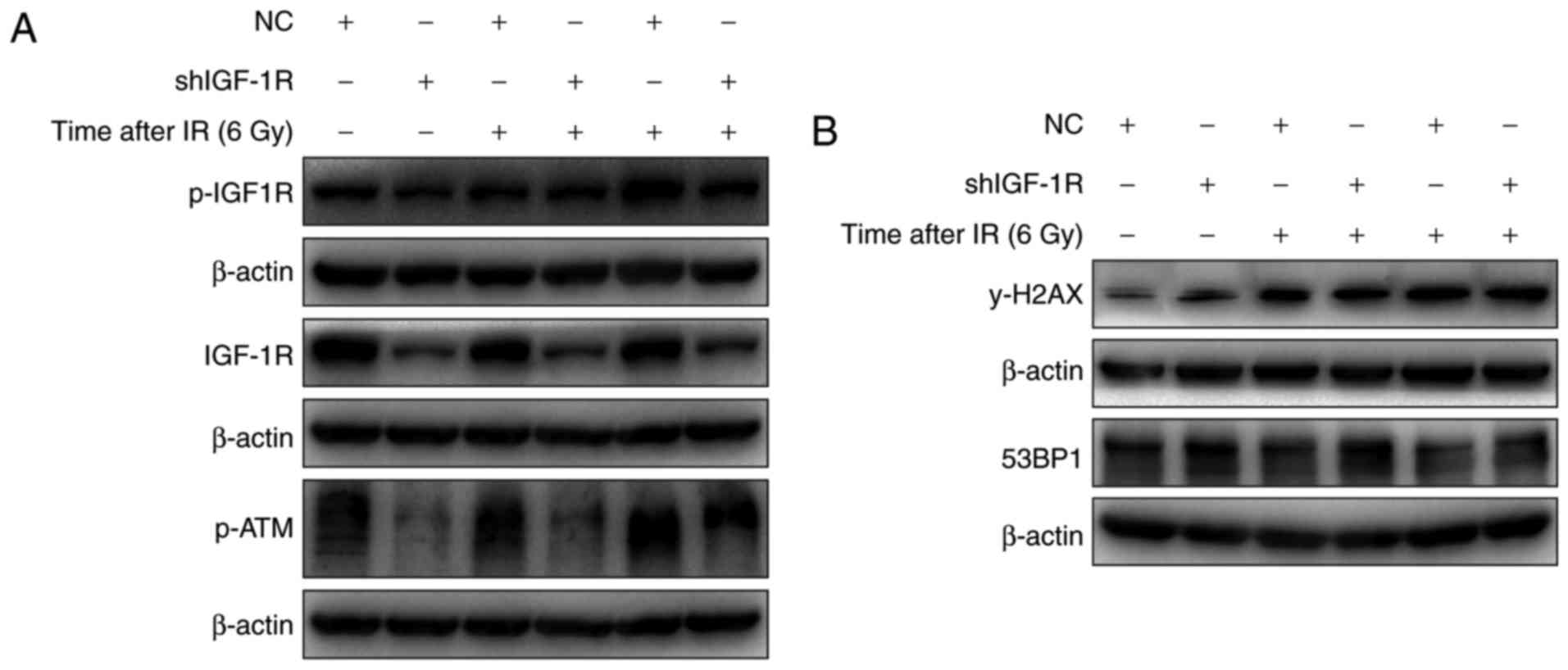
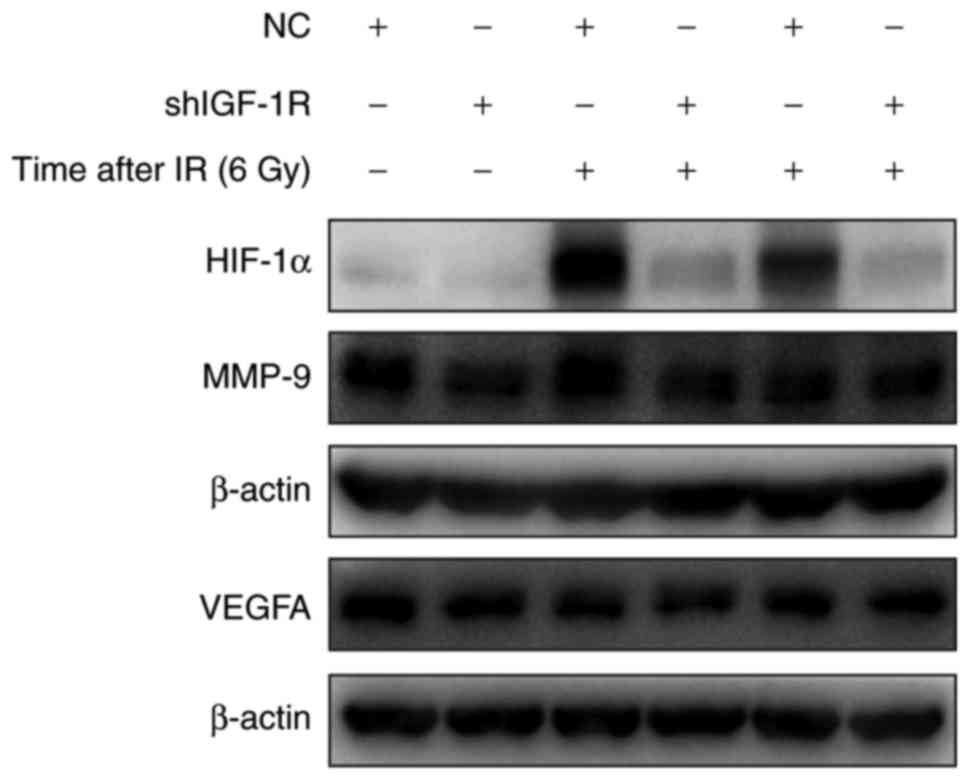
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dong JC, Gao H, Zuo SY, Zhang HQ, Zhao G,
Sun SL, Han HL, Jin LL, Shao LH, Wei W and Jin SZ: Neuropilin 1
expression correlates with the Radio-resistance of human
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med. 19:2286–2295.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Juchum M, Gunther M and Laufer SA:
Fighting cancer drug resistance: Opportunities and challenges for
mutation-specific EGFR inhibitors. Drug Resist Updat. 20:12–28.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kumarakulasinghe NB, van Zanwijk N and Soo
RA: Molecular targeted therapy in the treatment of advanced stage
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Respirology. 20:370–378. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Valenciano A, Henríquez-Hernández LA,
Moreno M, Lloret M and Lara PC: Role of IGF-1 receptor in radiation
response. Transl Oncol. 5:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cao H, Dong W, Shen H, Xu J, Zhu L, Liu Q
and Du J: Combinational therapy enhances the effects of anti-IGF-1R
mAb figitumumab to target small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01358442015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takahashi T, Uehara H, Ogawa H, Umemoto H,
Bando Y and Izumi K: Inhibition of EP2/EP4 signaling abrogates
IGF-1R-mediated cancer cell growth: Involvement of protein kinase
C-θ activation. Oncotarget. 6:4829–4844. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JS, Kim ES, Liu D, Lee JJ, Behrens C,
Lippman SM, Hong WK, Wistuba II, Lee E and Lee HY: Activation of
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in patients with non-small
cell lung cancer. Oncotarget. 6:16746–16756. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iwasa T, Okamoto I, Suzuki M, Hatashita E,
Yamada Y, Fukuoka M, Ono K and Nakagawa K: Inhibition of
insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor by CP-751,871 radiosensitizes
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 15:5117–5125.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morgan MA and Lawrence TS: Molecular
pathways: Overcoming radiation resistance by targeting DNA damage
response pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 21:2898–2904. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wakasugi M, Sasaki T, Matsumoto M, Nagaoka
M, Inoue K, Inobe M, Horibata K, Tanaka K and Matsunaga T:
Nucleotide excision repair-dependent DNA double-strand break
