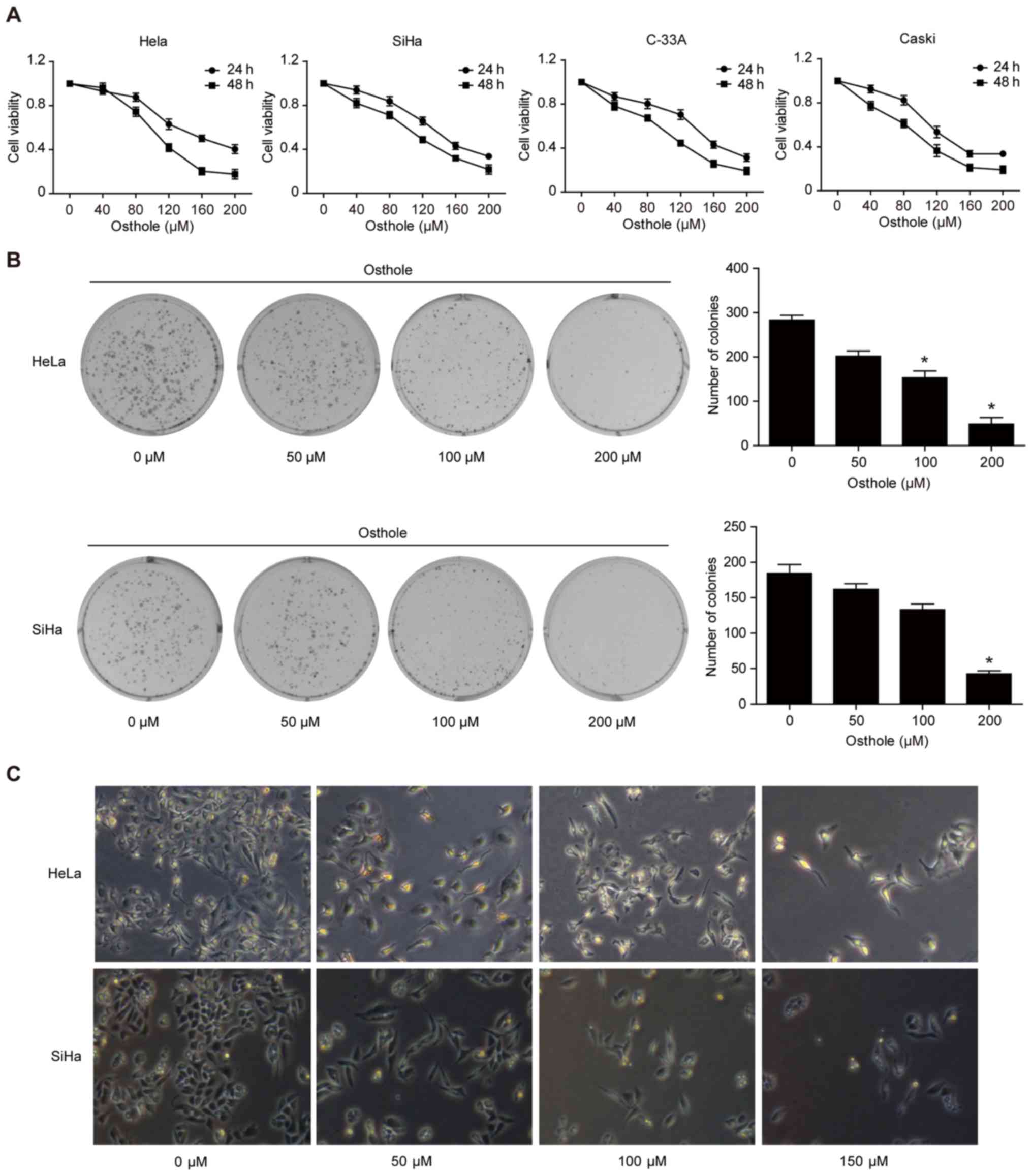
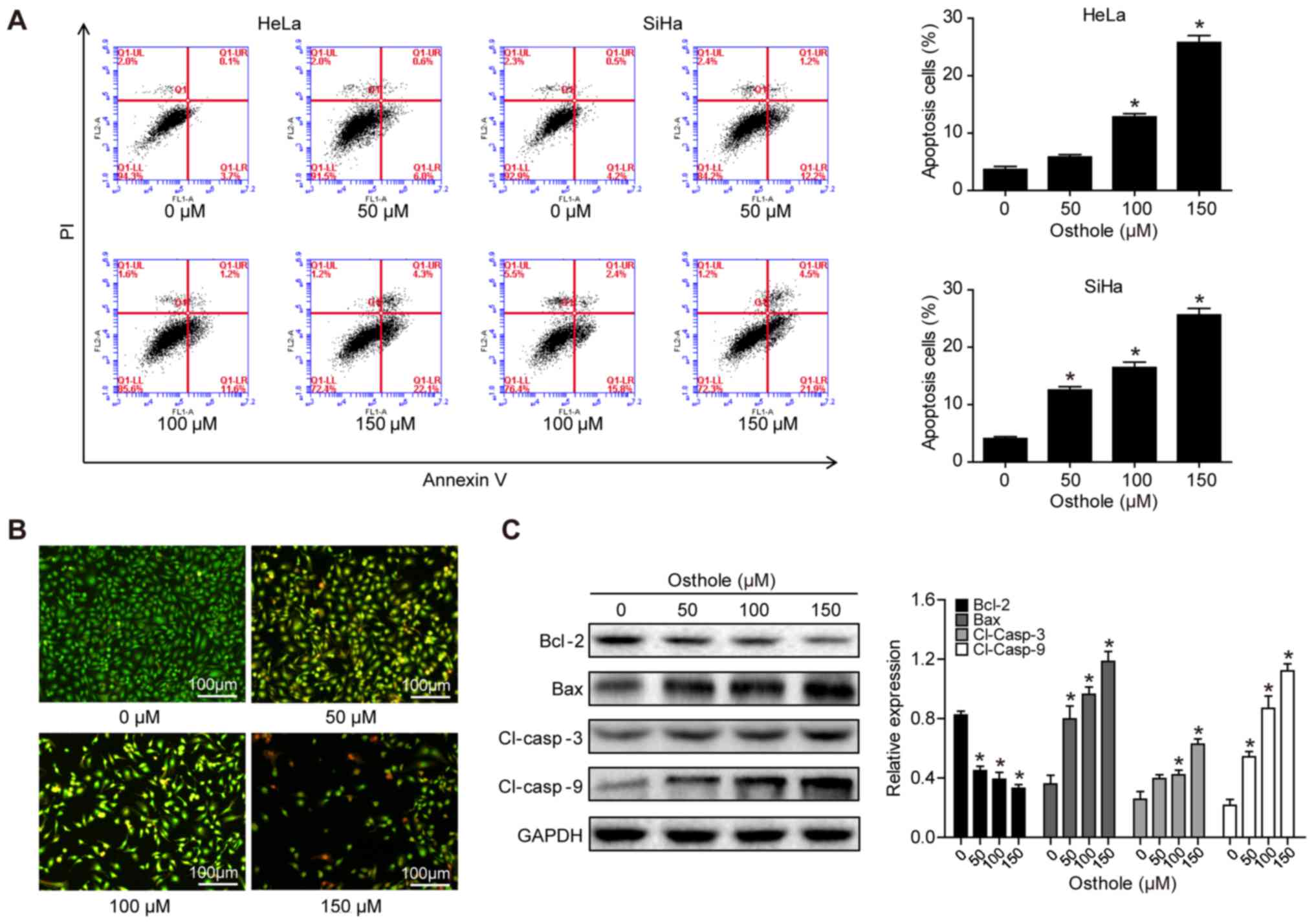
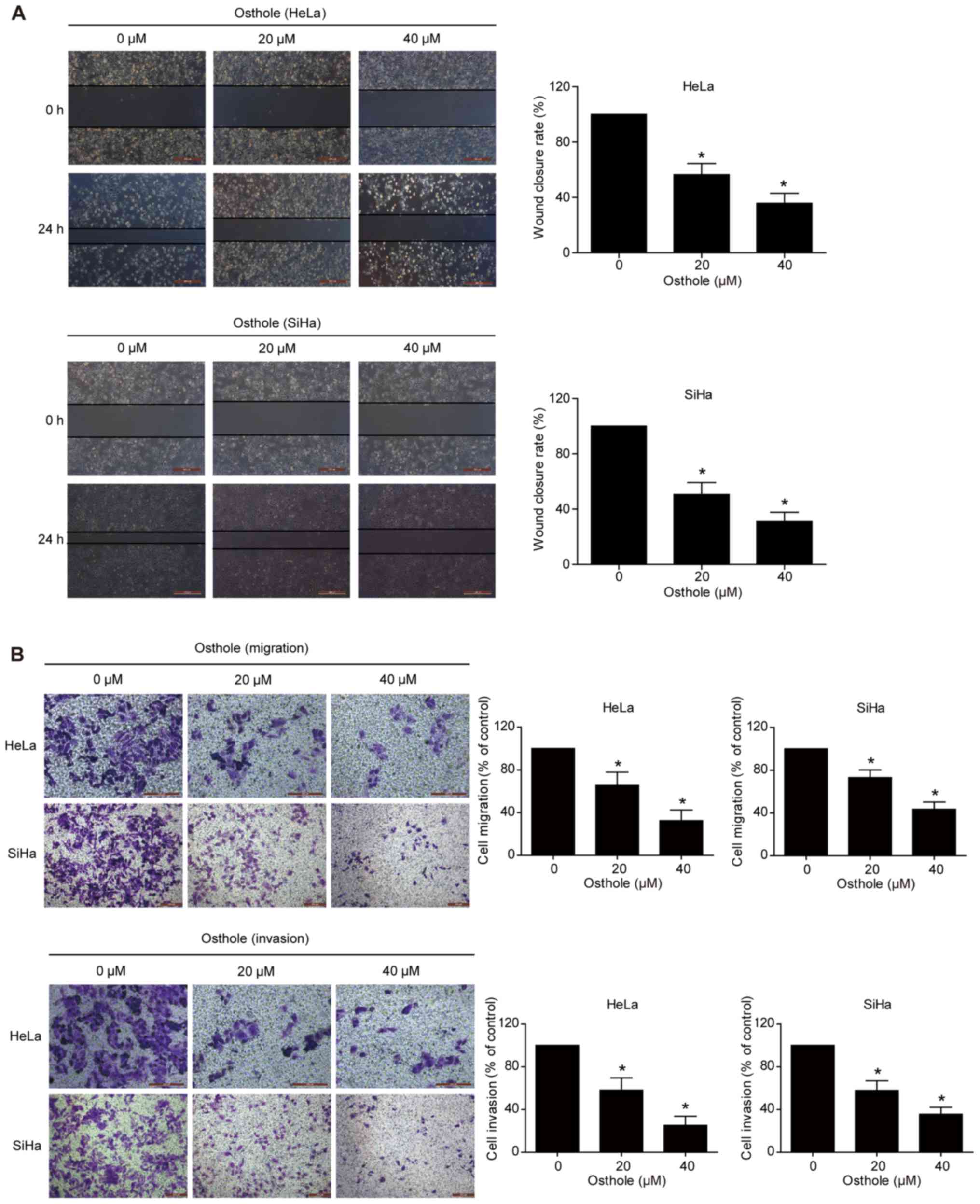
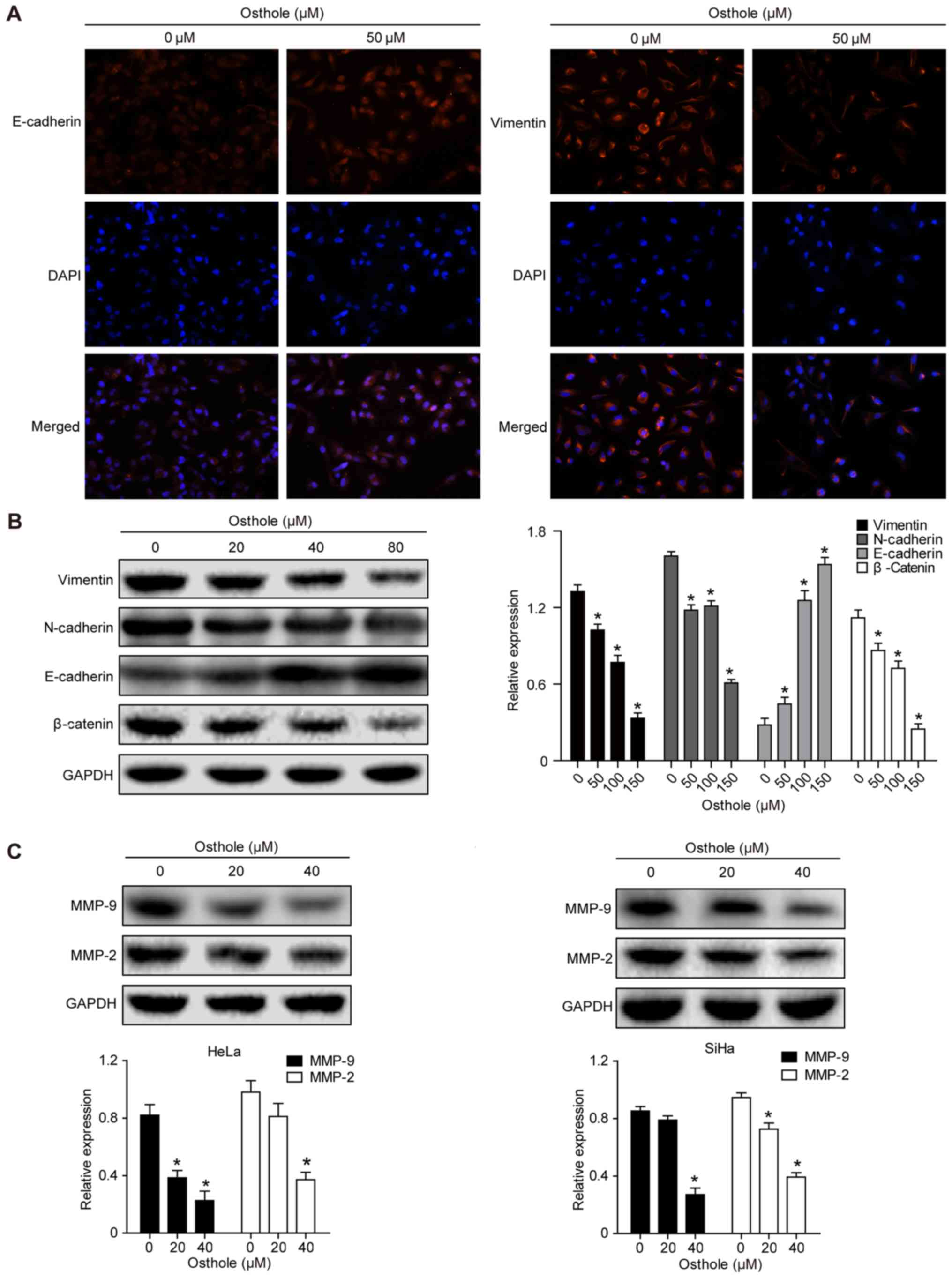
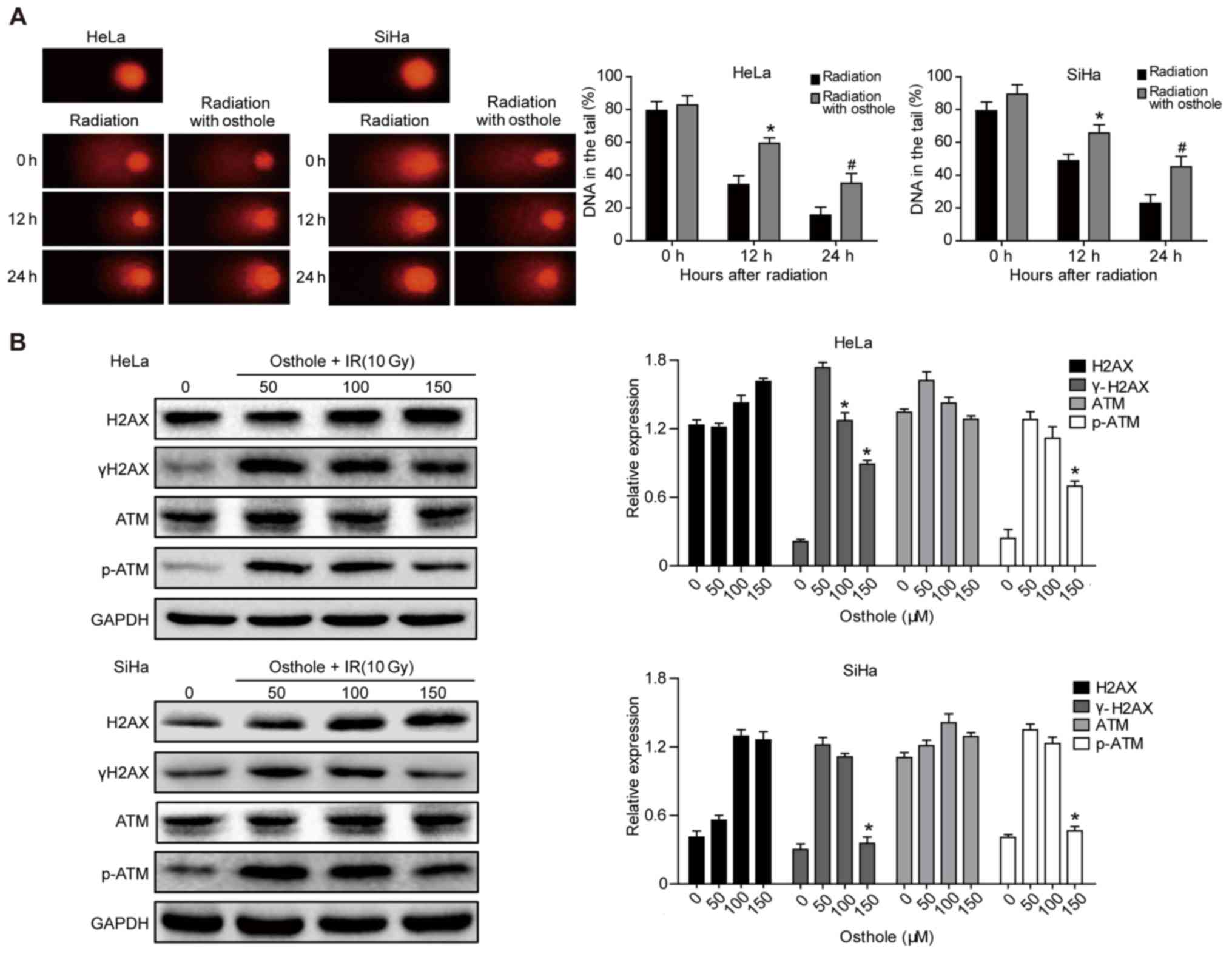
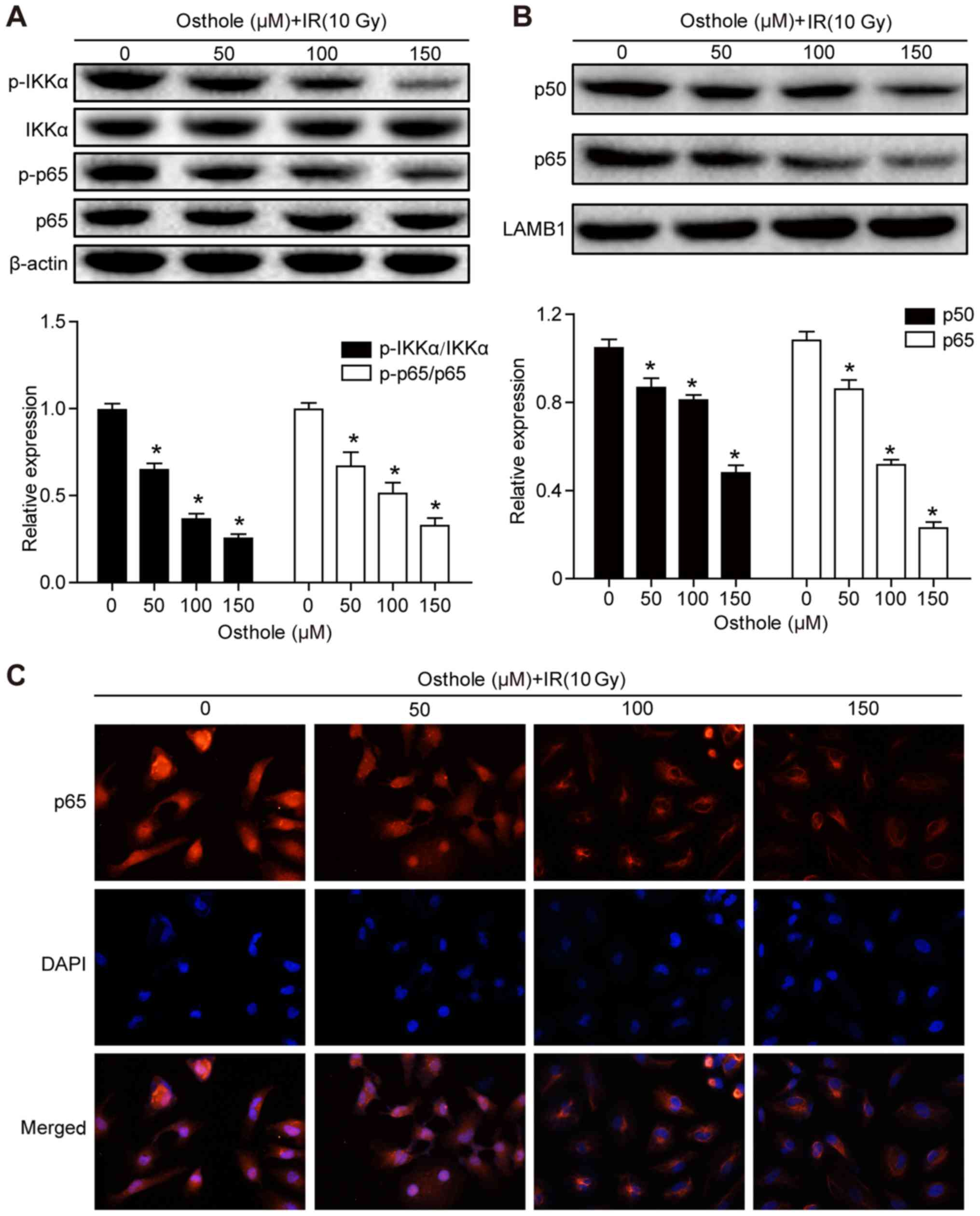
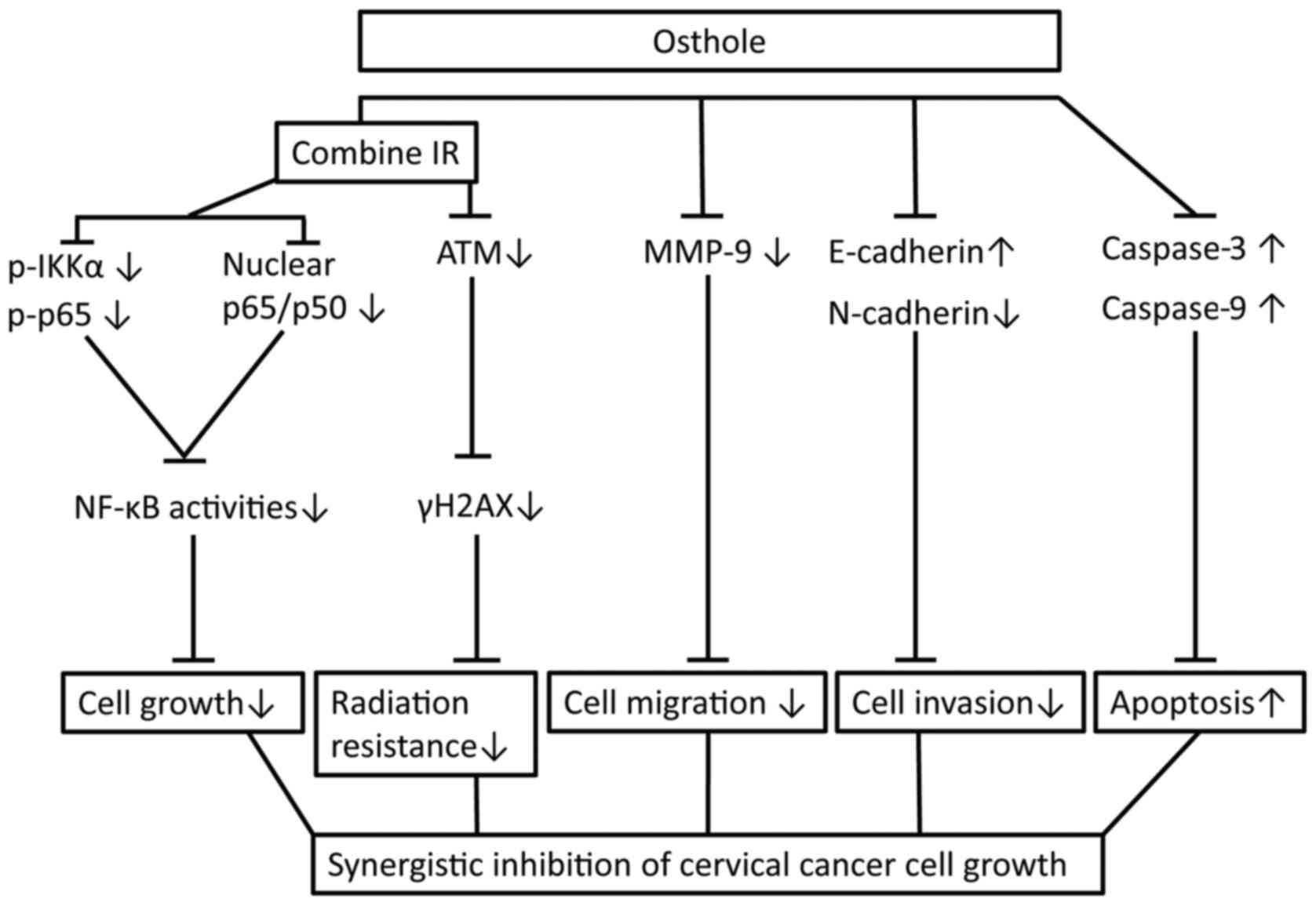
|
1
|
Ginsburg O, Bray F, Coleman MP, Vanderpuye
V, Eniu A, Kotha SR, Sarker M, Huong TT, Allemani C, Dvaladze A, et
