|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gazdar AF: Should we continue to use the
term non-small-cell lung cancer? Ann Oncol. 21 Suppl
7:vii225–vii229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zonderman AB, Ejiogu N, Norbeck J and
Evans MK: The influence of health disparities on targeting cancer
prevention efforts. Am J Prev Med. 46 3 Suppl 1:S87–S97. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kang YH, Kim D and Jin EJ: Down-regulation
of phospholipase D stimulates death of lung cancer cells involving
up-regulation of the long ncRNA ANRIL. Anticancer Res.
35:2795–2803. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu X, Xiao ZD, Han L, Zhang J, Lee SW,
Wang W, Lee H, Zhuang L, Chen J, Lin HK, et al: LncRNA NBR2
engages a metabolic checkpoint by regulating AMPK under energy
stress. Nat Cell Biol. 18:431–442. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Guo Q, Zhao Y, Chen J, Wang S, Hu
J and Sun Y: BRAF-activated long non-coding RNA contributes to cell
proliferation and activates autophagy in papillary thyroid
carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 8:1947–1952. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao Y, Guo Q, Chen J, Hu J, Wang S and
Sun Y: Role of long non-coding RNA HULC in cell proliferation,
apoptosis and tumor metastasis of gastric cancer: A clinical and in
vitro investigation. Oncol Rep. 31:358–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feng N, Ching T, Wang Y, Liu B, Lin H, Shi
O, Zhang X, Zheng M, Zheng X, Gao M, et al: Analysis of microarray
data on gene expression and methylation to identify long non-coding
RNAs in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 6:372332016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schmidt LH, Spieker T, Koschmieder S,
Schäffers S, Humberg J, Jungen D, Bulk E, Hascher A, Wittmer D,
