Spandidos Publications style
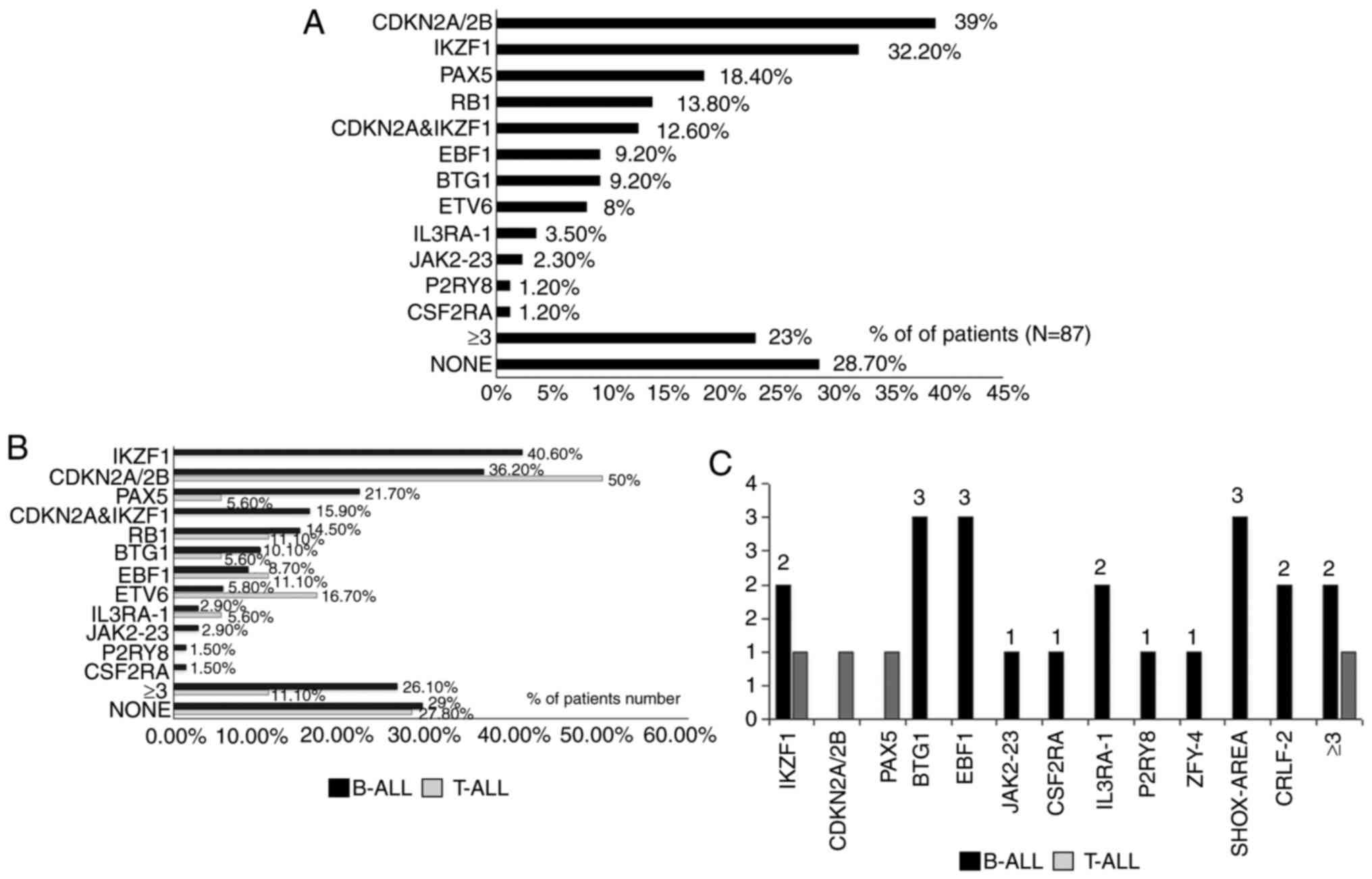
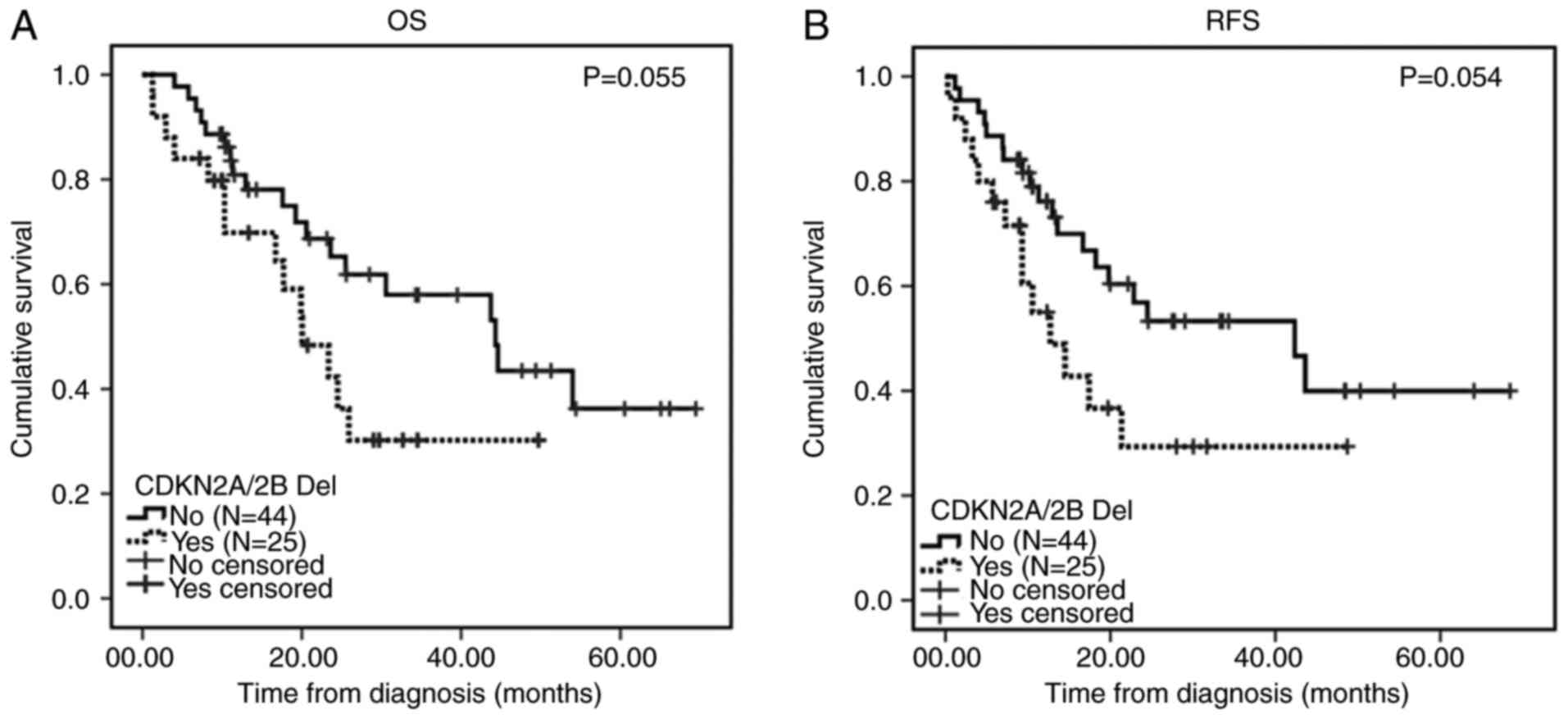
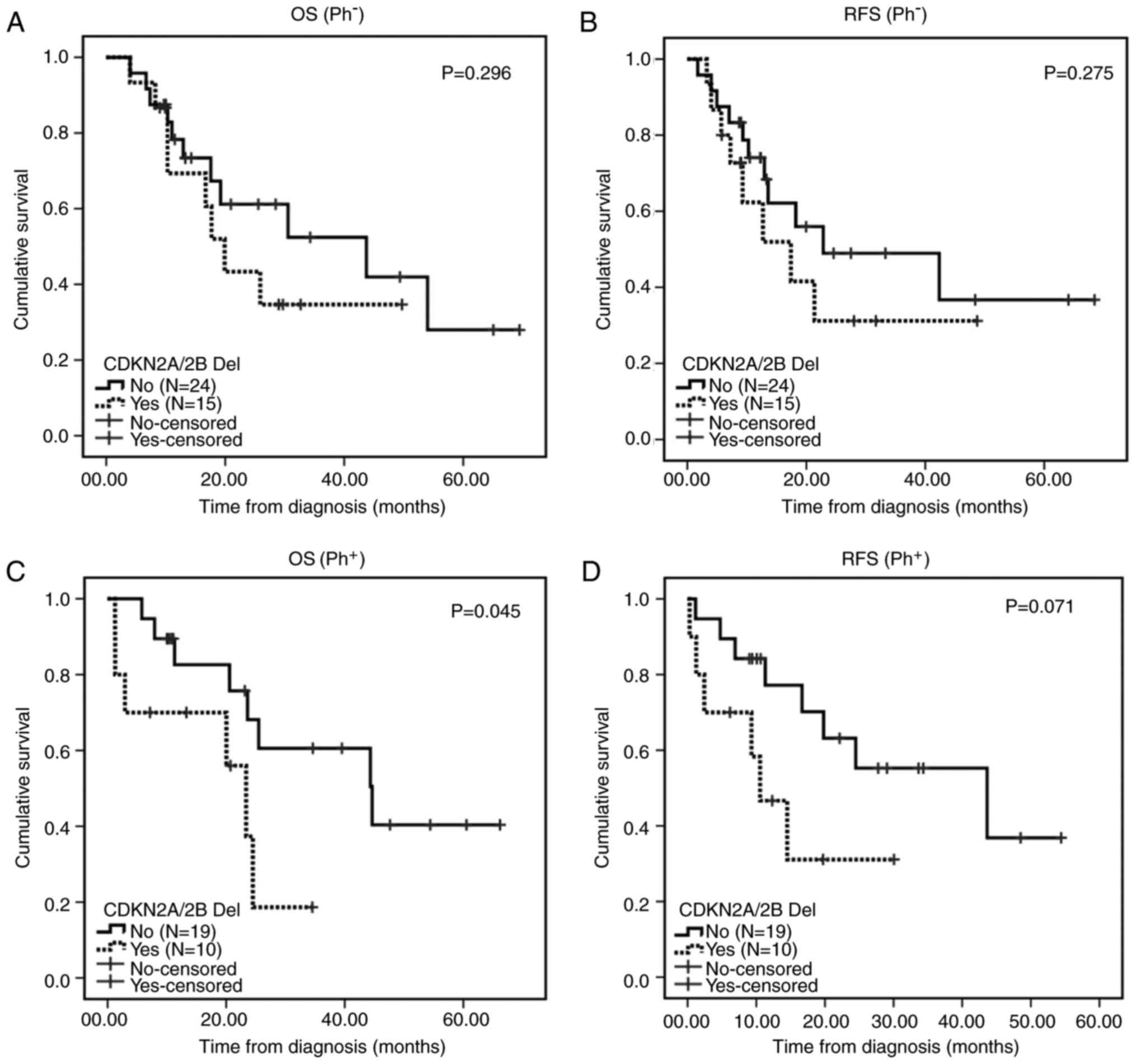
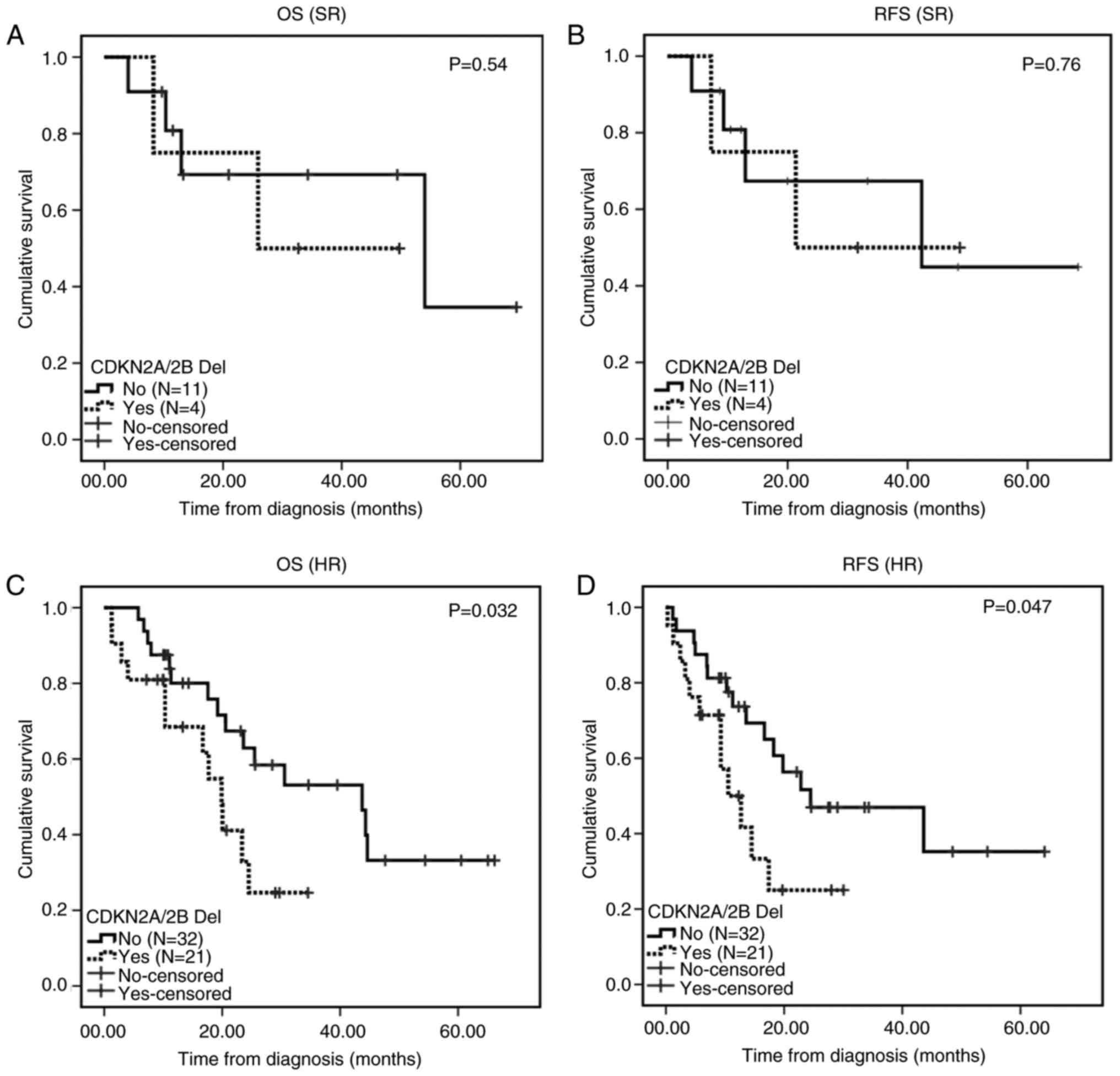
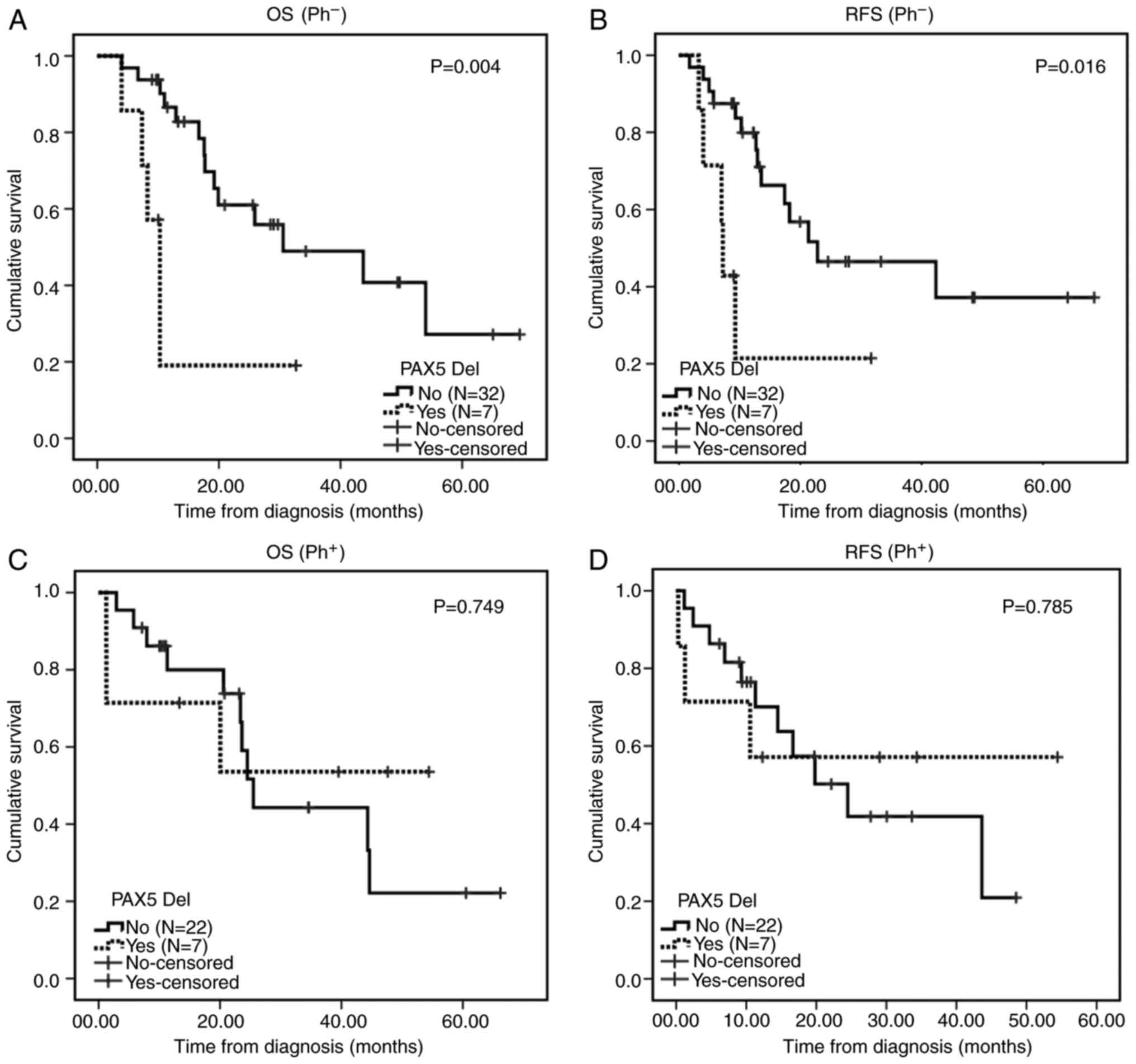
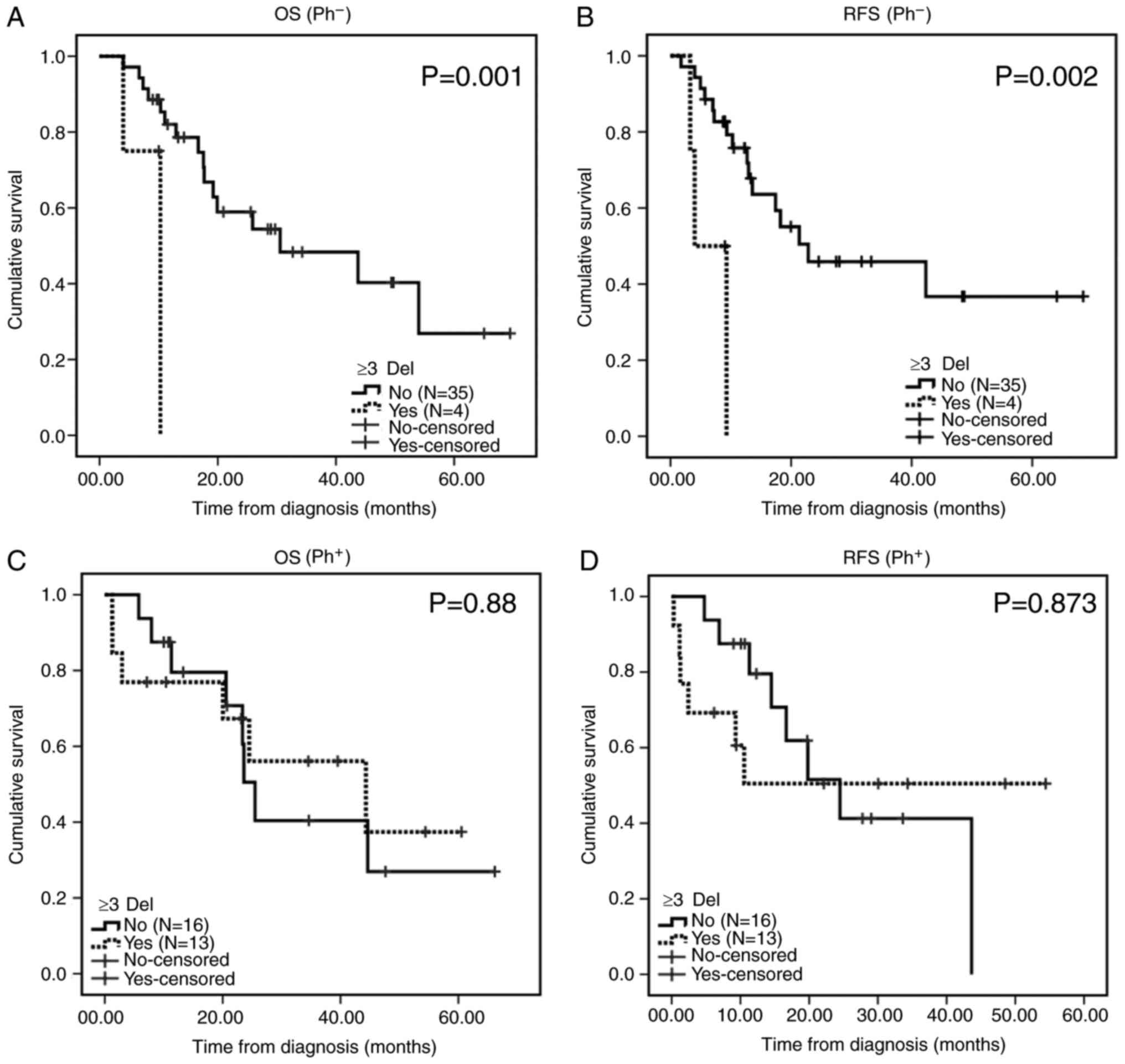
