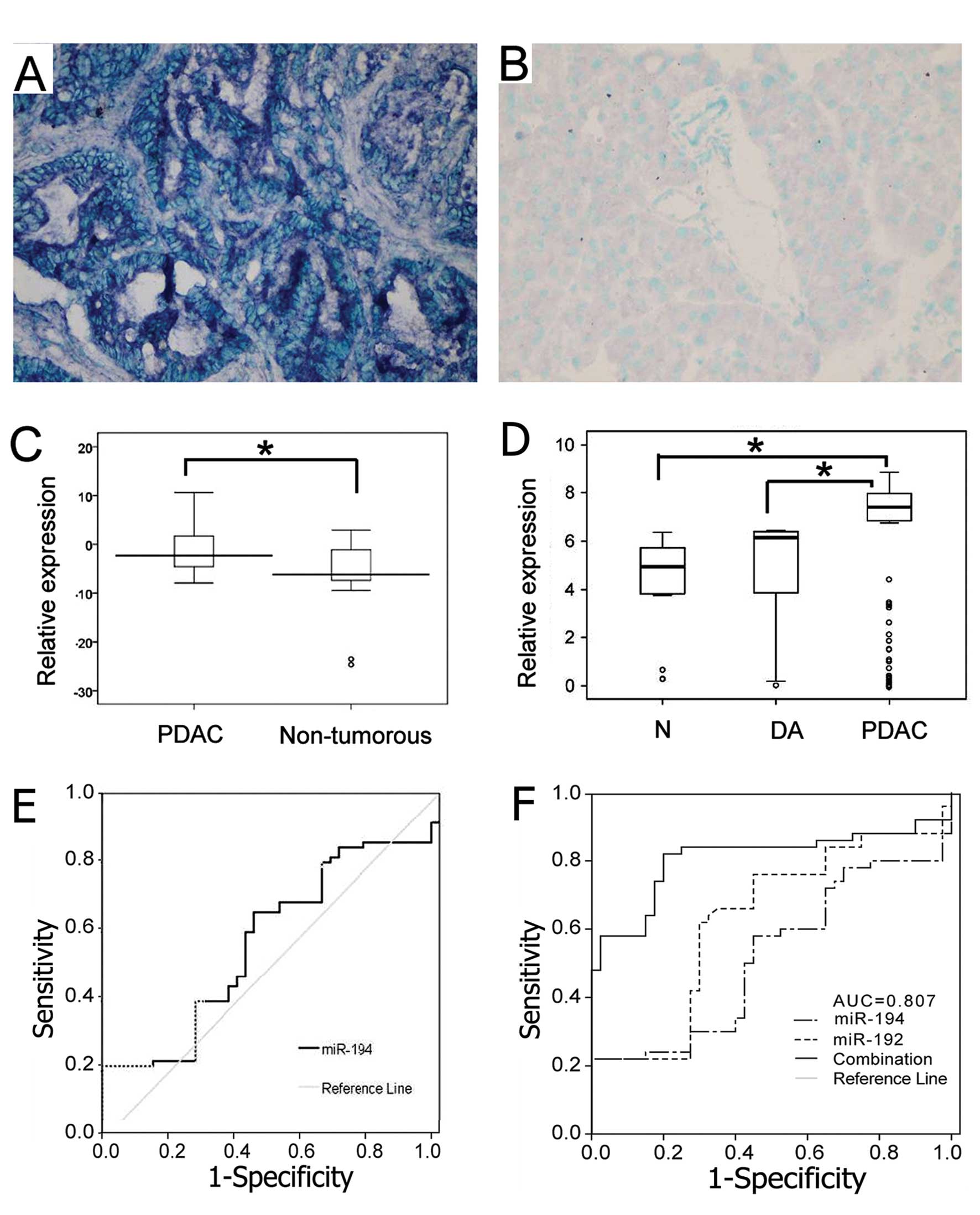
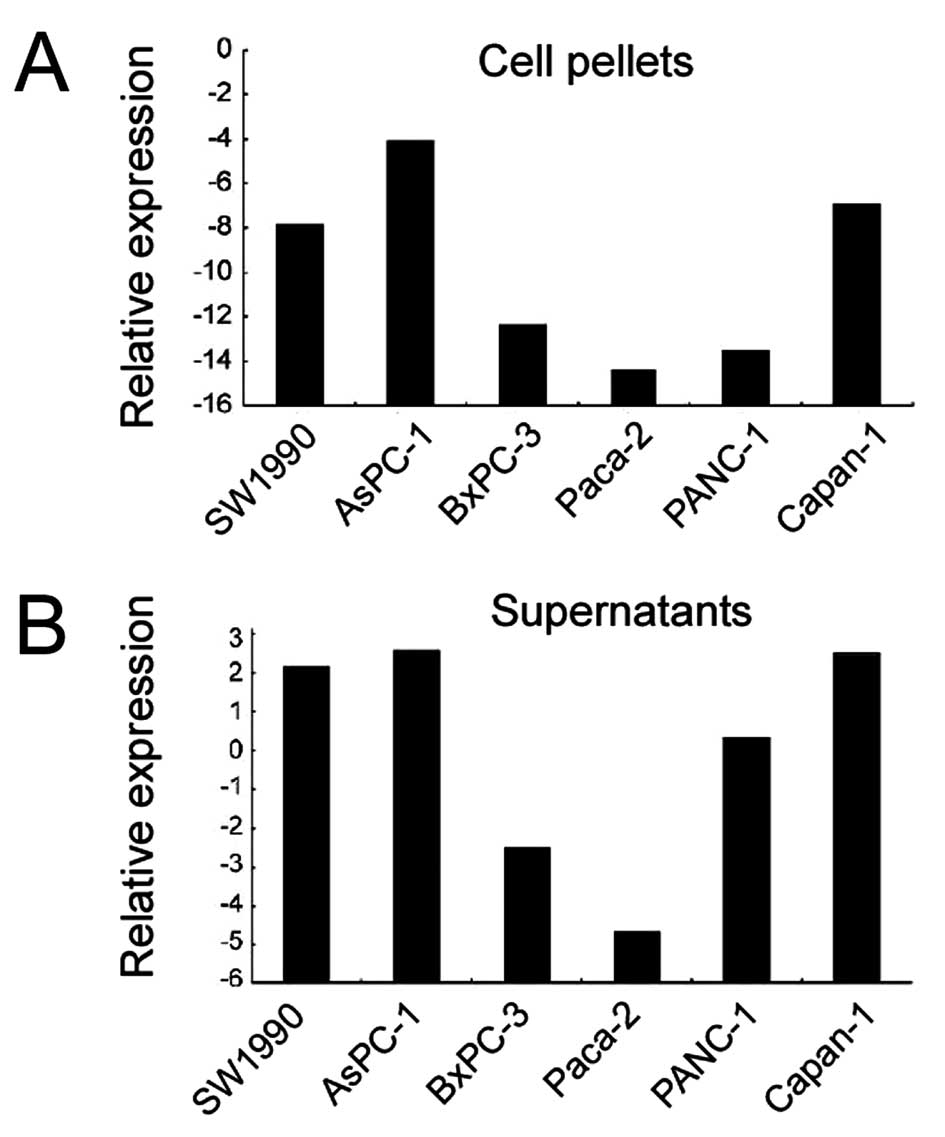
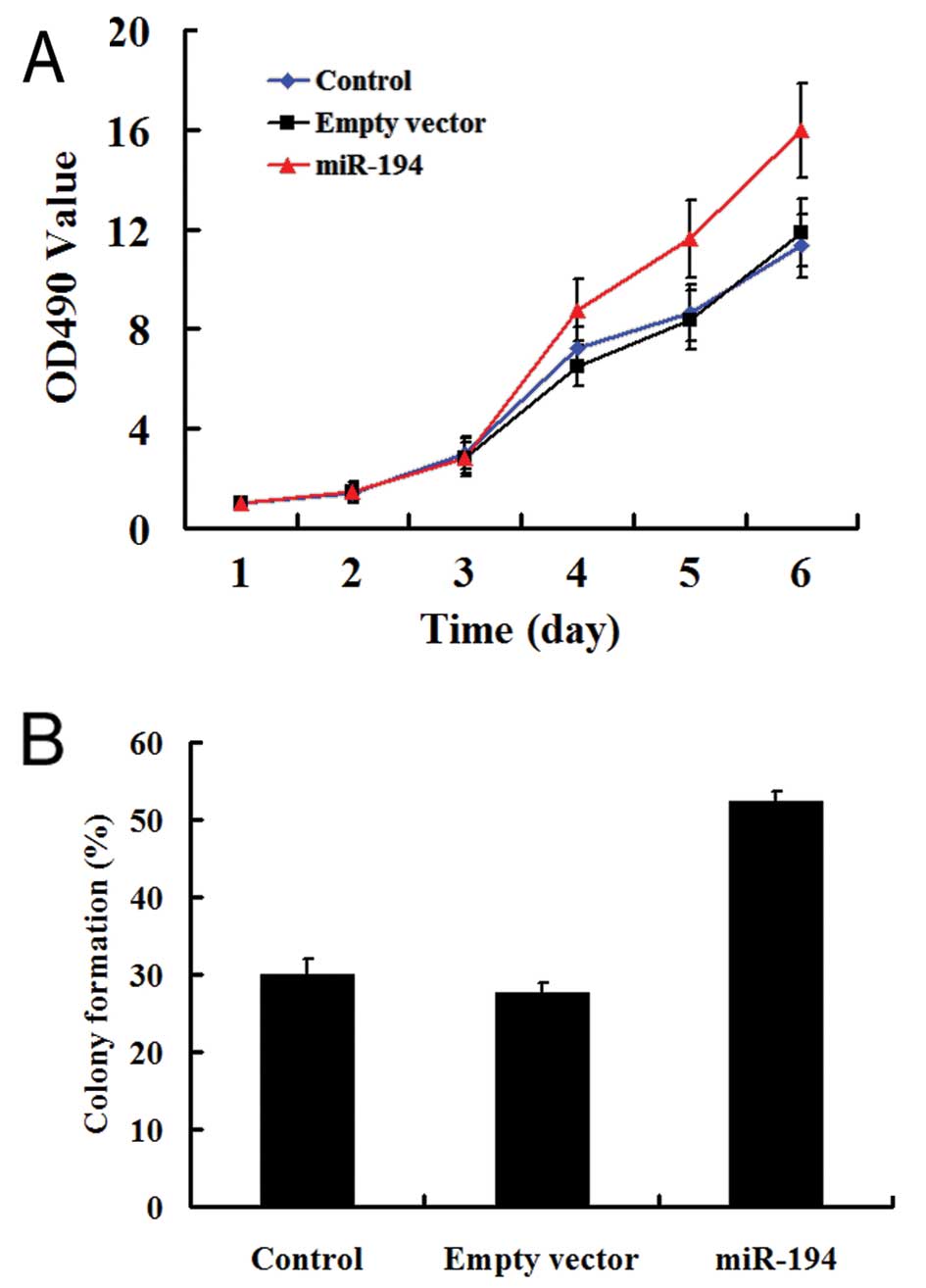
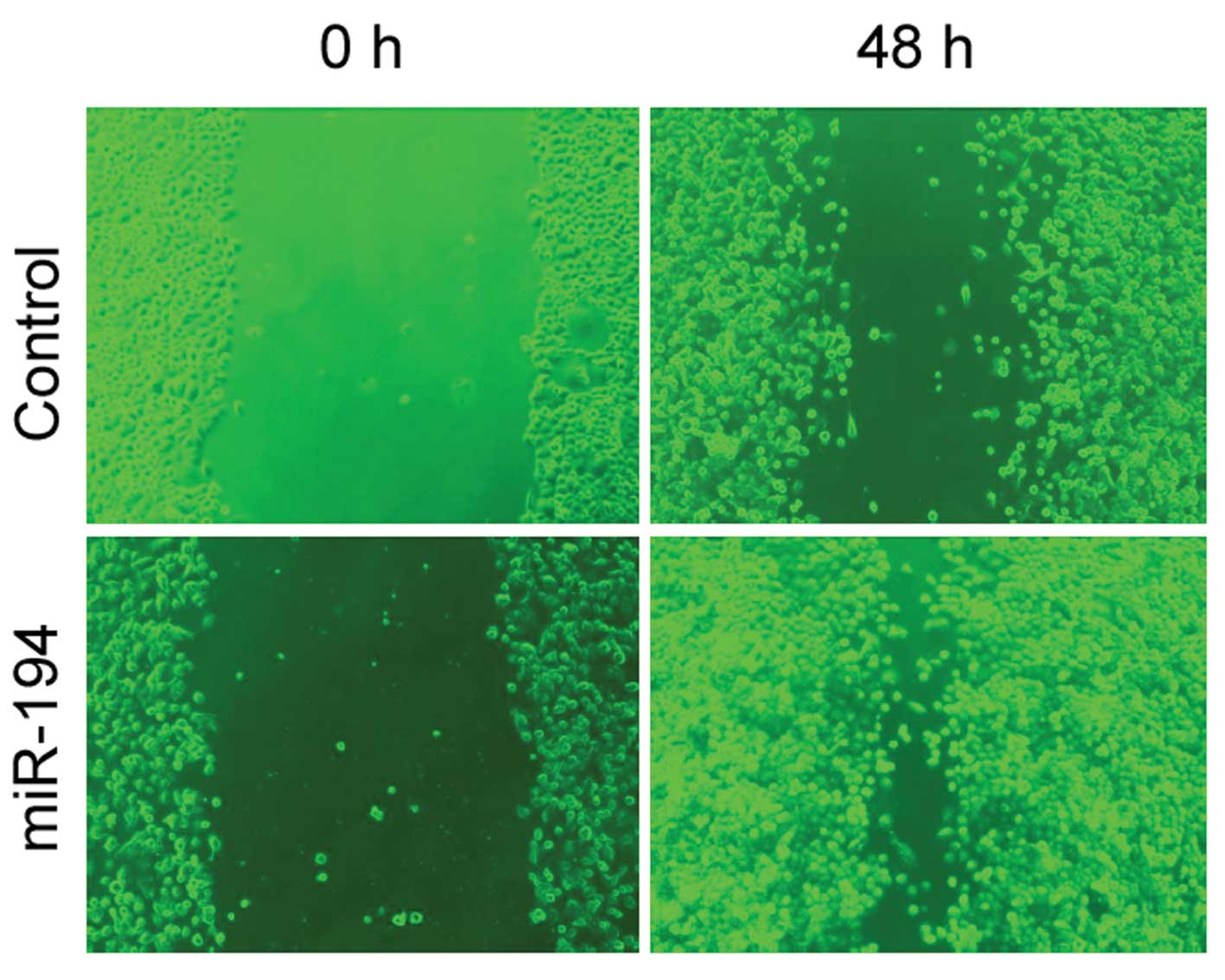
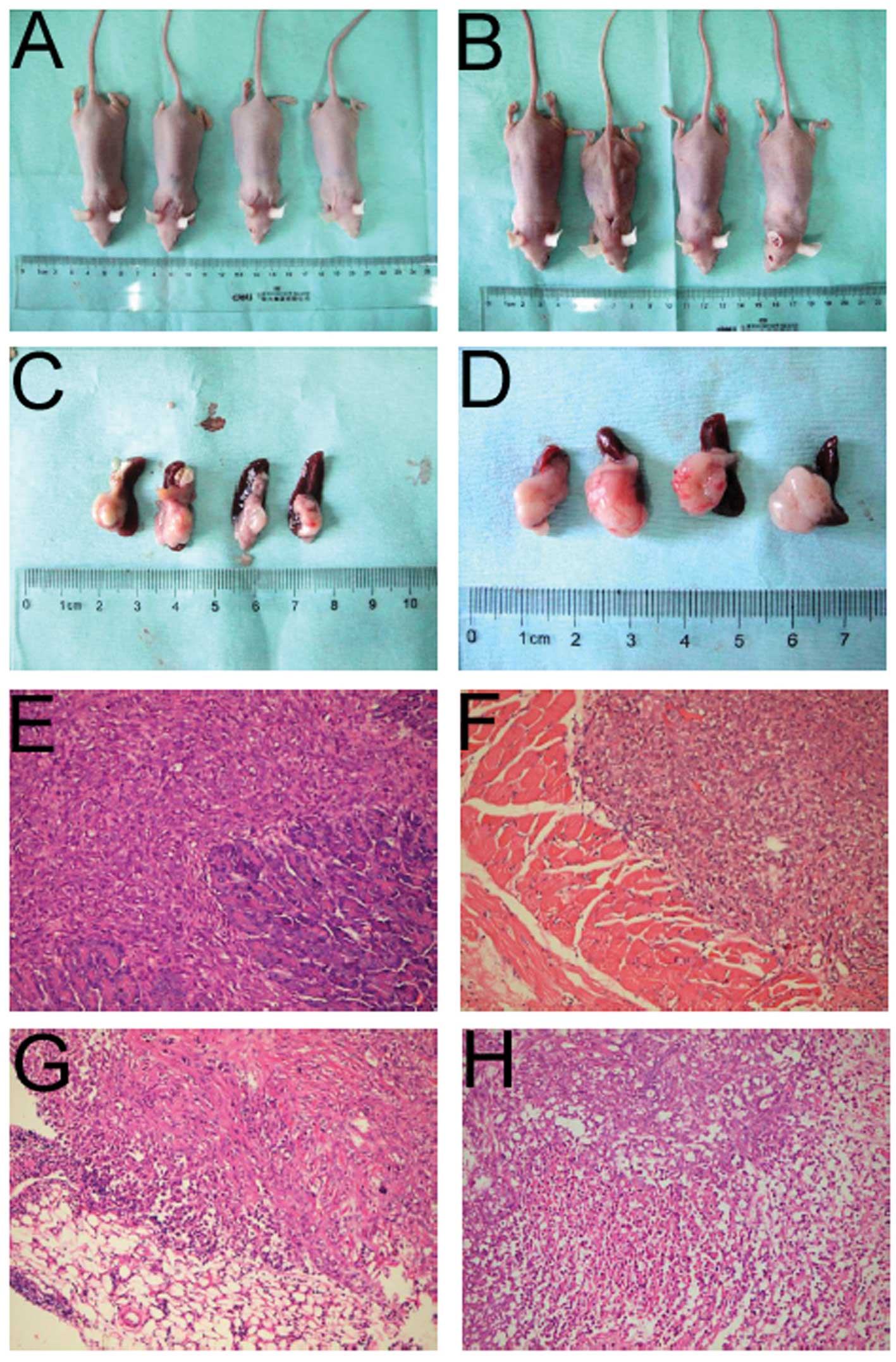
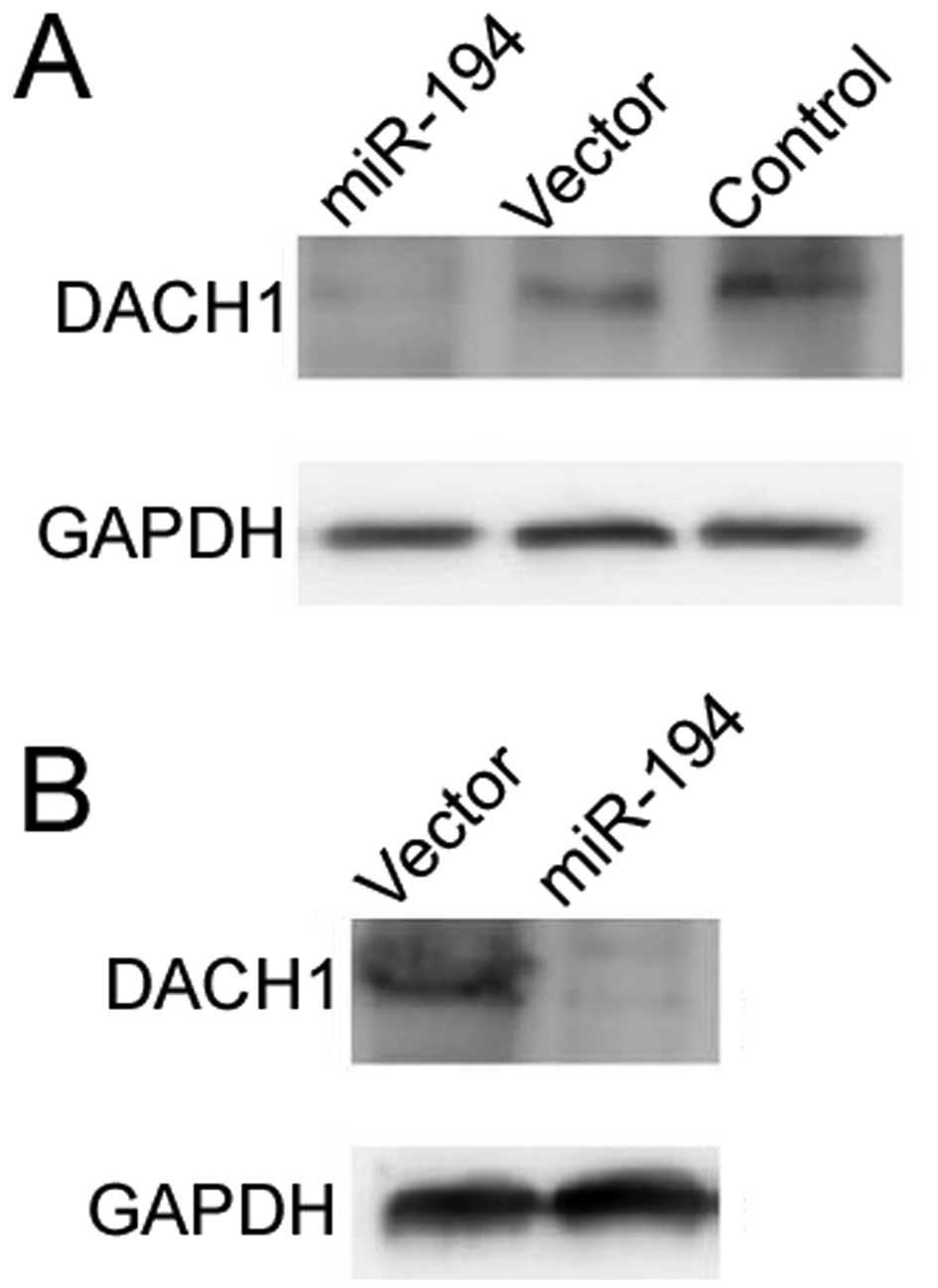
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R and Abbruzzese JL:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 363:1049–1057. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Brand RE and Matamoros A: Imaging
