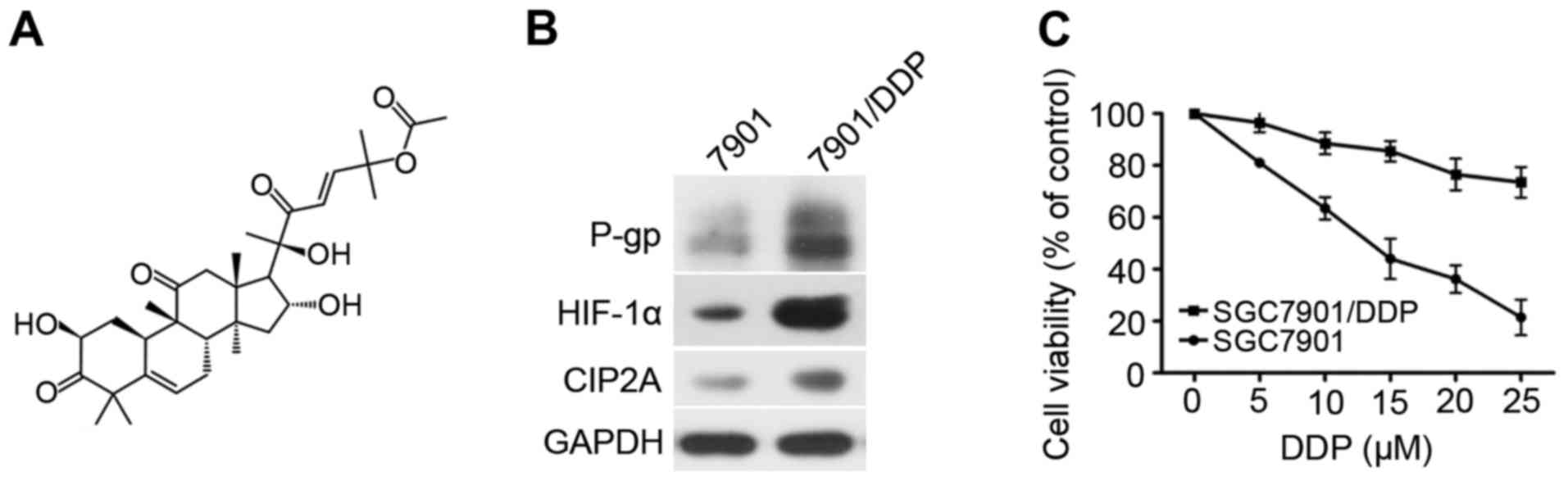
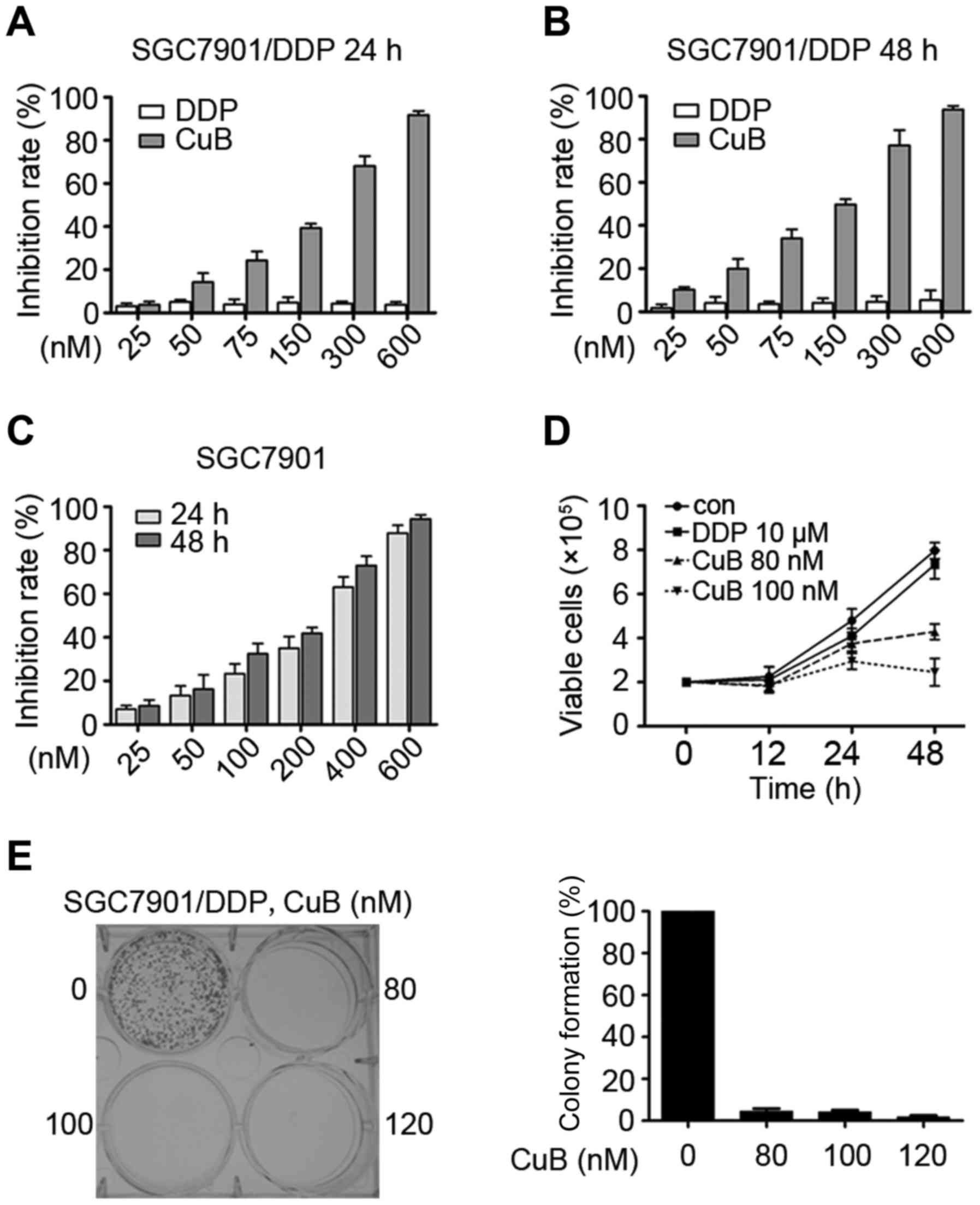
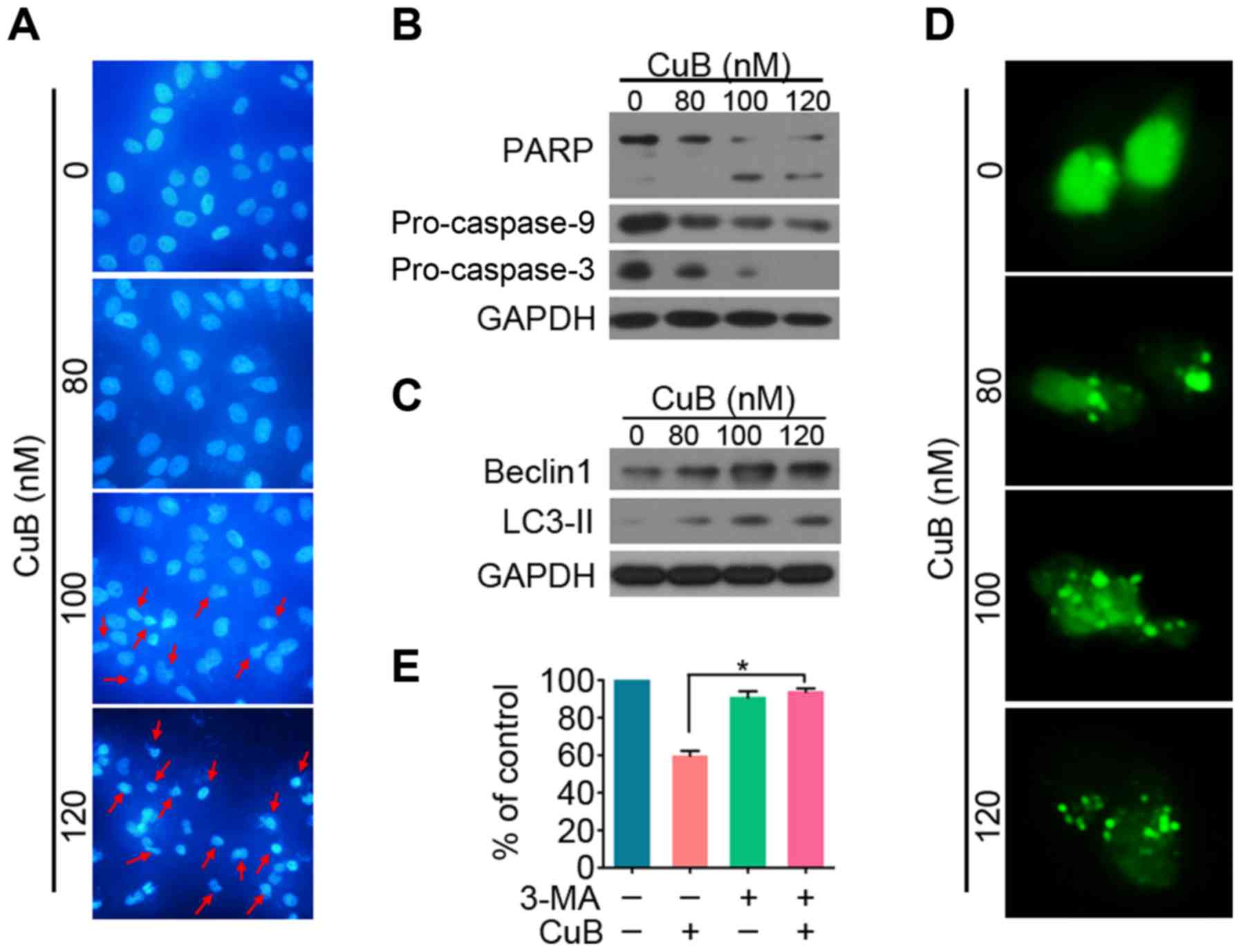
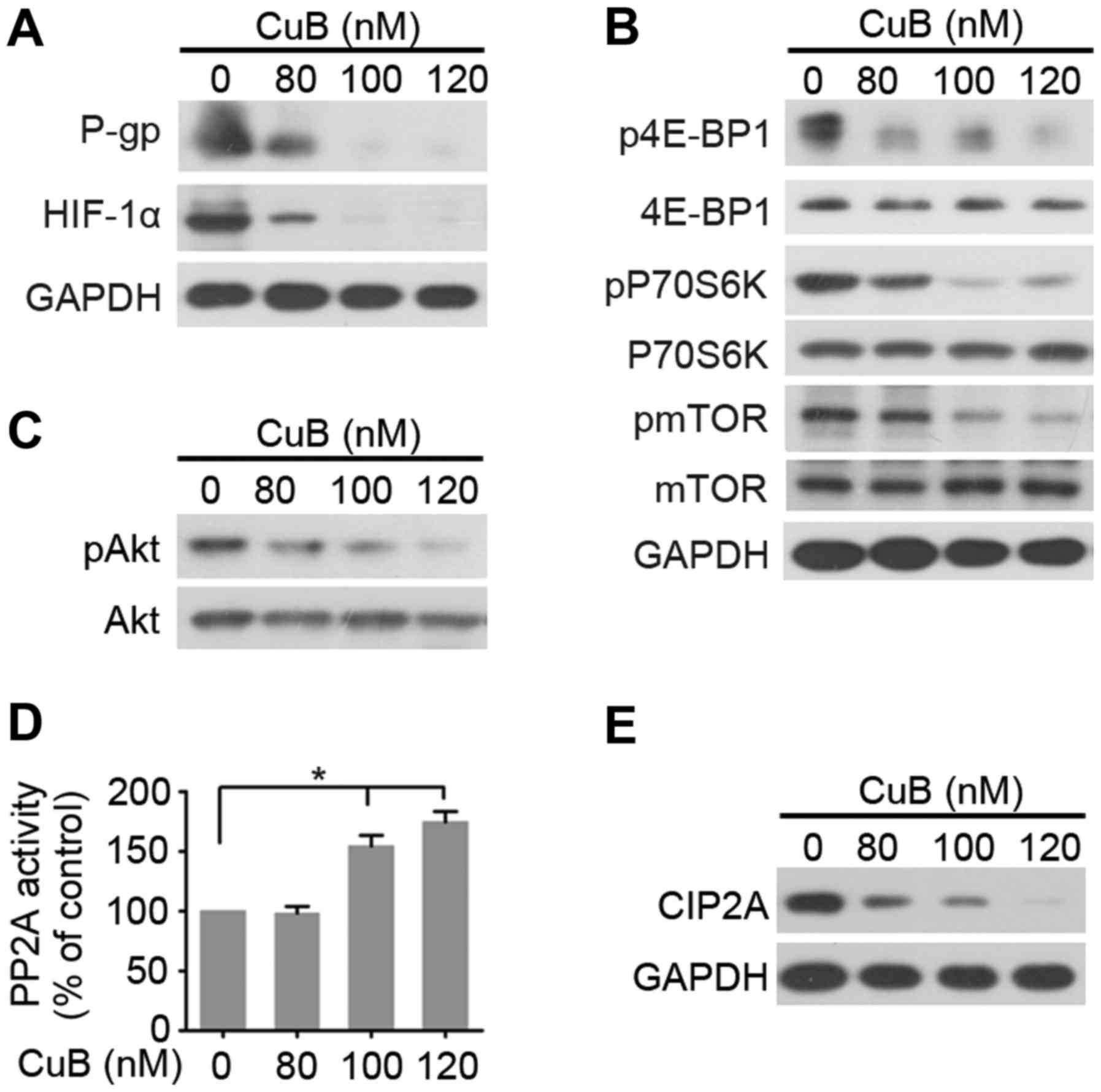
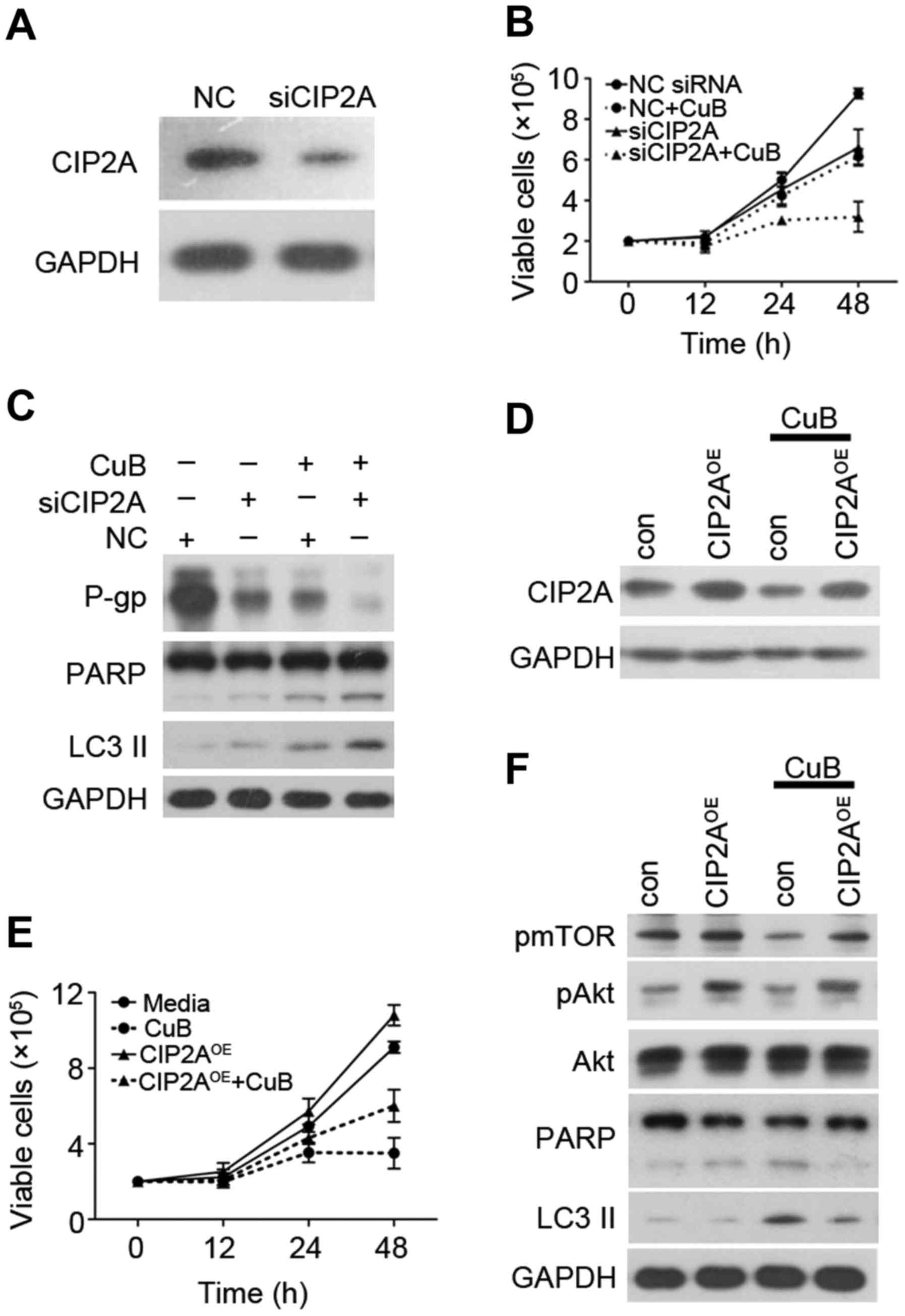
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang X, Cai H, Liang Y, Chen L, Wang X, Si
R, Qu K, Jiang Z, Ma B, Miao C, et al: Inhibition of c-Myc by