al: The global burden of women's cancers: A grand challenge in
global health. Lancet. 389:847–860. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee MY and Shen MR: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cervical carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 4:1–13.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zimecki M, Artym J, Cisowski W, Mazol I,
Włodarczyk M and Gleńsk M: Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory
activity of selected osthole derivatives. Z Naturforsch C.
64:361–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hao Y and Liu Y: Osthole alleviates
bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via modulating
angiotensin-converting enzyme 2/angiotensin-(1–7) axis and
decreasing inflammation responses in rats. Biol Pharm Bull.
39:457–465. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang G, Liu J, Ren B, Tang Y, Owusu L, Li
M, Zhang J, Liu L and Li W: Anti-tumor effects of osthole on
ovarian cancer cells in vitro. J Ethnopharmacol. 193:368–376. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding D, Wei S, Song Y, Li L, Du G, Zhan H
and Cao Y: Osthole exhibits anti-cancer property in rat glioma
cells through inhibiting PI3K/Akt and MAPK signaling pathways. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 32:1751–1760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang D, Gu T, Wang T, Tang Q and Ma C:
Effects of osthole on migration and invasion in breast cancer
cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 74:1430–1434. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu C, Sun Z, Guo B, Ye Y, Han X, Qin Y and
Liu S: Osthole inhibits bone metastasis of breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:58480–58493. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chou SY, Hsu CS, Wang KT, Wang MC and Wang
CC: Antitumor effects of Osthol from Cnidium monnieri: An in vitro
and in vivo study. Phytother Res. 21:226–230. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Okamoto T, Kobayashi T and Yoshida S:
Chemical aspects of coumarin compounds for the prevention of
hepatocellular carcinomas. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents.
