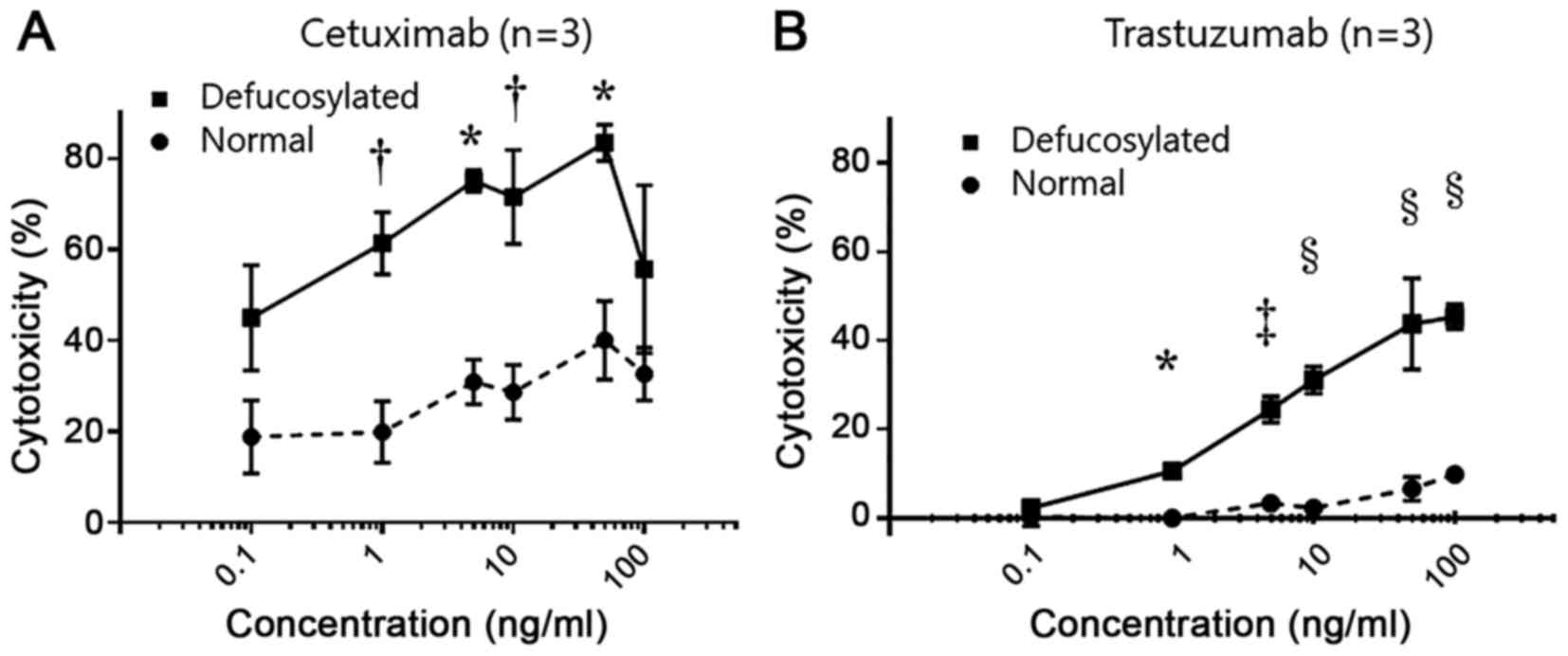
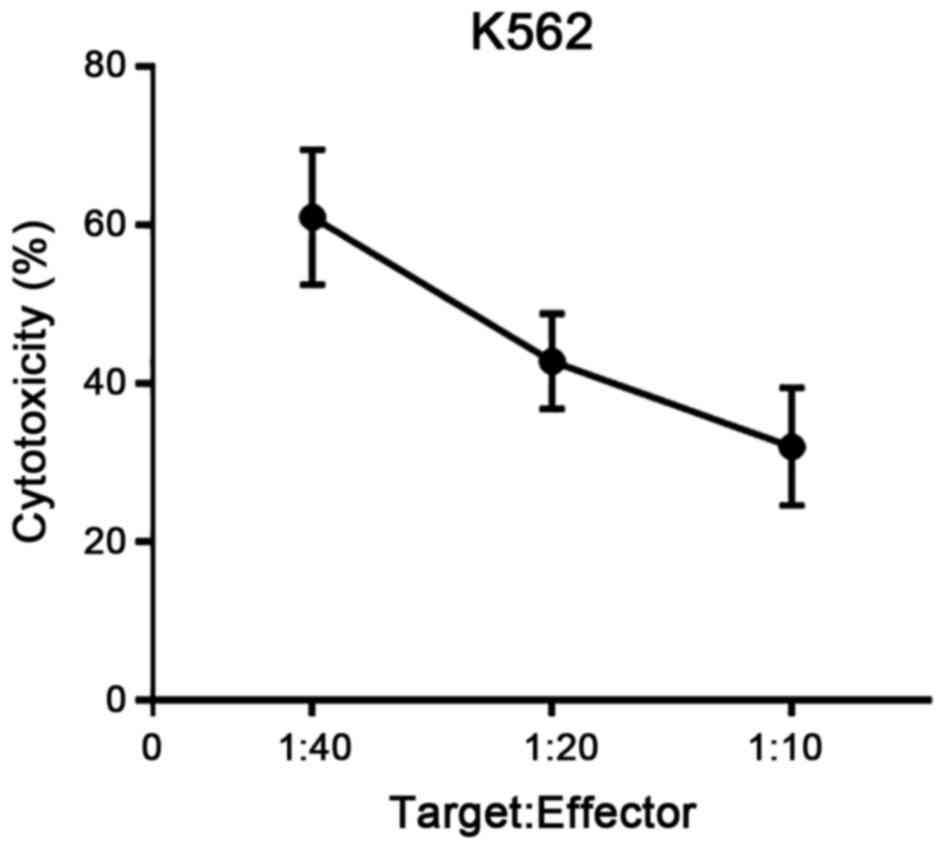
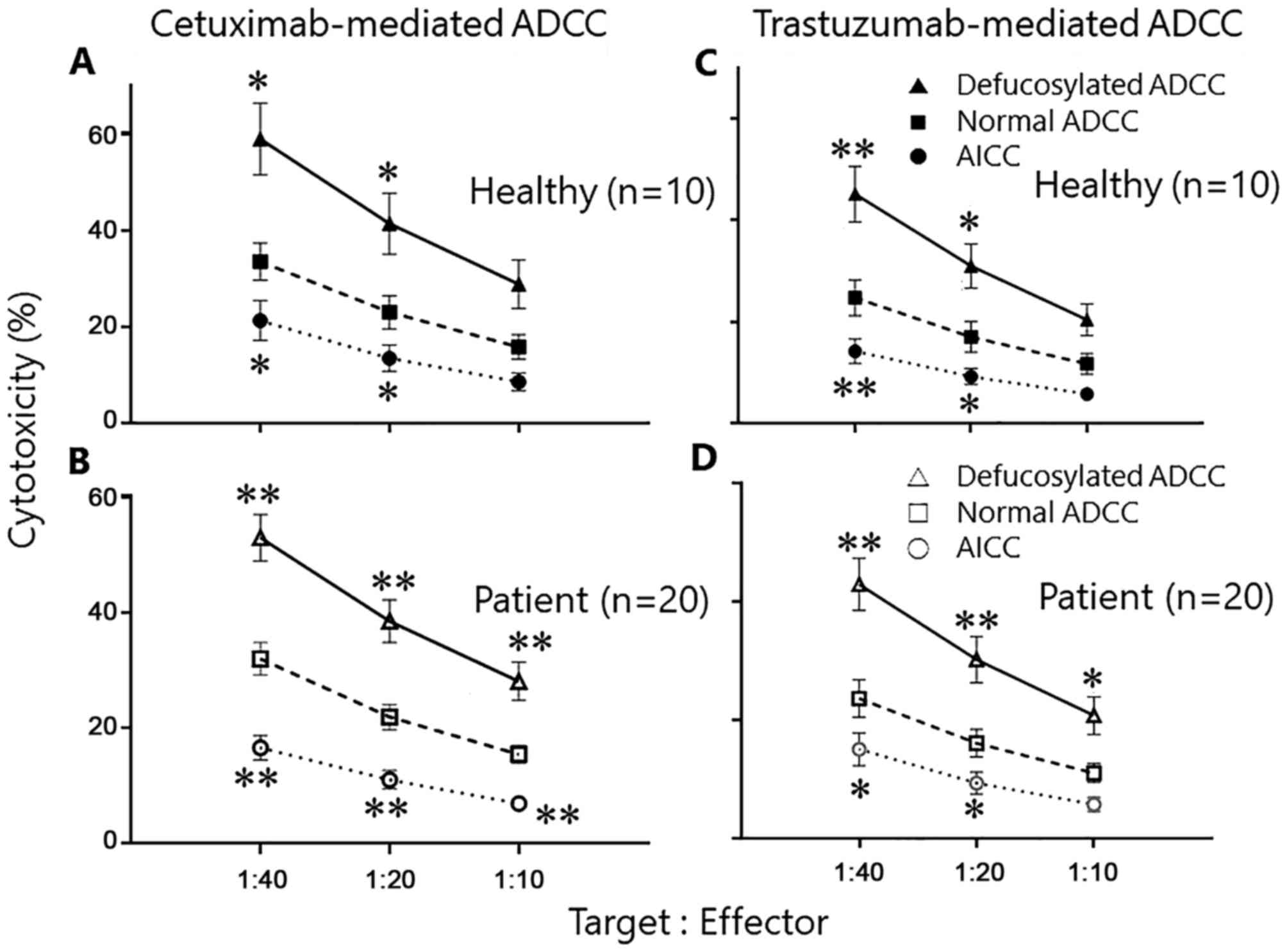
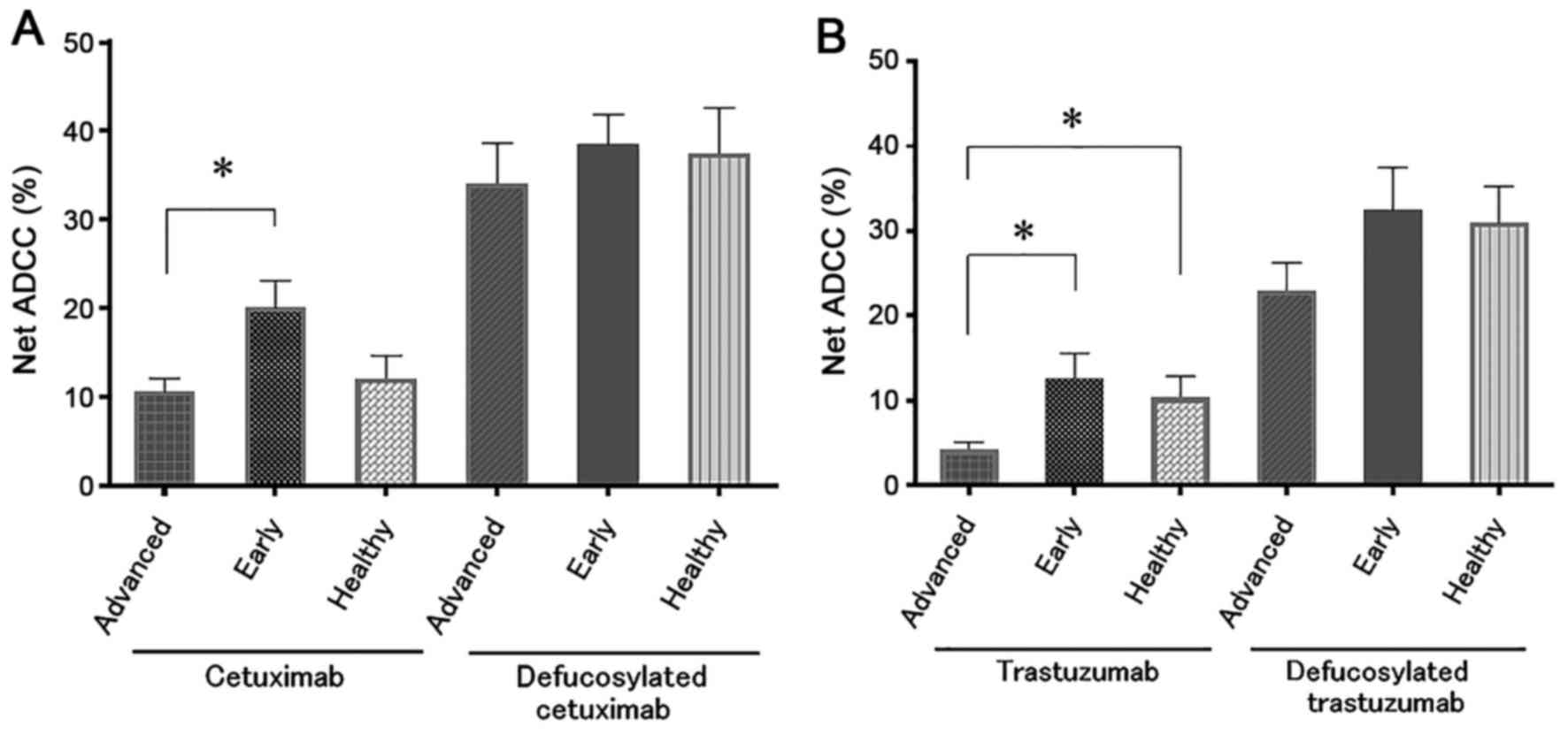
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric
or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li K and Li J: Current molecular targeted
therapy in advanced gastric cancer: A comprehensive review of
therapeutic mechanism, clinical trials, and practical application.
Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016:41056152016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arienti C, Zanoni M, Pignatta S, Del Rio
A, Carloni S, Tebaldi M, Tedaldi G and Tesei A: Preclinical
evidence of multiple mechanisms underlying trastuzumab resistance
in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:18424–18439. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Koene HR, Kleijer M, Algra J, Roos D, von
dem Borne AE and de Haas M: Fc gammaRIIIa-158V/F polymorphism
influences the binding of IgG by natural killer cell Fc gammaRIIIa,
independently of the Fc gammaRIIIa-48L/R/H phenotype. Blood.
90:1109–1114. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shields RL, Namenuk AK, Hong K, Meng YG,
Rae J, Briggs J, Xie D, Lai J, Stadlen A, Li B, et al: High
resolution mapping of the binding site on human IgG1 for Fc gamma
RI Fc gamma RII Fc gamma RIII, and FcRn and design of IgG1 variants
with improved binding to the Fc gamma R. J Biol Chem.
276:6591–6604. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Warmerdam PA, van de Winkel JG, Vlug A,
Westerdaal NA and Capel PJ: A single amino acid in the second
Ig-like domain of the human Fc gamma receptor II is critical for
human IgG2 binding. J Immunol. 147:1338–1343. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Watanabe M, Kono K, Kawaguchi Y, Mizukami
Y, Mimura K, Maruyama T, Izawa S and Fujii H: NK cell dysfunction
with down-regulated CD16 and up-regulated CD56 molecules in
patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus.
23:675–681. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Musolino A, Naldi N, Bortesi B, Pezzuolo
D, Capelletti M, Missale G, Laccabue D, Zerbini A, Camisa R,
Bisagni G, et al: Immunoglobulin G fragment C receptor
polymorphisms and clinical efficacy of trastuzumab-based therapy in
patients with HER-2/neu-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:1789–1796. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wormald S, Milla L and O'Connor L:
Association of candidate single nucleotide polymorphisms with
somatic mutation of the epidermal growth factor receptor pathway.
BMC Med Genomics. 6:432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shields RL, Lai J, Keck R, O'Connell LY,
Hong K, Meng YG, Weikert SH and Presta LG: Lack of fucose on human
IgG1 N-linked oligosaccharide improves binding to human Fcgamma
RIII and antibody-dependent cellular toxicity. J Biol Chem.
277:26733–26740. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shinkawa T, Nakamura K, Yamane N,
Shoji-Hosaka E, Kanda Y, Sakukrada M, Uchida K, Anazawa H, Satoh M,
Yamasaki M, et al: The absence of fucose but not the presence of
galactose or bisecting N-acetylglucosamine of human IgG1
complex-type oligosaccharides shows the critical role of enhancing
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem.
278:3466–3473. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Niwa R, Shoji-Hosaka E, Sakurada M,
Shinkawa T, Uchida K, Nakamura K, Matsushima K, Ueda R, Hanai N and
Shitara K: Defucosylated chimeric anti-CC chemokine receptor 4 IgG1
with enhanced antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity shows potent
therapeutic activity to T-cell leukemia and lymphoma. Cancer Res.
64:2127–2133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Okazaki A, Shoji-Hosaka E, Nakamura K,
Wakitani M, Uchida K, Kakita S, Tsumoto K, Kumagai I and Shitara K:
Fucose depletion from human IgG1 oligosaccharide enhances binding
enthalpy and association rate between IgG1 and FcgammaRIIIa. J Mol
Biol. 336:1239–1249. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Niwa R, Hatanaka S, Shoji-Hosaka E,
Sakurada M, Kobayashi Y, Uehara A, Yokoi H, Nakamura K and Shitara
K: Enhancement of the antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity of
low-fucose IgG1 Is independent of FcgammaRIIIa functional
polymorphism. Clin Cancer Res. 10:6248–6255. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suzuki E, Niwa R, Saji S, Muta M, Hirose
M, Iida S, Shiotsu Y, Satoh M, Shitara K, Kondo M and Toi M: A
nonfucosylated anti-HER2 antibody augments antibody-dependent
cellular cytotoxicity in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
13:1875–1882. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Capes-Davis A, Theodosopoulos G, Atkin I,
Drexler HG, Kohara A, MacLeod RA, Masters JR, Nakamura Y, Reid YA,
Reddel RR and Freshney RI: Check your cultures! A list of
cross-contaminated or misidentified cell lines. Int J Cancer.
