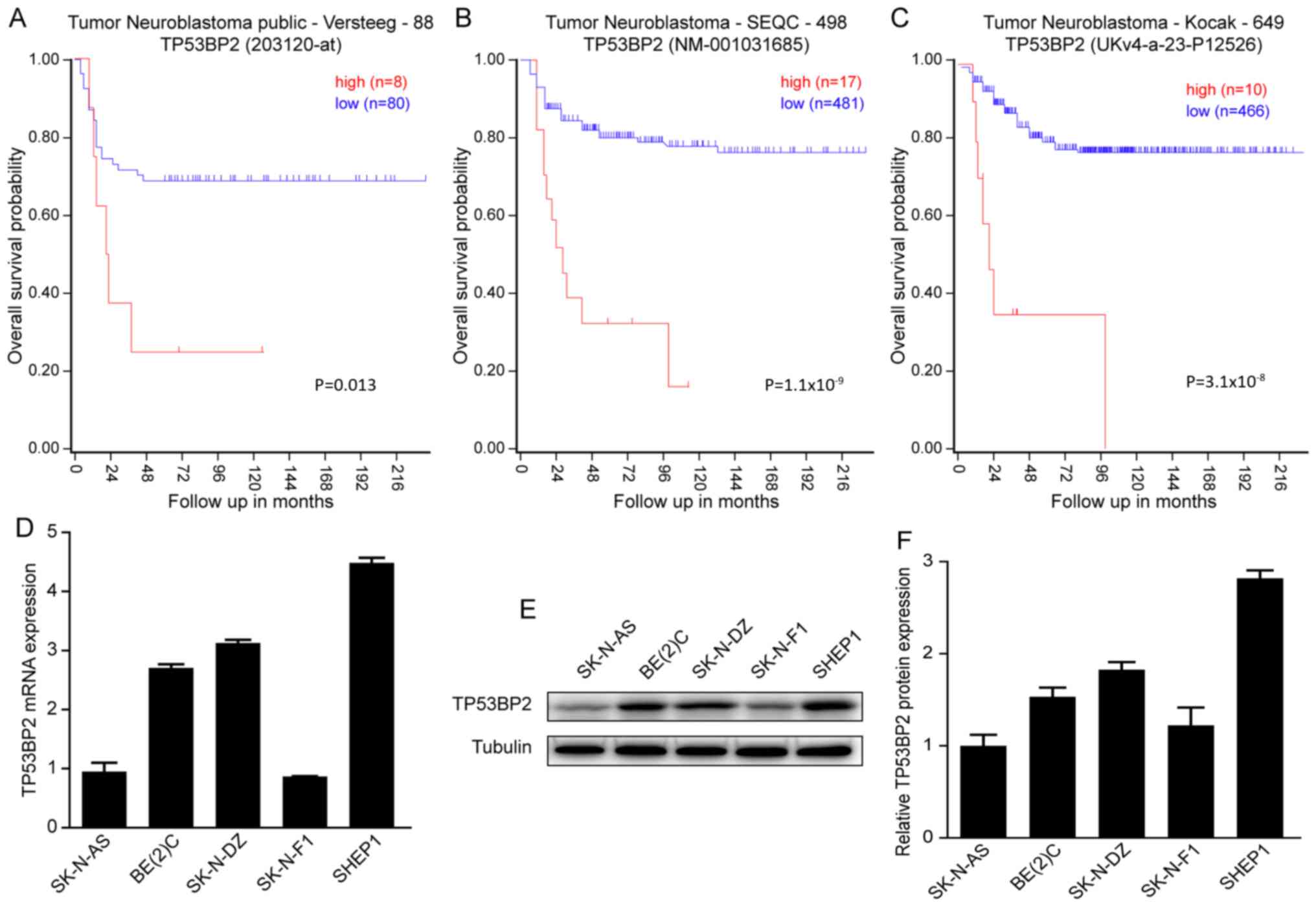
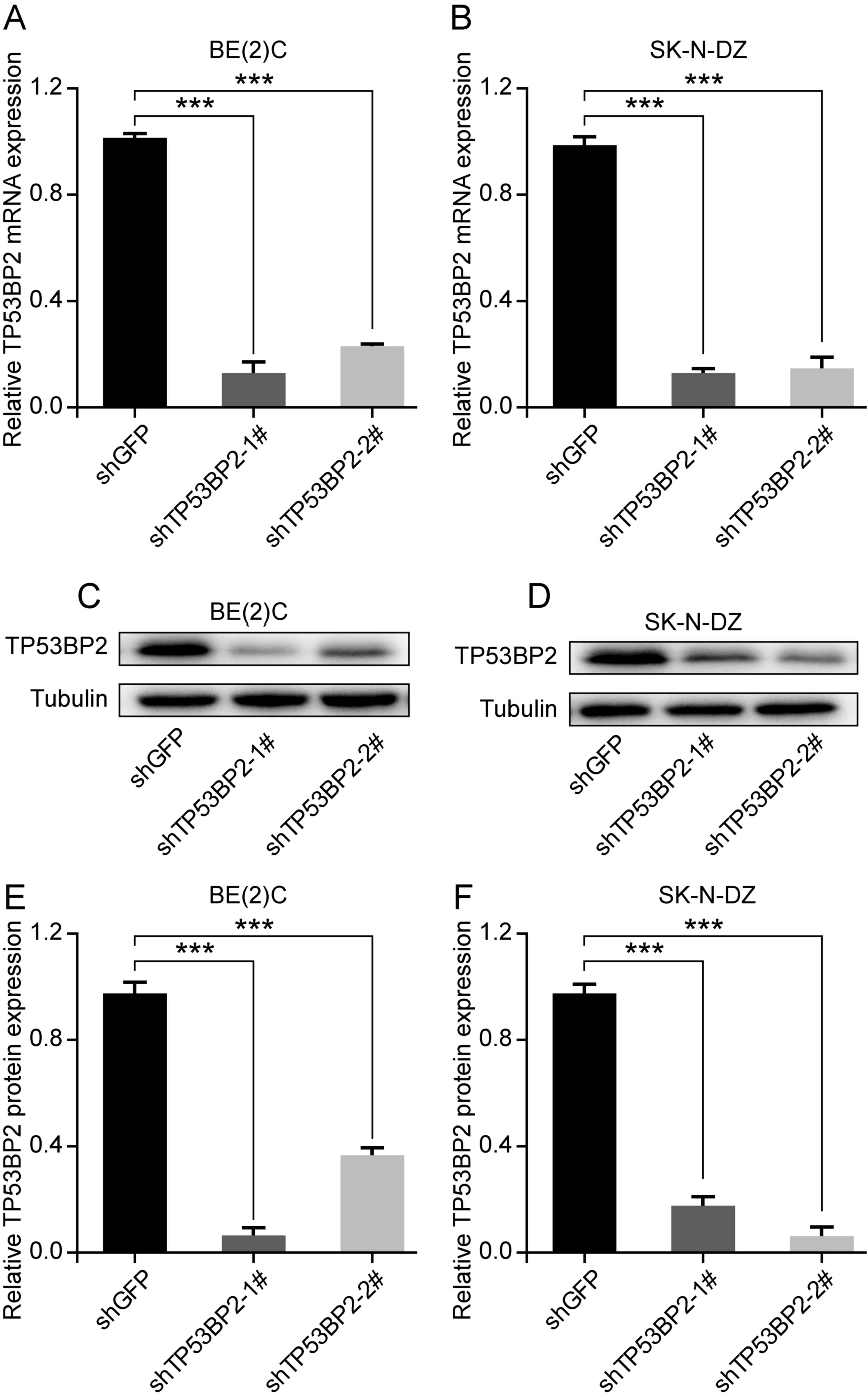
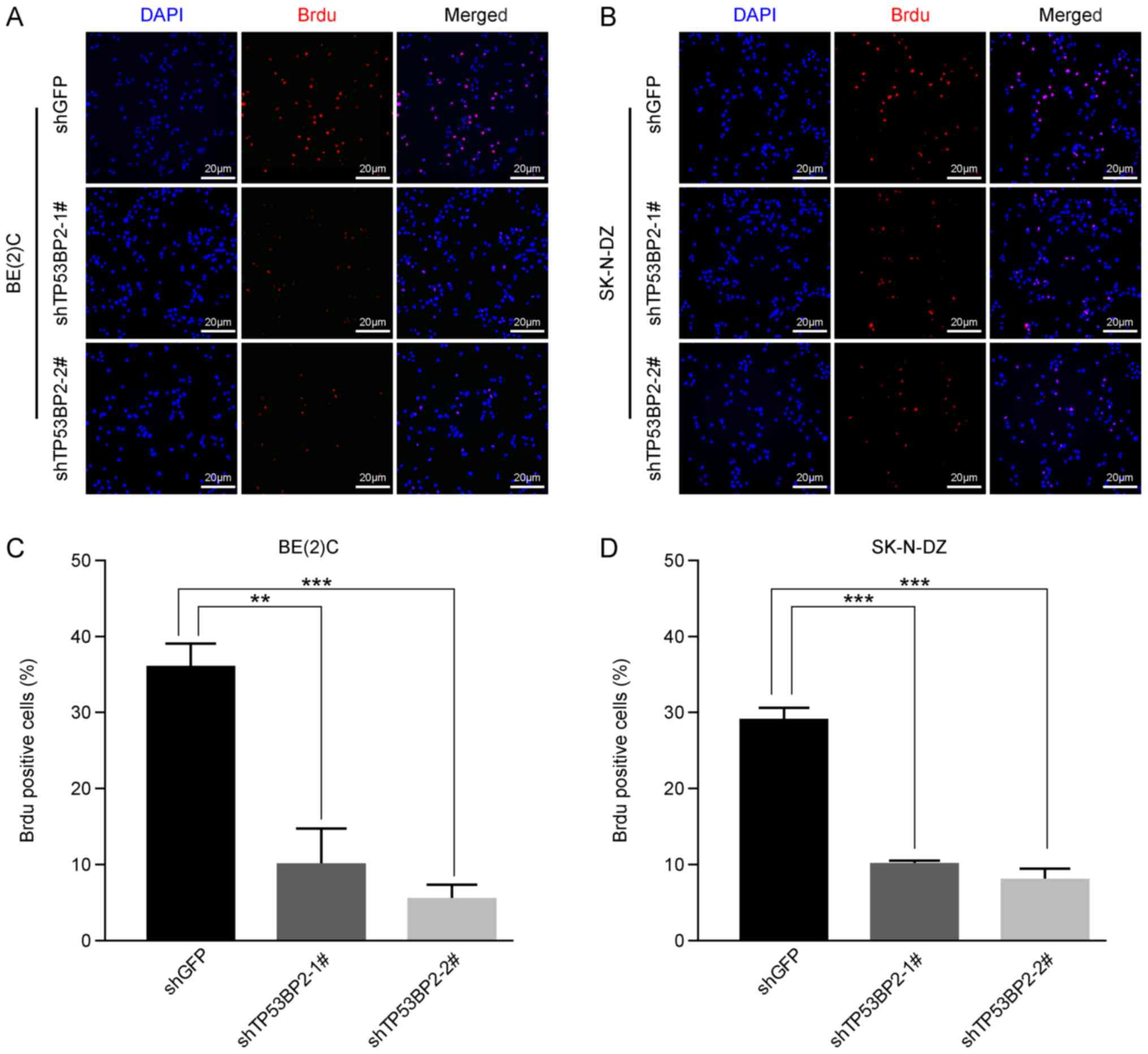
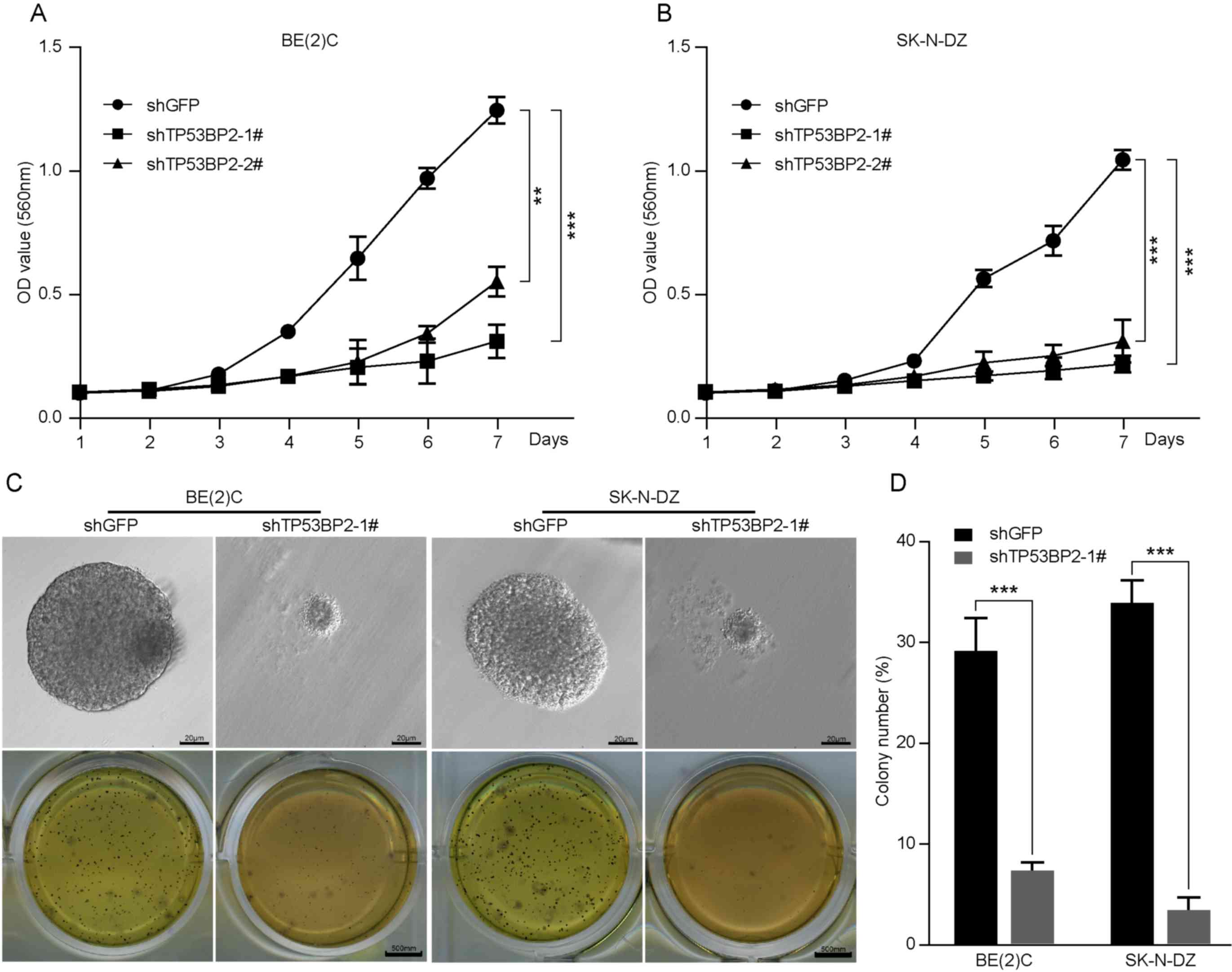
