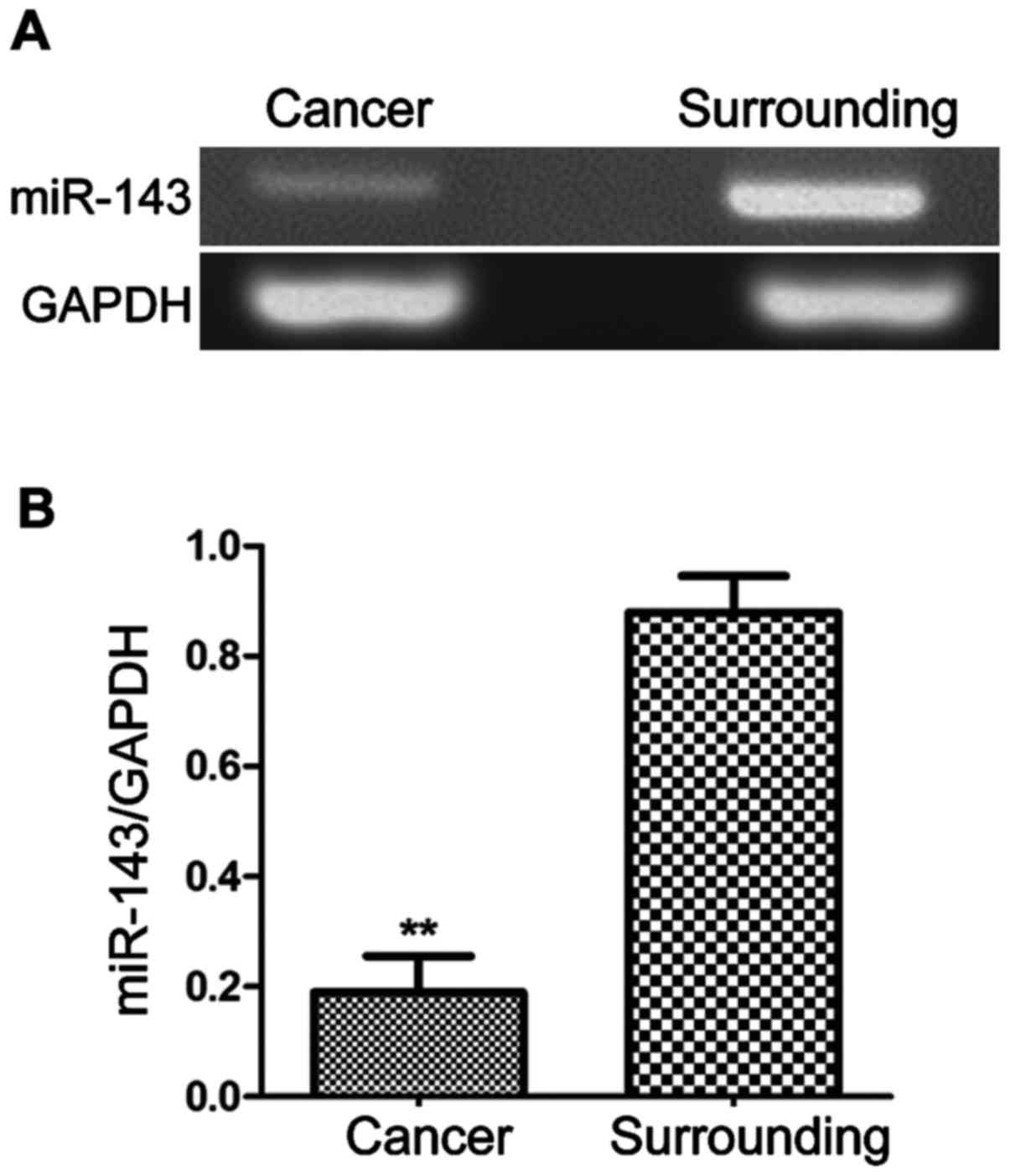
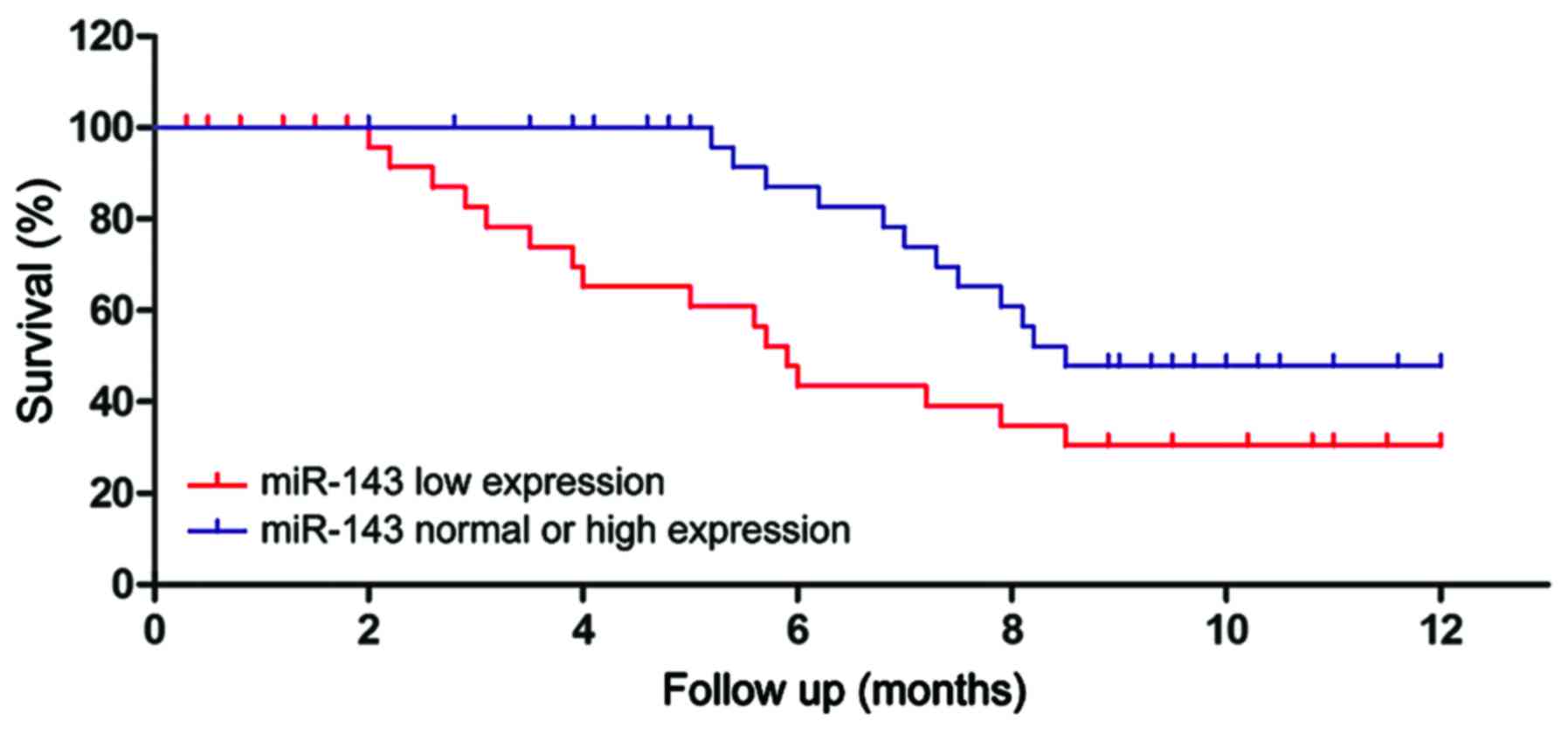
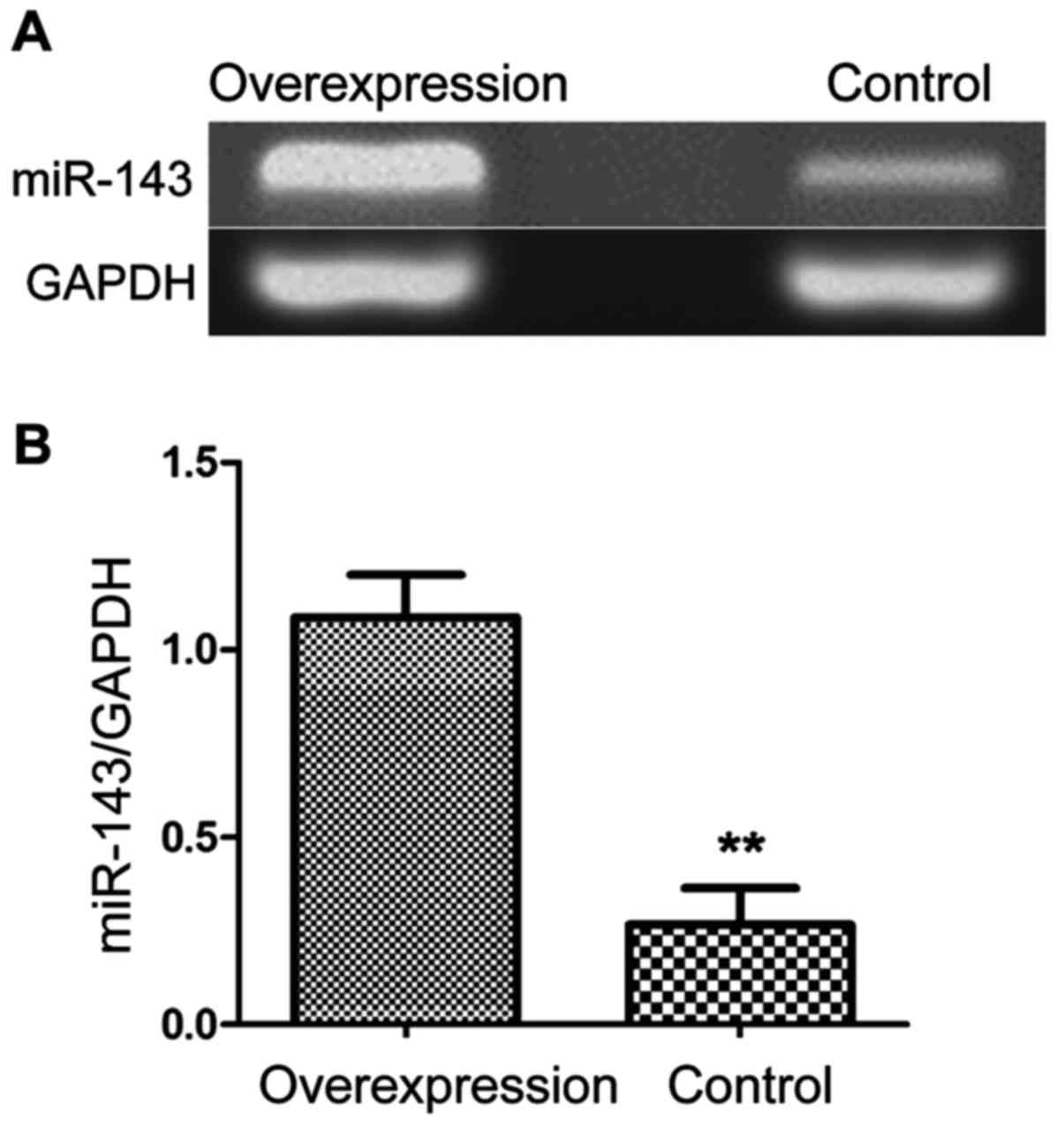