127:1–8. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shiraishi K, Mimura K, Izawa S, Inoue A,
Shiba S, Maruyama T, Watanabe M, Kawaguchi Y, Inoue M, Fujii H and
Kono K: Lapatinib acts on gastric cancer through both
antiproliferative function and augmentation of trastuzumab-mediated
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Gastric Cancer.
16:571–580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Carter P, Presta L, Gorman CM, Ridgway JB,
Henner D, Wong WL, Rowland AM, Kotts C, Carverr ME and Shepard HM:
Humanization of an anti-p185HER2 antibody for human cancer therapy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:pp. 4285–4289. 1992; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
DrugBANK. https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00002
|
|
21
|
Yamane-Ohnuki N, KInoshita S,
Inoue-Urakubo M, Kusunoki M, Iida S, Nakano R, Wakitani M, Niwa R,
Sakurada M, Uchida K, et al: Establishment of FUT8 knockout Chinese
hamster ovary cells: An ideal host cell line for producing
completely defucosylated antibodies with enhanced
antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Biotechnol Bioeng.
87:614–622. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mimura K, Kamiya T, Shiraishi K, Kua LF,
Shabbir A, So J, Yong WP, Suzuki Y, Yoshimoto Y, Nakano T, et al:
Therapeutic potential of highly cytotoxic natural killer cells for
gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 135:1390–1398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kono K, Takahashi A, Ichihara F, Sugai H,
Fujii H and Matsumoto Y: Impaired antibody-dependent cellular
cytotoxicity mediated by herceptin in patients with gastric cancer.
Cancer Res. 62:5813–5817. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mimura K, Kono K, Hanawa M, Kanzaki M,
Nakao A, Ooi A and Fujii H: Trastuzumab-mediated antibody-dependent
cellular cytotoxicity against esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:4898–4904. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moretta L, Locatelli F, Pende D, Marcenaro
E, Mingari MC and Moretta A: Killer Ig-like receptor-mediated
control of natural killer cell alloreactivity in haploidentical
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 117:764–771. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bae DS, Hwang YK and Lee JK: Importance of
NKG2D-NKG2D ligands interaction for cytolytic activity of natural
killer cell. Cell Immunol. 276:122–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Okita R, Mougiakakos D, Ando T, Mao Y,
Sarhan D, Wennerberg E, Seliger B, Lundqvist A, Mimura K and
Kiessling R: HER2/HER3 signaling regulates NK cell-mediated
cytotoxicity via MHC class I chain-related molecule A and B
expression in human breast cancer cell lines. J Immunol.
188:2136–2145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Watanabe Y, Asano R, Arai K, Shimomura I,
Ogata H, Kawaguchi H, Hayashi H, Ohtsuka H, Yoshida H, Katayose Y,
et al: In vitro and in vivo antitumor effects of recombinant
bispecific antibodies based on humanized anti-EGFR antibody. Oncol
Rep. 26:949–955. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baselga J, Carbonell X, Castañeda-Soto NJ,
Clemens M, Green M, Harvey V, Morales S, Barton C and Ghahramani P:
Phase II study of efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of
trastuzumab monotherapy administered on a 3-weekly schedule. J Clin
Oncol. 23:2162–2171. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hudis CA: Trastuzumab-mechanism of action
and use in clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 357:39–51. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs
H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, Fleming T, Eiermann W, Wolter J, Pegram M,
et al: Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2
for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med.
344:783–792. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kawaguchi Y, Kono K, Mimura K, Mitsui F,
Sugai H, Akaike H and Fujii H: Targeting EGFR and HER-2 with
cetuximab- and trastuzumab-mediated immunotherapy in oesophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 97:494–501. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kawaguchi Y, Kono K, Mimura K, Sugai H,
Akaike H and Fujii H: Cetuximab induce antibody-dependent cellular
cytotoxicity against EGFR-expressing esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 120:781–787. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Omori S, Hida M, Fujita H, Takahashi H,
Tanimura S, Kohno M and Awazu M: Extracellular signal-regulated
kinase inhibition slows disease progression in mice with polycystic
kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 17:1604–1614. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fujiwara Y, Hosokawa Y, Watanabe K,
Tanimura S, Ozaki K and Kohno M: Blockade of the
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase-Akt signaling pathway enhances the
induction of apoptosis by microtubule-destabilizing agents in tumor
cells in which the pathway is constitutively activated. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:1133–1142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|