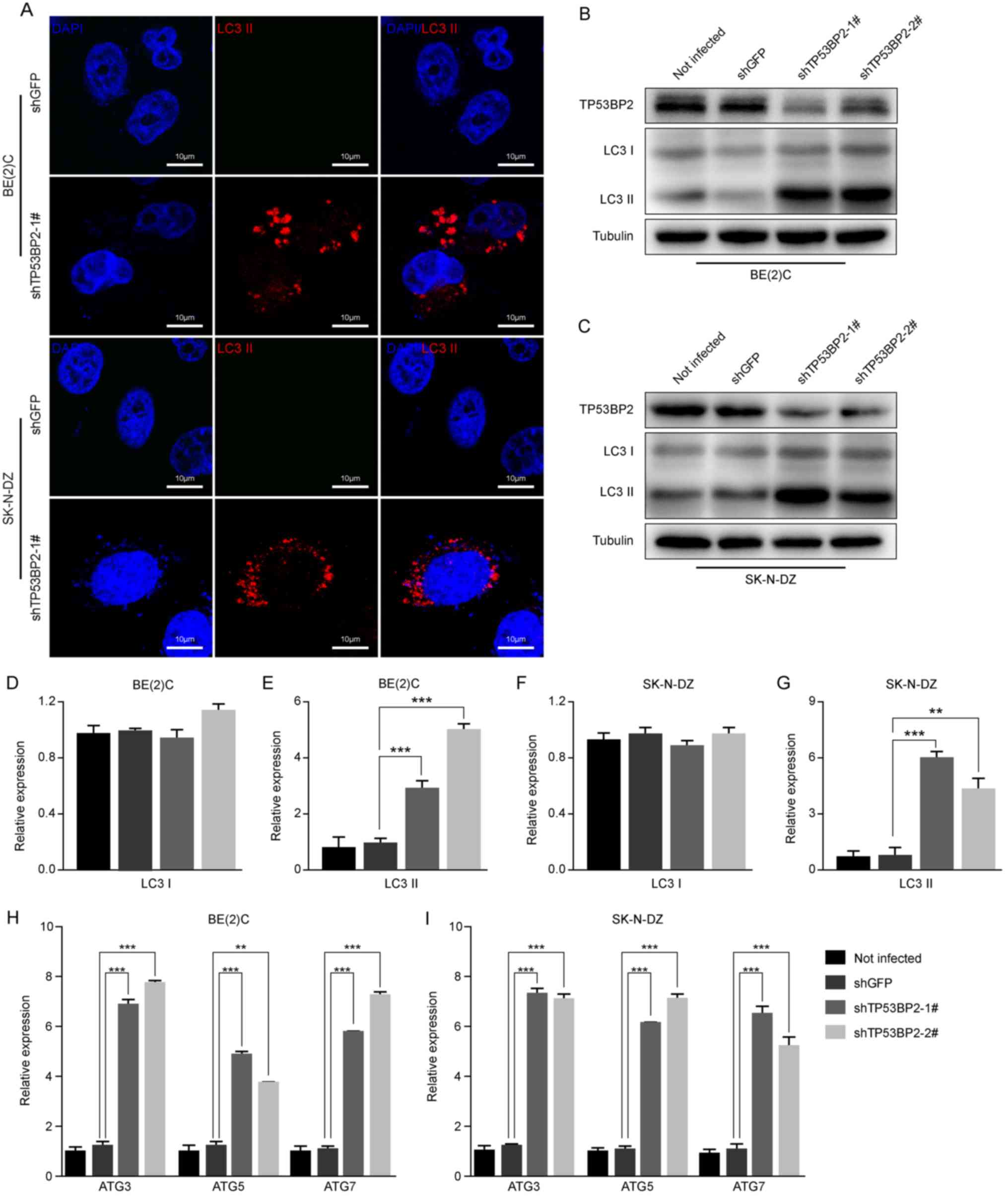
|
1
|
Li T, Cui ZB, Ke XX, Tan J, Li FF, Li T,
Wang XW and Cui HJ: Essential role for p53 and caspase-9 in DNA
damaging drug-induced apoptosis in neuroblastoma IMR32 cells. DNA
Cell Biol. 30:1045–1050. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li T, Wang L, Ke XX, Gong XY, Wan JH, Hao
XW, Xu M, Xiang Z, Cui ZB and Cui H: DNA-damaging drug-induced
apoptosis sensitized by N-myc in neuroblastoma cells. Cell Biol
Int. 36:331–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Askin FB and Perlman EJ: Neuroblastoma and
peripheral neuroectodermal tumors. Am J Clin Pathol. 109 (4 Suppl
1):S23–S30. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shah S and Ravindranath Y: Neuroblastoma.
