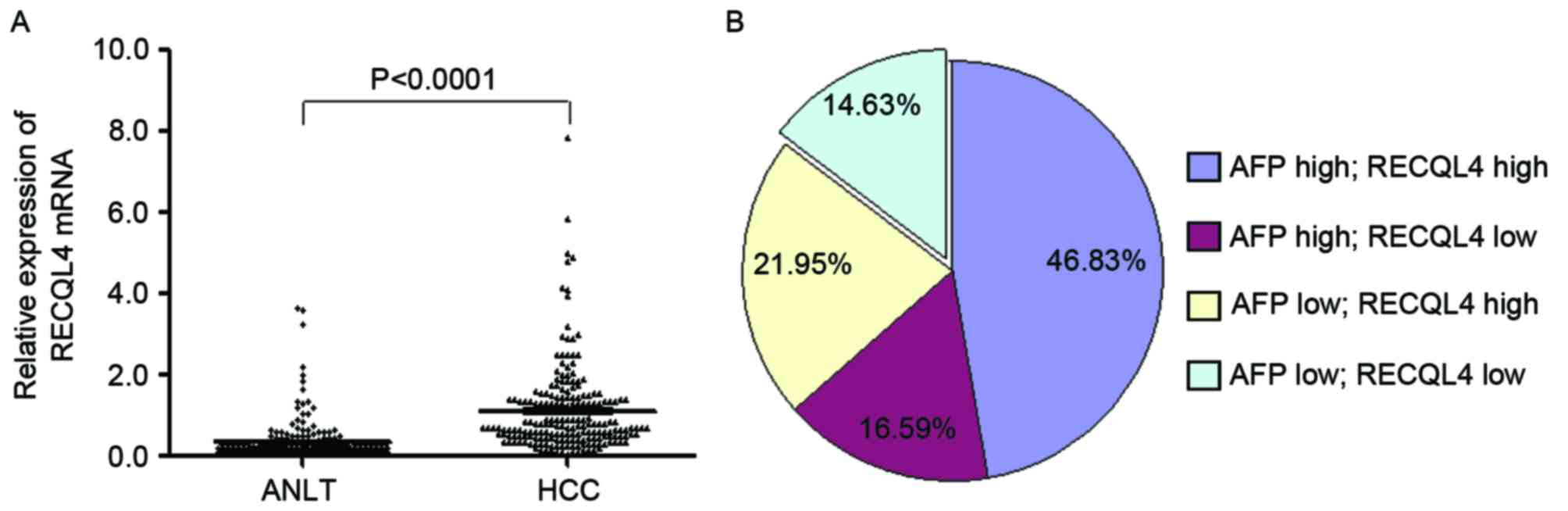
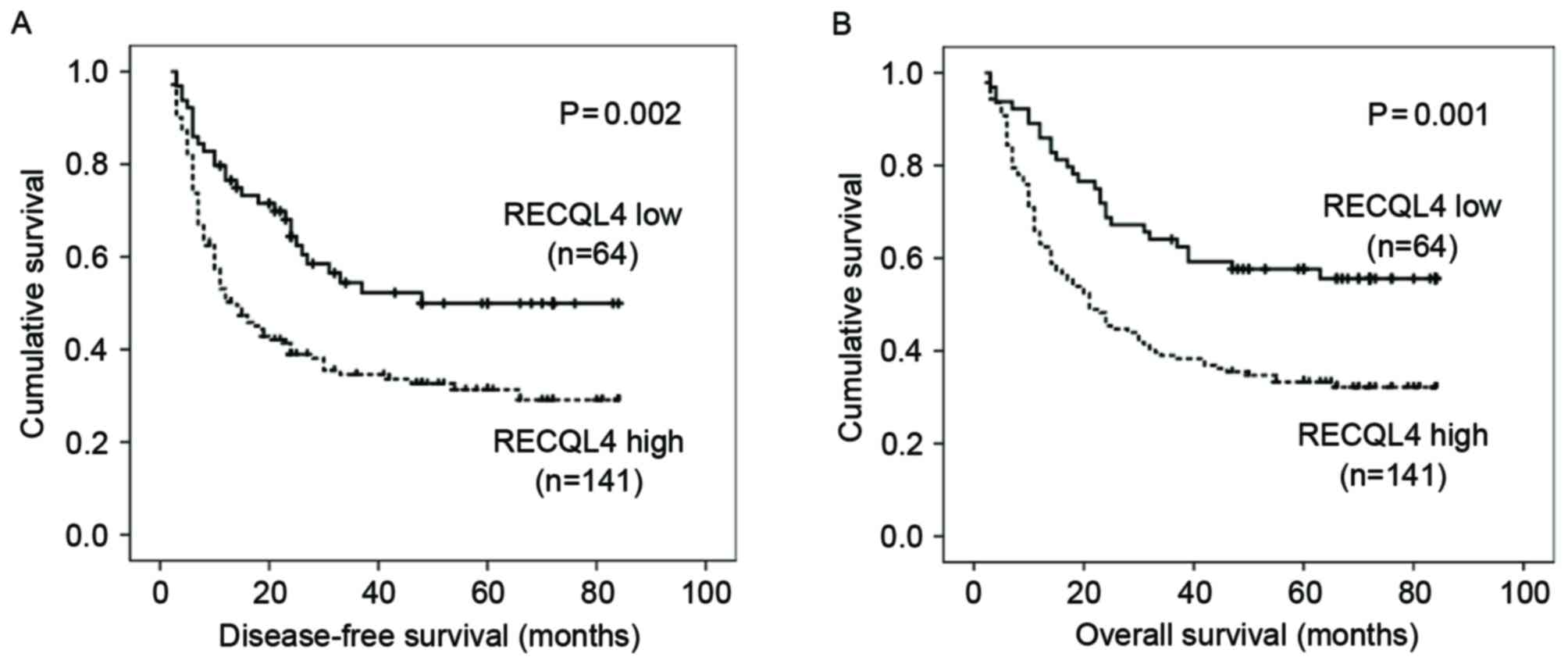
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID, Fritz AG,
Balch CM, Haller DG and Morrow M: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 6th.
Springer; Chicago, IL: 2002, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
A new prognostic system for hepatocellular
carcinoma: A retrospective study of 435 patients: The Cancer of the
Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology. 28:751–755.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Llovet JM, Brú C and Bruix J: Prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: The BCLC staging classification. Semin
Liver Dis. 19:329–338. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liao W, Liu W, Yuan Q, Liu X, Ou Y, He S,
Yuan S, Qin L, Chen Q, Nong K, et al: Silencing of DLGAP5 by siRNA
significantly inhibits the proliferation and invasion of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 8:e807892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liao W, Liu W, Liu X, Yuan Q, Ou Y, Qi Y,
Huang W, Wang Y and Huang J: Upregulation of FAM83D affects the
proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:24132–24147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Croteau DL, Singh DK, Hoh Ferrarelli L, Lu
H and Bohr VA: RECQL4 in genomic instability and aging. Trends
Genet. 28:624–631. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Petkovic M, Dietschy T, Freire R, Jiao R
