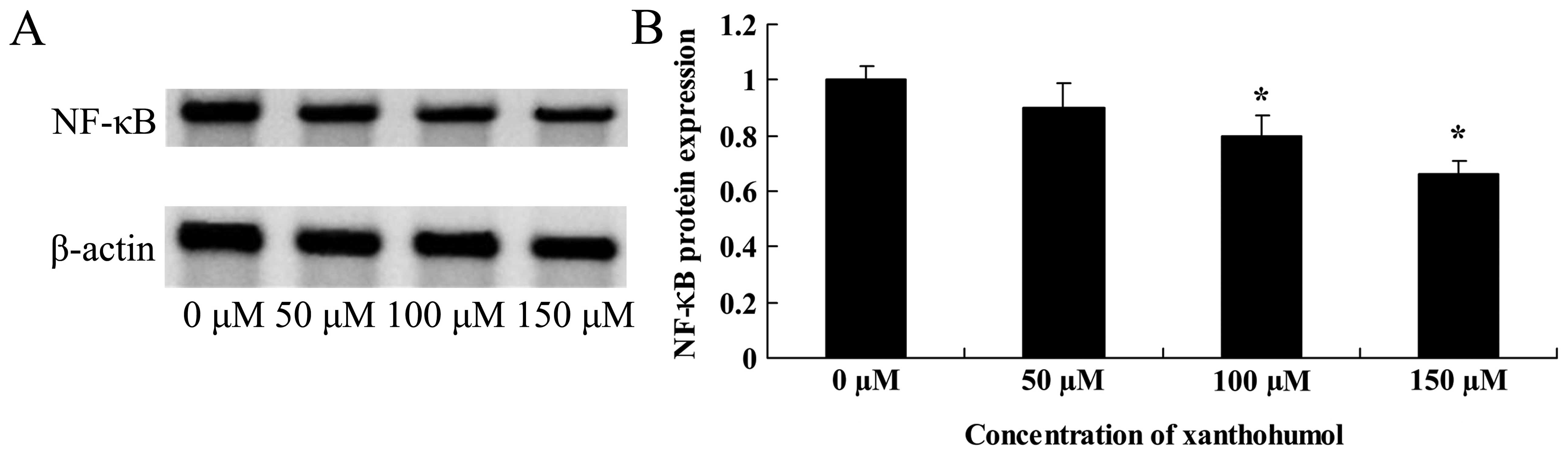
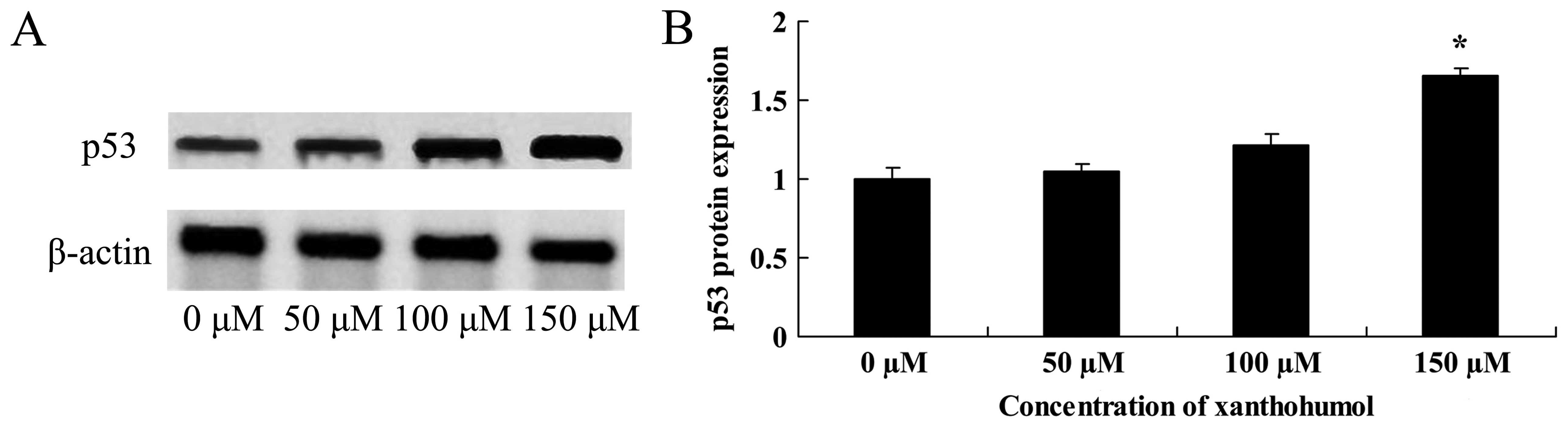
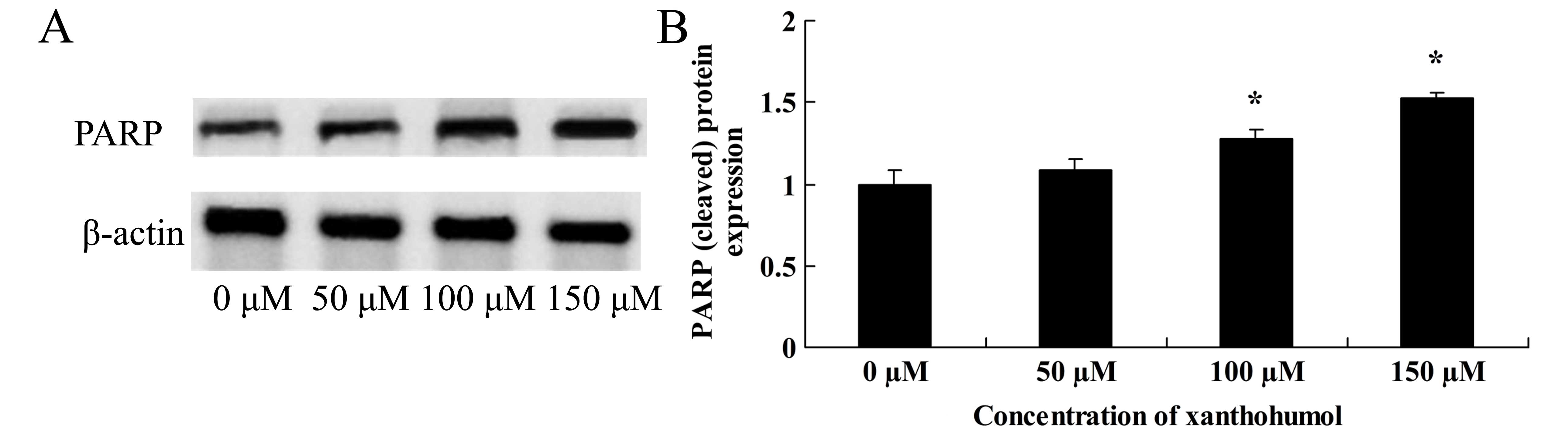
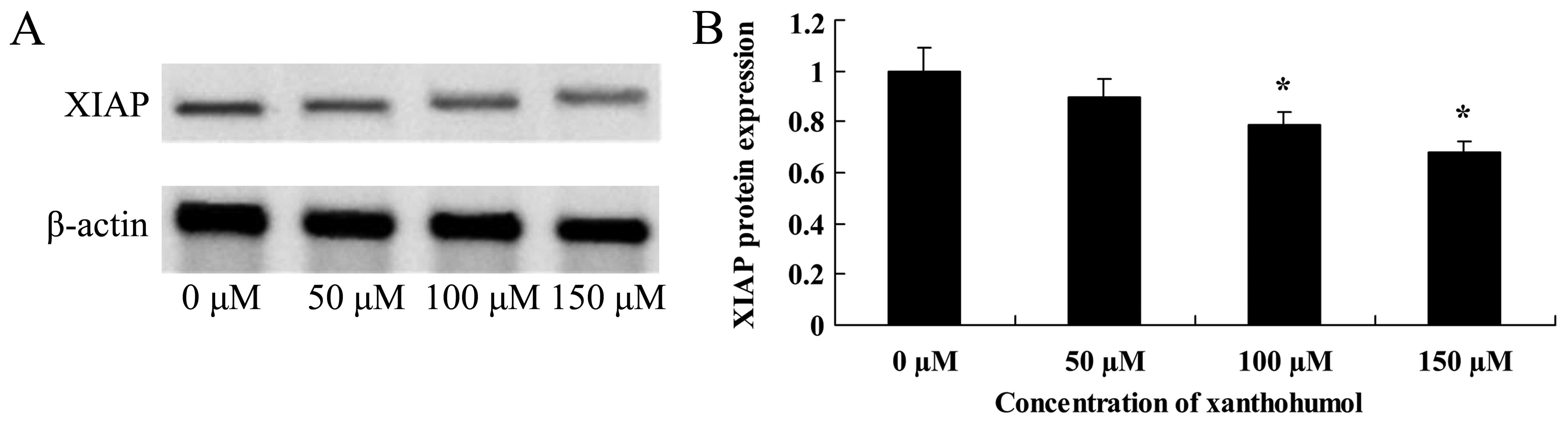
|
1
|
Bárcena C, Stefanovic M, Tutusaus A,
Martinez-Nieto GA, Martinez L, García-Ruiz C, de Mingo A,
Caballeria J, Fernandez-Checa JC, Marí M, et al: Angiogenin
secretion from hepatoma cells activates hepatic stellate cells to
amplify a self-sustained cycle promoting liver cancer. Sci Rep.