Indian J Pediatr. 65:691–705. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bessho F: Incidence of neuroblastoma.
Lancet. 353:701999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sridhar S, Al-Moallem B, Kamal H, Terrile
M and Stallings RL: New insights into the genetics of
neuroblastoma. Mol Diagn Ther. 17:63–69. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Beckwith JB and Martin RF: Observations on
the histopathology of neuroblastomas. J Pediatr Surg. 3:106–110.
1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhu S, Yan X, Xiang Z, Ding HF and Cui H:
Leflunomide reduces proliferation and induces apoptosis in
neuroblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e715552013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheung NK and Dyer MA: Neuroblastoma:
Developmental biology, cancer genomics and immunotherapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 13:397–411. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Morgenstern DA, Baruchel S and Irwin MS:
Current and future strategies for relapsed neuroblastoma:
Challenges on the road to precision therapy. J Pediatr Hematol
Oncol. 35:337–347. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu K, Shi Y, Guo X, Wang S, Ouyang Y, Hao
M, Liu D, Qiao L, Li N, Zheng J and Chen D: CHOP mediates
ASPP2-induced autophagic apoptosis in hepatoma cells by releasing
Beclin-1 from Bcl-2 and inducing nuclear translocation of Bcl-2.
Cell Death Dis. 5:e13232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma L, Chen ZM, Li XY, Wang XJ, Shou JX and
Fu XD: Nucleostemin and ASPP2 expression is correlated with
pituitary adenoma proliferation. Oncol Lett. 6:1313–1318. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vives V, Slee EA and Lu X: ASPP2: A gene
that controls life and death in vivo. Cell Cycle. 5:2187–2190.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tordella L, Koch S, Salter V, Pagotto A,
Doondeea JB, Feller SM, Ratnayaka I, Zhong S, Goldin RD, Lozano G,
et al: ASPP2 suppresses squamous cell carcinoma via
RelA/p65-mediated repression of p63. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:17969–17974. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Song Q, Song J, Wang Q, Ma Y, Sun N, Ma J,
Chen Q, Xia G, Huo Y, Yang L and Li B: MiR-548d-3p/TP53BP2 axis
regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of breast cancer cells.
Cancer Med. 5:315–324. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ju H, Lee KA, Yang M, Kim HJ, Kang CP,
Sohn TS, Rhee JC, Kang C and Kim JW: TP53BP2 locus is associated
with gastric cancer susceptibility. Int J Cancer. 117:957–960.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Berardi DE, Campodónico PB, Díaz Bessone
MI, Urtreger AJ and Todaro LB: Autophagy: Friend or foe in breast
cancer development, progression, and treatment. Int J Breast
Cancer. 2011:5950922011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fimia GM, Kroemer G and Piacentini M:
Molecular mechanisms of selective autophagy. Cell Death Differ.