let-7b mimic reverses mutidrug resistance in gastric cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 33:1723–1730. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Faneyte IF, Kristel PM, Maliepaard M,
Scheffer GL, Scheper RJ, Schellens JH and van de Vijver MJ:
Expression of the breast cancer resistance protein in breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1068–1074. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hong L, Piao Y, Han Y, Wang J, Zhang X, Du
Y, Cao S, Qiao T, Chen Z and Fan D: Zinc ribbon domain-containing 1
(ZNRD1) mediates multidrug resistance of leukemia cells through
regulation of P-glycoprotein and Bcl-2. Mol Cancer Ther.
4:1936–1942. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Radisavljevic Z: AKT as locus of cancer
multidrug resistance and fragility. J Cell Physiol. 228:671–674.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Puustinen P, Rytter A, Mortensen M,
Kohonen P, Moreira JM and Jäättelä M: CIP2A oncoprotein controls
cell growth and autophagy through mTORC1 activation. J Cell Biol.
204:713–727. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Demitrack ES, Gifford GB, Keeley TM,
Carulli AJ, VanDussen KL, Thomas D, Giordano TJ, Liu Z, Kopan R and
Samuelson LC: Notch signaling regulates gastric antral LGR5 stem
cell function. EMBO J. 34:2522–2536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Erazo T, Lorente M, López-Plana A,
Muñoz-Guardiola P, Fernández-Nogueira P, García-Martínez JA,
Bragado P, Fuster G, Salazar M, Espadaler J, et al: The new
antitumor drug ABTL0812 inhibits the Akt/mTORC1 axis by
upregulating Tribbles-3 pseudokinase. Clin Cancer Res.
