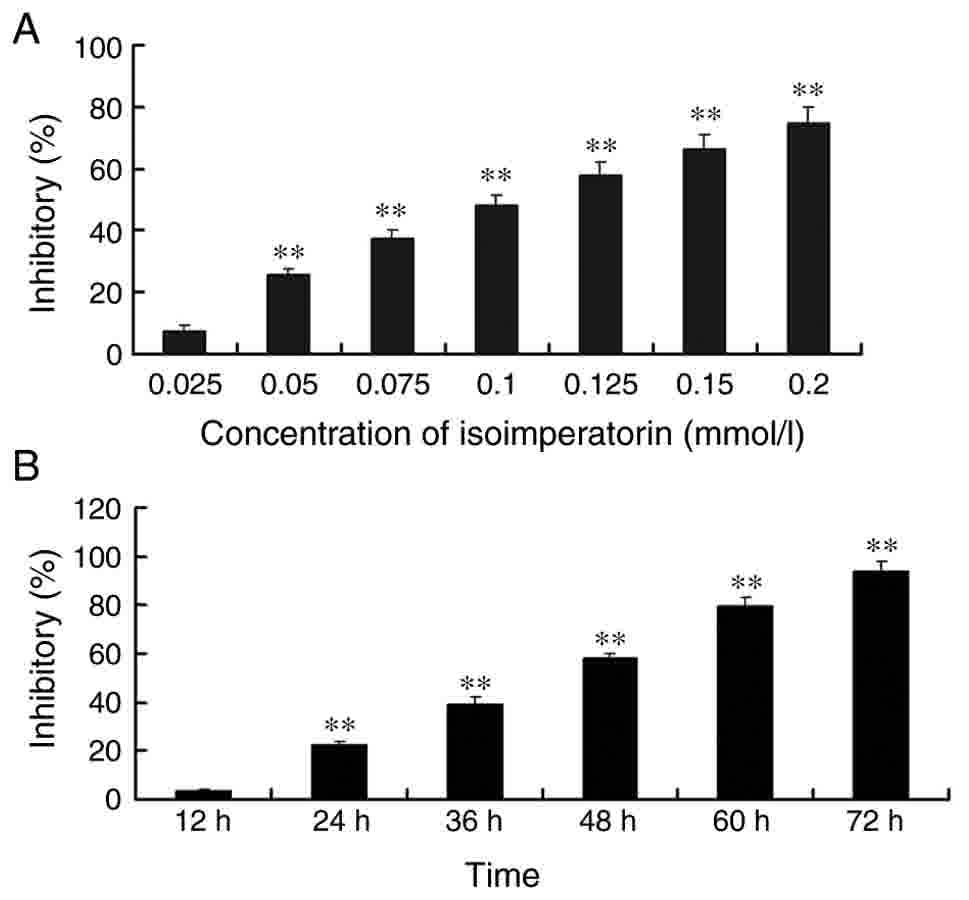
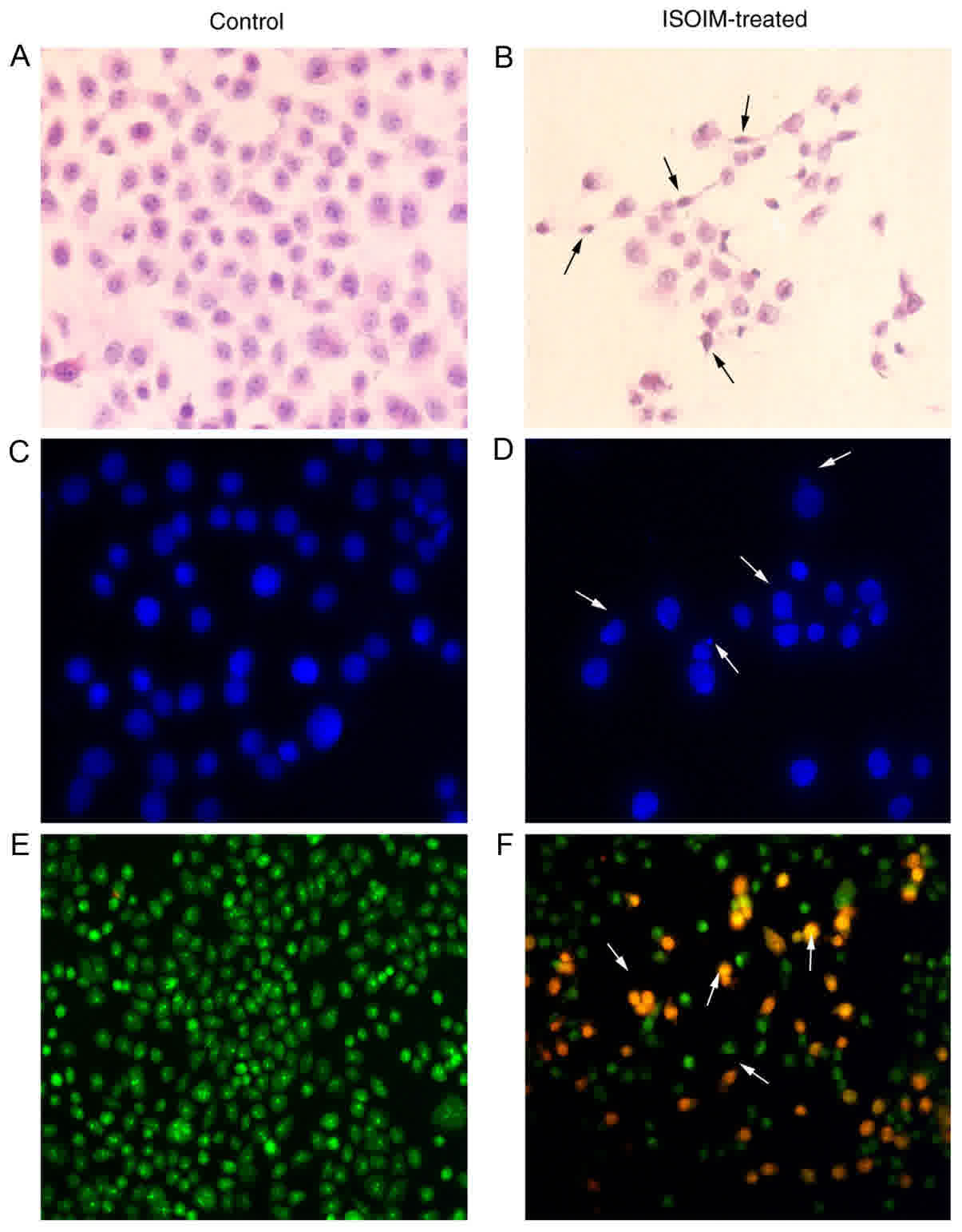
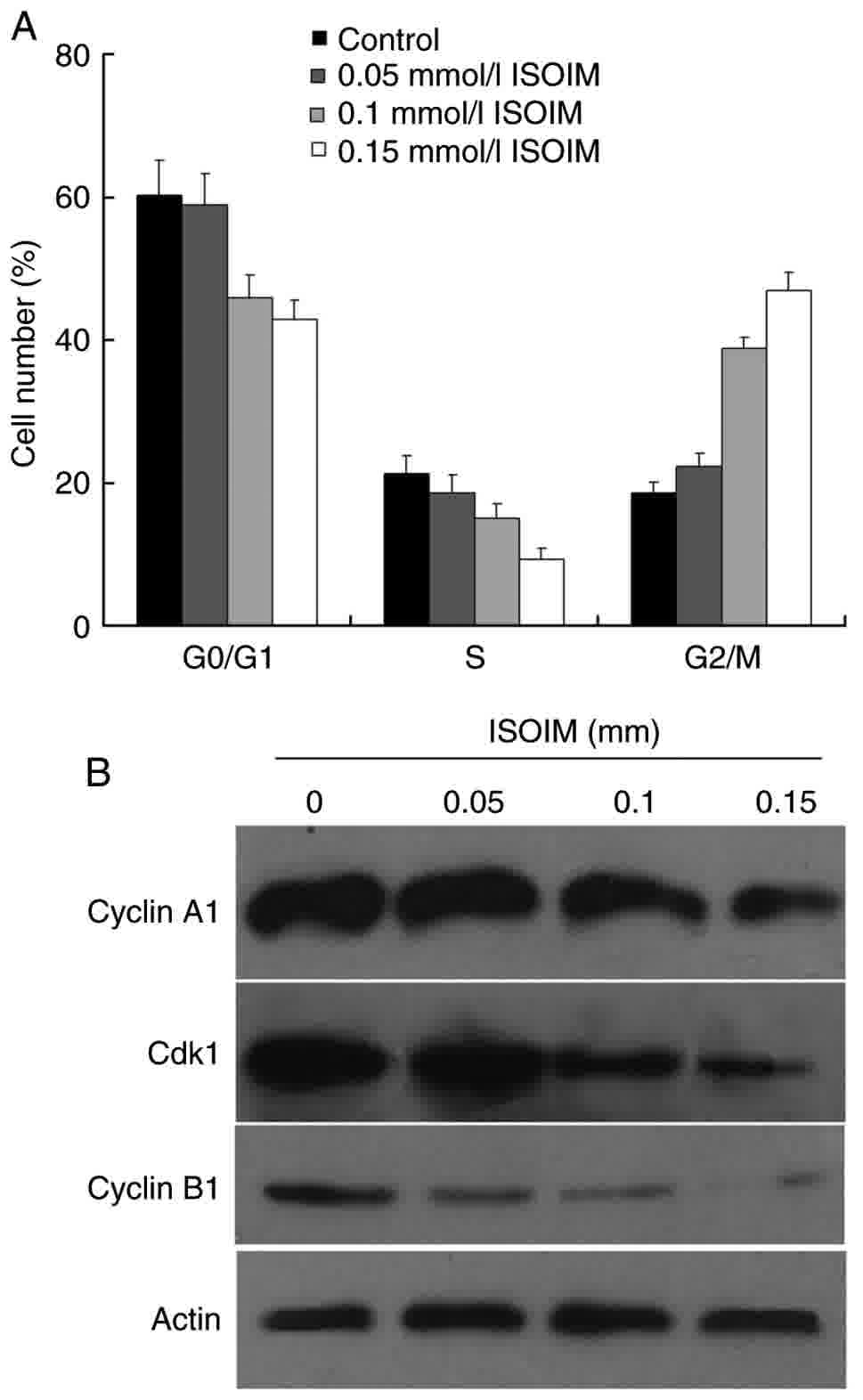
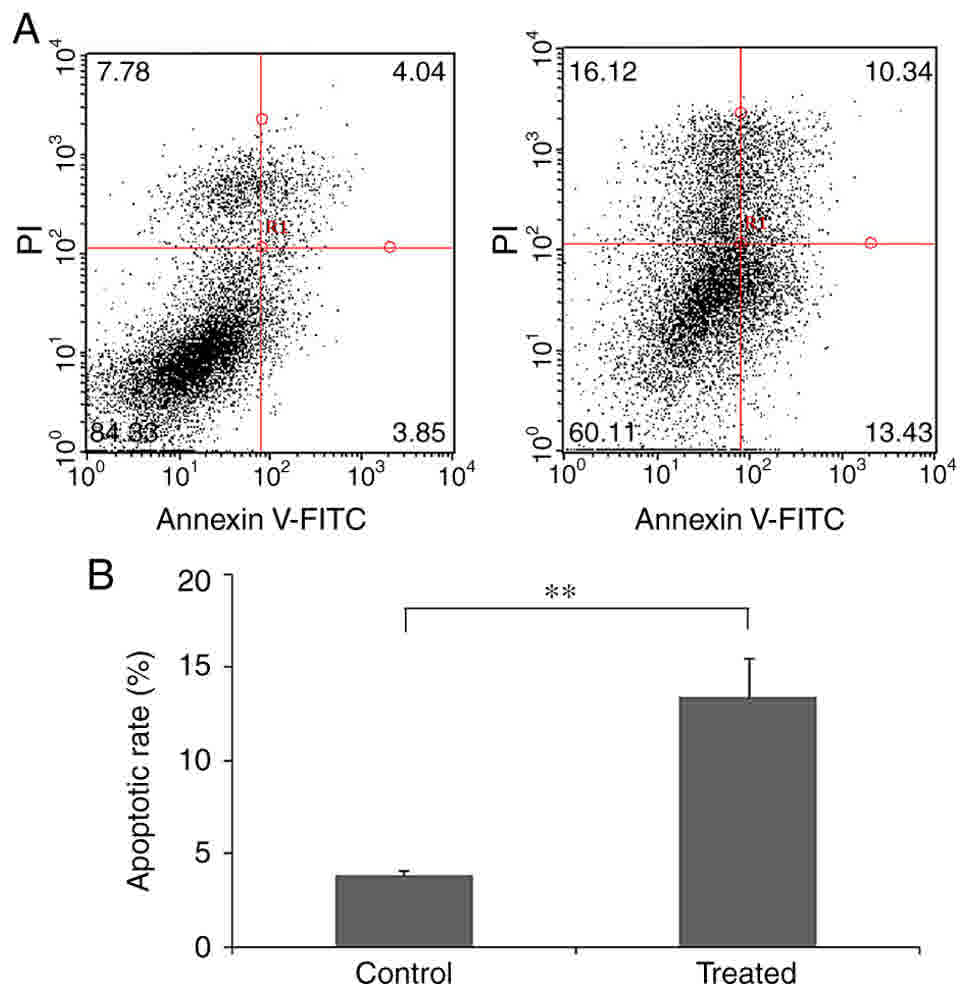
|
1
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jin Z and El-Deiry WS: Overview of cell
death signaling pathways. Cancer Biol Ther. 4:139–163. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei Y and Ito Y: Preparative isolation of
imperatorin, oxypeucedanin and isoimperatorin from traditional
Chinese herb ‘bai zhi’ Angelica dahurica (Fisch. ex Hoffm)
Benth. et Hook using multidimensional high-speed counter-current
chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 1115:112–117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kim YK, Kim YS and Ryu SY:
Antiproliferative effect of furanocoumarins from the root of
Angelica dahurica on cultured human tumor cell lines.
Phytother Res. 21:288–290. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moon TC, Jin M, Son JK and Chang HW: The
effects of isoimperatorin isolated from Angelicae dahuricae
on cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase in mouse bone marrow-derived
mast cells. Arch Pharm Res. 31:210–215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim DK, Lim JP, Yang JH, Eom DO, Eun JS
and Leem KH: Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the roots of
Angelica dahurica. Arch Pharm Res. 25:856–859. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park HY, Kwon SB, Heo NK, Chun WJ, Kim MJ