20:1–2. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy: From phenomenology
to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:931–937. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mehrpour M, Esclatine A, Beau I and
Codogno P: Overview of macroautophagy regulation in mammalian
cells. Cell Res. 20:748–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rubinsztein DC, Codogno P and Levine B:
Autophagy modulation as a potential therapeutic target for diverse
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 11:709–730. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mizushima N and Komatsu M: Autophagy:
Renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 147:728–741. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wirawan E, Vanden Berghe T, Lippens S,
Agostinis P and Vandenabeele P: Autophagy: For better or for worse.
Cell Res. 22:43–61. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Levine B, Mizushima N and Virgin HW:
Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature. 469:323–335. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Towers CG and Thorburn A: Therapeutic
targeting of autophagy. EBioMedicine. 14:15–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Han X, Liu JX and Li XZ: Salvianolic acid
B inhibits autophagy and protects starving cardiac myocytes. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 32:38–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Molenaar JJ, Koster J, Zwijnenburg DA, van
Sluis P, Valentijn LJ, van der Ploeg I, Hamdi M, van Nes J,
Westerman BA, van Arkel J, et al: Sequencing of neuroblastoma
identifies chromothripsis and defects in neuritogenesis genes.
Nature. 483:589–593. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang R, Wu Y, Zou J, Zhou J, Wang M, Hao X
and Cui H: The Hippo transducer TAZ promotes cell proliferation and
tumor formation of glioblastoma cells through EGFR pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:36255–36265. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang D, Wang F, Pang Y, Ke XX, Zhu S,
Zhao E, Zhang K, Chen L and Cui H: Down-regulation of CHERP
inhibits neuroblastoma cell proliferation and induces apoptosis
through ER stress induction. Oncotarget. 8:80956–80970.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang L, Huang M, Tan J, Hou J, He J, Wang
F, Cui H and Yi L: Transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding
motif overexpression promotes cell proliferation and
transcriptional co-activator with PDZ-binding motif deficiency
induces cell cycle arrest in neuroblastoma. Oncol Lett.
13:4295–4301. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Agrez MV, Kovach JS and Lieber MM: Cell
aggregates in the soft agar ‘human tumour stem-cell assay’. Br J
Cancer. 46:880–887. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ke XX, Zhang D, Zhu S, Xia Q, Xiang Z and
Cui H: Inhibition of H3K9 methyltransferase G9a repressed cell
proliferation and induced autophagy in neuroblastoma cells. PLoS
One. 9:e1069622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vives V, Su J, Zhong S, Ratnayaka I, Slee
E, Goldin R and Lu X: ASPP2 is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor
that cooperates with p53 to suppress tumor growth. Genes Dev.
20:1262–1267. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Bu F, Royer C, Serres S, Larkin
JR, Soto MS, Sibson NR, Salter V, Fritzsche F, Turnquist C, et al:
ASPP2 controls epithelial plasticity and inhibits metastasis
through β-catenin-dependent regulation of ZEB1. Nat Cell Biol.
16:1092–1104. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Turnquist C, Wang Y, Severson DT, Zhong S,
Sun B, Ma J, Constaninescu SN, Ansorge O, Stolp HB, Molnár Z, et
al: STAT1-induced ASPP2 transcription identifies a link between
neuroinflammation, cell polarity, and tumor suppression. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 111:9834–9839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mai S, Muster B, Bereiter-Hahn J and
Jendrach M: Autophagy proteins LC3B, ATG5 and ATG12 participate in
quality control after mitochondrial damage and influence lifespan.
Autophagy. 8:47–62. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hale AN, Ledbetter DJ, Gawriluk TR and
Rucker EB III: Autophagy: Regulation and role in development.
Autophagy. 9:951–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao H, Yang M, Zhao J, Wang J, Zhang Y
and Zhang Q: High expression of LC3B is associated with progression
and poor outcome in triple-negative breast cancer. Med Oncol.
30:4752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|