22:2508–2519. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin HO, Hong SE, Park JA, Chang YH, Hong
YJ, Park IC and Lee JK: Inhibition of JNK-mediated autophagy
enhances NSCLC cell sensitivity to mTORC1/2 inhibitors. Sci Rep.
6:289452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Agarwal S, Bell CM, Taylor SM and Moran
RG: p53 deletion or hotspot mutations enhance mTORC1 activity by
altering lysosomal dynamics of TSC2 and Rheb. Mol Cancer Res.
14:66–77. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu WD, Hu ZM, Shang MJ, Zhao DJ, Zhang CW,
Hong DF and Huang DS: Cordycepin down-regulates multiple drug
resistant (MDR)/HIF-1α through regulating AMPK/mTORC1 signaling in
GBC-SD gallbladder cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12778–12790.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Puustinen P and Jäättelä M: KIAA1524/CIP2A
promotes cancer growth by coordinating the activities of MTORC1 and
MYC. Autophagy. 10:1352–1354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Junttila MR, Puustinen P, Niemelä M, Ahola
R, Arnold H, Böttzauw T, Ala-aho R, Nielsen C, Ivaska J, Taya Y, et
al: CIP2A inhibits PP2A in human malignancies. Cell. 130:51–62.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li W, Ge Z, Liu C, Liu Z, Björkholm M, Jia
J and Xu D: CIP2A is overexpressed in gastric cancer and its
depletion leads to impaired clonogenicity, senescence, or
differentiation of tumor cells. Clin Cancer Res. 14:3722–3728.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Z, Ma L, Wen ZS, Hu Z, Wu FQ, Li W,
Liu J and Zhou GB: Cancerous inhibitor of PP2A is targeted by
natural compound celastrol for degradation in non-small-cell lung
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 35:905–914. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ren J, Li W, Yan L, Jiao W, Tian S, Li D,
Tang Y, Gu G, Liu H and Xu Z: Expression of CIP2A in renal cell
carcinomas correlates with tumour invasion, metastasis and
patients' survival. Br J Cancer. 105:1905–1911. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu CY, Shiau CW, Kuo HY, Huang HP, Chen
MH, Tzeng CH and Chen KF: Cancerous inhibitor of protein
phosphatase 2A determines bortezomib-induced apoptosis in leukemia
cells. Haematologica. 98:729–738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Xu B, Sun C, Wang L and Miao X:
Knockdown of CIP2A sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin: An
in vitro study. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:16941–16947. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
El-Senduny FF, Badria FA, El-Waseef AM,
Chauhan SC and Halaweish F: Approach for chemosensitization of
cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer by Cucurbitacin B. Tumour Biol.
37:685–698. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chan KT, Meng FY, Li Q, Ho CY, Lam TS, To
Y, Lee WH, Li M, Chu KH and Toh M: Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis
and S phase cell cycle arrest in BEL-7402 human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells and is effective via oral administration. Cancer
Lett. 294:118–124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chan KT, Li K, Liu SL, Chu KH, Toh M and
Xie WD: Cucurbitacin B inhibits STAT3 and the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway
in leukemia cell line K562. Cancer Lett. 289:46–52. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu Y, Cao W, Zhang B, Liu YQ, Wang ZY, Wu
YP, Yu XJ, Zhang XD, Ming PH, Zhou GB, et al: The natural compound
magnolol inhibits invasion and exhibits potential in human breast
cancer therapy. Sci Rep. 3:30982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Feng T, Cao W, Shen W, Zhang L, Gu X, Guo
Y, Tsai H, Liu X, Li J, Zhang J, et al: Arctigenin inhibits STAT3
and exhibits anticancer potential in human triple-negative breast
cancer therapy. Oncotarget. 8:329–344. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao W, Liu Y, Zhang R, Zhang B, Wang T,
Zhu X, Mei L, Chen H, Zhang H, Ming P, et al: Homoharringtonine
induces apoptosis and inhibits STAT3 via IL-6/JAK1/STAT3 signal
pathway in Gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells. Sci Rep.