formation and ATM signaling activation in mammalian quiescent
cells. J Biol Chem. 289:28730–28737. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sears CR, Cooney SA, Chin-Sinex H,
Mendonca MS and Turchi JJ: DNA damage response (DDR) pathway
engagement in cisplatin radiosensitization of non-small cell lung
cancer. DNA Repair (Amst). 40:35–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Lu P, Liang Z, Zhang Z, Shi W, Cai
X and Chen C: Increased insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
(IGF1R) expression in small cell lung cancer and the effect of
inhibition of IGF1R expression by RNAi on growth of human small
cell lung cancer NCI-H446 cell. Growth Factors. 33:337–346. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cao H, Dong W, Qu X, Shen H, Xu J, Zhu L,
Liu Q and Du J: Metformin enhances the therapy effects of
anti-IGF-1R mAb figitumumab to NSCLC. Sci Rep. 6:310722016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Furukawa J, Wraight CJ, Freier SM, Peralta
E, Atley LM, Monia BP, Gleave ME and Cox ME: Antisense
oligonucleotide targeting of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor
(IGF-1R) in prostate cancer. Prostate. 70:206–218. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Huang F, Bai Z, Chi B, Wu J and
Chen X: Curcumol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of
colorectal cancer LoVo cell line via IGF-1R and p38 MAPK pathway.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:19851–19867. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou X, Shen F, Ma P, Hui H, Pei S, Chen
M, Wang Z, Zhou W and Jin B: GSK1838705A, an IGF-1R inhibitor,
inhibits glioma cell proliferation and suppresses tumor growth in
vivo. Mol Med Rep. 12:5641–5646. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ramcharan R, Aleksic T, Kamdoum WP, Gao S,
Pfister SX, Tanner J, Bridges E, Asher R, Watson AJ, Margison GP,
et al: IGF-1R inhibition induces schedule-dependent sensitization
of human melanoma to temozolomide. Oncotarget. 6:39877–39890. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Y, Zhu C, Peng Z, Dai Y and Gu Y:
Lentivirus-mediated short-hairpin RNA targeting IGF-1R inhibits
growth and lymphangiogenesis in breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
28:1778–1784. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao H and Gu X: Silencing of insulin-like
growth factor-1 receptor enhances the radiation sensitivity of
human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo.