and Kwon YS: Constituents of the stem of Angelica gigas with
rat lens aldose reductase inhibitory activity. J Korean Society
Applied Biol Chem. 54:194–199. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Baek NI, Ahn EM, Kim HY and Park YD:
Furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica dahurica. Arch
Pharm Res. 23:467–470. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kleiner HE, Reed MJ and DiGiovanni J:
Naturally occurring coumarins inhibit human cytochromes P450 and
block benzo[a]pyrene and 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene DNA adduct
formation in MCF-7 cells. Chem Res Toxicol. 16:415–422. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tong K, Chang X and Chen W: Isoimperatorin
induces apoptosis of the SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cell line
via the mitochondria-mediated pathway. Oncol Lett. 13:518–524.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan S, Yuan L, Hong L, Jin L, Xiaohua S
and Wenchang Z: 2,5-Hexanedione induces human ovarian granulosa
cell apoptosis through Bcl-2, BAX, and CASPASE-3 signaling
pathways. Arch Toxicol. 86:205–215. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao X, Yang W, Shi C, Ma W, Liu J, Wang Y
and Jiang G: The G1 phase arrest and apoptosis by intrinsic pathway
induced by valproic acid inhibit proliferation of BGC-823 gastric
carcinoma cells. Tumour Biol. 32:335–346. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cohen GM: Caspases: The executioners of