5:84772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chou CC, Yang JS, Lu HF, Ip SW, Lo C, Wu
CC, Lin JP, Tang NY, Chung JG, Chou MJ, et al: Quercetin-mediated
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis involving activation of a caspase
cascade through the mitochondrial pathway in human breast cancer
MCF-7 cells. Arch Pharm Res. 33:1181–1191. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiao X, He Z, Cao W, Cai F, Zhang L, Huang
Q, Fan C, Duan C, Wang X, Wang J, et al: Oridonin inhibits
gefitinib-resistant lung cancer cells by suppressing
EGFR/ERK/MMP-12 and CIP2A/Akt signaling pathways. Int J Oncol.
48:2608–2618. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cai F, Zhang L, Xiao X, Duan C, Huang Q,
Fan C, Li J, Liu X, Li S and Liu Y: Cucurbitacin B reverses
multidrug resistance by targeting CIP2A to reactivate protein
phosphatase 2A in MCF-7/adriamycin cells. Oncol Rep. 36:1180–1186.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qian HR and Yang Y: Functional role of
autophagy in gastric cancer. Oncotarget. 7:17641–17651.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin L and Baehrecke EH: Autophagy, cell
death, and cancer. Mol Cell Oncol. 2:e985913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rincón R, Cristóbal I, Zazo S, Arpí O,
Menéndez S, Manso R, Lluch A, Eroles P, Rovira A, Albanell J, et
al: PP2A inhibition determines poor outcome and doxorubicin
resistance in early breast cancer and its activation shows
promising therapeutic effects. Oncotarget. 6:4299–4314. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Simonian PL, Grillot DA and Nuñez G: Bcl-2
and Bcl-XL can differentially block chemotherapy-induced cell
death. Blood. 90:1208–1216. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alcantara LM, Kim J, Moraes CB, Franco CH,
Franzoi KD, Lee S, Freitas-Junior LH and Ayong LS:
Chemosensitization potential of P-glycoprotein inhibitors in
malaria parasites. Exp Parasitol. 134:235–243. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Luo L, Sun YJ, Yang L, Huang S and Wu YJ:
Avermectin induces P-glycoprotein expression in S2 cells via the
calcium/calmodulin/NF-κB pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 203:430–439.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Zhu ZA, Liu QH, Kong QY, Liu L, Cui
T and Wu YP: RAD001 can reverse drug resistance of SGC7901/DDP
cells. Tumour Biol. 35:9171–9177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Marostica LL, Silva IT, Kratz JM, Persich
L, Geller FC, Lang KL, Caro MS, Durán FJ, Schenkel EP and Simões
CM: Synergistic antiproliferative effects of a new Cucurbitacin B
derivative and chemotherapy drugs on lung cancer cell line A549.
Chem Res Toxicol. 28:1949–1960. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen W, Leiter A, Yin D, Meiring M, Louw
VJ and Koeffler HP: Cucurbitacin B inhibits growth, arrests the
cell cycle, and potentiates antiproliferative efficacy of cisplatin
in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Oncol.
37:737–743. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu T, Peng H, Zhang M, Deng Y and Wu Z:
Cucurbitacin B, a small molecule inhibitor of the Stat3 signaling
pathway, enhances the chemosensitivity of laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma cells to cisplatin. Eur J Pharmacol. 641:15–22. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nicholson DW: Caspase structure,
proteolytic substrates, and function during apoptotic cell death.
Cell Death Differ. 6:1028–1042. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA and Lowe SW:
Apoptosis: A link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell.
108:153–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang M, Zhang H, Tang F, Wang Y, Mo Z,
Lei X and Tang S: Doxorubicin resistance mediated by cytoplasmic
macrophage colony-stimulating factor is associated with switch from
apoptosis to autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 241:2086–2093. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Come C, Laine A, Chanrion M, Edgren H,
Mattila E, Liu X, Jonkers J, Ivaska J, Isola J, Darbon JM, et al:
CIP2A is associated with human breast cancer aggressivity. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:5092–5100. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|