5:47–51. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang LL, Wang MC, Chen LG and Wang CC:
Cytotoxic activity of coumarins from the fruits of Cnidium monnieri
on leukemia cell lines. Planta Med. 69:1091–1095. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kao SJ, Su JL, Chen CK, Yu MC, Bai KJ,
Chang JH, Bien MY, Yang SF and Chien MH: Osthole inhibits the
invasive ability of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via suppression
of NF-κB-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 261:105–115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jarząb A, Łuszczki J, Guz M,
Skalicka-Woźniak K, Hałasa M, Smok-Kalwat J, Polberg K and Stepulak
A: Combination of osthole and cisplatin against rhabdomyosarcoma
TE671 cells yielded additive pharmacologic interaction by means of
isobolographic analys. Anticancer Res. 38:205–210. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Small W Jr, Bacon MA, Bajaj A, Chuang LT,
Fisher BJ, Harkenrider MM, Jhingran A, Kitchener HC, Mileshkin LR,
Viswanathan AN, et al: Cervical cancer: A global health crisis.
Cancer. 123:2404–2412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin VC, Chou CH, Lin YC, Lin JN, Yu CC,
Tang CH, Lin HY and Way TD: Osthole suppresses fatty acid synthase
expression in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells through
modulating Akt/mTOR pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 58:4786–4793. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu X, Zhang Y, Qu D, Jiang T and Li S:
Osthole induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in lung cancer A549 cells
by modulating PI3K/Akt pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:332011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dien PH, Nhan NT, Le Thuy HT and Quang DN:
Main constituents from the seeds of Vietnamese Cnidium monnieri and
cytotoxic activity. Nat Prod Res. 26:2107–2111. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Jiang G, Yao F, He Y, Liang G,
Zhang Y, Hu B, Wu Y, Li Y and Liu H: Growth inhibition and
apoptosis induced by osthole, a natural coumarin, in hepatocellular
carcinoma. PLoS One. 7:e378652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yao C, Cao X, Fu Z, Tian J, Dong W, Xu J,
An K, Zhai L and Yu J: Boschniakia rossica polysaccharide triggers
laryngeal carcinoma cell apoptosis by regulating expression of
Bcl-2, Caspase-3, and P53. Med Sci Monit. 23:2059–2064. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG and Schumacher
U: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Focus on metastatic cascade,
alternative splicing, non-coding RNAs and modulating compounds. Mol
Cancer. 12:1072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cruz-Solbes AS and Youker K: Epithelial to
Mesenchymal transition (EMT) and endothelial to mesenchymal
transition (EndMT): Role and implications in kidney fibrosis.
Results Probl Cell Differ. 60:345–372. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Verma RP and Hansch C: Matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs): Chemical-biological functions and
(Q)SARs. Bioorg Med Chem. 15:2223–2268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee MY, Chou CY, Tang MJ and Shen MR:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cervical cancer: Correlation
with tumor progression, epidermal growth factor receptor
overexpression, and snail up-regulation. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4743–4750. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Moreno-Acosta P, Gamboa O, Sanchez de
Gomez M, Cendales R, Diaz GD, Romero A, Balart Serra J, Conrado Z,
Levy A, Chargari C and Magné N: IGF1R gene expression as a
predictive marker of response to ionizing radiation for patients
with locally advanced HPV16-positive cervical cancer. Anticancer
Res. 32:4319–4325. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang J, Yue JB, Liu J and Yu JM:
Repopulation of tumor cells during fractionated radiotherapy and
detection methods (Review). Oncol Lett. 7:1755–1760. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsuoka S, Rotman G, Ogawa A, Shiloh Y,
Tamai K and Elledge SJ: Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated
phosphorylates Chk2 in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:10389–10394. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nambiar DK, Rajamani P, Deep G, Jain AK,
Agarwal R and Singh RP: Silibinin preferentially radiosensitizes
prostate cancer by inhibiting DNA repair signaling. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:2722–2734. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao J, Guo Z, Pei S, Song L, Wang C, Ma
J, Jin L, Ma Y, He R, Zhong J, et al: pATM and γH2AX are effective
radiation biomarkers in assessing the radiosensitivity of 12C6+ in
human tumor cells. Cancer Cell Int. 17:492017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ahmed KM and Li JJ: NF-kappa B-mediated
adaptive resistance to ionizing radiation. Free Radic Biol Med.
44:1–13. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shokoohinia Y, Jafari F, Mohammadi Z,
Bazvandi L, Hosseinzadeh L, Chow N, Bhattacharyya P, Farzaei MH,
Farooqi AA, Nabavi SM, et al: Potential anticancer properties of
osthol: A comprehensive mechanistic review. Nutrients. 10:pii: E36.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|