Marra A, et al: The long noncoding MALAT-1 RNA indicates a poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer and induces migration and
tumor growth. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1984–1992. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loewen G, Jayawickramarajah J, Zhuo Y and
Shan B: Functions of lncRNA HOTAIR in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol.
7:902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fei ZH, Yu XJ, Zhou M, Su HF, Zheng Z and
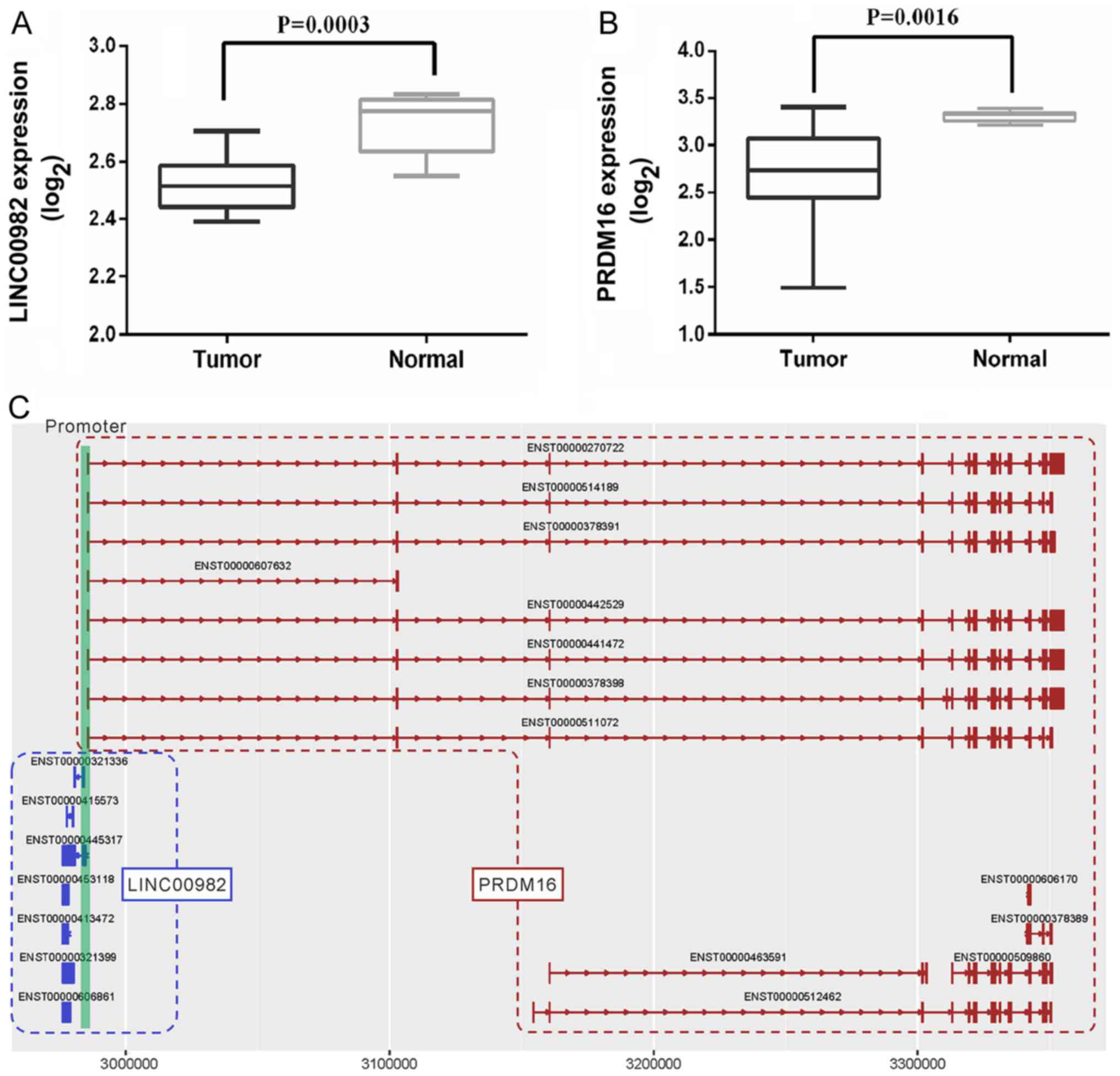
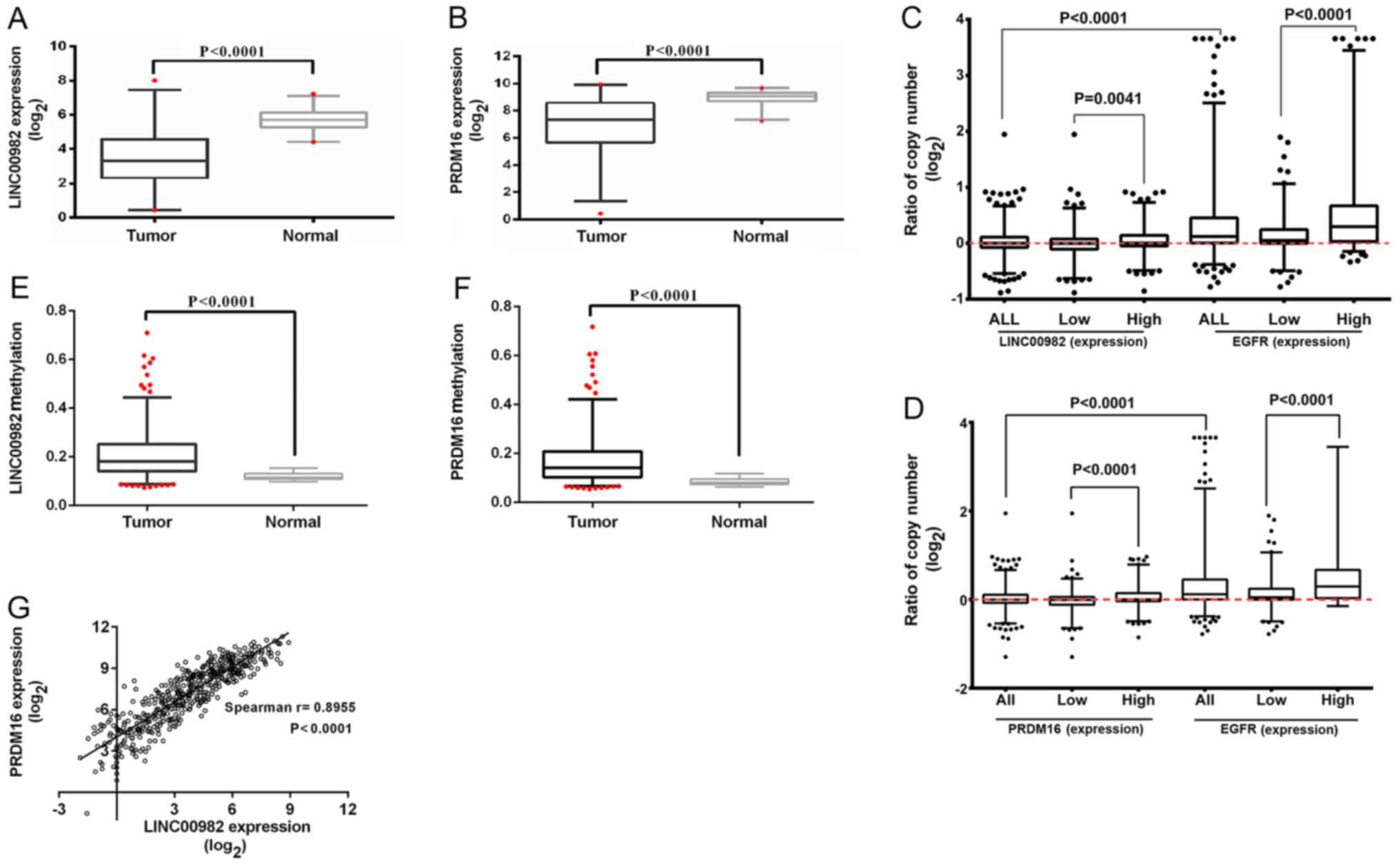
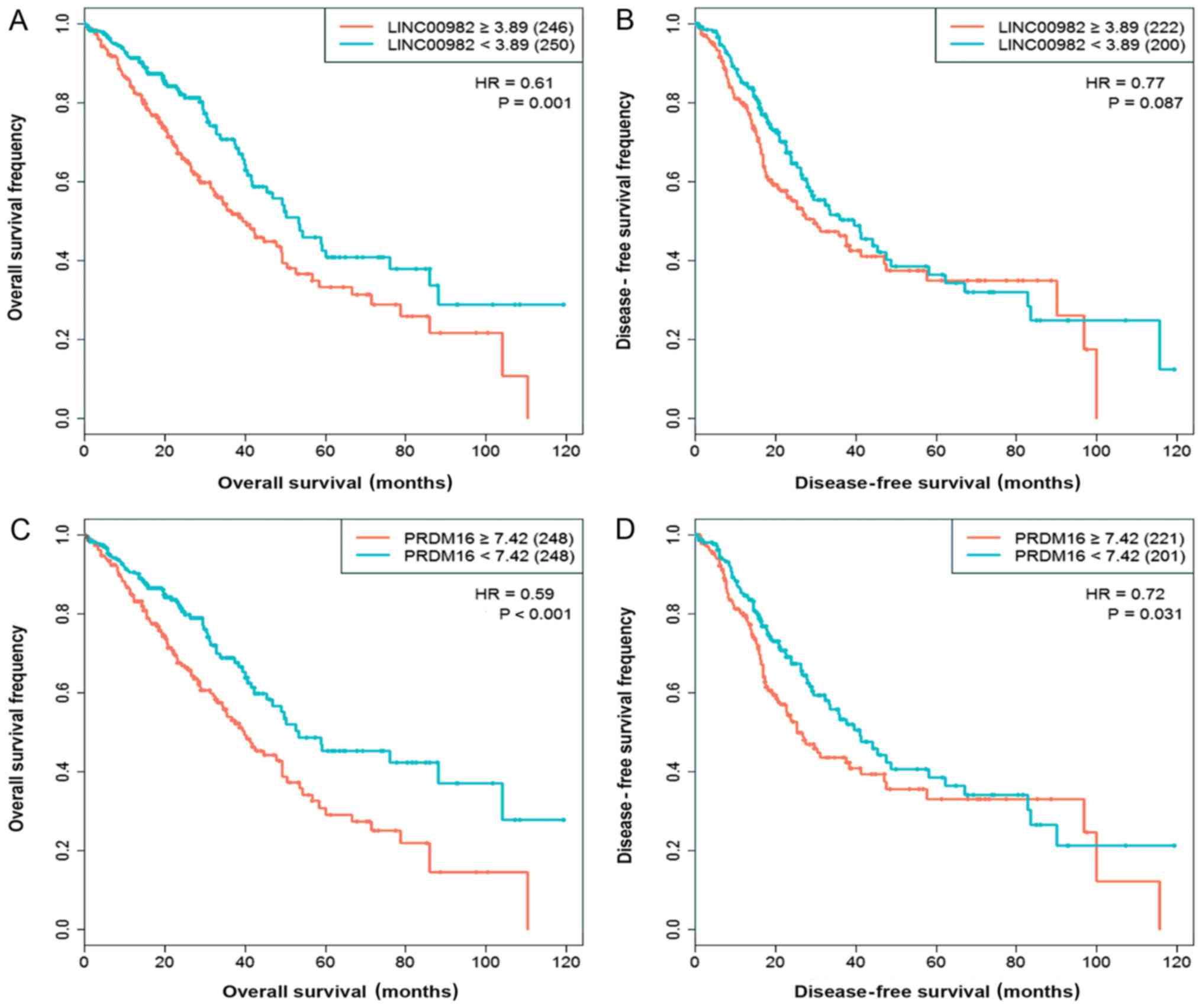
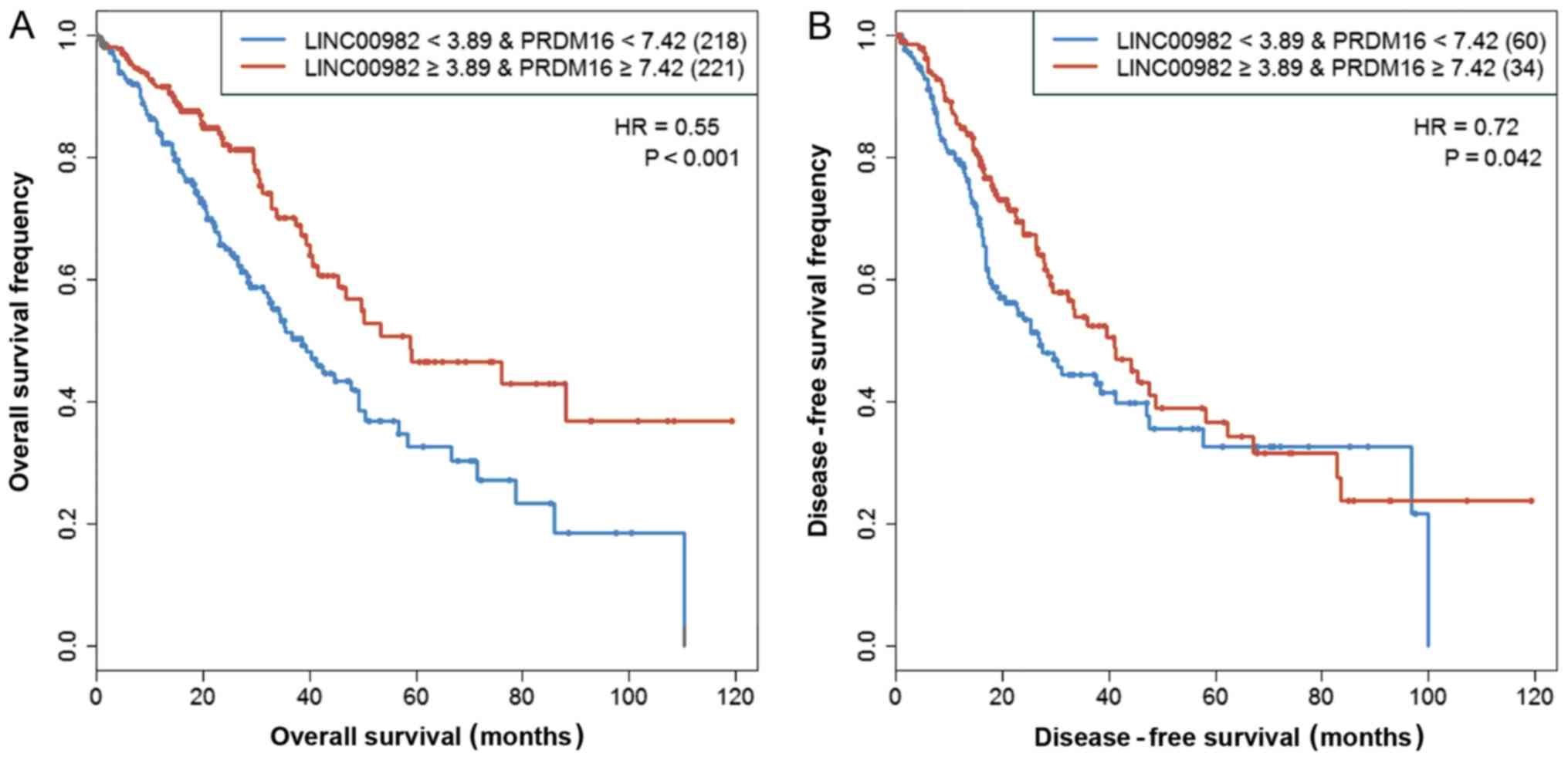
Xie CY: Upregulated expression of long non-coding RNA LINC00982
regulates cell proliferation and its clinical relevance in patients
with gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:1983–1993. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao WJ, Wu HL, He BS, Zhang YS and Zhang
