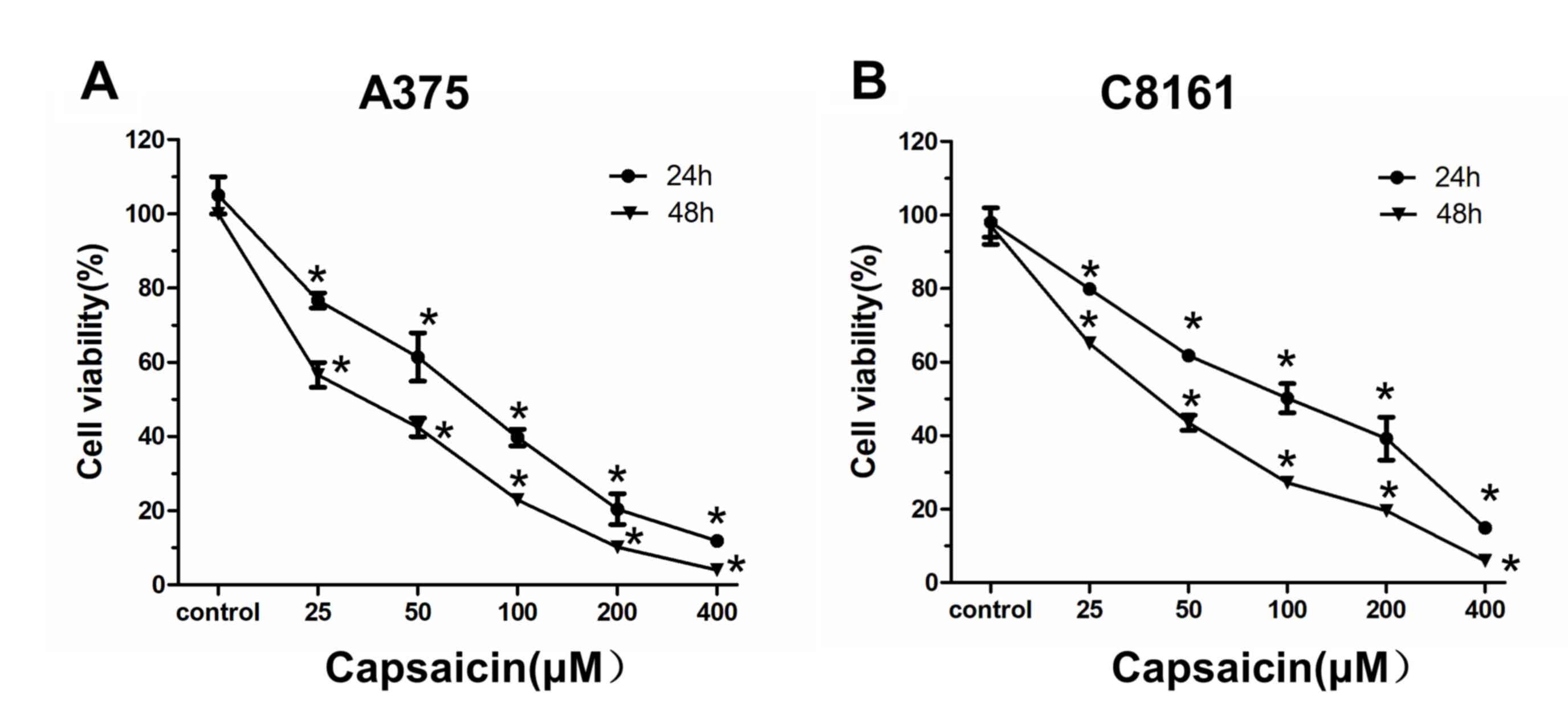
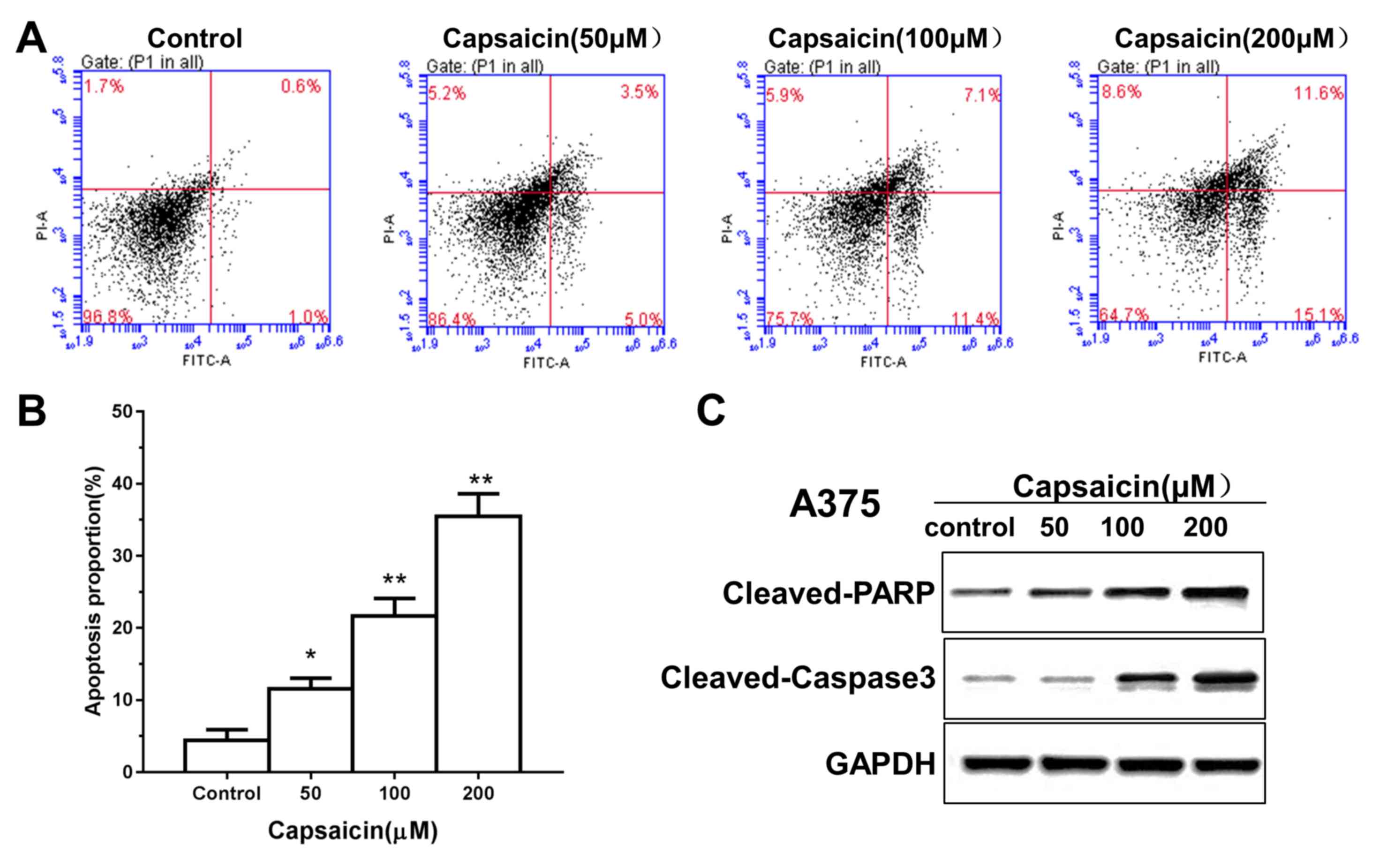
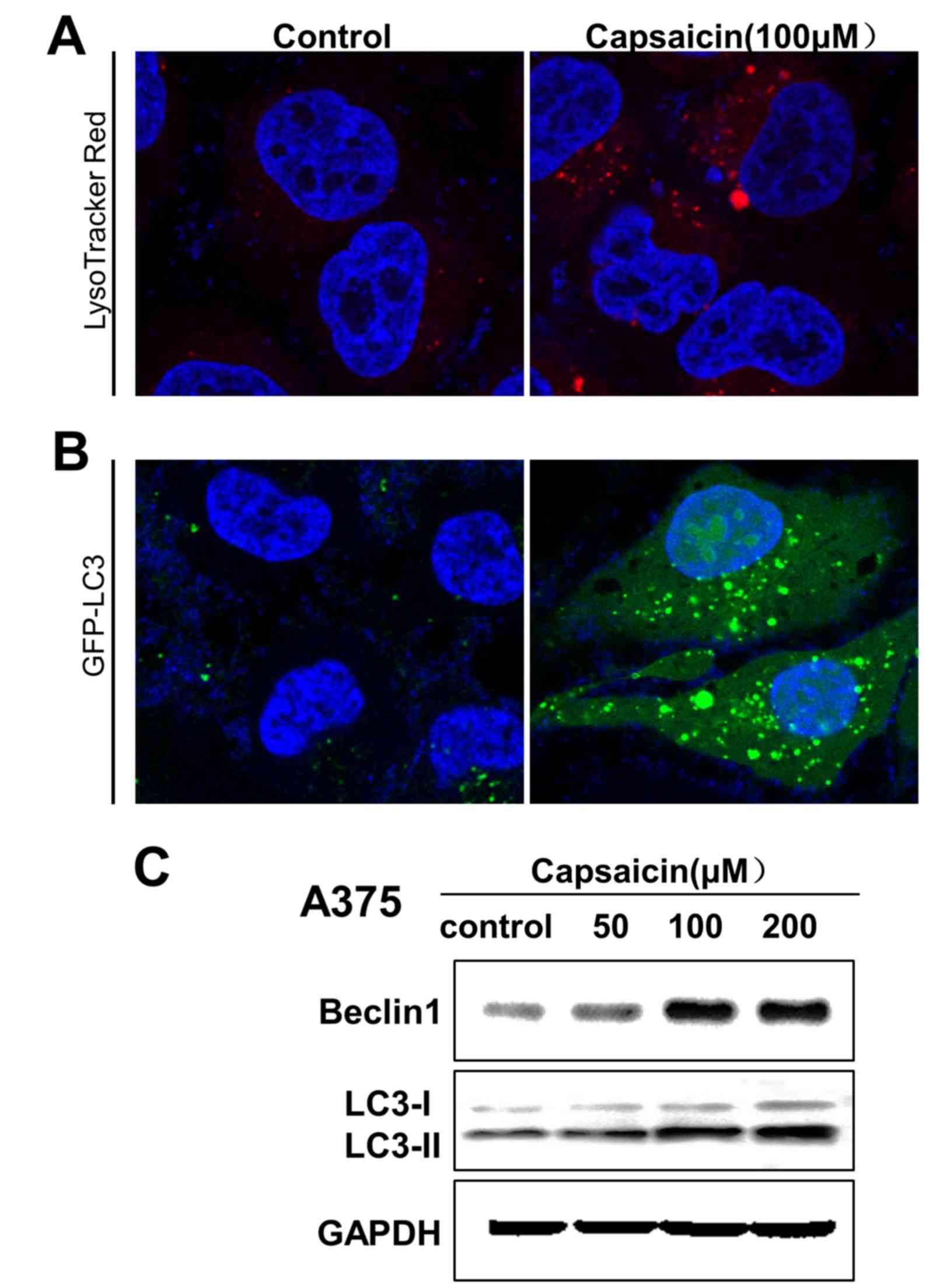
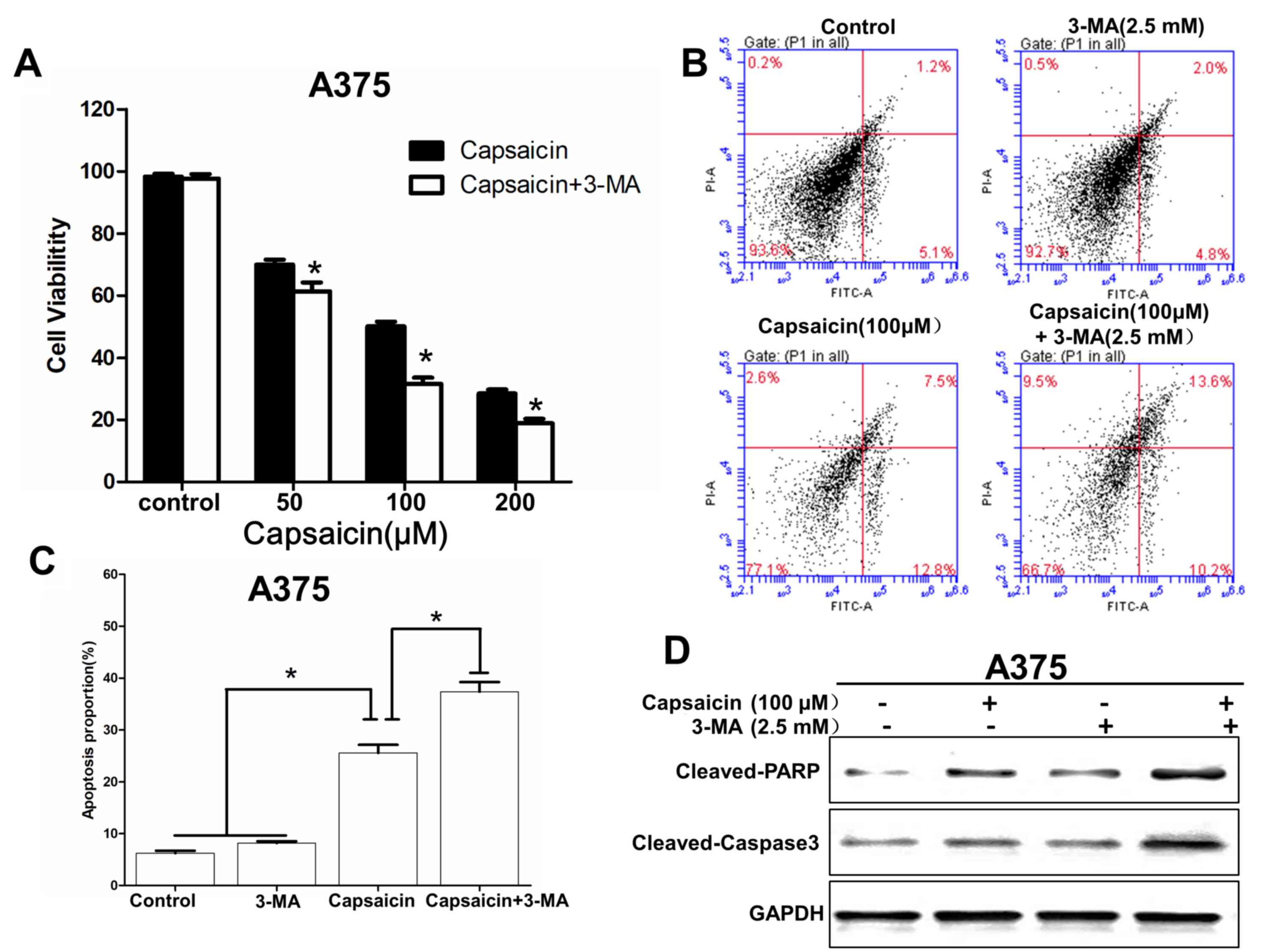
|
1
|
Schadendorf D, Fisher DE, Garbe C,
Gershenwald JE, Grob JJ, Halpern A, Herlyn M, Marchetti MA,
McArthur G, Ribas A, et al: Melanoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
1:150032015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Leiter U and Garbe C: Epidemiology of
melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer-the role of sunlight. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 624:89–103. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wei W, Ehlerding EB, Lan X, Luo Q and Cai
W: PET and SPECT imaging of melanoma: The state of the art. Eur J
Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 45:132–150. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schadendorf D and Hauschild A: Melanoma in
2013: Melanoma-the run of success continues. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
11:75–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Balch CM, Gershenwald JE, Soong SJ,
Thompson JF, Atkins MB, Byrd DR, Buzaid AC, Cochran AJ, Coit DG,
Ding S, et al: Final version of 2009 AJCC melanoma staging and
classification. J Clin Oncol. 27:6199–6206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Srinivasan K: Biological activities of red
pepper (Capsicum annuum) and its pungent principle capsaicin: A
review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 56:1488–1500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ludy MJ, Moore GE and Mattes RD: The
effects of capsaicin and capsiate on energy balance: Critical
review and meta-analyses of studies in humans. Chem Senses.