5:79162015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin CL, Chien RN, Yeh C, Hsu CW, Chang ML,
Chen YC and Yeh CT: Significant renoprotective effect of
telbivudine during preemptive antiviral therapy in advanced liver
cancer patients receiving cisplatin-based chemotherapy: A
case-control study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 49:1456–1464. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iwazawa J, Ohue S, Hashimoto N, Muramoto O
and Mitani T: Clinical utility and limitations of tumor-feeder
detection software for liver cancer embolization. Eur J Radiol.
82:1665–1671. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Padhy AK and Dondi M: A report on the
implementation aspects of the International Atomic Energy Agency's
first doctoral coordinated research project, 'Management of liver
cancer using radionuclide methods with special emphasis on
trans-arterial radio-conjugate therapy and internal dosimetry'.
Semin Nucl Med. 38:S5–S12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nagel D, Vincendeau M, Eitelhuber AC and
Krappmann D: Mechanisms and consequences of constitutive NF-κB
activation in B-cell lymphoid malignancies. Oncogene. 33:5655–5665.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wan S, Pestka S, Jubin RG, Lyu YL, Tsai YC
and Liu LF: Chemotherapeutics and radiation stimulate MHC class I
expression through elevated interferon-beta signaling in breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e325422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chaturvedi MM, Sung B, Yadav VR, Kannappan
R and Aggarwal BB: NF-κB addiction and its role in cancer: 'one
size does not fit all'. Oncogene. 30:1615–1630. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Athar M, Back JH, Kopelovich L, Bickers DR
and Kim AL: Multiple molecular targets of resveratrol:
Anti-carcinogenic mechanisms. Arch Biochem Biophys. 486:95–102.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Venè R, Benelli R, Minghelli S, Astigiano
S, Tosetti F and Ferrari N: Xanthohumol impairs human prostate
cancer cell growth and invasion and diminishes the incidence and
progression of advanced tumors in TRAMP mice. Mol Med.
18:1292–1302. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yoshimaru T, Komatsu M, Tashiro E, Imoto
M, Osada H, Miyoshi Y, Honda J, Sasa M and Katagiri T: Xanthohumol
suppresses oestrogen-signalling in breast cancer through the
inhibition of BIG3-PHB2 interactions. Sci Rep. 4:73552014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chie WC, Blazeby JM, Hsiao CF, Chiu HC,
Poon RT, Mikoshiba N, Al-Kadhimi G, Heaton N, Calara J, Collins P,
et al: EORTC Quality of Life Group: International cross-cultural
field validation of an European Organization for Research and
Treatment of Cancer questionnaire module for patients with primary
liver cancer, the European Organization for Research and Treatment
of Cancer quality-of-life questionnaire HCC18. Hepatology.