World J Surg Oncol. 12:3252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sahlberg SH, Gustafsson AS, Pendekanti PN,
Glimelius B and Stenerlöw B: The influence of AKT isoforms on
radiation sensitivity and DNA repair in colon cancer cell lines.
Tumour Biol. 35:3525–3534. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Héron-Milhavet L, Karas M, Goldsmith CM,
Baum BJ and LeRoith D: Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I)
receptor activation rescues UV-damaged cells through a p38
signaling pathway. Potential role of the IGF-I receptor in DNA
repair. J Biol Chem. 276:18185–18192. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Héron-Milhavet L and LeRoith D:
Insulin-like growth factor I induces MDM2-dependent degradation of
p53 via the p38 MAPK pathway in response to DNA damage. J Biol
Chem. 277:15600–15606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Osipov AN, Pustovalova M, Grekhova A,
Eremin P, Vorobyova N, Pulin A, Zhavoronkov A, Roumiantsev S,
Klokov DY and Eremin I: Low doses of X-rays induce prolonged and
ATM-independent persistence of γH2AX foci in human gingival
mesenchymal stem cells. Oncotarget. 6:27275–27287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kurashige T, Shimamura M and Nagayama Y:
Differences in quantification of DNA double-strand breaks assessed
by 53BP1/γH2AX focus formation assays and the comet assay in
mammalian cells treated with irradiation and N-acetyl-L-cysteine. J
Radiat Res. 57:312–317. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baldock RA, Day M, Wilkinson OJ, Cloney R,
Jeggo PA, Oliver AW, Watts FZ and Pearl LH: ATM localization and
heterochromatin repair depend on direct interaction of the
53BP1-BRCT2 domain with γH2AX. Cell Rep. 13:2081–2089. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lima M, Bouzid H, Soares DG, Selle F,
Morel C, Galmarini CM, Henriques JA, Larsen AK and Escargueil AE:
Dual inhibition of ATR and ATM potentiates the activity of
trabectedin and lurbinectedin by perturbing the DNA damage response
and homologous recombination repair. Oncotarget. 7:25885–25901.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ghattass K, Assah R, El-Sabban M and
Gali-Muhtasib H: Targeting hypoxia for sensitization of tumors to
radio- and chemotherapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 13:670–685.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pei J, Lou Y, Zhong R and Han B: MMP9
activation triggered by epidermal growth factor induced FoxO1
nuclear exclusion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol.
