|
1
|
Albores-Saavedra J, Schwartz AM, Batich K
and Henson DE: Cancers of the ampulla of vater: Demographics,
morphology, and survival based on 5,625 cases from the SEER
program. J Surg Oncol. 100:598–605. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsuei J, Chau T, Mills D and Wan YJ: Bile
acid dysregulation, gut dysbiosis, and gastrointestinal cancer. Exp
Biol Med. 239:1489–1504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ye W, Chow WH, Lagergren J, Yin L and
Nyrén O: Risk of adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastric
cardia in patients with gastroesophageal reflux diseases and after
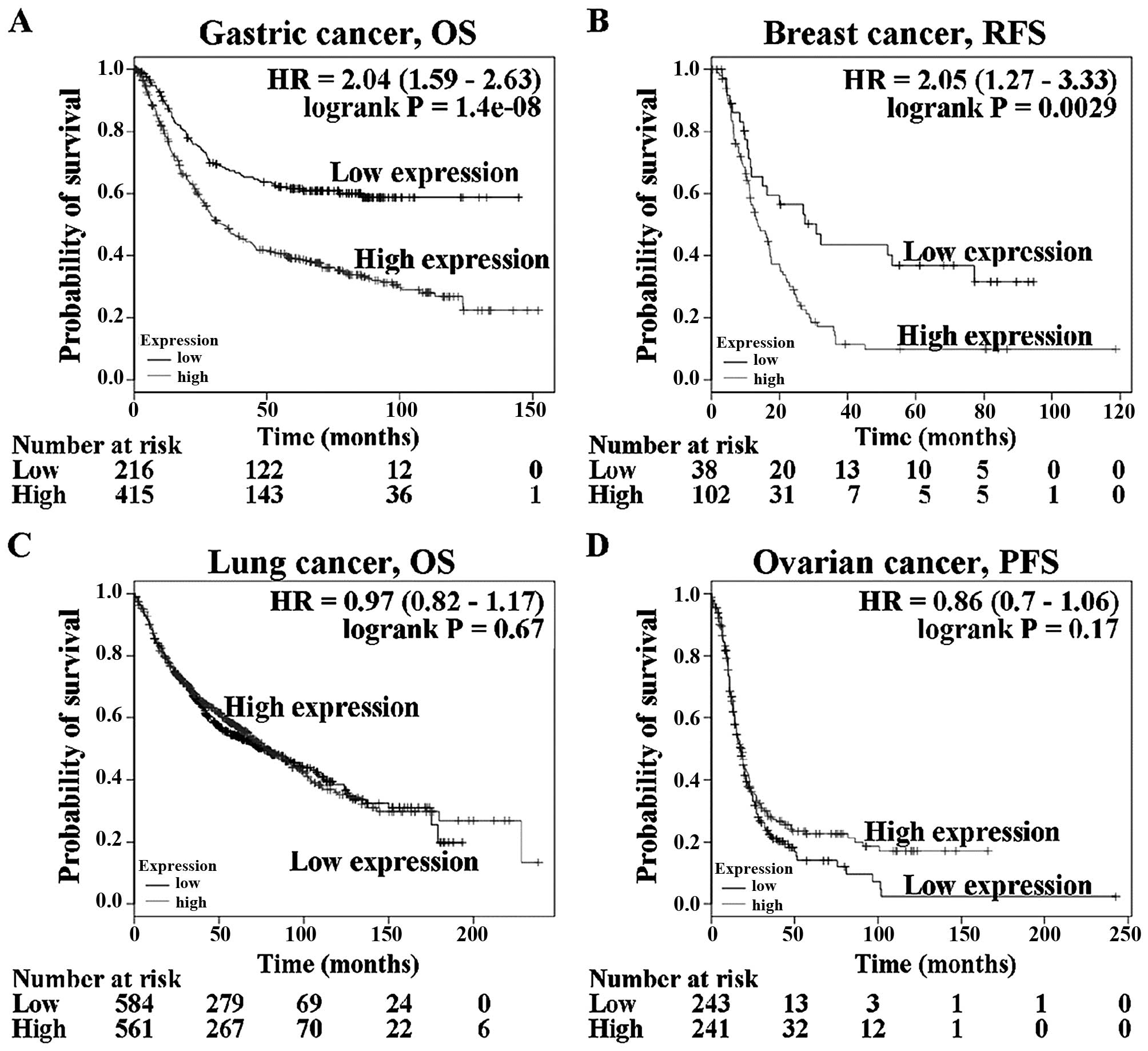
antireflux surgery. Gastroenterology. 121:1286–1293. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