techniques in the evaluation of adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Dig
Dis. 16:242–252. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yates LA, Norbury CJ and Gilbert RJ: The
long and short of microRNA. Cell. 153:516–519. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fabbri M: MicroRNAs and cancer: towards a
personalized medicine. Curr Mol Med. 13:751–756. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ahmed FE: Role of miRNA in carcinogenesis
and biomarker selection: a methodological view. Expert Rev Mol
Diagn. 7:569–603. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cowland JB, Hother C and Grønbaek K:
MicroRNAs and cancer. APMIS. 115:1090–1106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Madhavan D, Cuk K, Burwinkel B and Yang R:
Cancer diagnosis and prognosis decoded by blood-based circulating
microRNA signatures. Front Genet. 4:1162013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liffers ST, Munding JB, Vogt M, et al:
MicroRNA-148a is down-regulated in human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinomas and regulates cell survival by targeting
CDC25B. Lab Invest. 91:1472–1479. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bhatti I, Lee A, James V, et al: Knockdown
of microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation and increases cell death by
targeting programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 15:199–208. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu R, Chen X, Du Y, et al: Serum microRNA
expression profile as a biomarker in the diagnosis and prognosis of
pancreatic cancer. Clin Chem. 58:610–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Munding JB, Adai AT, Maghnouj A, et al:
Global microRNA expression profiling of microdissected tissues
identifies miR-135b as a novel biomarker for pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 131:E86–E95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ekström K, Bossios A, Sjöstrand M, Lee JJ
and Lötvall JO: Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is
a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol.