55:1122–1129. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yong WK and Abd Malek SN: Xanthohumol
induces growth inhibition and apoptosis in ca ski human cervical
cancer cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:9213062015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
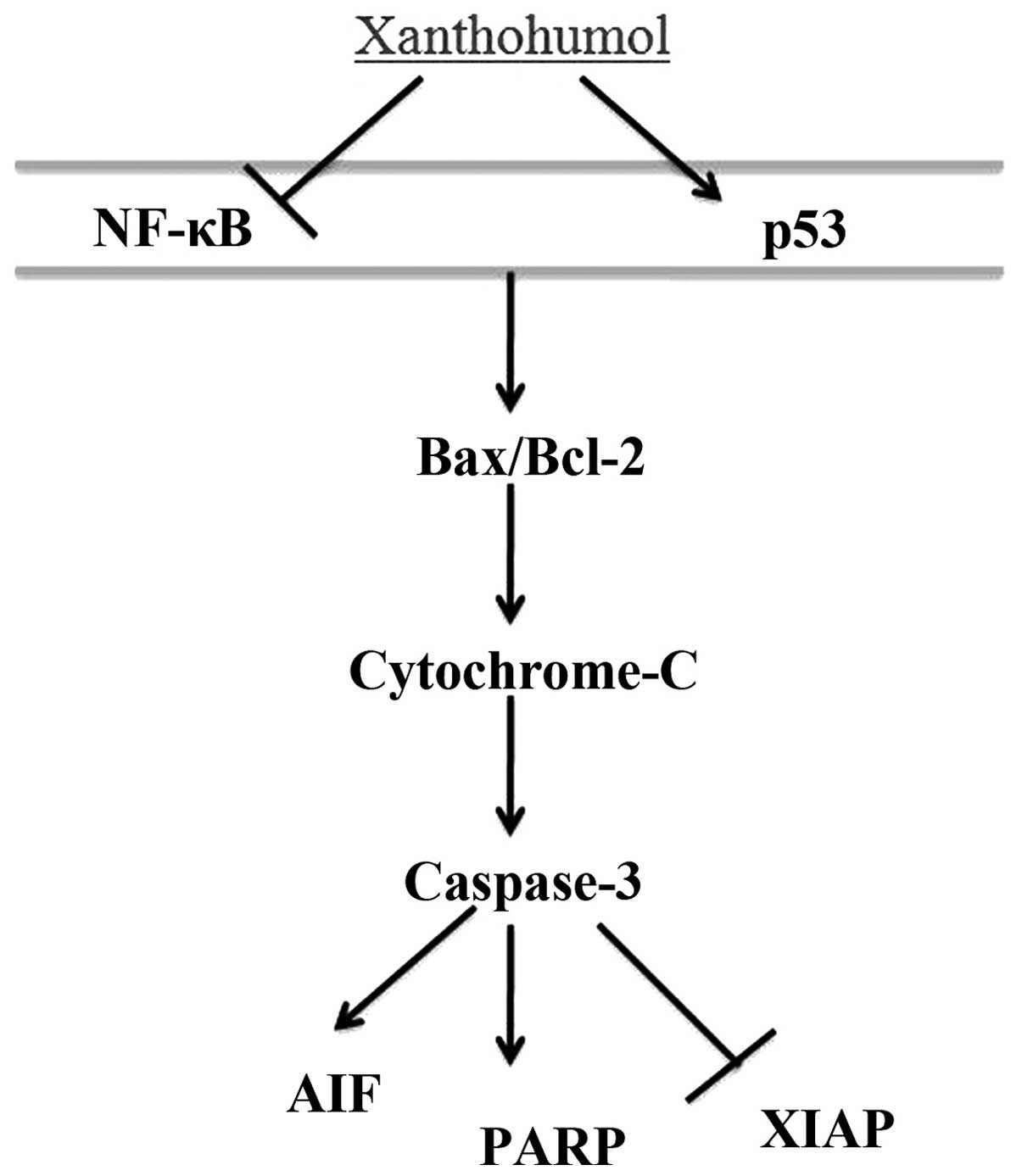
Dey A, Tergaonkar V and Lane DP:
Double-edged swords as cancer therapeutics: Simultaneously
targeting p53 and NF-kappaB pathways. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
7:1031–1040. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chariot A: The NF-kappaB-independent
functions of IKK subunits in immunity and cancer. Trends Cell Biol.
