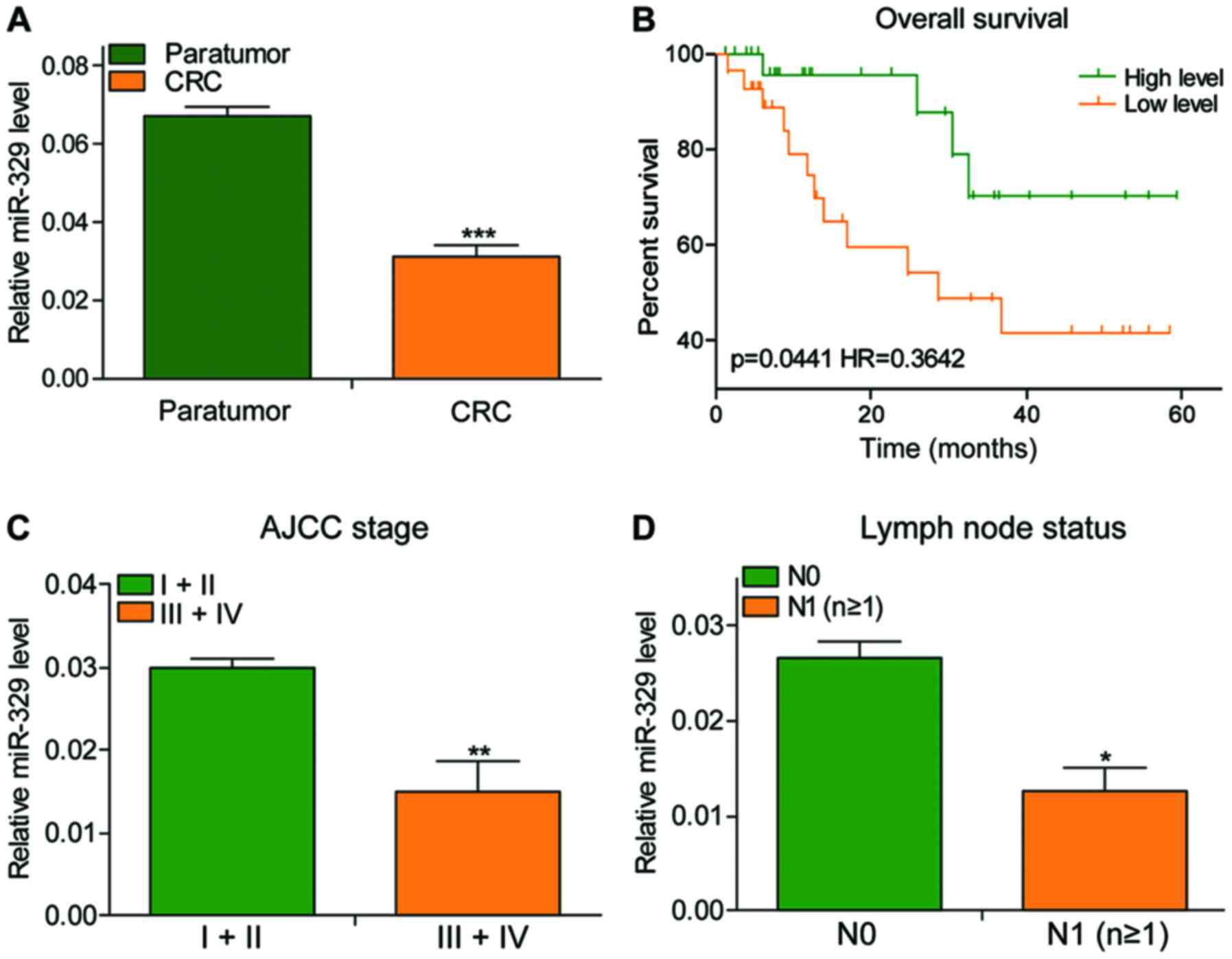
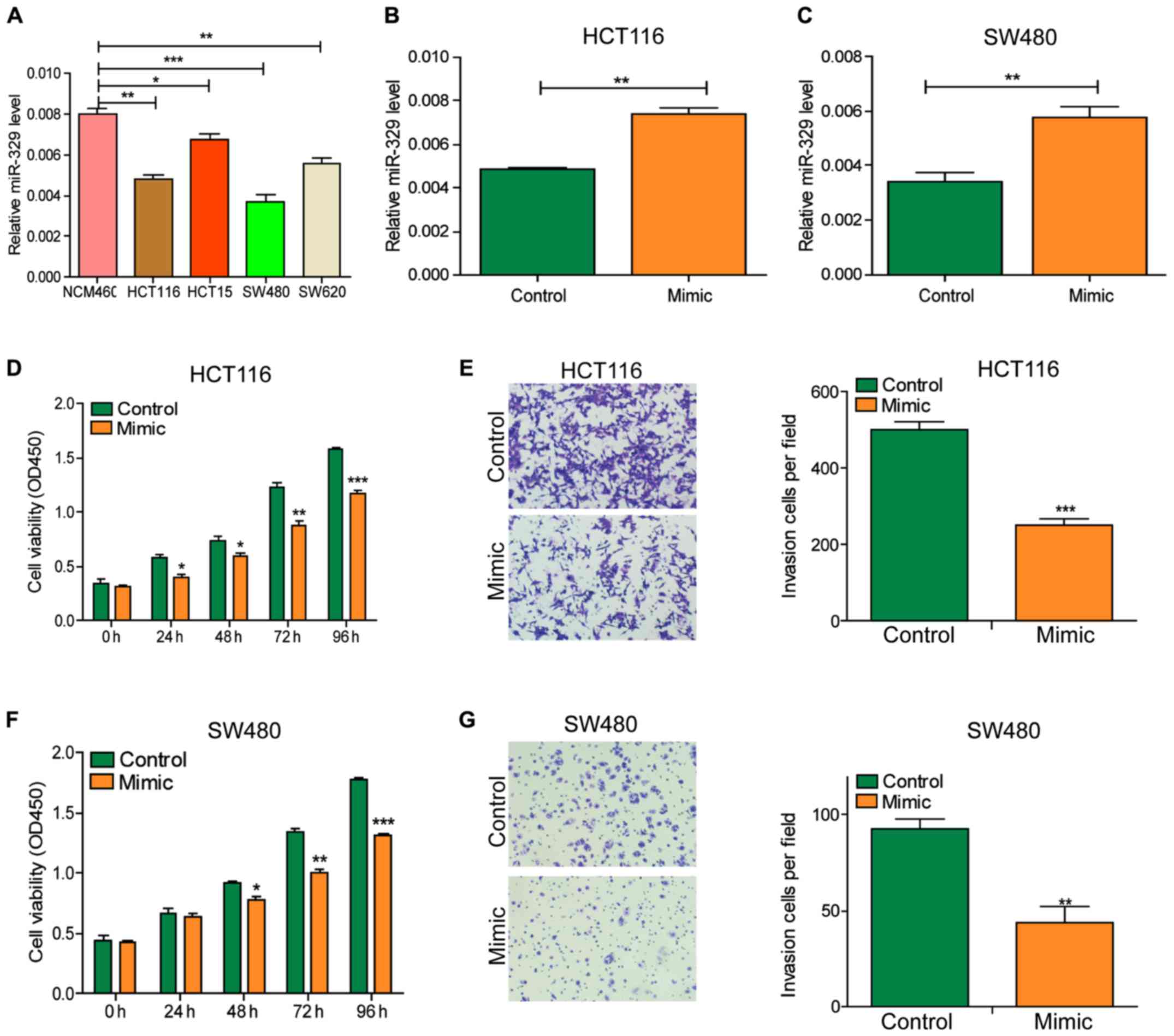