ZY: Analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in gastric
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 19:3658–3664. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lei Q, Liu X, Fu H, Sun Y, Wang L, Xu G,
Wang W, Yu Z, Liu C, Li P, et al: miR-101 reverses hypomethylation
of the PRDM16 promoter to disrupt mitochondrial function in
astrocytoma cells. Oncotarget. 7:5007–5022. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu S, Xu Y, Song M, Chen G, Wang H, Zhao
Y, Wang Z and Li F: PRDM16 is associated with evasion of apoptosis
by prostatic cancer cells according to RNA interference screening.
Mol Med Rep. 14:3357–3361. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Burghel GJ, Lin WY, Whitehouse H, Brock I,
Hammond D, Bury J, Stephenson Y, George R and Cox A: Identification
of candidate driver genes in common focal chromosomal aberrations
of microsatellite stable colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e838592013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Momi N, Wali RK, Chhaparia A, Calderwood
AH, Tiwari AK, Ledbetter SE, DeLaCruz M and Roy HK: Su2000 PRDM16
is a novel proto-oncogene in colorectal cancer (CRC): Modulation of
the early warburg effect in field carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology.
150:S6062016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Matsuo H, Goyama S, Kamikubo Y and Adachi
S: The subtype-specific features of EVI1 and PRDM16 in acute
myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 100:e116–e117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li L, Zhao CT, Cui BL, Wu SL, Liu XD, Su
Z, Yang J, Wang W, Cui ZG and Zhao HG: Expression of HOXB4, PRDM16
and HOXA9 in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and its clinical
significance. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 24:326–331.