19:404–413. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johnson RF and Perkins ND: Nuclear
factor-κB, p53, and mitochondria: Regulation of cellular metabolism
and the Warburg effect. Trends Biochem Sci. 37:317–324. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He XX, Zhang YN, Yan JW, Yan JJ, Wu Q and
Song YH: CP-31398 inhibits the growth of p53-mutated liver cancer
cells in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol. Aug 7–2015.Epub ahead of
print.
|
|
17
|
Zhang X, Zhang H and Ye L: Effects of
hepatitis B virus X protein on the development of liver cancer. J
Lab Clin Med. 147:58–66. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dell'Eva R, Ambrosini C, Vannini N,
Piaggio G, Albini A and Ferrari N: AKT/NF-kappaB inhibitor
xanthohumol targets cell growth and angiogenesis in hematologic
malignancies. Cancer. 110:2007–2011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kulkarni A, Oza J, Yao M, Sohail H,
Ginjala V, Tomas-Loba A, Horejsi Z, Tan AR, Boulton SJ and Ganesan
S: Tripartite Motif-containing 33 (TRIM33) protein functions in the
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP)-dependent DNA damage response
through interaction with Amplified in Liver Cancer 1 (ALC1)
protein. J Biol Chem. 288:32357–32369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Booth L, Cruickshanks N, Ridder T, Dai Y,
Grant S and Dent P: PARP and CHK inhibitors interact to cause DNA
damage and cell death in mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther.
14:458–465. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ciccarone F, Klinger FG, Catizone A,
Calabrese R, Zampieri M, Bacalini MG, De Felici M and Caiafa P:
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation acts in the DNA demethylation of mouse
primordial germ cells also with DNA damage-independent roles. PLoS
One. 7:e469272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Drenzek JG, Seiler NL, Jaskula-Sztul R,
Rausch MM and Rose SL: Xanthohumol decreases Notch1 expression and
cell growth by cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis in
epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines. Gynecol Oncol. 122:396–401.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
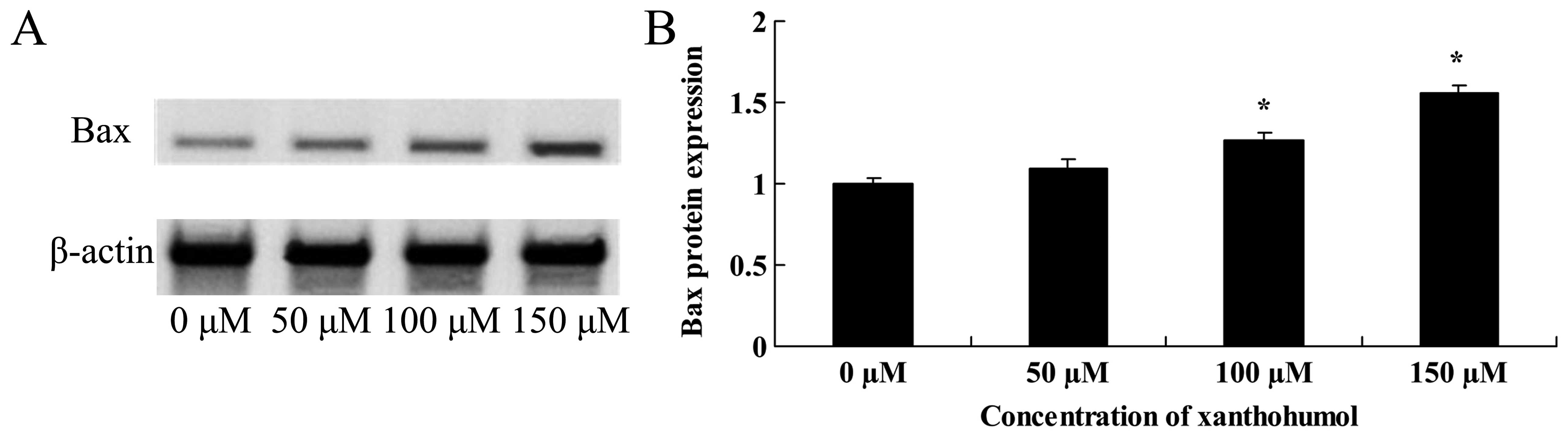
Hehlgans S, Petraki C, Reichert S, Cordes
N, Rödel C and Rödel F: Double targeting of Survivin and XIAP
radiosensitizes 3D grown human colorectal tumor cells and decreases
migration. Radiother Oncol. 108:32–39. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Srivastava AK, Singh PK, Singh D, Dalela
D, Rath SK, Goel MM and Bhatt ML: Evaluation of urinary XIAP as a
diagnostic biomarker of carcinoma of urinary bladder. Tumour Biol.