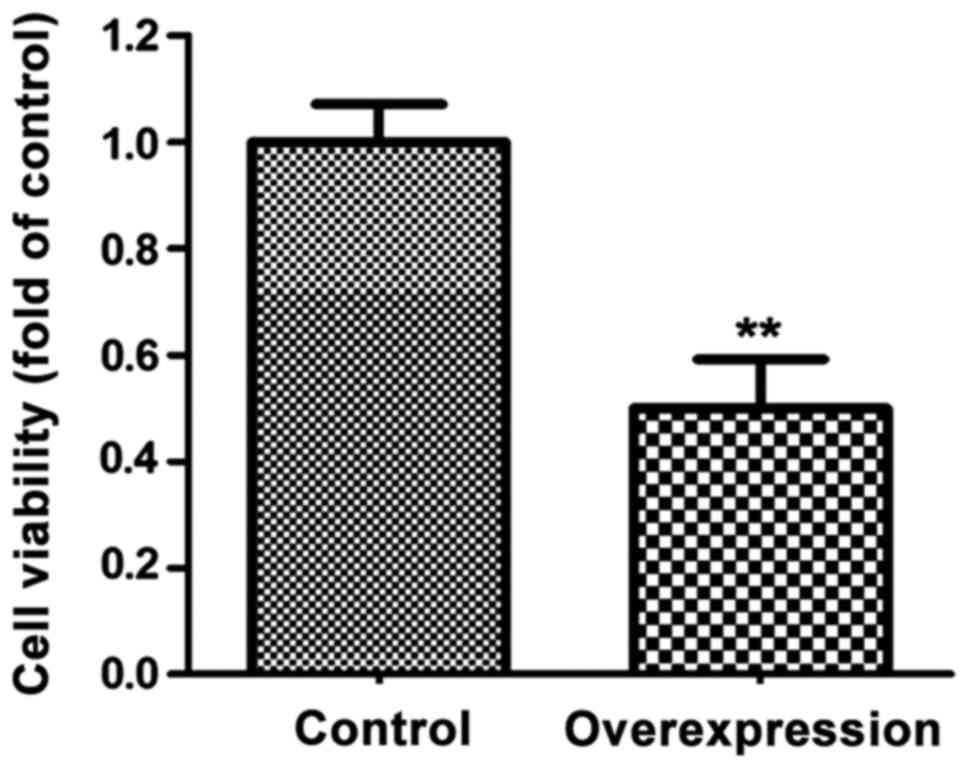
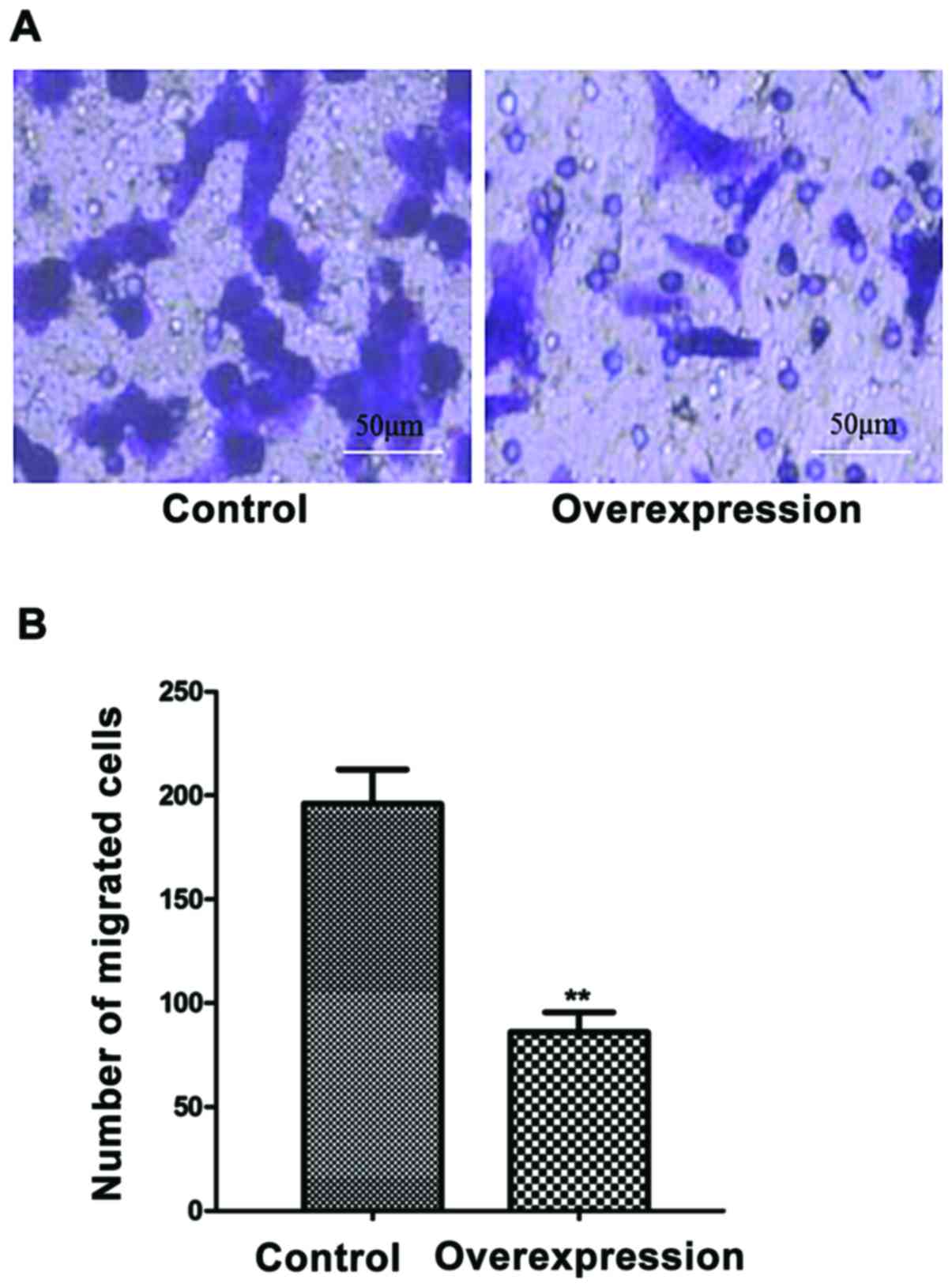
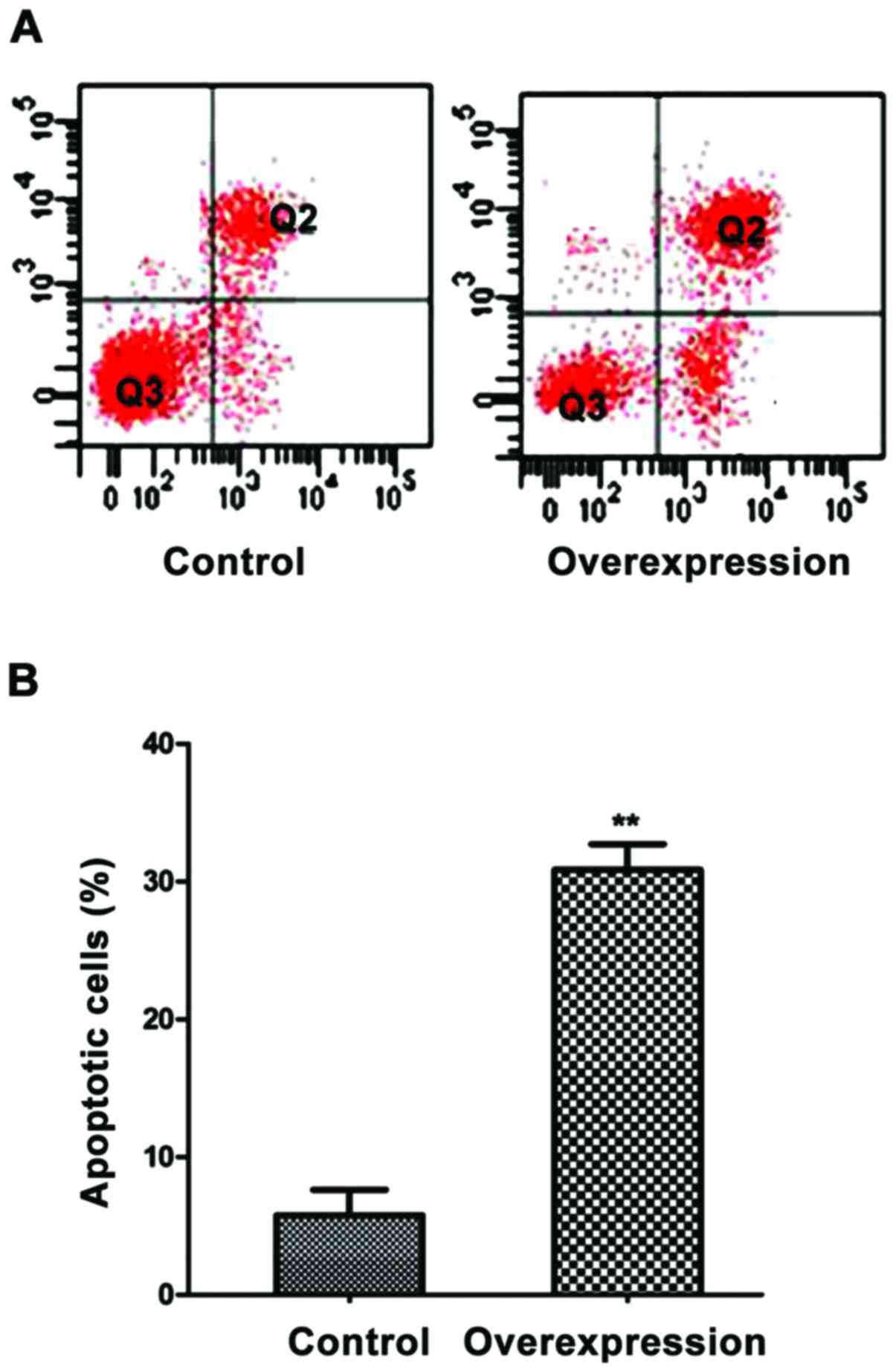
|
1
|
Chen X-Z, Chen H, Castro FA, Hu JK and
Brenner H: Epstein-Barr virus infection and gastric cancer: A
systematic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:563–568. 2015.
|
|
2
|
Lee JH, Kim JG, Jung HK, Kim JH, Jeong WK,
Jeon TJ, Kim JM, Kim YI, Ryu KW, Kong SH, et al: Clinical practice
guidelines for gastric cancer in Korea: An evidence-based approach.