Fang Q, Yuan T, Li Y, Feng J, Gong X, Li Q, Zhao X, Liu K, Tang K, Tian Z, Tian Z, et al: Prognostic significance of copy number alterations detected by multi‑link probe amplification of multiple genes in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncol Lett 15: 5359-5367, 2018.
APA
Fang, Q., Yuan, T., Li, Y., Feng, J., Gong, X., Li, Q. ... Mi, Y. (2018). Prognostic significance of copy number alterations detected by multi‑link probe amplification of multiple genes in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Oncology Letters, 15, 5359-5367. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.7985
MLA
Fang, Q., Yuan, T., Li, Y., Feng, J., Gong, X., Li, Q., Zhao, X., Liu, K., Tang, K., Tian, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Liu, B., Wang, M., Ru, K., Wang, J., Mi, Y."Prognostic significance of copy number alterations detected by multi‑link probe amplification of multiple genes in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia". Oncology Letters 15.4 (2018): 5359-5367.
Chicago
Fang, Q., Yuan, T., Li, Y., Feng, J., Gong, X., Li, Q., Zhao, X., Liu, K., Tang, K., Tian, Z., Zhang, Q., Wang, Y., Liu, B., Wang, M., Ru, K., Wang, J., Mi, Y."Prognostic significance of copy number alterations detected by multi‑link probe amplification of multiple genes in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia". Oncology Letters 15, no. 4 (2018): 5359-5367. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.7985