response in predicting survival in patients
with primary operable cancer. Future Oncol. 6:149–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bizzo SM, Meira DD, Lima JM, Mororó Jda S,
Moreira FC, Casali-da-Rocha JC and Ornellas MH: Serum albumin and
vascular endothelial growth factor in epithelial ovarian cancer:
Looking at adnexal tumor drainage. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
283:855–859. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fujii T, Sutoh T, Morita H, Katoh T,
Yajima R, Tsutsumi S, Asao T and Kuwano H: Serum albumin is
superior to prealbumin for predicting short-term recurrence in
patients with operable colorectal cancer. Nutr Cancer.
64:1169–1173. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Adly L, Hill D, Sherman ME, Sturgeon SR,
Fears T, Mies C, Ziegler RG, Hoover RN and Schairer C: Serum
concentrations of estrogens, sex hormone-binding globulin, and
androgens and risk of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. Int J
Cancer. 119:2402–2407. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao Y, Zhao M, Yuan D, Gu X, Liu H and
Song Y: Elevated pretreatment serum globulin albumin ratio predicts
poor prognosis for advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients. J
Thorac Dis. 6:1261–1270. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rassouli A, Saliba J, Castano R, Hier M
and Zeitouni AG: Systemic inflammatory markers as independent
prognosticators of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head
Neck. 37:103–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kum RO, Ozcan M, Baklaci D, Kum NY, Yilmaz
YF, Gungor V and Unal A: Elevated neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in
squamous cell carcinoma of larynx compared to benign and
precancerous laryngeal lesions. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:7351–7355. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
American Joint Committee on Cancer, .
LarynxAJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th. Springer; New York, NY: pp.
57–62. 2010
|
|
24
|
Zhou X, Du Y, Huang Z, Xu J, Qiu T, Wang
J, Wang T, Zhu W and Liu P: Prognostic value of PLR in various
cancers: A meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e1011192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Freedman GM, Hanlon AL, Fowble BL,
Anderson PR and Nicolaou N: Recursive partitioning identifies
patients at high and low risk for ipsilateral tumor recurrence
after breast-conserving surgery and radiation. J Clin Oncol.
20:4015–4021. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hess KR, Abbruzzese MC, Lenzi R, Raber MN
and Abbruzzese JL: Classification and regression tree analysis of
1000 consecutive patients with unknown primary carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 5:3403–3410. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rassouli A, Saliba J, Castano R, Hier M
and Zeitouni AG: Systemic inflammatory markers as independent
prognosticators of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head
Neck. 37:103–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grivennikov SI and Karin M: Inflammation
and oncogenesis: A vicious connection. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
20:65–71. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Templeton AJ, McNamara MG, Šeruga B,
Vera-Badillo FE, Aneja P, Ocaña A, Leibowitz-Amit R, Sonpavde G,
Knox JJ, Tran B, et al: Prognostic role of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio in solid tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 106:dju1242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Arrieta O, Michel Ortega RM,
Villanueva-Rodríguez G, Serna-Thomé MG, Flores-Estrada D,
Diaz-Romero C, Rodríguez CM, Martínez L and Sánchez-Lara K:
Association of nutritional status and serum albumin levels with
development of toxicity in patients with advanced non-small cell
lung cancer treated with paclitaxel-cisplatin chemotherapy: A
prospective study. BMC cancer. 10:502010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Asher V, Lee J and Bali A: Preoperative
serum albumin is an independent prognostic predictor of survival in
ovarian cancer. Med Oncol. 29:2005–2009. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kristal AR, Schenk JM, Song Y, Arnold KB,
Neuhouser ML, Goodman PJ, Lin DW, Stanczyk FZ and Thompson IM:
Serum steroid and sex hormone-binding globulin concentrations and
the risk of incident benign prostatic hyperplasia: Results from the
prostate cancer prevention trial. Am J Epidemiol. 168:1416–1424.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen ZY, Raghav K, Lieu CH, Jiang ZQ, Eng
C, Vauthey JN, Chang GJ, Qiao W, Morris J, Hong D, et al: Cytokine
profile and prognostic significance of high neutrophil-lymphocyte
ratio in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 112:1088–1097. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Wang S, Shang P,
Gao Y and Chen X: Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio before
platelet-lymphocyte ratio predicts clinical outcome in patients
with cervical cancer treated with initial radical surgery. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 24:1319–1325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|