35:8243–8248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee FA, Zee BC, Cheung FY, Kwong P, Chiang
CL, Leung KC, Siu SW, Lee C, Lai M, Kwok C, et al: Randomized phase
II study of the X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) antisense
AEG35156 in combination with sorafenib in patients with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Am J Clin Oncol. Jun 23–2014.Epub
ahead of print.
|
|
26
|
Lewis EM, Wilkinson AS, Davis NY, Horita
DA and Wilkinson JC: Nondegradative ubiquitination of apoptosis
inducing factor (AIF) by X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis at a
residue critical for AIF-mediated chromatin degradation.
Biochemistry. 50:11084–11096. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
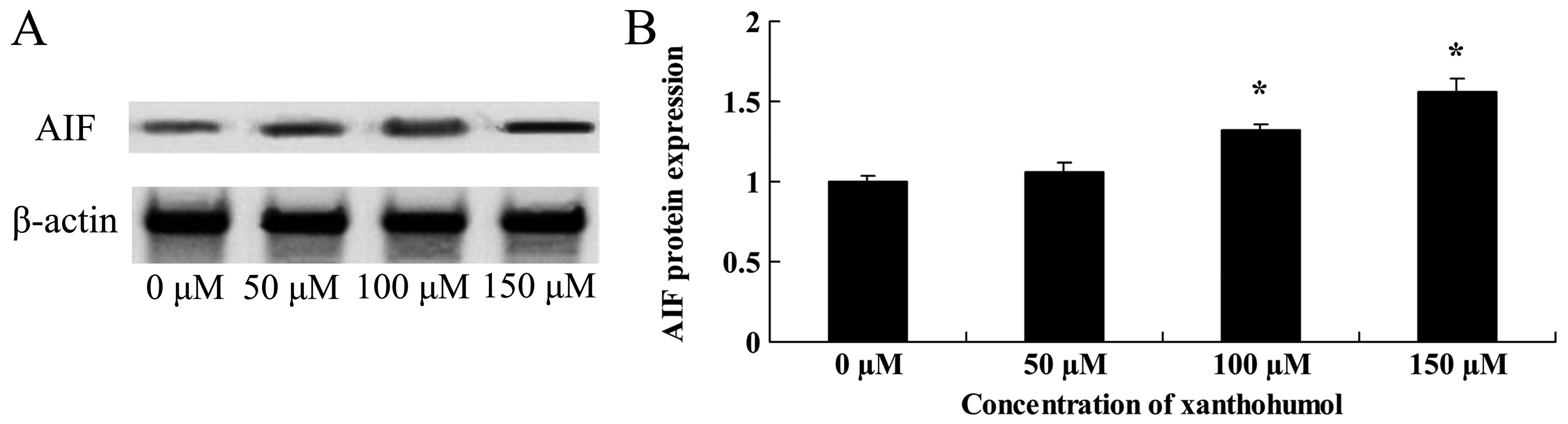
27
|
Mendivil-Perez M, Velez-Pardo C and
Jimenez-Del-Rio M: TPEN induces apoptosis independently of zinc
chelator activity in a model of acute lymphoblastic leukemia and ex
vivo acute leukemia cells through oxidative stress and mitochondria
caspase-3- and AIF-dependent pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2012:3132752012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Park SY, Kim HY, Lee JH, Yoon KH, Chang MS
and Park SK: The age-dependent induction of apoptosis-inducing
factor (AIF) in the human semitendinosus skeletal muscle. Cell Mol
Biol Lett. 15:1–12. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Doti N, Reuther C, Scognamiglio PL, Dolga
AM, Plesnila N, Ruvo M and Culmsee C: Inhibition of the AIF/CypA
complex protects against intrinsic death pathways induced by
oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 5:e9932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Festa M, Capasso A, D'Acunto CW, Masullo
M, Rossi AG, Pizza C and Piacente S: Xanthohumol induces apoptosis
in human malignant glioblastoma cells by increasing reactive oxygen
species and activating MAPK pathways. J Nat Prod. 74:2505–2513.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|