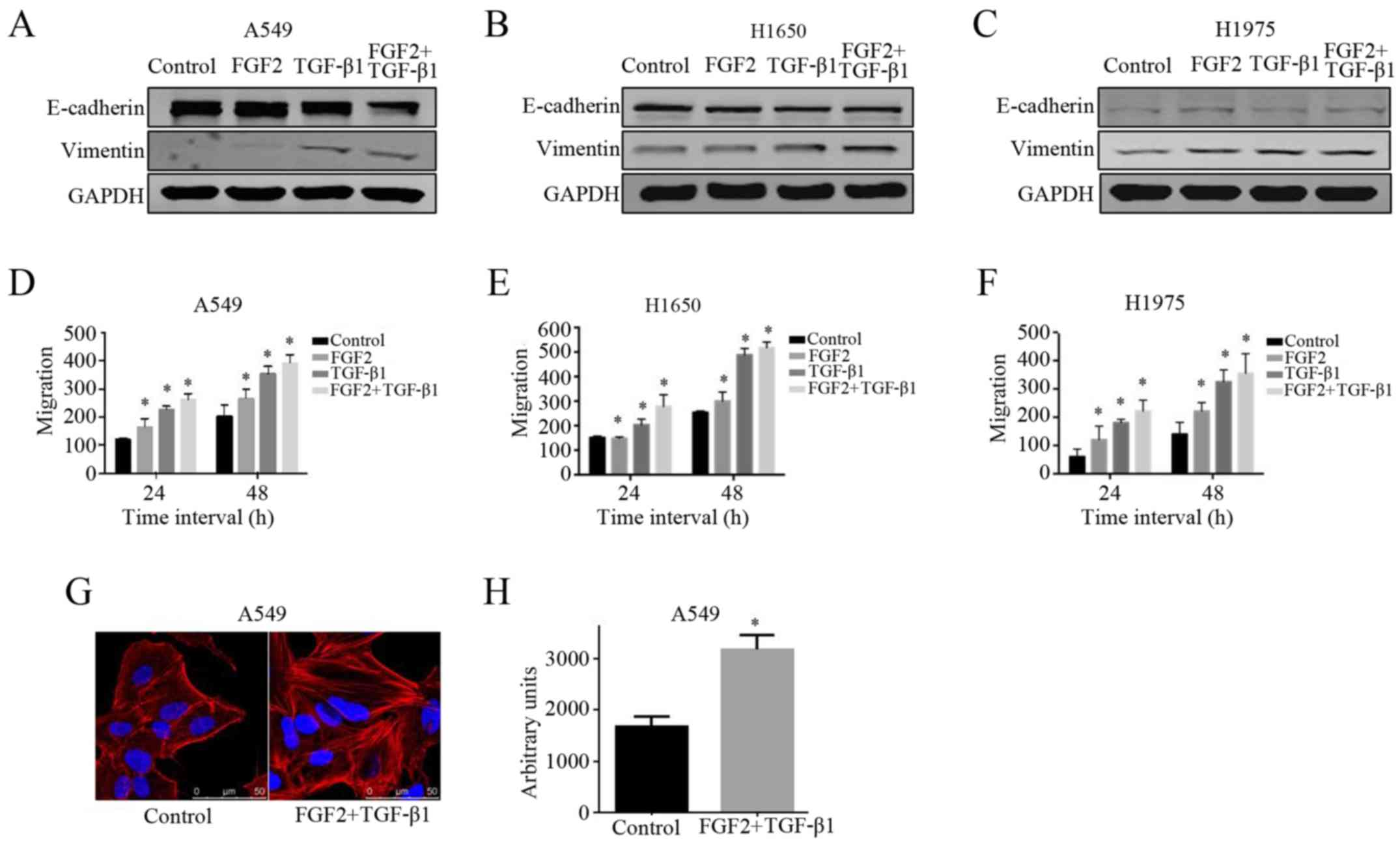
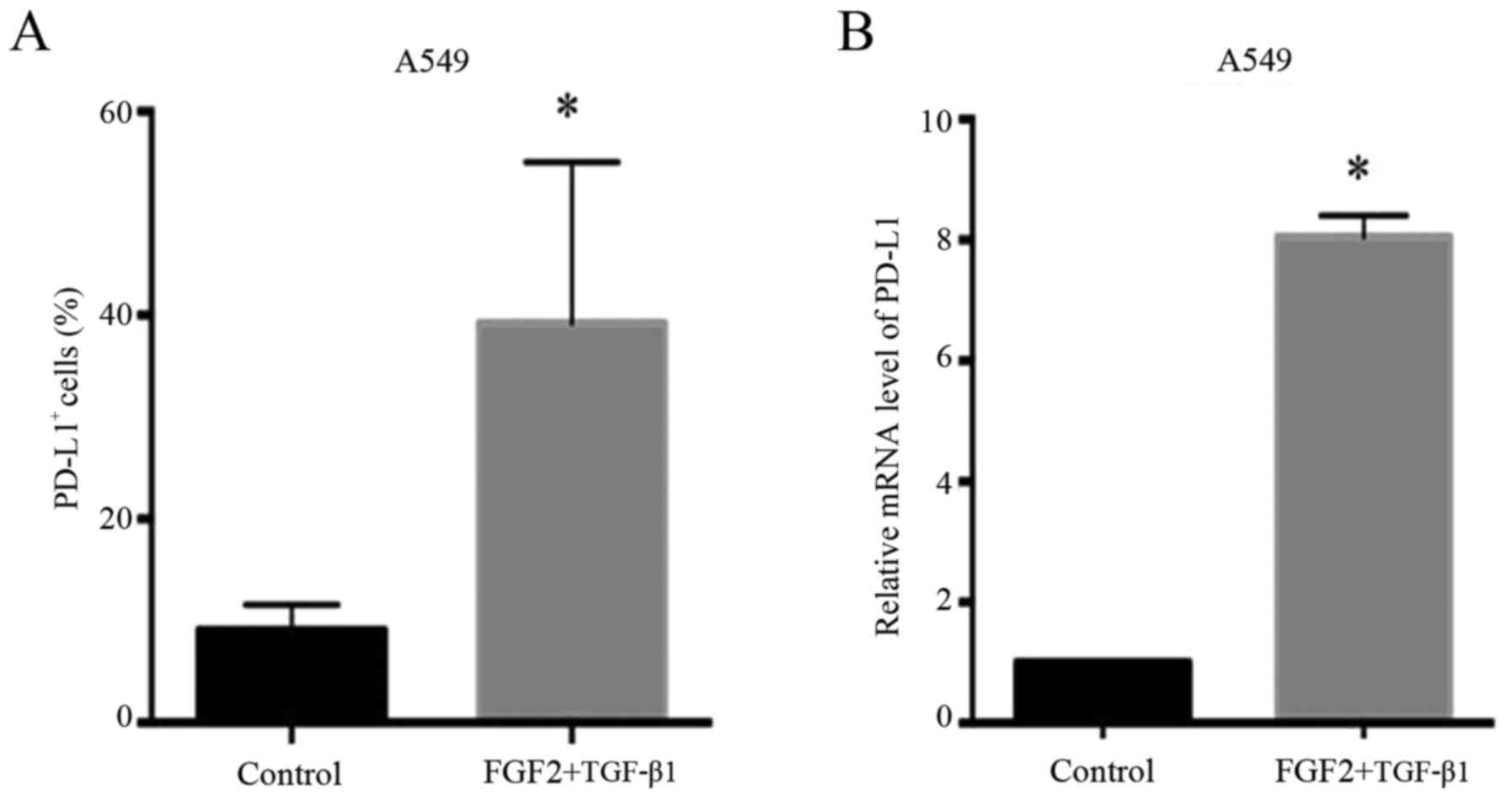
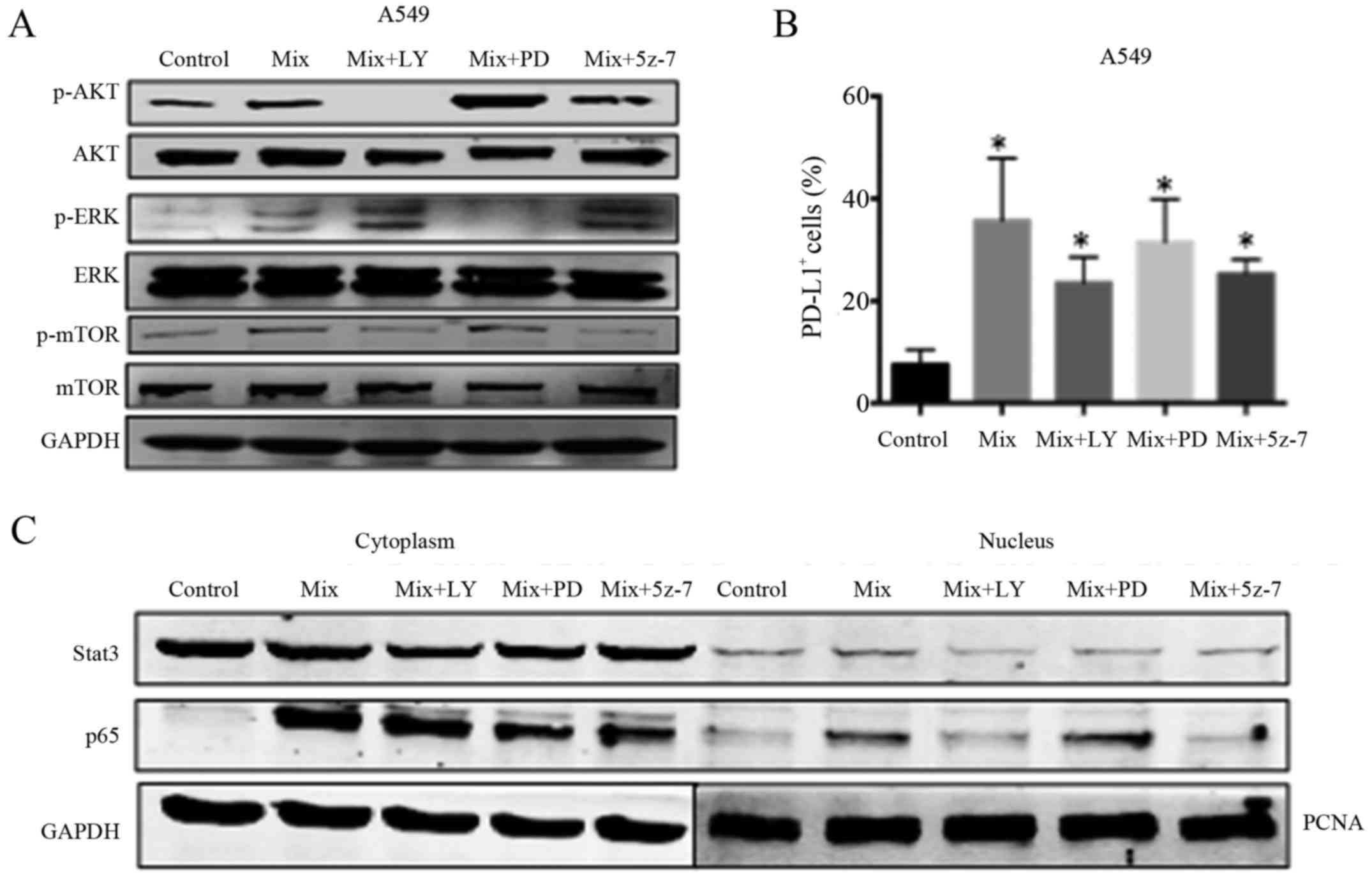
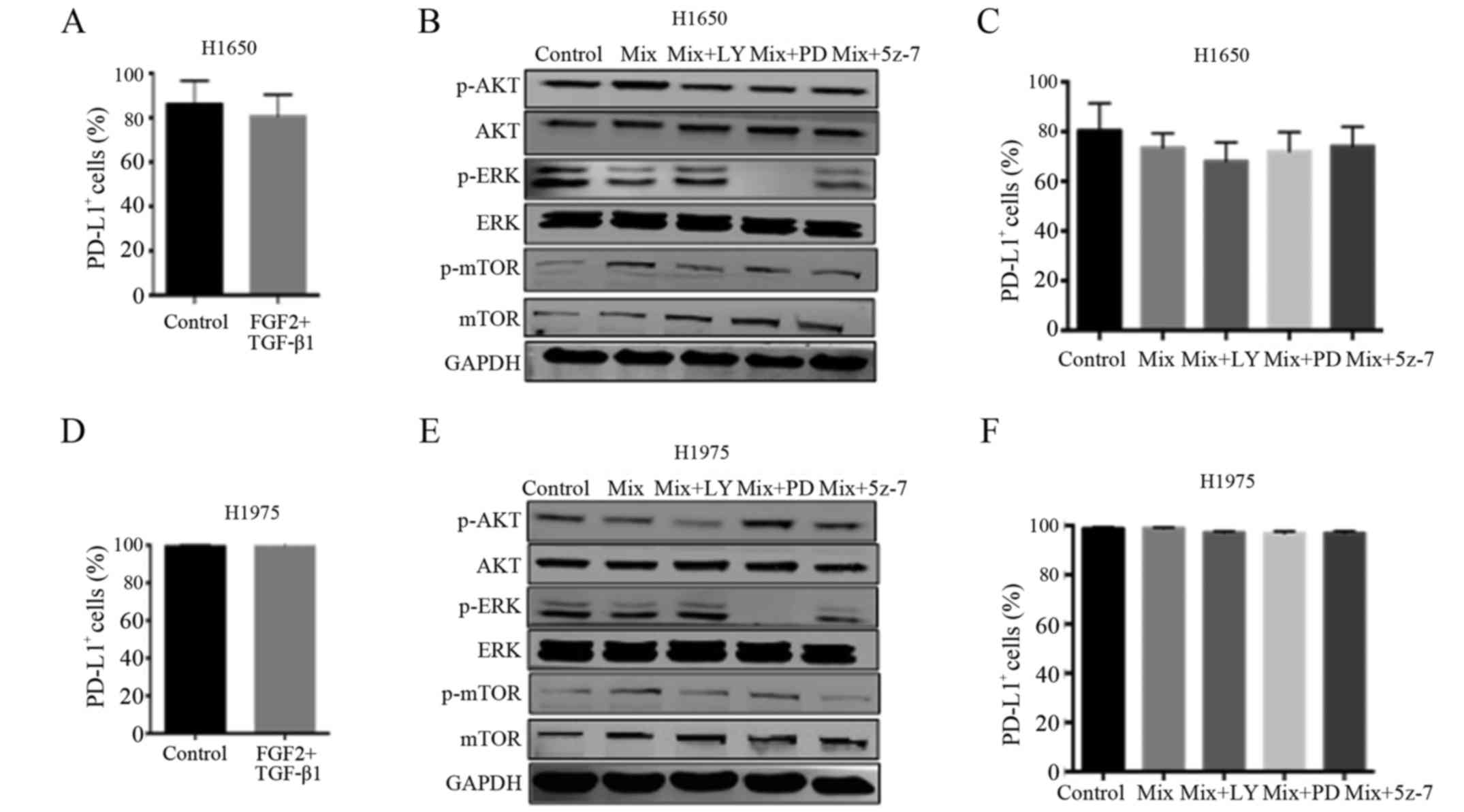
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL and Jemal A: Lung
cancer statistics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 893:1–19. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shi L, Tang J, Tong L and Liu Z: Risk of
interstitial lung disease with gefitinib and erlotinib in advanced
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
of clinical trials. Lung Cancer. 83:231–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li H, Schmid-Bindert G, Wang D, Zhao Y,
Yang X, Su B and Zhou C: Blocking the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK
signaling pathways can overcome gefitinib-resistance in non-small
cell lung cancer cell lines. Adv Med Sci. 56:275–284. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rolff J, Becker M, Merk J, Hoffmann J and
Fichtner I: Preclinical study of a combination of erlotinib and
bevacizumab in early stages of unselected non-small cell lung
cancer patient-derived xenografts. Target Oncol. 11:507–514. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin L and Bivona TG: Mechanisms of
resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors and novel
therapeutic strategies to overcome resistance in NSCLC patients.
Chemother Res Pract. 2012:8172972012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sato M, Shames DS and Hasegawa Y: Emerging
evidence of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in lung
carcinogenesis. Respirology. 17:1048–1059. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Voena C, Varesio LM, Zhang L, Menotti M,
Poggio T, Panizza E, Wang Q, Minero VG, Fagoonee S, Compagno M, et
al: Oncogenic ALK regulates EMT in non-small cell lung carcinoma
through repression of the epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1.