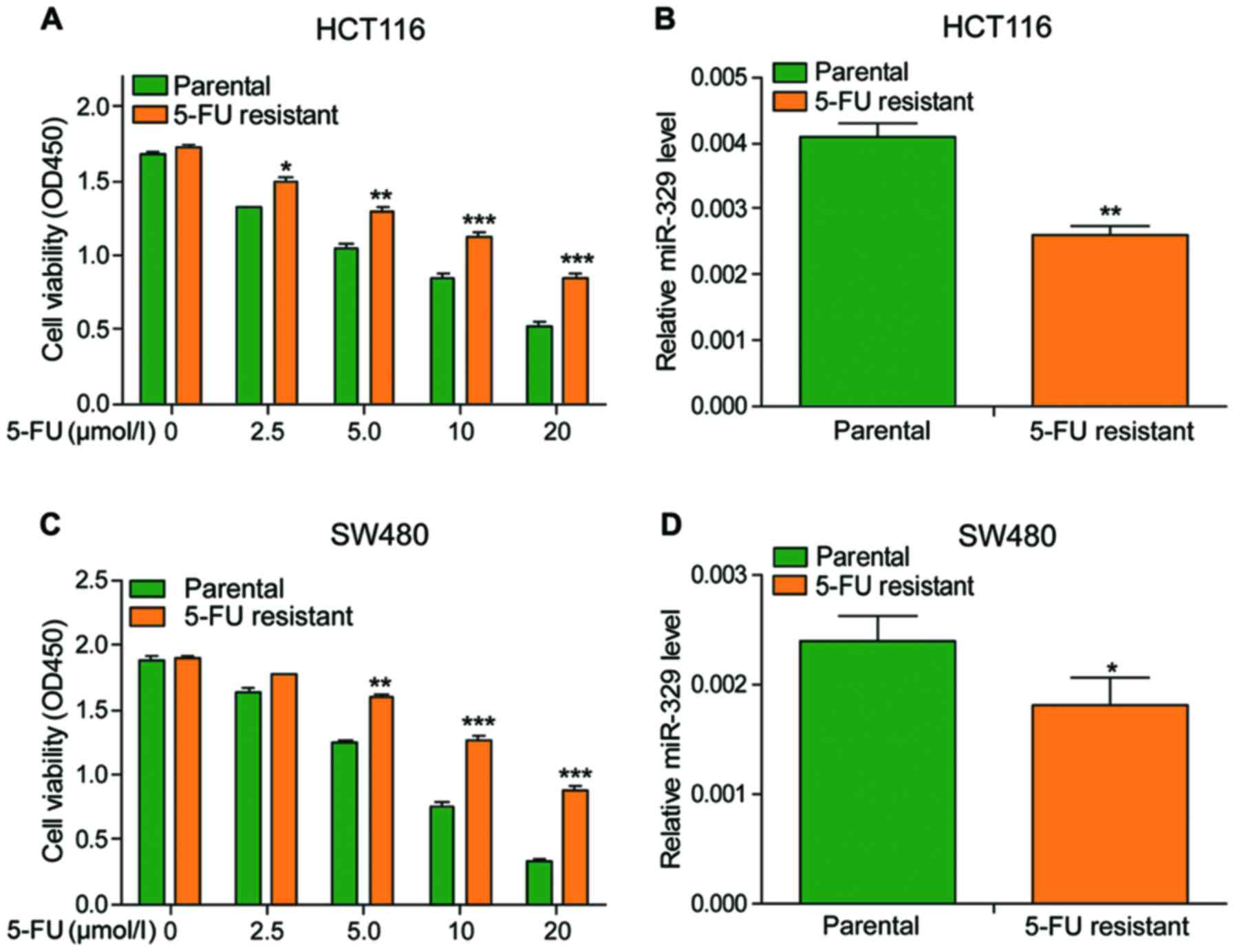
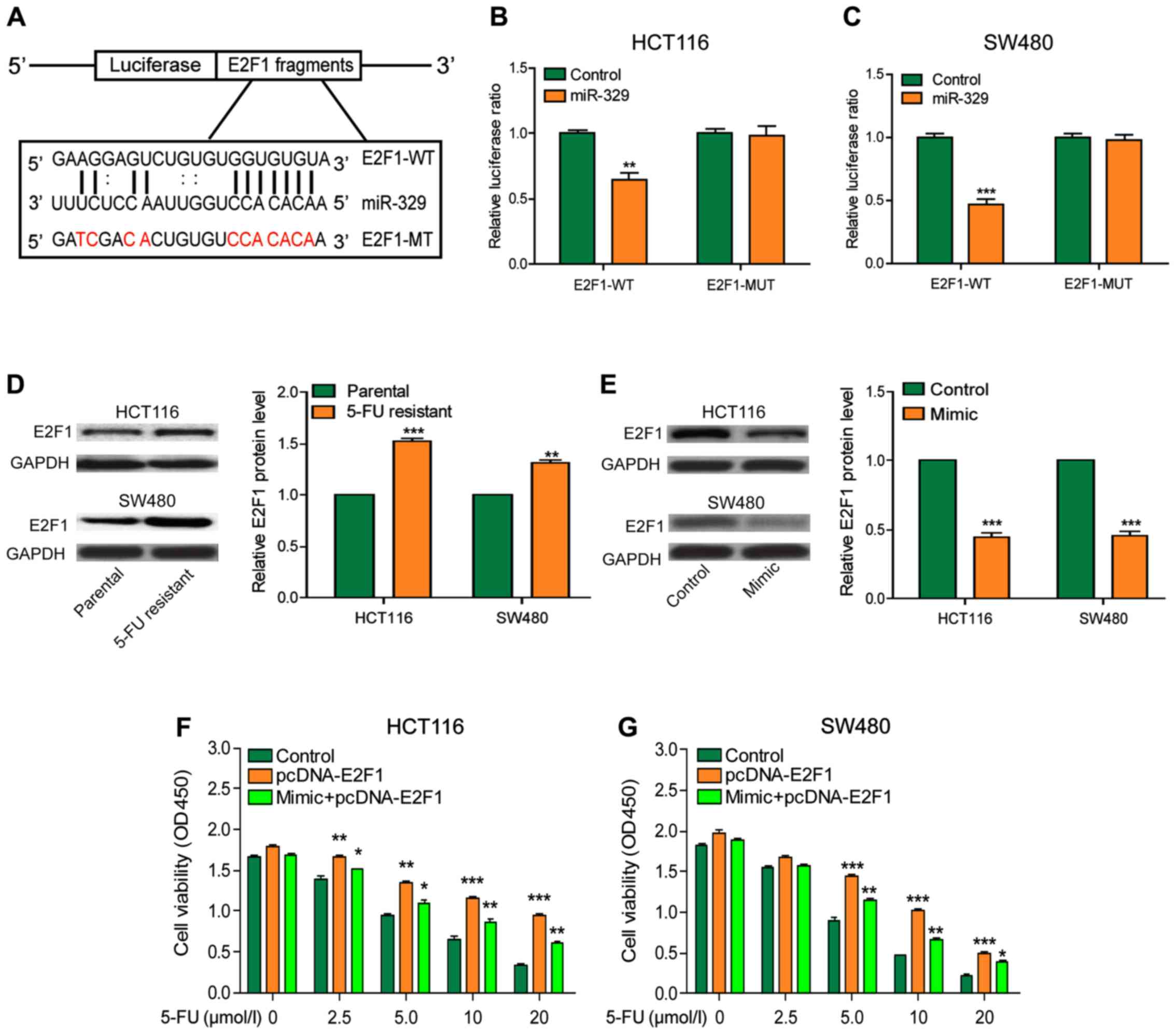
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hu T, Li Z, Gao CY and Cho CH: Mechanisms
of drug resistance in colon cancer and its therapeutic strategies.