35:6673–6678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Miyasaka A, Oda K, Ikeda Y, Sone K, Fukuda
T, Inaba K, Makii C, Enomoto A, Hosoya N, Tanikawa M, et al:
PPI3K/mTOR pathway inhibition overcomes radioresistance via
suppression of the HIF1-α/VEGF pathway in endometrial cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 138:174–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Harada H: Hypoxia-inducible factor
1-mediated characteristic features of cancer cells for tumor
radioresistance. J Radiat Res. 57(Suppl 1): i99–i105. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Helbig L, Koi L, Brüchner K, Gurtner K,
Hess-Stumpp H, Unterschemmann K, Pruschy M, Baumann M, Yaromina A
and Zips D: Hypoxia-inducible factor pathway inhibition resolves
tumor hypoxia and improves local tumor control after single-dose
irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 88:159–166. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fotia C, Massa A, Boriani F, Baldini N and
Granchi D: Hypoxia enhances proliferation and stemness of human
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology.
67:1073–1084. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fu Z, Chen D, Cheng H and Wang F:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α protects cervical carcinoma cells from
apoptosis induced by radiation via modulation of vascular
endothelial growth factor and p53 under hypoxia. Med Sci Monit.
21:318–325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gao Q, Guo M, Zeng W, Wang Y, Yang L, Pang
X, Li H, Suo Y, Jiang X and Yu C: Matrix metalloproteinase 9
secreted by hypoxia cardiac fibroblasts triggers cardiac stem cell
migration in vitro. Stem Cells Int. 2015:8363902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ondrej M, Cechakova L, Durisova K, Pejchal
J and Tichy A: To live or let die: Unclear task of autophagy in the
radiosensitization battle. Radiother Oncol. 119:265–275. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Milczarek M, Wiktorska K, Mielczarek L,
Koronkiewicz M, Dąbrowska A, Lubelska K, Matosiuk D and Chilmonczyk
Z: Autophagic cell death and premature senescence: New mechanism of
5-fluorouracil and sulforaphane synergistic anticancer effect in
MDA-MB-231 triple negative breast cancer cell line. Food Chem
Toxicol. 111:1–8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jo GH, Bögler O, Chwae YJ, Yoo H, Lee SH,
Park JB, Kim YJ, Kim JH and Gwak HS: Radiation-induced autophagy
contributes to cell death and induces apoptosis partly in malignant
glioma cells. Cancer Res Treat. 47:221–241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ryan F, Khodagholi F, Dargahi L,
Minai-Tehrani D and Ahmadiani A: Temporal pattern and crosstalk of
necroptosis markers with autophagy and apoptosis associated
proteins in ischemic hippocampus. Neurotox Res. Jan 8. 2018, (Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Suzuki R, Kang Y, Li X, Roife D, Zhang R
and Fleming JB: Genistein potentiates the antitumor effect of
5-Fluorouracil by inducing apoptosis and autophagy in human
pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 34:4685–4692.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|