J Gastric Cancer. 14:87–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Son T, Kwon IG and Hyung WJ: Minimally
invasive surgery for gastric cancer treatment: Current status and
future perspectives. Gut Liver. 8:229–236. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yoon H and Kim N: Diagnosis and management
of high risk group for gastric cancer. Gut Liver. 9:5–17. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miki K: Gastric cancer screening by
combined assay for serum anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG antibody and
serum pepsinogen levels - ‘ABC method’. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys
Biol Sci. 87:405–414. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu HH, Lin WC and Tsai KW: Advances in
molecular biomarkers for gastric cancer: miRNAs as emerging novel
cancer markers. Expert Rev Mol Med. 16:e12014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang HB, Sun LC, Ling L, Cong LH and Lian
R: miR-143 suppresses the proliferation of NSCLC cells by
inhibiting the epidermal growth factor receptor. Exp Ther Med.
12:1795–1802. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su J, Liang H, Yao W, Wang N, Zhang S, Yan
X, Feng H, Pang W, Wang Y, Wang X, et al: MiR-143 and MiR-145
regulate IGF1R to suppress cell proliferation in colorectal cancer.
PLoS One. 9:e1144202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Adlakha YK and Saini N: Brain microRNAs
and insights into biological functions and therapeutic potential of
brain enriched miRNA-128. Mol Cancer. 13:332014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Soares RJ, Cagnin S, Chemello F,
Silvestrin M, Musaro A, De Pitta C, Lanfranchi G and Sandri M:
Involvement of microRNAs in the regulation of muscle wasting during
catabolic conditions. J Biol Chem. 289:21909–21925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lamontagne J, Steel LF and Bouchard MJ:
Hepatitis B virus and microRNAs: Complex interactions affecting
hepatitis B virus replication and hepatitis B virus-associated
diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 21:7375–7399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu Y, Jiang Q, Lou X, Ji X, Wen Z, Wu J,
Tao H, Jiang T, He W, Wang C, et al: : MicroRNAs up-regulated by
CagA of Helicobacter pylori induce intestinal metaplasia of gastric
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 7:e351472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jianjun Z, Fan W, Yihua L, Juan X and Mei
X: MicroRNA transcriptome profile analysis in porcine muscle and
the effect of miR-143 on the MYH7 gene and protein. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 10:215–237. 2015.
|
|
14
|
Khafaei M, Samie S, Mowla SJ, Alvanegh AG,
Mirzaei B, Chavoshei S, Dorraj GS, Esmailnejad M, Tavallaie M and
Nourani M: Evaluation of miR-9 and miR-143 expression in urine
specimens of sulfur mustard exposed patients. Interdiscip Toxicol.
8:169–174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang S, Bonaroti J, Unlu S, Liang X, Tang
D, Zeh HJ and Lotze MT: Sweating the small stuff: microRNAs and
genetic changes define pancreatic cancer. Pancreas. 42:740–759.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li A, Omura N, Hong SM, Vincent A, Walter
K, Griffith M, Borges M and Goggins M: Pancreatic cancers
epigenetically silence SIP1 and hypomethylate and overexpress
miR-200a/200b in association with elevated circulating miR-200a and
miR-200b levels. Cancer Res. 70:5226–5237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yan X, Chen X, Liang H, Deng T, Chen W,
Zhang S, Liu M, Gao X, Liu Y, Zhao C, et al: miR-143 and miR-145
synergistically regulate ERBB3 to suppress cell proliferation and
invasion in breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 13:2202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hongyan Z, Urszula D, Victoria R and Reba
M: EGFR signals down-regulate tumor suppressors miR-143 and miR-145
in Western diet-promoted murine colon cancer: Role of G1
regulators. Mol Cancer Res. 9:176–184. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Wu XL, Cheng B, Li PY, Huang HJ, Zhao Q,
Dan ZL, Tian DA and Zhang P: MicroRNA-143 suppresses gastric cancer
cell growth and induces apoptosis by targeting COX-2. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:7758–7765. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|