World J Gastroenterol. 22:6876–6889. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rajewsky N: MicroRNA target predictions in
animals. Nat Genet. 38 Suppl:S8–S13. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wijnhoven BP, Michael MZ and Watson DI:
MicroRNAs and cancer. Br J Surg. 94:23–30. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brower JV, Clark PA, Lyon W and Kuo JS:
MicroRNAs in cancer: Glioblastoma and glioblastoma cancer stem
cells. Neurochem Int. 77:68–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Møller HG, Rasmussen AP, Andersen HH,
Johnsen KB, Henriksen M and Duroux M: A systematic review of
microRNA in glioblastoma multiforme: Micro-modulators in the
mesenchymal mode of migration and invasion. Mol Neurobiol.
47:131–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yadunandam AK, Yoon JS, Seong YA, Oh CW
and Kim GD: Prospective impact of 5-FU in the induction of
endoplasmic reticulum stress, modulation of GRP78 expression and
autophagy in Sk-Hep1 cells. Int J Oncol. 41:1036–1042. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Deng YH, Pu XX, Huang MJ, Xiao J, Zhou JM,
Lin TY and Lin EH: 5-Fluorouracil upregulates the activity of Wnt
signaling pathway in CD133-positive colon cancer stem-like cells.
Chin J Cancer. 29:810–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hotta T, Takifuji K, Arii K, Yokoyama S,
Matsuda K, Higashiguchi T, Tominaga T, Oku Y and Yamaue H: Clinical
impact of adjuvant chemotherapy on patients with stage III
colorectal cancer: l-LV/5FU chemotherapy as a modified RPMI regimen
is an independent prognostic factor for survival. Anticancer Res.
26(2B): 1425–1432. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ogawa H, Ishiguro K, Gaubatz S, Livingston
DM and Nakatani Y: A complex with chromatin modifiers that occupies
E2F- and Myc-responsive genes in G0 cells. Science. 296:1132–1136.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dong F and Lou D: MicroRNA-34b/c
suppresses uveal melanoma cell proliferation and migration through
multiple targets. MOL VIS. 18:537–546. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Westphalen CB, Asfaha S, Hayakawa Y,
Takemoto Y, Lukin DJ, Nuber AH, Brandtner A, Setlik W, Remotti H,
Muley A, et al: Long-lived intestinal tuft cells serve as colon
cancer-initiating cells. J Clin Invest. 124:1283–1295. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tournigand C, André T, Achille E, Lledo G,
Flesh M, Mery-Mignard D, Quinaux E, Couteau C, Buyse M, Ganem G, et
al: FOLFIRI followed by FOLFOX6 or the reverse sequence in advanced
colorectal cancer: A randomized GERCOR study. J Clin Oncol.
22:229–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wurdinger T and Costa FF: Molecular
therapy in the microRNA era. Pharmacogenomics J. 7:297–304. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R,
Zupo S, Noch E, Aldler H, Rattan S, Keating M, Rai K, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Visone R and Croce CM: miRNAs and cancer.
Am J Pathol. 174:1131–1138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song B, Wang Y, Xi Y, Kudo K, Bruheim S,
Botchkina GI, Gavin E, Wan Y, Formentini A, Kornmann M, et al:
Mechanism of chemoresistance mediated by miR-140 in human
osteosarcoma and colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 28:4065–4074. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yamasaki L, Bronson R, Williams BO, Dyson
NJ, Harlow E and Jacks T: Loss of E2F-1 reduces tumorigenesis and
extends the lifespan of Rb1(+/-) mice. Nat Genet. 18:360–364. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Evangelou K,
Karakaidos P, Vassiliou LV, Rezaei N, Kyroudi A, Kittas C,
Patsouris E, Papavassiliou AG, et al: Distinct expression patterns
of the transcription factor E2F-1 in relation to tumour growth
parameters in common human carcinomas. J Pathol. 203:744–753. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|