2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tan SX, Hu RC, Liu JJ, Tan YL and Liu WE:
Methylation of PRDM2, PRDM5 and PRDM16 genes in lung cancer cells.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:2305–2311. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G,
Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, et al:
Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical
profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal. 6:pl12013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA Jr,
Di Maria MV, Veve R, Bremmes RM, Barón AE, Zeng C and Franklin WA:
Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas:
Correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and
impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 21:3798–3807. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network:
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Castillo J, Stueve TR and Marconett CN:
Intersecting transcriptomic profiling technologies and long
non-coding RNA function in lung adenocarcinoma: Discovery,
mechanisms, and therapeutic applications. Oncotarget.
8:81538–81557. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qiu M, Xu Y, Yang X, Wang J, Hu J, Xu L
and Yin R: CCAT2 is a lung adenocarcinoma-specific long non-coding
RNA and promotes invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour
Biol. 35:5375–5380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lavallée VP, Lemieux S, Boucher G, Gendron
P, Boivin I, Girard S, Hébert J and Sauvageau G: Identification of
MYC mutations in acute myeloid leukemias with NUP98-NSD1
translocations. Leukemia. 30:1621–1624. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Duhoux FP, Ameye G, Montano-Almendras CP,
Bahloula K, Mozziconacci MJ, Laibe S, Wlodarska I, Michaux L,
Talmant P, Richebourg S, et al: PRDM16 (1p36) translocations define
a distinct entity of myeloid malignancies with poor prognosis but
may also occur in lymphoid malignancies. Br J Haematol. 156:76–88.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pagano M and Draetta G: Cyclin A, cell
cycle control and oncogenesis. Prog Growth Factor Res. 3:267–277.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yue W, Zhao X, Zhang L, Xu S, Liu Z, Ma L,
Jia W, Qian Z, Zhang C, Wang Y and Yang X: Cell cycle protein
cyclin Y is associated with human non-small-cell lung cancer
proliferation and tumorigenesis. Clin Lung Cancer. 12:43–50. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lamb R, Lehn S, Rogerson L, Clarke RB and
Landberg G: Cell cycle regulators cyclin D1 and CDK4/6 have
estrogen receptor-dependent divergent functions in breast cancer
migration and stem cell-like activity. Cell Cycle. 12:2384–2394.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jhanwar-Uniyal M: BRCA1 in cancer, cell
cycle and genomic stability. Front Biosci. 8:s1107–s1117. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paternot S, Bockstaele L, Bisteau X,
Kooken H, Coulonval K and Roger PP: Rb inactivation in cell cycle
and cancer: The puzzle of highly regulated activating
phosphorylation of CDK4 versus constitutively active CDK-activating
kinase. Cell Cycle. 9:689–699. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chuikov S, Levi BP, Smith ML and Morrison
SJ: Prdm16 promotes stem cell maintenance in multiple tissues,
partly by regulating oxidative stress. Nat Cell Biol. 12:999–1006.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wishart DS: Emerging applications of
metabolomics in drug discovery and precision medicine. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 15:473–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang EB, Yin DD, Sun M, Kong R, Liu XH,
You LH, Han L, Xia R, Wang KM, Yang JS, et al: P53-regulated long
non-coding RNA TUG1 affects cell proliferation in human non-small
cell lung cancer, partly through epigenetically regulating HOXB7
expression. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang X, Song JH, Cheng Y, Wu W, Bhagat T,
Yu Y, Abraham JM, Ibrahim S, Ravich W, Roland BC, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HNF1A-AS1 regulates proliferation and migration in
oesophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Gut. 63:881–890. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, McGranahan N,
Birkbak NJ, Watkins TB, Veeriah S, Shafi S, Johnson DH, Mitter R,
Rosenthal R, et al: Tracking the evolution of non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 376:2109–2121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|