Oncotarget. 7:33316–33330. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wu F, Li J, Jang C, Wang J and Xiong J:
The role of Axl in drug resistance and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition of non-small cell lung carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
7:6653–6661. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jiao D, Wang J, Lu W, Tang X, Chen J, Mou
H and Chen QY: Curcumin inhibited HGF-induced EMT and angiogenesis
through regulating c-Met dependent PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways
in lung cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 3:160182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu ZC, Chen XH, Song HX, Wang HS, Zhang
G, Wang H, Chen DY, Fang R, Liu H, Cai SH and Du J: Snail regulated
by PKC/GSK-3β pathway is crucial for EGF-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of cancer cells. Cell
Tissue Res. 358:491–502. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bi WR, Yang CQ and Shi Q: Transforming
growth factor-β1 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatic fibrosis. Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1960–1963.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kaminska B, Wesolowska A and Danilkiewicz
M: TGF beta signalling and its role in tumour pathogenesis. Acta
Biochim Pol. 52:329–337. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shintani Y, Okimura A, Sato K, Nakagiri T,
Kadota Y, Inoue M, Sawabata N, Minami M, Ikeda N, Kawahara K, et
al: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of
sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann
Thorac Surg. 92:1794–1804; discussion 1804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen XF, Zhang HJ, Wang HB, Zhu J, Zhou
WY, Zhang H, Zhao MC, Su JM, Gao W, Zhang L, et al: Transforming
growth factor-β1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
human lung cancer cells via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk1/2 signaling
pathways. Mol Biol Rep. 39:3549–3556. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang HJ, Wang HY, Zhang HT, Su JM, Zhu J,
Wang HB, Zhou WY, Zhang H, Zhao MC, Zhang L and Chen XF:
Transforming growth factor-β1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma invasion
and metastasis by epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol Cell
Biochem. 355:309–314. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cervantes-Arias A, Pang LY and Argyle DJ:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition as a fundamental mechanism
underlying the cancer phenotype. Vet Comp Oncol. 11:169–184. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dai S, Jia R, Zhang X, Fang Q and Huang L:
The PD-1/PD-Ls pathway and autoimmune diseases. Cell Immunol.
290:72–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bachy E and Coiffier B: Anti-PD1 antibody:
A new approach to treatment of lymphomas. Lancet Oncol. 15:7–8.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gunturi A and McDermott DF: Potential of
new therapies like anti-PD1 in kidney cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 15:137–146. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T and
Kawakami Y: Cancer metastasis is accelerated through
immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 15:195–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ye LY, Chen W, Bai XL, Xu XY, Zhang Q, Xia
XF, Sun X, Li GG, Hu QD, Fu QH and Liang TB: Hypoxia-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma
induces an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment to promote
metastasis. Cancer Res. 76:818–830. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li F, Zhu T, Cao B, Wang J and Liang L:
Apatinib enchance antitumor activity of EGFR-TKIs in non-small cell
lung cancer with EGFR-TKI resistance. Eur J Cancer. 84:184–192.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hellmann M, Rizvi N, Wolchok JD and Chan
TA: Genomic profile, smoking, and response to anti-PD-1 therapy in
non-small cell lung carcinoma. Mol Cell Oncol. 3:e10489292015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Riihimäki M, Hemminki A, Fallah M, Thomsen
H, Sundquist K, Sundquist J and Hemminki K: Metastatic sites and
survival in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 86:78–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singh D, Attri BK, Gill RK and Bariwal J:
Review on EGFR Inhibitors: Critical updates. Mini Rev Med Chem.
16:1134–1166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nurwidya F, Takahashi F, Murakami A,
Kobayashi I, Kato M, Shukuya T, Tajima K, Shimada N and Takahashi
K: Acquired resistance of non-small cell lung cancer to epidermal
growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Respir Investig.
52:82–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Lee JC, Lin L, Olivas V, Au V,
LaFramboise T, Abdel-Rahman M, Wang X, Levine AD, Rho JK, et al:
Activation of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted
therapy in lung cancer. Nat Genet. 44:852–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nurwidya F, Takahashi F, Murakami A and
Takahashi K: Epithelial mesenchymal transition in drug resistance
and metastasis of lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 44:151–156. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger
S, Cosper AK, et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung
cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra26. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Saijo N: Present status and problems on
molecular targeted therapy of cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 44:1–10.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M,
Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS and Kalluri R:
Epithelial-to-mesemchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis
but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature.
527:525–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Diepenbruck M and Christofori G:
Epithelial to mesemchymal transition (EMT) and metastais: Yes, no,
maybe? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 43:7–13. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Strippoli R, Benedicto I, Perez Lozano ML,
Pellinen T, Sandoval P, Lopez-Cabrera M and del Pozo MA: Inhibition
of transforming growth factor-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) blocks and
reverses epithelial to mesenchymal transition of mesothelial cells.
PLoS One. 7:e314922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu W, Kovacevic Z, Peng Z, Jin R, Wang P,
Yue F, Zheng M, Huang ML, Jansson PJ, Richardson V, et al: The
molecular effect of metastasis suppressors on Src signaling and
tumorigenesis: New therapeutic targets. Oncotarget. 6:35522–35541.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sequist LV, Bell DW, Lynch TJ and Haber
DA: Molecular predictors of response to epidermal growth factor
receptor antagonists in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol.
25:587–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Said NA and Williams ED: Growth factors in
induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis.
Cells Tissues Organs. 193:85–97. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|