9:654–659. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao C, Zhang J, Zhang S, et al:
Diagnostic and biological significance of microRNA-192 in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 30:276–284.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rabinowits G, Gerçel-Taylor C, Day JM,
Taylor DD and Kloecker GH: Exosomal microRNA: a diagnostic marker
for lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:42–46. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods.
25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xue Y, Abou Tayoun AN, Abo KM, et al:
MicroRNAs as diagnostic markers for pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and its precursor, pancreatic intraepithelial
neoplasm. Cancer Genet. 206:217–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kawaguchi T, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, et al:
Clinical impact of circulating miR-221 in plasma of patients with
pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 108:361–369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Giovannetti E, van der Velde A, Funel N,
et al: High-throughput microRNA (miRNAs) arrays unravel the
prognostic role of miR-211 in pancreatic cancer. PLoS One.
7:e491452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mees ST, Mardin WA, Wendel C, et al: EP300
- a miRNA-regulated metastasis suppressor gene in ductal
adenocarcinomas of the pancreas. Int J Cancer. 126:114–124. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Yoshioka Y, Takeshita
F, Matsuki Y and Ochiya T: Secretory mechanisms and intercellular
transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J Biol Chem.
285:17442–17452. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, et al:
Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:10513–10518. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Redova M, Poprach A, Nekvindova J, et al:
Circulating miR-378 and miR-451 in serum are potential biomarkers
for renal cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 10:552012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang J, Chen J, Chang P, et al: MicroRNAs
in plasma of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients as novel
blood-based biomarkers of disease. Cancer Prev Res. 2:807–813.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Khella HW, Bakhet M, Allo G, et al:
miR-192, miR-194 and miR-215: a convergent microRNA network
suppressing tumor progression in renal cell carcinoma.
Carcinogenesis. 34:2231–2239. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Meng Z, Fu X, Chen X, et al: miR-194 is a
marker of hepatic epithelial cells and suppresses metastasis of
liver cancer cells in mice. Hepatology. 52:2148–2157. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iizuka D, Imaoka T, Nishimura M, Kawai H,
Suzuki F and Shimada Y: Aberrant microRNA expression in
radiation-induced rat mammary cancer: the potential role of miR-194
overexpression in cancer cell proliferation. Radiat Res.
179:151–159. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sundaram P, Hultine S, Smith LM, et al:
p53-responsive miR-194 inhibits thrombospondin-1 and promotes
angiogenesis in colon cancers. Cancer Res. 71:7490–7501. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Popov VM, Zhou J, Shirley LA, et al: The
cell fate determination factor DACH1 is expressed in estrogen
receptor-α-positive breast cancer and represses estrogen receptor-α
signaling. Cancer Res. 69:5752–5760. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Watanabe A, Ogiwara H, Ehata S, et al:
Homozygously deleted gene DACH1 regulates tumor-initiating activity
of glioma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:12384–12389. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu K, Katiyar S, Witkiewicz A, et al: The
cell fate determination factor dachshund inhibits androgen receptor
signaling and prostate cancer cellular growth. Cancer Res.
69:3347–3355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|