and Stagljar I: The human Rothmund-Thomson syndrome gene product,
RECQL4, localizes to distinct nuclear foci that coincide with
proteins involved in the maintenance of genome stability. J Cell
Sci. 118:4261–4269. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kitao S, Shimamoto A, Goto M, Miller RW,
Smithson WA, Lindor NM and Furuichi Y: Mutations in RECQL4 cause a
subset of cases of Rothmund-Thomson syndrome. Nat Genet. 22:82–84.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Siitonen HA, Kopra O, Kääriäinen H,
Haravuori H, Winter RM, Säämänen AM, Peltonen L and Kestilä M:
Molecular defect of RAPADILINO syndrome expands the phenotype
spectrum of RECQL diseases. Hum Mol Genet. 12:2837–2844. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Van Maldergem L, Siitonen HA, Jalkh N,
Chouery E, De Roy M, Delague V, Muenke M, Jabs EW, Cai J, Wang LL,
et al: Revisiting sis-radial ray hypoplasia association:
Baller-Gerold syndrome caused by mutations in the RECQL4 gene. J
Med Genet. 43:148–152. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sangrithi MN, Bernal JA, Madine M,
Philpott A, Lee J, Dunphy WG and Venkitaraman AR: Initiation of DNA
replication requires the RECQL4 protein mutated in Rothmund-Thomson
syndrome. Cell. 121:887–898. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu X and Liu Y: Dual DNA unwinding
activities of the Rothmund-Thomson syndrome protein, RECQ4. EMBO J.