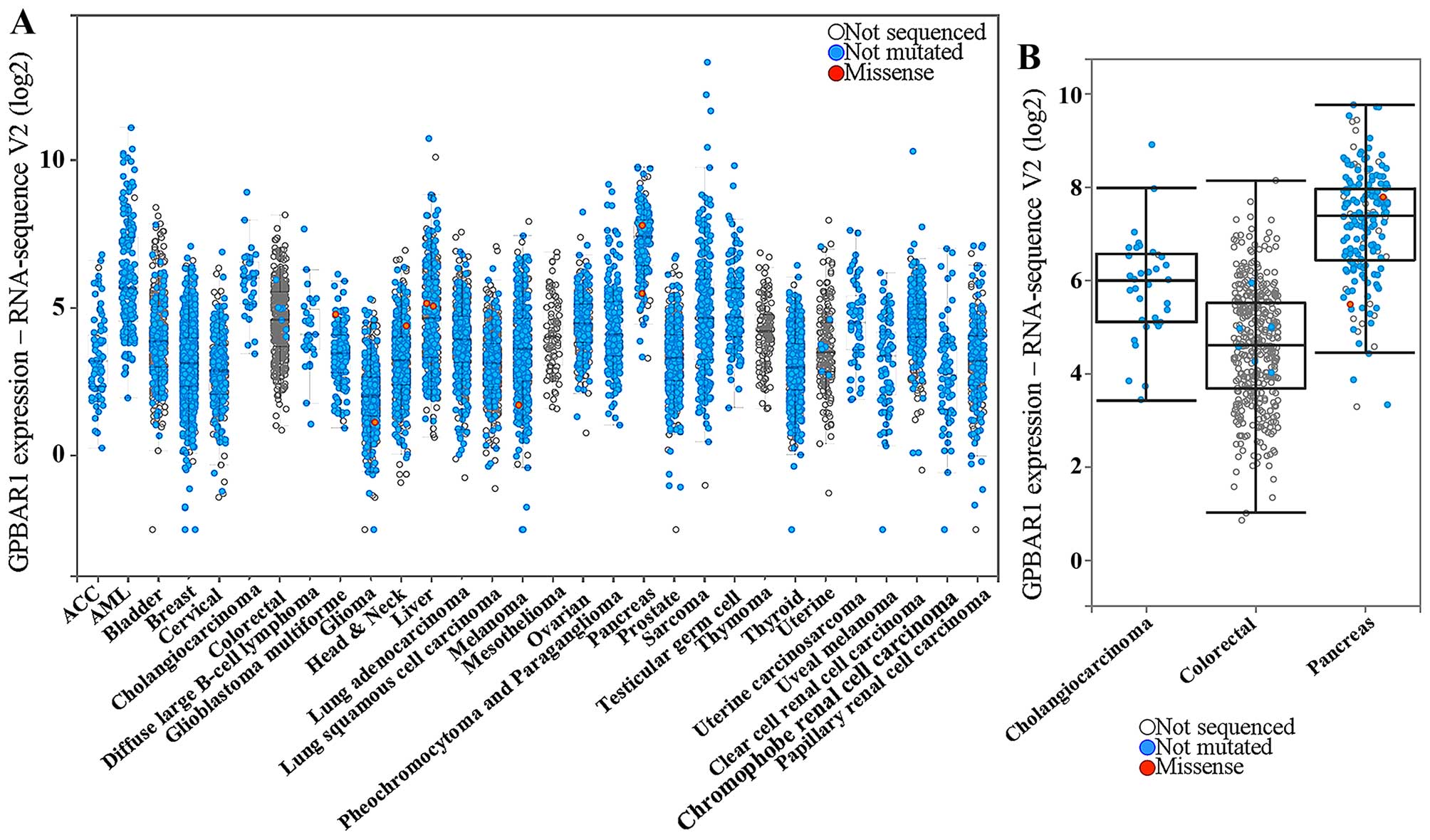
|
4
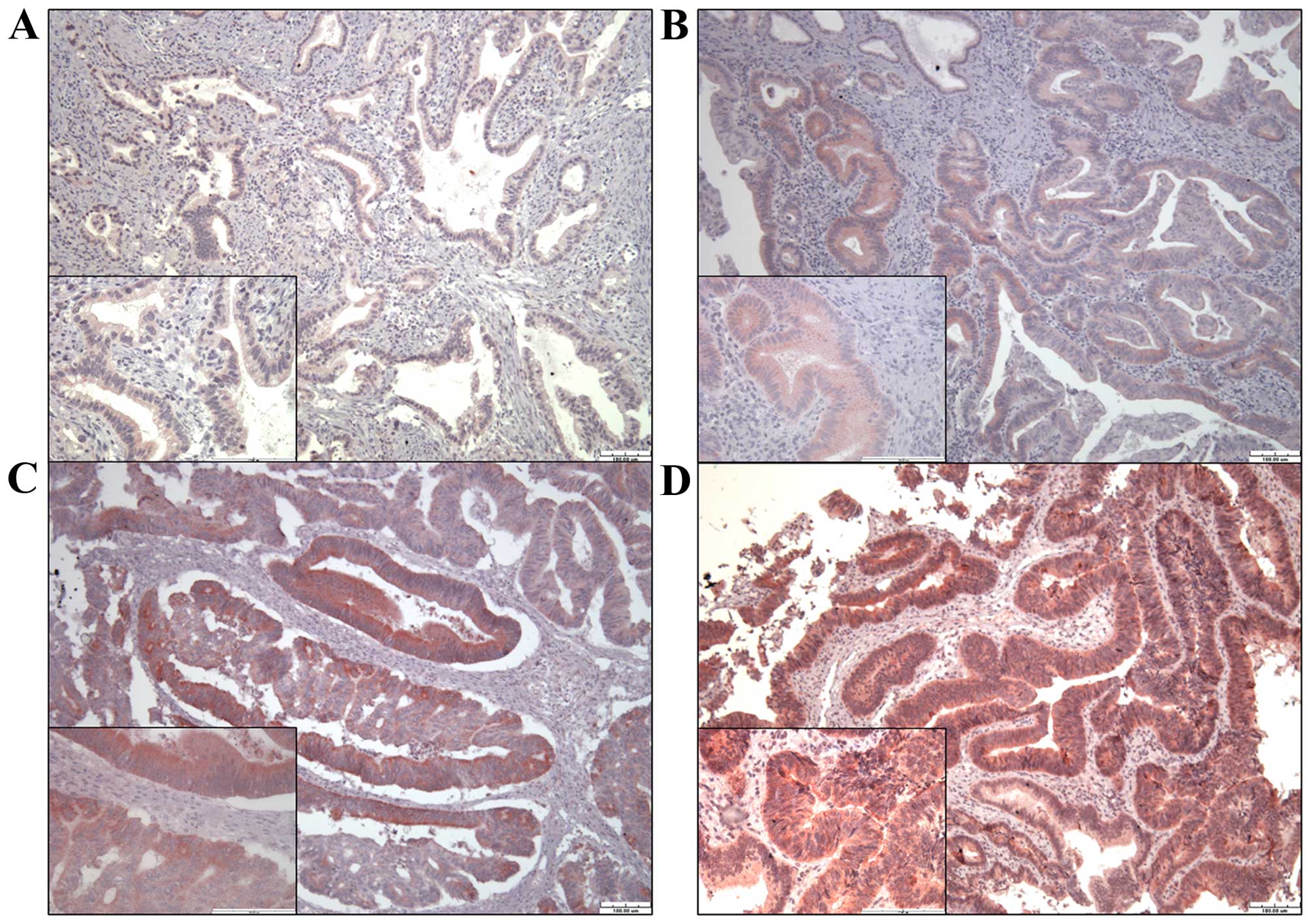
|
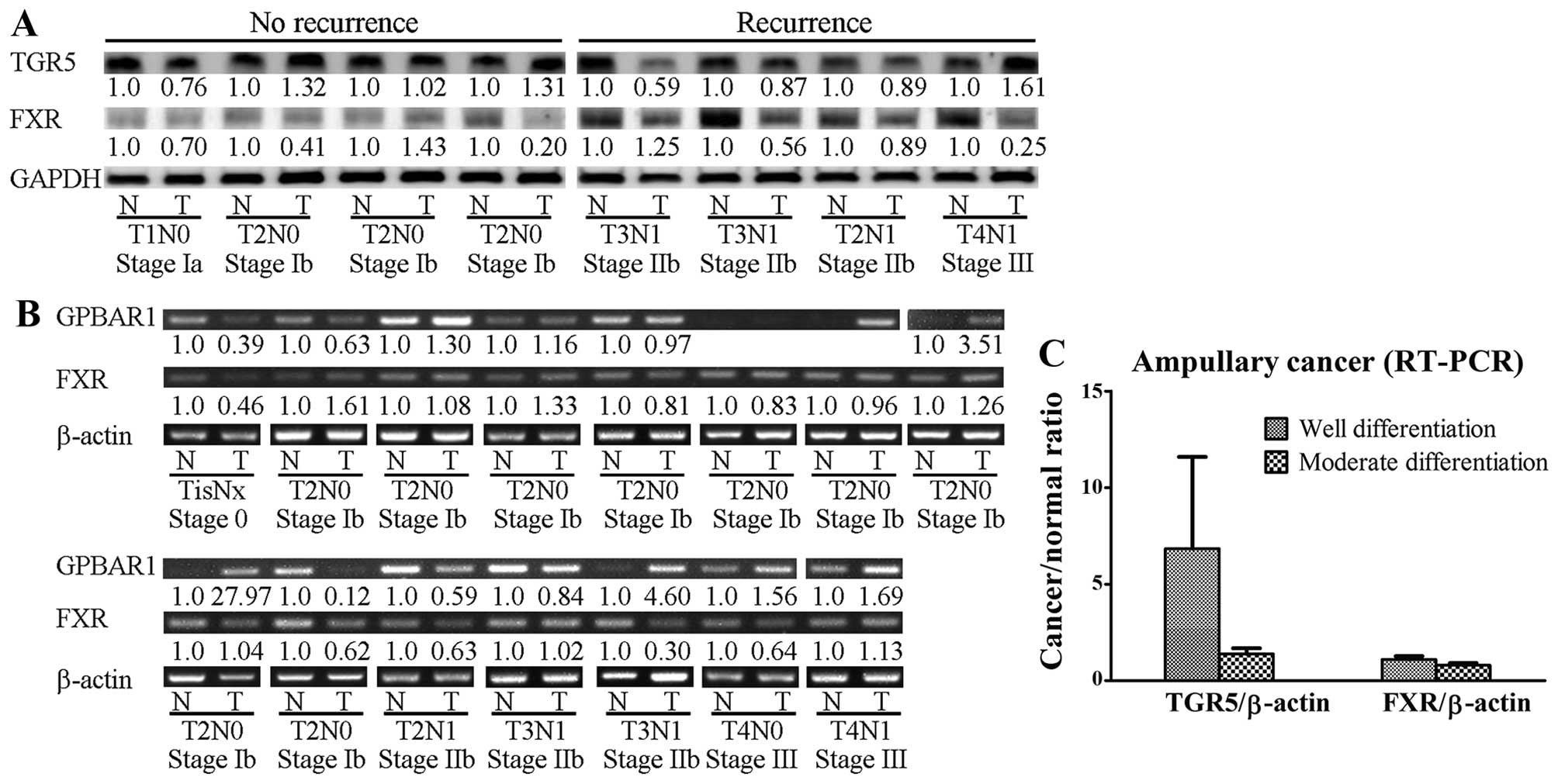
Nishioka K, Doki Y, Miyata H, Tamura S,
Yasuda T, Kimura Y, Kishi K, Yoshida K, Fujiwara Y, Yano M, et al:
Bile acid promotes the proliferation of squamous cell carcinoma of
the esophagus, independent of its inducing COX-2 expression. J Surg
Res. 132:130–135. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bernstein C, Payne CM and Bernstein H:
Bile acids: Promoters or carcinogens in colon cancer? J Carcinogene
Mutagene. 2:101e View Article : Google Scholar : 2011.
|
|
6
|
Payne CM, Bernstein C, Dvorak K and
Bernstein H: Hydrophobic bile acids, genomic instability, Darwinian
selection, and colon carcinogenesis. Clin Exp Gastroenterol.