37:103–121. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patel S, Trueman D, Bentley A, Poole C and
Chambers C: Cost-effectiveness of capsaicin 8% patch (Qutenza(tm))
compared with pregabalin for the treatment of patients with
peripheral neuropathic pain (Pnp) in Scotland. Value Health.
17:A5312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fattori V, Hohmann MS, Rossaneis AC,
Pinho-Ribeiro FA and Verri WA: Capsaicin: Current understanding of
its mechanisms and therapy of pain and other pre-clinical and
clinical uses. Molecules. 21(pii): E8442016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bernstein JA, Davis BP, Picard JK, Cooper
JP, Zheng S and Levin LS: A randomized, double-blind, parallel
trial comparing capsaicin nasal spray with placebo in subjects with
a significant component of nonallergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma
Immunol. 107:171–178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Díaz-Laviada I and Rodríguez-Henche N: The
potential antitumor effects of capsaicin. Prog Drug Res.
68:181–208. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ramos-Torres Á, Bort A, Morell C,
Rodríguez-Henche N and Díaz-Laviada I: The pepper's natural
ingredient capsaicin induces autophagy blockage in prostate cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 7:1569–1583. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lin YT, Wang HC, Hsu YC, Cho CL, Yang MY
and Chien CY: Capsaicin induces autophagy and apoptosis in human
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by downregulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E13432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang KM, Pyo JO, Kim GY, Yu R, Han IS, Ju
SA, Kim WH and Kim BS: Capsaicin induces apoptosis by generating
reactive oxygen species and disrupting mitochondrial transmembrane
potential in human colon cancer cell lines. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
14:497–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang R, Xia Y, Wang Z, Zheng J, Chen Y,
Li X, Wang Y and Ming H: Serum long non coding RNA MALAT-1
protected by exosomes is up-regulated and promotes cell
proliferation and migration in non-small cell lung cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 490:406–414. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang SP, Chen JC, Wu CC, Chen CT, Tang
NY, Ho YT, Lo C, Lin JP, Chung JG and Lin JG: Capsaicin-induced
apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells. Anticancer Res.
29:165–174. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ouyang L, Shi Z, Zhao S, Wang FT, Zhou TT,
Liu B and Bao JK: Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A
review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell
Prolif. 45:487–498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jun HS, Park T, Lee CK, Kang MK, Park MS,
Kang HI, Surh YJ and Kim OH: Capsaicin induced apoptosis of B16-F10
melanoma cells through down-regulation of Bcl-2. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:708–715. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A and Kimchi A: The
paradox of autophagy and its implication in cancer etiology and
therapy. Apoptosis. 14:376–391. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S and Sinicrope
FA: The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maiuri MC, Zalckvar E, Kimchi A and
Kroemer G: Self-eating and self-killing: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:741–752. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lo JA and Fisher DE: The melanoma
revolution: From UV carcinogenesis to a new era in therapeutics.
Science. 346:945–949. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin JY and Fisher DE: Melanocyte biology
and skin pigmentation. Nature. 445:843–850. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dong J, Phelps RG, Qiao R, Yao S, Benard
O, Ronai Z and Aaronson SA: BRAF oncogenic mutations correlate with
progression rather than initiation of human melanoma. Cancer Res.