28:568–577. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Collart C, Allen GE, Bradshaw CR, Smith JC
and Zegerman P: Titration of four replication factors is essential
for the Xenopus laevis midblastula transition. Science.
341:893–896. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fan W and Luo J: RecQ4 facilitates UV
light-induced DNA damage repair through interaction with nucleotide
excision repair factor xeroderma pigmentosum group A (XPA). J Biol
Chem. 283:29037–29044. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schurman SH, Hedayati M, Wang Z, Singh DK,
Speina E, Zhang Y, Becker K, Macris M, Sung P, Wilson DM III, et
al: Direct and indirect roles of RECQL4 in modulating base excision
repair capacity. Hum Mol Genet. 18:3470–3483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Singh DK, Karmakar P, Aamann M, Schurman
SH, May A, Croteau DL, Burks L, Plon SE and Bohr VA: The
involvement of human RECQL4 in DNA double-strand break repair.
Aging Cell. 9:358–371. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Maire G, Yoshimoto M, Chilton-MacNeill S,
Thorner PS, Zielenska M and Squire JA: Recurrent RECQL4 imbalance
and increased gene expression levels are associated with structural
chromosomal instability in sporadic osteosarcoma. Neoplasia.
11:260–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Su Y, Meador JA, Calaf GM, Proietti
De-Santis L, Zhao Y, Bohr VA and Balajee AS: Human RecQL4 helicase
plays critical roles in prostate carcinogenesis. Cancer Res.
70:9207–9217. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang H, Nie L, Chi Z, Liu J, Guo D, Lu X,
Hei TK, Balajee AS and Zhao Y: RecQL4 helicase amplification is
involved in human breast tumorigenesis. PLoS One. 8:e696002013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zegerman P and Diffley JF: Phosphorylation
of Sld2 and Sld3 by cyclin-dependent kinases promotes DNA
replication in budding yeast. Nature. 445:281–285. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu X, Rochette PJ, Feyissa EA, Su TV and
Liu Y: MCM10 mediates RECQ4 association with MCM2-7 helicase
complex during DNA replication. EMBO J. 28:3005–3014. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bruix J and Sherman M; American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, : Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ng KK, Vauthey JN, Pawlik TM, Lauwers GY,
Regimbeau JM, Belghiti J, Ikai I, Yamaoka Y, Curley SA, Nagorney
DM, et al: Is hepatic resection for large or multinodular
hepatocellular carcinoma justified? Results from a
multi-institutional database. Ann Surg Oncol. 12:364–373. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kow AW, Kwon CH, Song S, Shin M, Kim JM
and Joh JW: Risk factors of peritoneal recurrence and outcome of
resected peritoneal recurrence after liver resection in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Review of 1222 cases of hepatectomy in a
tertiary institution. Ann Surg Oncol. 19:2246–2255. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ishizawa T, Hasegawa K, Aoki T, Takahashi
M, Inoue Y, Sano K, Imamura H, Sugawara Y, Kokudo N and Makuuchi M:
Neither multiple tumors nor portal hypertension are surgical
contraindications for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
134:1908–1916. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Giannini EG, Farinati F, Ciccarese F,
Pecorelli A, Rapaccini GL, Di Marco M, Benvegnù L, Caturelli E,
Zoli M, Borzio F, et al: Prognosis of untreated hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 61:184–190. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu PH, Hsu CY, Hsia CY, Lee YH, Su CW,
Huang YH, Lee FY, Lin HC and Huo TI: Prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma: Assessment of eleven staging systems. J Hepatol.
64:601–608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gomaa AI, Hashim MS and Waked I: Comparing
staging systems for predicting prognosis and survival in patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma in Egypt. PLoS One. 9:e909292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|