1:19–47. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Komichi D, Tazuma S, Nishioka T, Hyogo H
and Chayama K: Glycochenodeoxycholate plays a carcinogenic role in
immortalized mouse cholangiocytes via oxidative DNA damage. Free
Radic Biol Med. 39:1418–1427. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yoon JH, Higuchi H, Werneburg NW, Kaufmann
SH and Gores GJ: Bile acids induce cyclooxygenase-2 expression via
the epidermal growth factor receptor in a human cholangiocarcinoma
cell line. Gastroenterology. 122:985–993. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Thomas C, Pellicciari R, Pruzanski M,
Auwerx J and Schoonjans K: Targeting bile-acid signalling for
metabolic diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:678–693. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lax S, Schauer G, Prein K, Kapitan M,
Silbert D, Berghold A, Berger A and Trauner M: Expression of the
nuclear bile acid receptor/farnesoid X receptor is reduced in human
colon carcinoma compared to nonneoplastic mucosa independent from
site and may be associated with adverse prognosis. Int J Cancer.
130:2232–2239. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
van de Winkel A, van Zoest KP, van Dekken
H, Moons LM, Kuipers EJ and van der Laan LJ: Differential
expression of the nuclear receptors farnesoid X receptor (FXR) and
pregnane X receptor (PXR) for grading dysplasia in patients with
Barrett's oesophagus. Histopathology. 58:246–253. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim I, Morimura K, Shah Y, Yang Q, Ward JM
and Gonzalez FJ: Spontaneous hepatocarcinogenesis in farnesoid X
receptor-null mice. Carcinogenesis. 28:940–946. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Li T, Holmstrom SR, Kir S, Umetani M,
Schmidt DR, Kliewer SA and Mangelsdorf DJ: The G protein-coupled
bile acid receptor, TGR5, stimulates gallbladder filling. Mol
Endocrinol. 25:1066–1071. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Thomas C, Gioiello A, Noriega L, Strehle
A, Oury J, Rizzo G, Macchiarulo A, Yamamoto H, Mataki C, Pruzanski
M, et al: TGR5-mediated bile acid sensing controls glucose
homeostasis. Cell Metab. 10:167–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Duboc H, Taché Y and Hofmann AF: The bile
acid TGR5 membrane receptor: From basic research to clinical
application. Dig Liver Dis. 46:302–312. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cao W, Tian W, Hong J, Li D, Tavares R,
Noble L, Moss SF and Resnick MB: Expression of bile acid receptor
TGR5 in gastric adenocarcinoma. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 304:G322–G327. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Hong J, Behar J, Wands J, Resnick M, Wang
LJ, DeLellis RA, Lambeth D, Souza RF, Spechler SJ and Cao W: Role
of a novel bile acid receptor TGR5 in the development of
oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut. 59:170–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Casaburi I, Avena P, Lanzino M, Sisci D,
Giordano F, Maris P, Catalano S, Morelli C and Andò S:
Chenodeoxycholic acid through a TGR5-dependent CREB signaling
activation enhances cyclin D1 expression and promotes human
endometrial cancer cell proliferation. Cell Cycle. 11:2699–2710.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang JI, Yoon JH, Myung SJ, Gwak GY, Kim
W, Chung GE, Lee SH, Lee SM, Kim CY and Lee HS: Bile acid-induced
TGR5-dependent c-Jun-N terminal kinase activation leads to enhanced
caspase 8 activation in hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
361:156–161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen WD, Yu D, Forman BM, Huang W and Wang
YD: Deficiency of G-protein-coupled bile acid receptor Gpbar1
(TGR5) enhances chemically induced liver carcinogenesis.