apoptosis. Biochem J. 326:1–16. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reed JC: Cytochrome c: Can't live with
it-can't live without it. Cell. 91:559–562. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kroemer G and Reed JC: Mitochondrial
control of cell death. Nat Med. 6:513–519. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang JY, Della-Fera MA and Baile CA:
Esculetin induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Apoptosis. 11:1371–1378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Singh RK, Lange TS, Kim KK and Brard L: A
coumarin derivative (RKS262) inhibits cell-cycle progression,
causes pro-apoptotic signaling and cytotoxicity in ovarian cancer
cells. Invest New Drugs. 29:63–72. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: Arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Łazarenkow A, Nawrot-Modranka J,
Brzezińska E, Krajewska U and Różalski M: Synthesis, preliminary
cytotoxicity evaluation of new 3-formylchromone hydrazones and
phosphorohydrazone derivatives of coumarin and chromone. Med Chem
Res. 21:1861–1868. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Marumoto S and Miyazawa M: Beta-secretase
inhibitory effects of furanocoumarins from the root of Angelica
dahurica. Phytother Res. 24:510–513. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang SY and Kim YC: Neuroprotective
coumarins from the root of Angelica gigas:
Structure-activity relationships. Arch Pharm Res. 30:1368–1373.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okuyama T, Takata M, Nishino H, Nishino A,
Takayasu J and Iwashima A: Studies on the antitumor-promoting
activity of naturally occurring substances. II. Inhibition of
tumor-promoter-enhanced phospholipid metabolism by umbelliferous
materials. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 38:1084–1086. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kleiner HE, Vulimiri SV, Reed MJ,
Uberecken A and DiGiovanni J: Role of cytochrome P450 1a1 and 1b1
in the metabolic activation of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene and
the effects of naturally occurring furanocoumarins on skin tumor
initiation. Chem Res Toxicol. 15:226–235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang PY, Rui YC, Li K, Huang XH, Jiang JM
and Yu L: Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in U937
foam cells and inhibitory effect of imperatorin. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 23:327–330. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kleiner HE, Vulimiri SV, Miller L, Johnson
WH Jr, Whitman CP and DiGiovanni J: Oral administration of
naturally occurring coumarins leads to altered phase I and II
enzyme activities and reduced DNA adduct formation by polycyclic
aromatic hydrocarbons in various tissues of SENCAR mice.
Carcinogenesis. 22:73–82. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Green DR and Kroemer G: The
pathophysiology of mitochondrial cell death. Science. 305:626–629.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Q and Lesnefsky EJ: Blockade of
electron transport during ischemia preserves bcl-2 and inhibits
opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. FEBS
Lett. 585:921–926. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jurgensmeier JM, Xie Z, Deveraux Q,
Ellerby L, Bredesen D and Reed JC: Bax directly induces release of
cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:4997–5002. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Merino D and Bouillet P: The Bcl-2 family
in autoimmune and degenerative disorders. Apoptosis. 14:570–583.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhivotovsky B: Caspases: The enzymes of
death. Essays Biochem. 39:25–40. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA
Jr, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I and Flavell RA: Caspases 3 and 7:
Key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science.
311:847–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nobuhiro M, Keiko N, Hiromi T, Takehiko S
and Yukuto Y: An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific caspase
cascade in apoptosis. Cytochrome c-independent activation of
caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem. 277:34287–34294. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Porter AG and Janicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|