63:3883–3885. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A,
McArthur GA, Sosman JA, O'Dwyer PJ, Lee RJ, Grippo JF, Nolop K and
Chapman PB: Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 363:809–819. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary
T, Gutzmer R, Millward M, Rutkowski P, Blank CU, Miller WH Jr,
Kaempgen E, et al: Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma:
A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 380:358–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen
JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et
al: Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E
mutation. N Engl J Med. 364:2507–2516. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ribas A, Gonzalez R, Pavlick A, Hamid O,
Gajewski TF, Daud A, Flaherty L, Logan T, Chmielowski B, Lewis K,
et al: Combination of vemurafenib and cobimetinib in patients with
advanced BRAF (V600)-mutated melanoma: A phase 1b study. Lancet
Oncol. 15:954–965. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dvořánková B, Szabo P, Kodet O, Strnad H,
Kolář M, Lacina L, Krejčí E, Naňka O, Šedo A and Smetana K Jr:
Intercellular crosstalk in human malignant melanoma. Protoplasma.
254:1143–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Toh CC, Lee TS and Kiang AK: The
pharmacological actions of capsaicin and analogues. Br J Pharmacol
Chemother. 10:175–182. 1955. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sekine R, Satoh T, Takaoka A, Saeki K and
Yokozeki H: Anti pruritic effects of topical crotamiton, capsaicin,
and a corticosteroid on pruritogen-induced scratching behavior. Exp
Dermatol. 21:201–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liao HT, Lee HJ, Ho YC and Chiou LC:
Capsaicin in the periaqueductal gray induces analgesia via
metabotropic glutamate receptor-mediated endocannabinoid retrograde
disinhibition. Br J Pharmacol. 163:330–345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Clark R and Lee SH: Anticancer properties
of capsaicin against human cancer. Anticancer Res. 36:837–843.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chapa-Oliver AM and Mejía-Teniente L:
Capsaicin: From plants to a cancer-suppressing agent. Molecules.
21(pii): E9312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shin DH, Kim OH, Jun HS and Kang MK:
Inhibitory effect of capsaicin on B16-F10 melanoma cell migration
via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/Rac1 signal pathway. Exp
Mol Med. 40:486–494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin CH, Lu WC, Wang CW, Chan YC and Chen
MK: Capsaicin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human KB
cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 13:462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu Z, Ouyang L, Peng H and Zhang WZ:
Oridonin: Targeting programmed cell death pathways as an
anti-tumour agent. Cell Prolif. 45:499–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hail N Jr, Carter BZ, Konopleva M and
Andreeff M: Apoptosis effector mechanisms: A requiem performed in
different keys. Apoptosis. 11:889–904. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mukhopadhyay S, Panda PK, Sinha N, Das DN
and Bhutia SK: Autophagy and apoptosis: Where do they meet?
Apoptosis. 19:555–566. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V,
Stoica BA, Wang G, Iyer S and Smulson M: Role of poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis. Caspase 3-resistant PARP
mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol
Chem. 274:22932–22940. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kulms D and Schwarz T: Molecular
mechanisms of UV-induced apoptosis. Photodermatol Photoimmunol
Photomed. 16:195–201. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu YP, Dong FX, Chai X, Zhu S, Zhang BL
and Gao DS: Role of autophagy in capsaicin-induced apoptosis in
U251 glioma cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 36:737–743. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Radogna F, Dicato M and Diederich M:
Cancer-type-specific crosstalk between autophagy, necroptosis and
apoptosis as a pharmacological target. Biochem Pharmacol. 94:1–11.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li M, Tan J, Miao Y, Lei P and Zhang Q:
The dual role of autophagy under hypoxia-involvement of interaction
between autophagy and apoptosis. Apoptosis. 20:769–777. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Fu D, Yu JY, Yang S, Wu M, Hammad SM,
Connell AR, Du M, Chen J and Lyons TJ: Survival or death: A dual
role for autophagy in stress-induced pericyte loss in diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetologia. 59:2251–2261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ravegnini G, Sammarini G, Nannini M,
Pantaleo MA, Biasco G, Hrelia P and Angelini S: Gastrointestinal
stromal tumors (GIST): Facing cell death between autophagy and
apoptosis. Autophagy. 13:452–463. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|