Hepatology. 57:656–666. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Györffy B, Lánczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert
C, Budczies J, Li Q and Szallasi Z: An online survival analysis
tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer
prognosis using microarray data of 1,809 patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 123:725–731. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Győrffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J and
Lanczky A: Online survival analysis software to assess the
prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in
non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 8:e82241.1–e82241.8. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Győrffy B, Lánczky A and Szállási Z:
Implementing an online tool for genome-wide validation of
survival-associated biomarkers in ovarian-cancer using microarray
data from 1287 patients. Endocr Relat Cancer. 19:197–208. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBio-Portal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Remmele W and Schicketanz KH:
Immunohistochemical determination of estrogen and progesterone
receptor content in human breast cancer. Computer-assisted image
analysis (QIC score) vs. subjective grading (IRS). Pathol Res
Pract. 189:862–866. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schiergens TS, Reu S, Neumann J, Renz BW,
Niess H, Boeck S, Heinemann V, Bruns CJ, Jauch KW and Kleespies A:
Histomorphologic and molecular phenotypes predict gemcitabine
response and overall survival in adenocarcinoma of the ampulla of
Vater. Surgery. 158:151–161. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hsu HP, Shan YS, Jin YT, Lai MD and Lin
PW: Loss of E-cadherin and beta-catenin is correlated with poor
prognosis of ampullary neoplasms. J Surg Oncol. 101:356–362.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shan YS, Chen YL, Lai MD and Hsu HP:
Nestin predicts a favorable prognosis in early ampullary
adenocarcinoma and functions as a promoter of metastasis in
advanced cancer. Oncol Rep. 33:40–48. 2015.
|
|
30
|
Piscuoglio S, Lehmann FS, Zlobec I,
Tornillo L, Dietmaier W, Hartmann A, Wünsch PH, Sessa F, Rümmele P,
Baumhoer D, et al: Effect of EpCAM, CD44, CD133 and CD166
expression on patient survival in tumours of the ampulla of Vater.
J Clin Pathol. 65:140–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Rostain F, Hamza S, Drouillard A, Faivre
J, Bouvier AM and Lepage C: Trends in incidence and management of
cancer of the ampulla of Vater. World J Gastroenterol.
20:10144–10150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hsu HP, Yang TM, Hsieh YH, Shan YS and Lin
PW: Predictors for patterns of failure after
pancreaticoduodenectomy in ampullary cancer. Ann Surg Oncol.
14:50–60. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Goldstein SR, Yang GY, Curtis SK, Reuhl
KR, Liu BC, Mirvish SS, Newmark HL and Yang CS: Development of
esophageal metaplasia and adenocarcinoma in a rat surgical model
without the use of a carcinogen. Carcinogenesis. 18:2265–2270.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pols TW, Noriega LG, Nomura M, Auwerx J
and Schoonjans K: The bile acid membrane receptor TGR5: A valuable
metabolic target. Dig Dis. 29:37–44. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Stepanov V, Stankov K and Mikov M: The
bile acid membrane receptor TGR5: A novel pharmacological target in
metabolic, inflammatory and neoplastic disorders. J Recept Signal
Transduct Res. 33:213–223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo C, Su J, Li Z, Xiao R, Wen J, Li Y,
Zhang M, Zhang X, Yu D, Huang W, et al: The G-protein-coupled bile
acid receptor Gpbar1 (TGR5) suppresses gastric cancer cell
proliferation and migration through antagonizing STAT3 signaling
pathway. Oncotarget. 6:34402–34413. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yasuda H, Hirata S, Inoue K, Mashima H,
Ohnishi H and Yoshiba M: Involvement of membrane-type bile acid
receptor M-BAR/TGR5 in bile acid-induced activation of epidermal
growth factor receptor and mitogen-activated protein kinases in
gastric carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 354:154–159.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jensen DD, Godfrey CB, Niklas C, Canals M,
Kocan M, Poole DP, Murphy JE, Alemi F, Cottrell GS, Korbmacher C,
et al: The bile acid receptor TGR5 does not interact with
β-arrestins or traffic to endosomes but transmits sustained signals
from plasma membrane rafts. J Biol Chem. 288:22942–22960. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|